Topic 13- Electromagnetic Induction
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Electromagnetic Induction (generator effect)
A voltage is induced in a conductor when there is relative motion between the conductor and another magnetic field
caused by coil/conductor cutting through field lines
how to produce an electric current by the generator effect on a small scale in a lab
either:
move a conductor relative to the magnetic field of magnets
or move a magnet through the centre of a coil
measured with a centre-zero meter (a voltmeter or ammeter that has an arow that deflects)
when a magnet is moved into a coil, the induced current will cause the ______ end to become the North pole (of the coil)
nearest
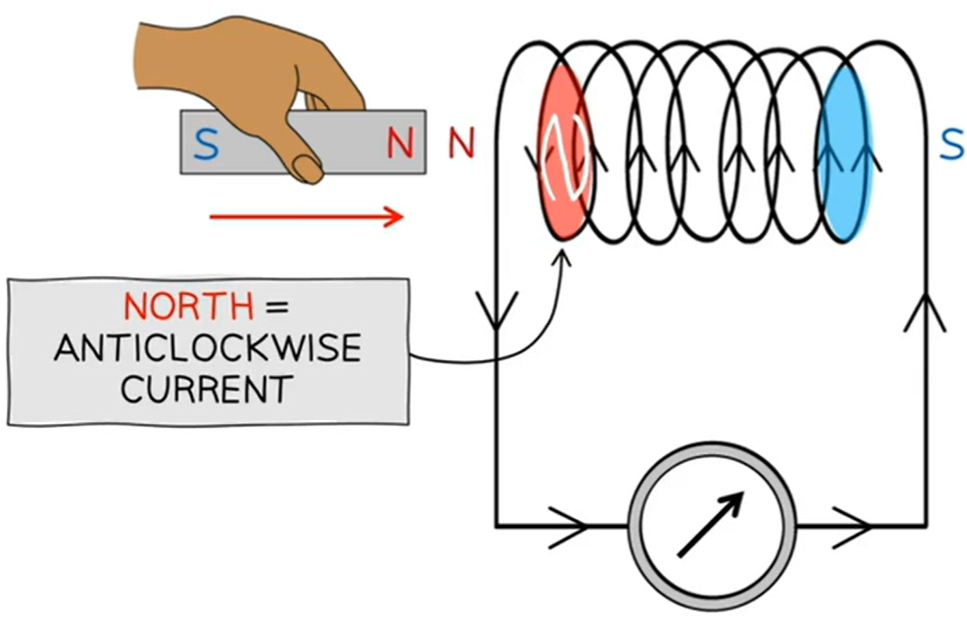
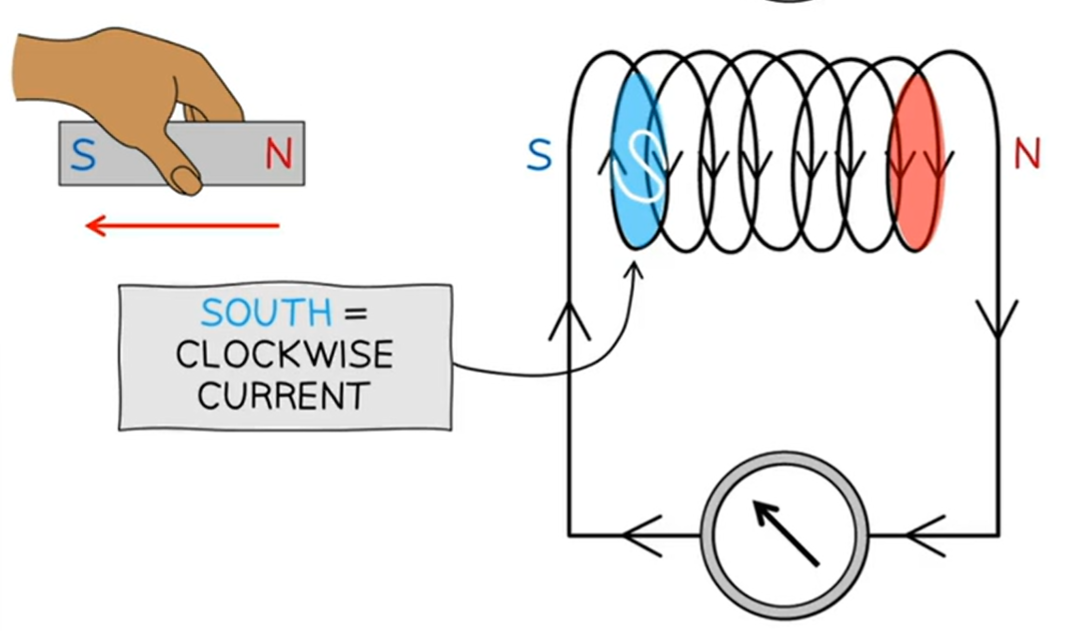
when a magnet is moved out of a coil, the nearest end to the magnet becomes the induced _____ pole.
South
the generator effect use in the large-scale generation of electricity (a.c. generator)
water heated and evaporates to form steam
steam put under pressure and forced into a turbine, connected to a huge coil of wire in a strong mag field
steam causes turbine to spin, spinning coil
current is generated in the coil by the spinning motion of the coil through the field
this is the main form of electricity found in the mains supply of a building
effect of increasing speed at which coil wire or magnet is moved
increase rate at which mag field lines are cut
increases induced p.d.
effect of increasing number of turns in the coil
more coils will cut mag field lines
so total p.d. will increase
effect of increasing size of coils (area)
more wire cutting field lines
so increased p.d.
effect of increasing strength of mag field
increased p.d.
effect of reversing orientation of the magnet poles
reversed direction of current produced
magnetic field produced in the coil by EM induction always…
opposes the original change
so will always try to stop the magnet moving in or out by repelling it
e.g. magnet is pushed N end first into a coil, the end nearest the magnet becomes the N pole of the coil, to repel the magnet
e.g. magnet is pulled out of coil south end first, the end of the coil nearest the magnet will become the south pole, to try to attract the magnet in.
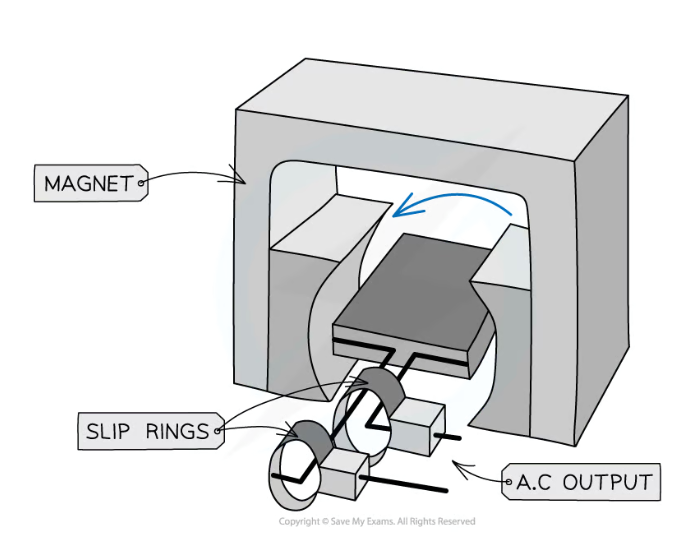
how does an alternator (a.c. generator) work?
coil spun in a uniform field
coil connected to a circuit by metal brushes that maintain continuous contact with 2 slip rings connected to each end of coil wire
as the coil cuts through the magnetic field lines, it induces a potential difference, causing current to flow.
current changes direction every half turn, as the mag field of the coil also spins, cutting across the field lines in alternating directions
this is known as alternating current
produces a sine graph of potential difference
how does a dynamo (d.c. generator) work
coil spun in a uniform electric field
connected to a circuit through a split ring commutator, contact made by brushes
as it rotates it cuts through mad field lines, inducing a p.d. in the coil, causing current to flow in circuit
split ring commutator changes connections between coil and brushes every half turn, so current continues leaving the dynamo in the same direction
p.d. does not reverse, so current remains positive
known as direct current, produced in pulses (as the coil goes vertical it doesn’t induce any p.d.)
how does a microphone work with EM induction?
when sound waves reach the microphone, the pressure variations cause the sensitive diaphragm to vibrate
in turn, this moves the coil back and forth through the mag field of the magnet, cutting field lines
induces an alternating p.d. in the coil → alternating current
frequency of the current is proportional to the sound signal frequency, sent to a loudspeaker
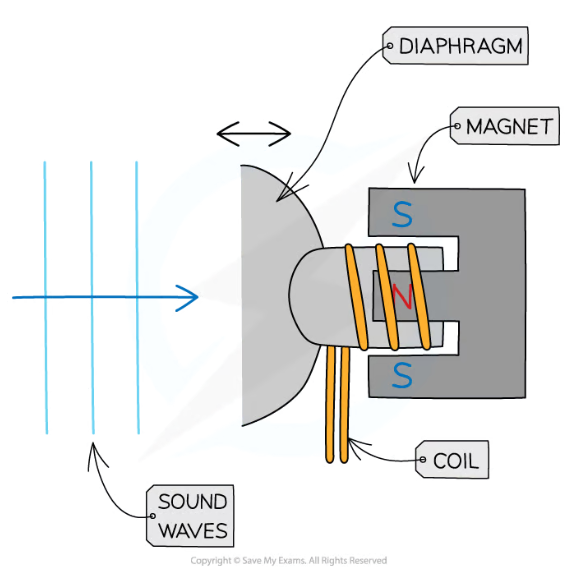
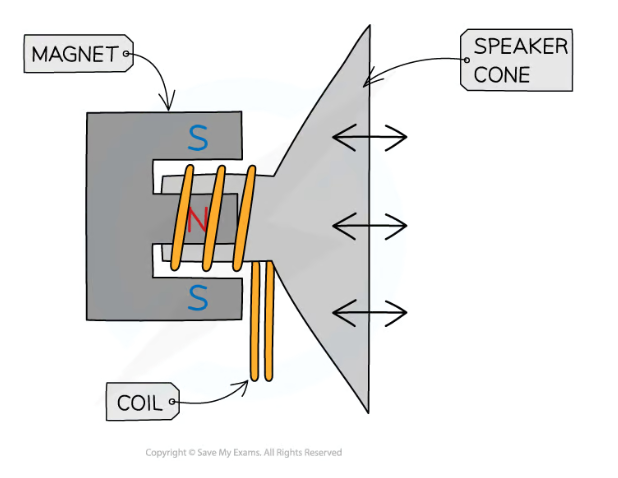
how does a loudspeaker work using magnetic forces (motor effect)
a.c. current passes through coil, creating a constantly changing magnetic field around the coil
this field interacts with the field from the permanent magnet, exerting a force on the coil, moving it back and forth (oscillation)
connected to speaker cone, which also oscillates, creating changes in pressure that are sound waves
what are transformers used for
can be used to increase or decrease the p.d. of an alternating current between two coils
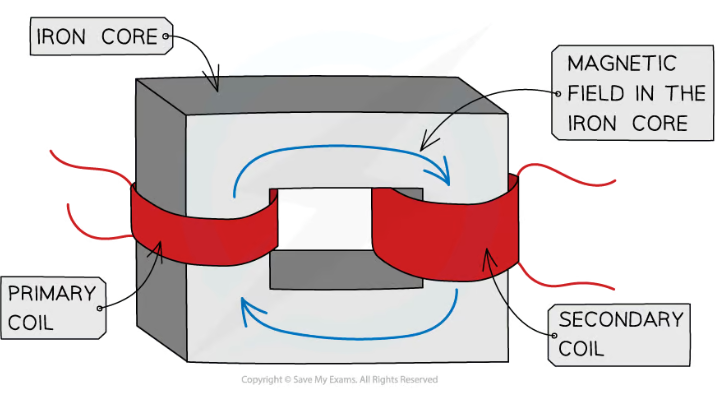
how do transformers work?
a.c. supplied to primary coil
produces a changing magnetic field around itself due to changing current
iron core is easily magnetised so field passes through it
therefore there is now a moving mag field around the secondary coil, so induces an alternating p.d. of same frequency as the a.c. supplied to primary coil
if secondary connected in a complete circuit then a.c. produced
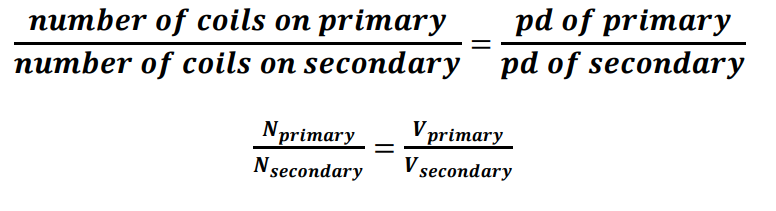
ratio equation for transformers
step up transformer
more coils on secondary
voltage increased, as changing field will cut through more wire in the secondary coil, inducing a larger p.d.
step down transformer
less coils on the secondary
voltage decreased, changing field will cut through less wire in the secondary coil, so smaller p.d. induces
what happens to electricity at high currents over long distances?
the wires heat up! (so current must be reduced)
but, to maintain the same power (because power can’t be created), the voltage can be INCREASED
because Power = Voltage x Current
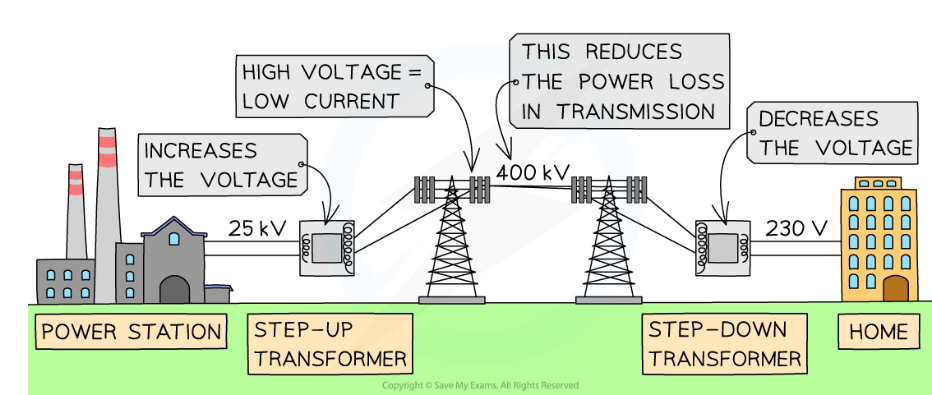
national grid electrical energy
energy transferred at high voltages from power stations
current low (to reduce heat loss in power lines so improve efficiency)
step-up transformer makes voltage high (because power is constant)
transferred at lower voltages in each locality for domestic uses
current increased
because step-down transformer decreases voltage (because high V can be very dangerous)
what kind of transformer is used in adapters?
step-down
they lower the main voltage to lower voltages used by many electronic devices
power equation for a 100% efficient transformer
Vp x Ip = Vs x Is
AKA Pp = Ps
advantage of high voltage transmission cables
transformers cannot increased the total power output, so a step-up transformer can increase the voltage, meaning that current must decrease
lower current = less resistance and therefore energy lost
therefore more efficient
power (energy per second) lost in a wire
P = I2R
total energy lost in a certain time (t) by a wire
E = P x t