Lecture 28: Thyroid Gland, Parathyroid Gland, Hormonal Regulation of Calcium
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10/23 Online 3 Kahoots
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
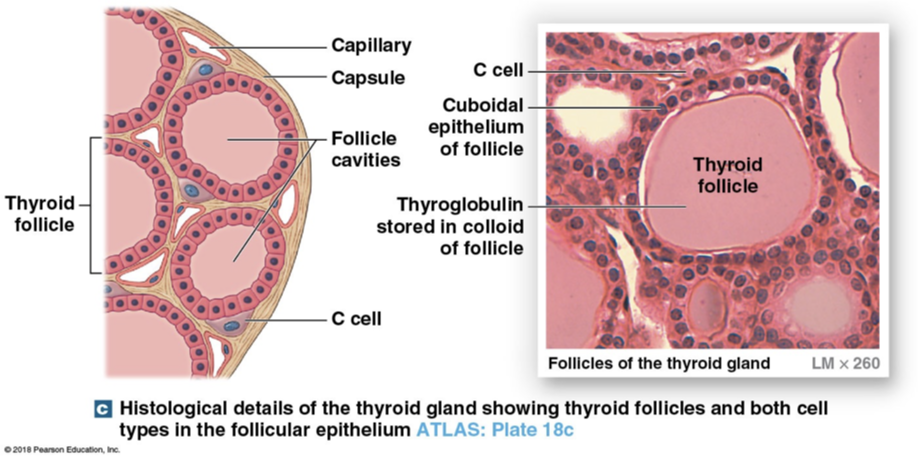
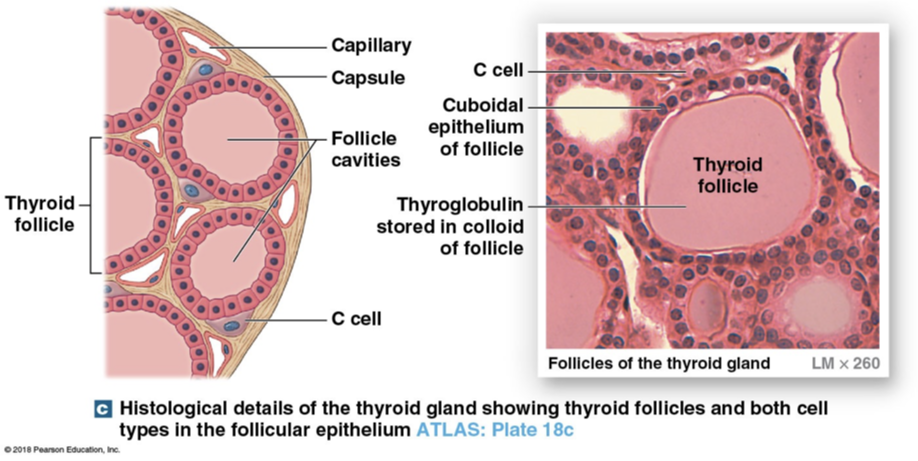
Types of cells in thyroid gland
C cells (parafollicular cells) and Follicle cells
C cells (parafollicular cells)
Produce calcitonin in response to high calcium levels
Calcitonin
Inhibits osteoclasts and increase calcium ion excretion by kidney (pee it out)
Tone down calcium levels in blood
Thyroid Gland
Sits anterior to trachea → when it becomes enlarged you can feel it
Gland that secretes thyroid hormone and also regulates calcium levels
Acts like a lipid in terms of crossing the membranes
Follicle Cells
Release thyroid hormones (T4 and T3)
Where receptors are for TSH (produced and released into bloodstream depending on TSH and iodine levels
Follicle cavity is filled with sticky substance
T4
Thyroxine
has 4 iodide ions
Inactive form
T3
Triiodothyronine
three iodide ions
Active form
Thyroid Hormones
Form of tyrosine (amino acid) with attached iodide ions
How much of secretion is T4?
90%
Why is T4 important for the negative feedback loop?
This is the only hormone that the hypothalamus detects (not T3)
How does T4 become activated and what does it become?
Converted to T3 by enzymes in peripheral tissue, enzyme cleaves off one iodide ion leaving T3 the active form
What are thyroid hormones attached to in bloodstream?
Transport proteins creating large reserve supply of T4 and T3
What is the synthesis and release of TH controlled by?
TSH from adenohypophysis
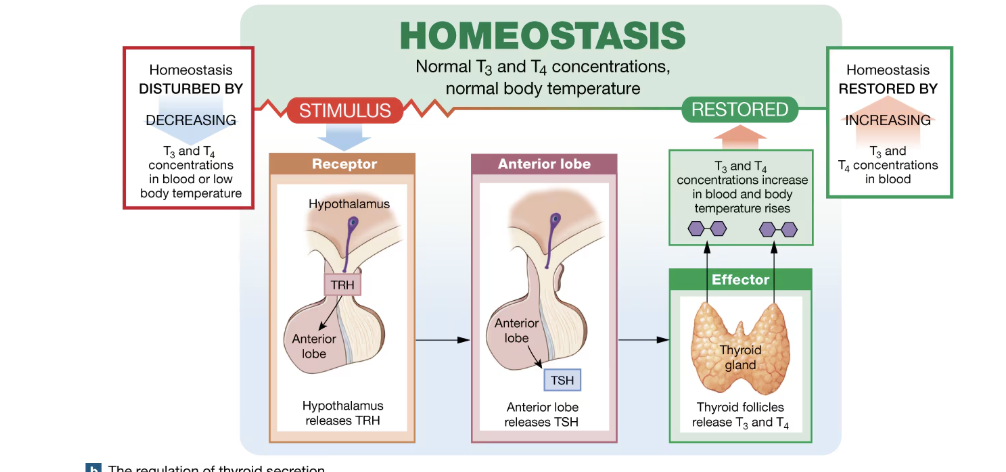
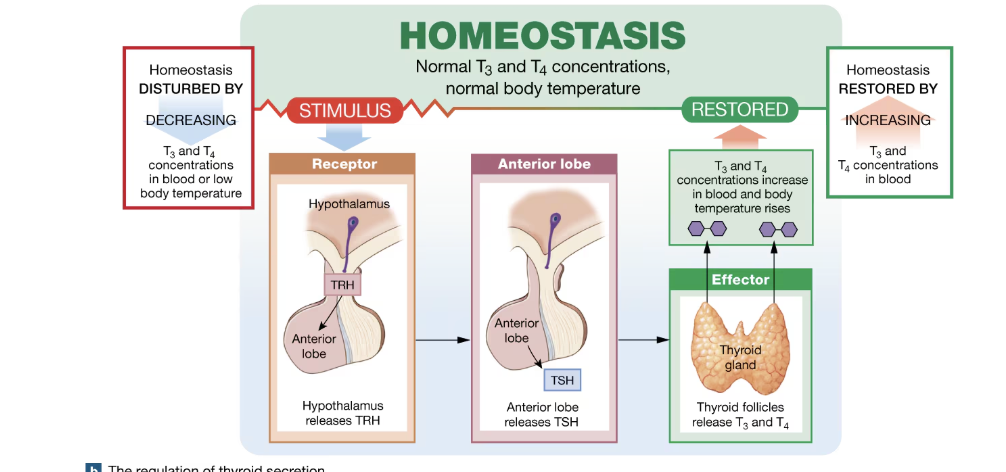
Negative feedback loop example if T3 and T4
Homeostasis is disturbed by decreasing T3 and T4 concentration in blood or low body temperature
Receptors in hypothalamus that is response for T4 detection drops, secretes TRH
Anterior lop release TSH after being stimulated by TRH
Thyroid then releases T3 and T4
Homeostasis is restored
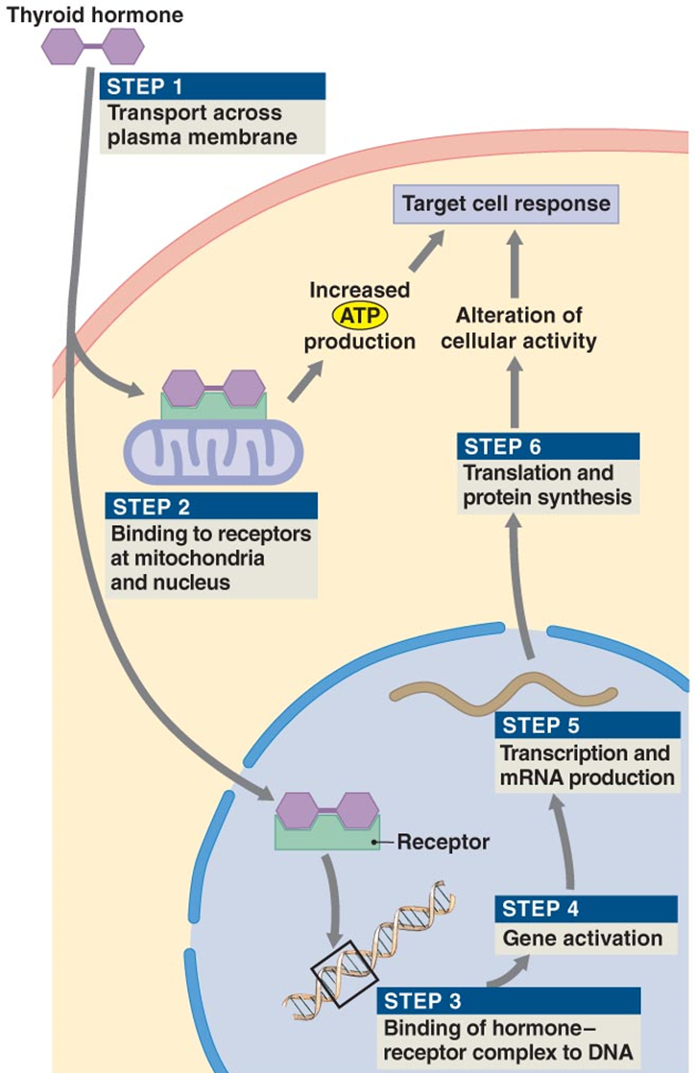
Function of thyroid hormones
produce strong, immediate, short-lasting increase in the rate of cellular metabolism and use of energy
Cross cell membrane and bind to intracellular receptors
bind to mitochondria and increase rate of ATP production
BInd to receptors activating genes that control energy utilization
increases metabolism (body temp goes up)
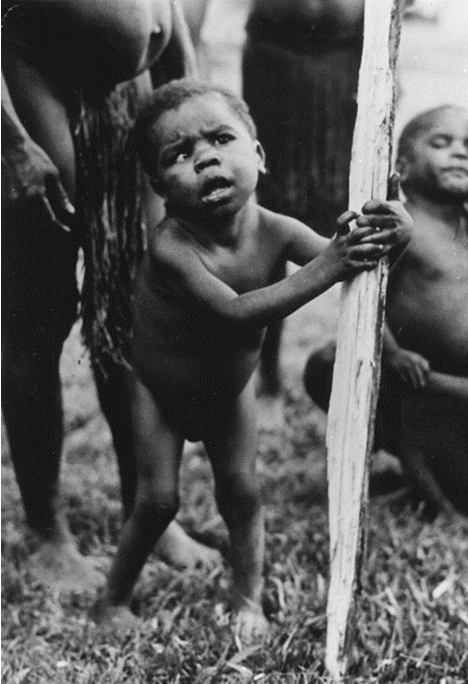
What is thyroid hormone’s function in development?
Essential for normal development of skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems during childhood
Cretinism
During growth periods you also secrete thyroid hormones because you need more energy to grow
excess thyroid hormone is produced in the process because you need to make more ATP
Hyposecretion occurs → low thyroid hormone levels during growth that causes abnormal growth of all your systems

Thyroid hormone is essential for normal what control in adults?
Metabolic
What are metabolic abnormalities due to thyroid abnormalities
Hypothyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Goiter
Hypothyroidism
Common in females
Caused by autoimmune (Hasimatos’s) which makes antibodies that block TSH receptors → thyroid hormone levels drop → metabolic rate slows down → core has colder body temp (metabolism) → likely to gain weight, lethargic
Hyperthyroidism
Autoimmune (Grave’s disease) causes, antibodies mimic TSH → thyroid gland overproduces TH → lose weight → high metabolic rate → high body temp → dangerous (“constant fever”) → can denature proteins
Treatment for hyperthyroidism?
Thyroid gland removal or radioactive iodide, only thyroide can absorb/take iodide, radioactive iodide would destroy
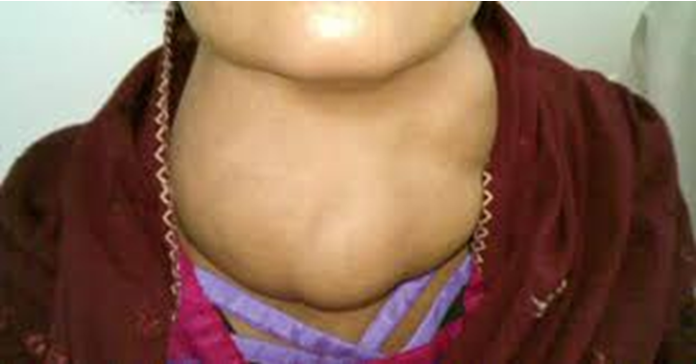
Goiter
Enlarged thyroid
Lack of iodide (mainly iodized salt)
Essentially you make a bunch of precursor but no iodide to finish the process which leaves it lingering
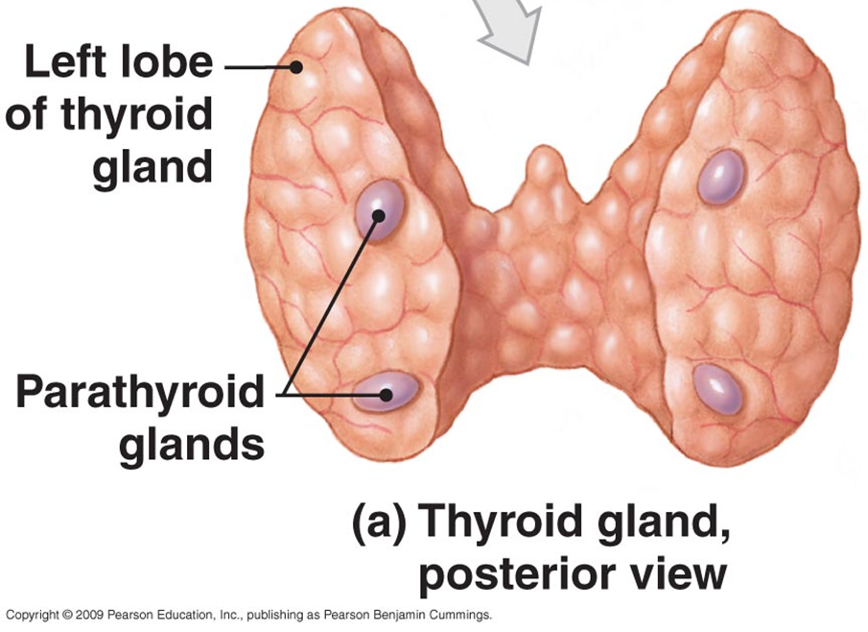
Parathyroid Glands
Four glands embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland
Secretes PTH
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Secreted by parathyroid gland when calcium concentration is lower than normal
Increases calcium ion concentration (does opposite of calcitonin)
What are some ways that PTH increase Ca2+ conc?
Stimulating osteoclasts
Inhibiting Osteoblasts
Decreasing Ca2+ excretion by kidneys
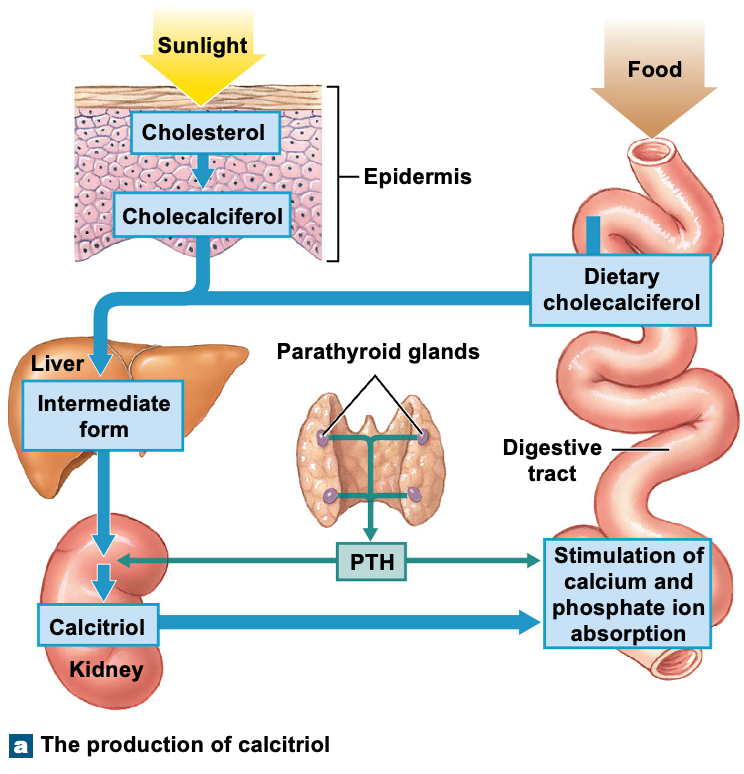
Stimulate formation of calcitriol by kidneys
How would stimulating osteoclasts increase Ca2+ conc in blood?
Osteoclasts are phagocytic bone cells that will dissolve bony matrix and release calcium into blood
How would inhibiting osteoblasts increase Ca2+ conc?
Osteoblasts are building cells
By stopping the remodeling of our bones we can use calcium that would’ve been used for our bones on other things
How would you decrease calcium excretion by kidneys?
Less calcium would be peed out and reabsorbed back into blood
What is calcium levels maintained by?
Negative feedback loop
What does Ca2+ conc affect?
Nerve and muscle cell excitability
What is Ca2+ conc maintained by?
Negative feedback system involving both PTH and calcitonin
Bones and calcium
Storage of calcium ions (osteoclasts and osteoblasts)
Digestive tract and calcium
Absorption of calcium ions
calcitriol
Kidney - Excretion of calcium ions
Calcitriol
Steroid hormone derived from vitamin D from the kidney, binds vitamin D to tissue in order to increase calcium levels