Tissues
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key concepts about tissues: muscle (skeletal, smooth, cardiac), nervous and connective tissues, epithelial tissues and their subtypes, cells and components of blood, and neuron/glial cells.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Muscle tissue
Tissue that contracts to produce movement; includes skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle.
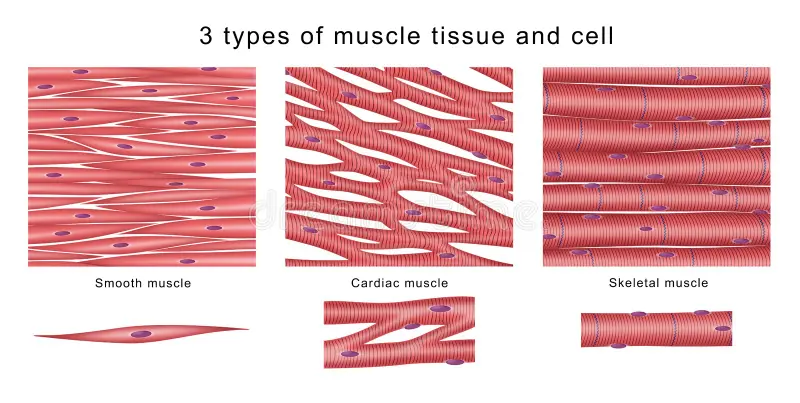
Skeletal muscle tissue
Voluntary muscle attached to bones that moves the body.
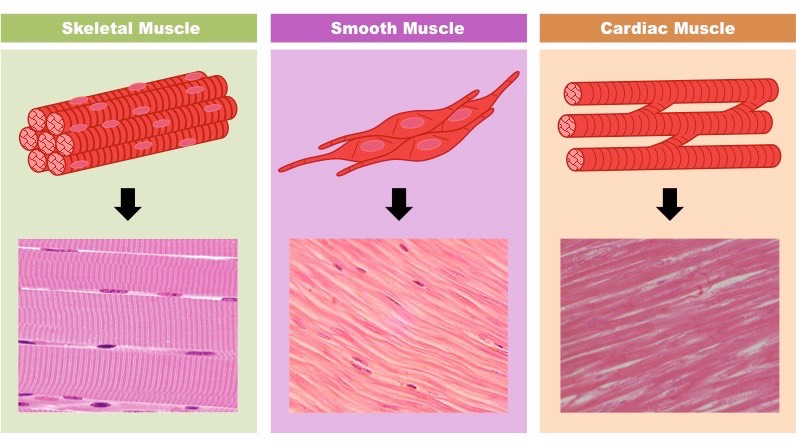
Smooth muscle tissue
Involuntary muscle in walls of hollow organs that moves substances through organs.
Cardiac muscle tissue
Involuntary muscle of the heart that pumps blood.
Nervous tissue
Tissue that controls the body and transmits electrical signals between brain, spinal cord, and other areas.
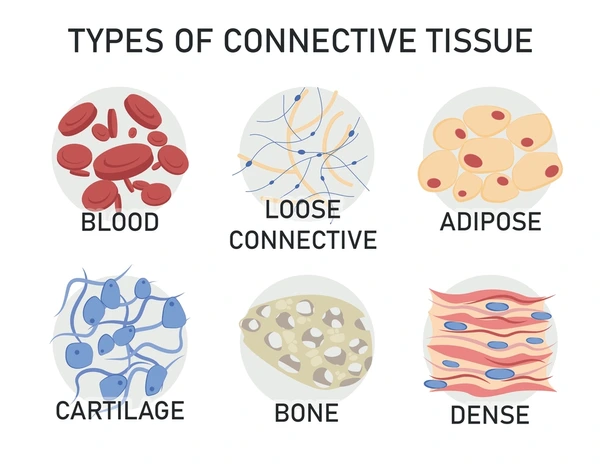
Connective tissue
Tissue that supports, protects, and binds organs; includes bone, cartilage, blood, and adipose. It also transports nutrients.
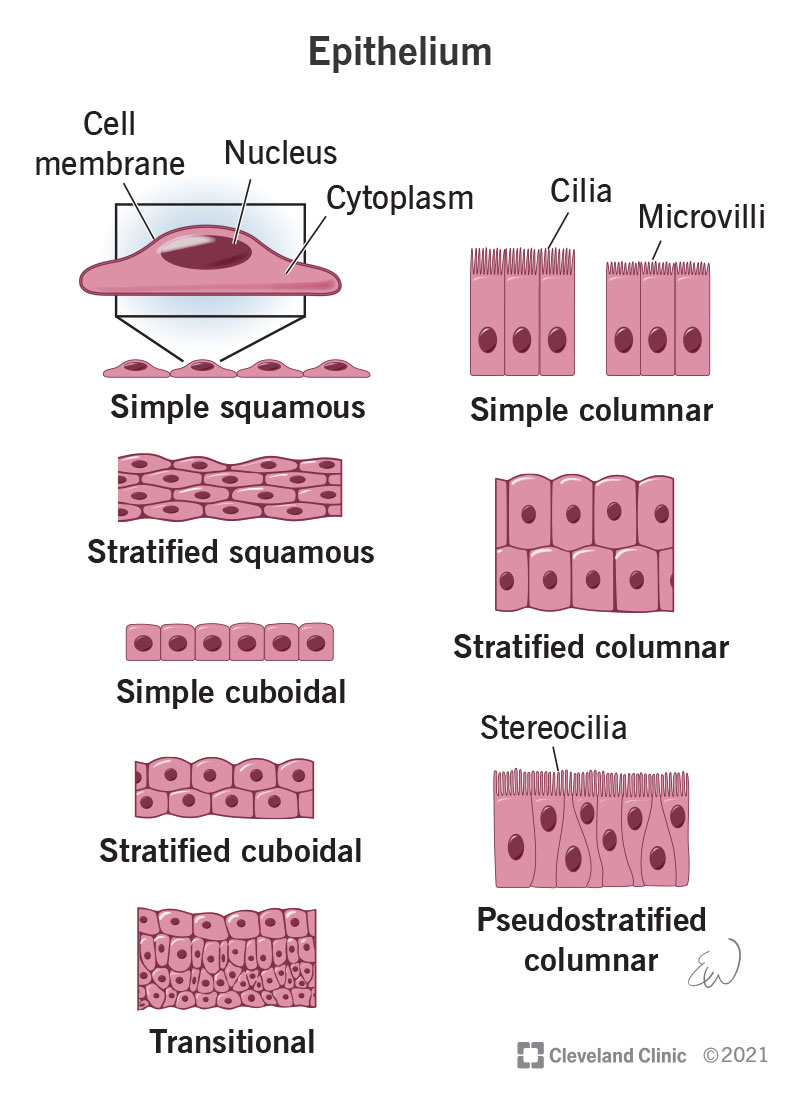
Epithelial tissue
Tissue that lines and protects surfaces of the body, absorbs nutrients, and secretes substances such as hormones, enzymes, mucus, sweat, or oils.
Bone tissue
Tissue that provides support and protection; long bones act as levers in movement.
Cartilage tissue
Structure, cushioning, and shock absorption; found in ears, nose, and between bones.
Adipose tissue
Tissue that stores energy, cushions, and insulates.
Blood
Connective tissue that transports gases, nutrients, and wastes; composed of cells and plasma.
Erythrocyte (RBC)
________ carries oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
Leukocyte (WBC)
White blood cell; fights microorganisms.
Thrombocyte (Platelet)
Cell fragment essential for blood clotting.
Tissue
A group of cells working together to perform a function.
Four main tissue types
Epithelial, nervous, muscle, and connective tissues.
Role of epithelial tissue
Protects surfaces, absorbs nutrients, and secretes; forms lining of skin, cavities, and organs.
Location of epithelial tissue
Found on the skin and lining cavities and internal organs.
Squamous epithelium
Flat, irregular-shaped epithelial cells.
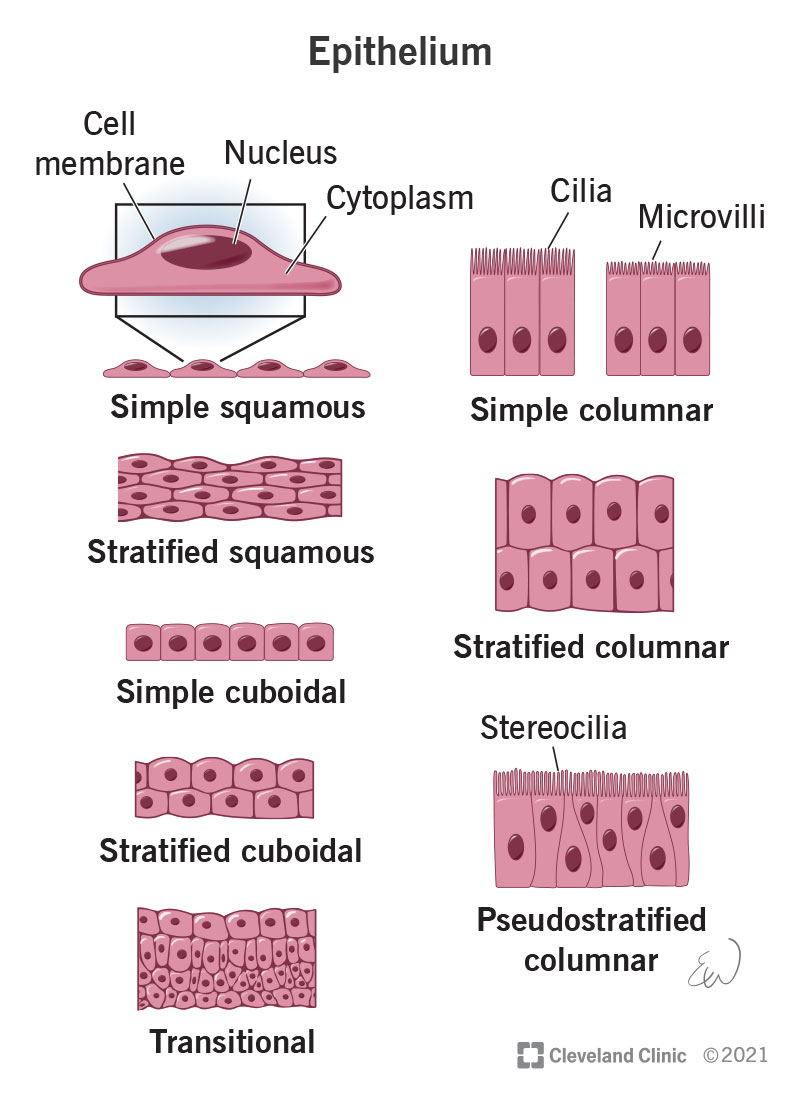
Cuboidal epithelium
Cube-shaped epithelial cells.
Columnar epithelium
Tall, column-shaped epithelial cells.
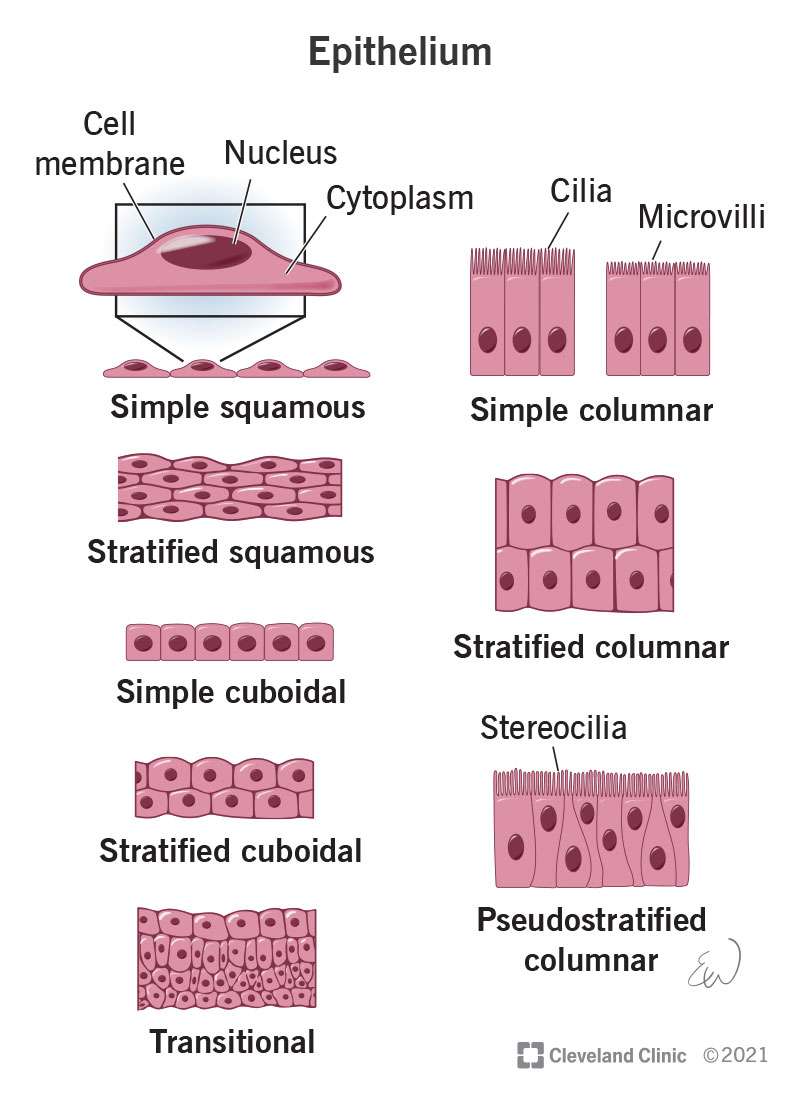
Simple epithelium
One layer of epithelial cells.
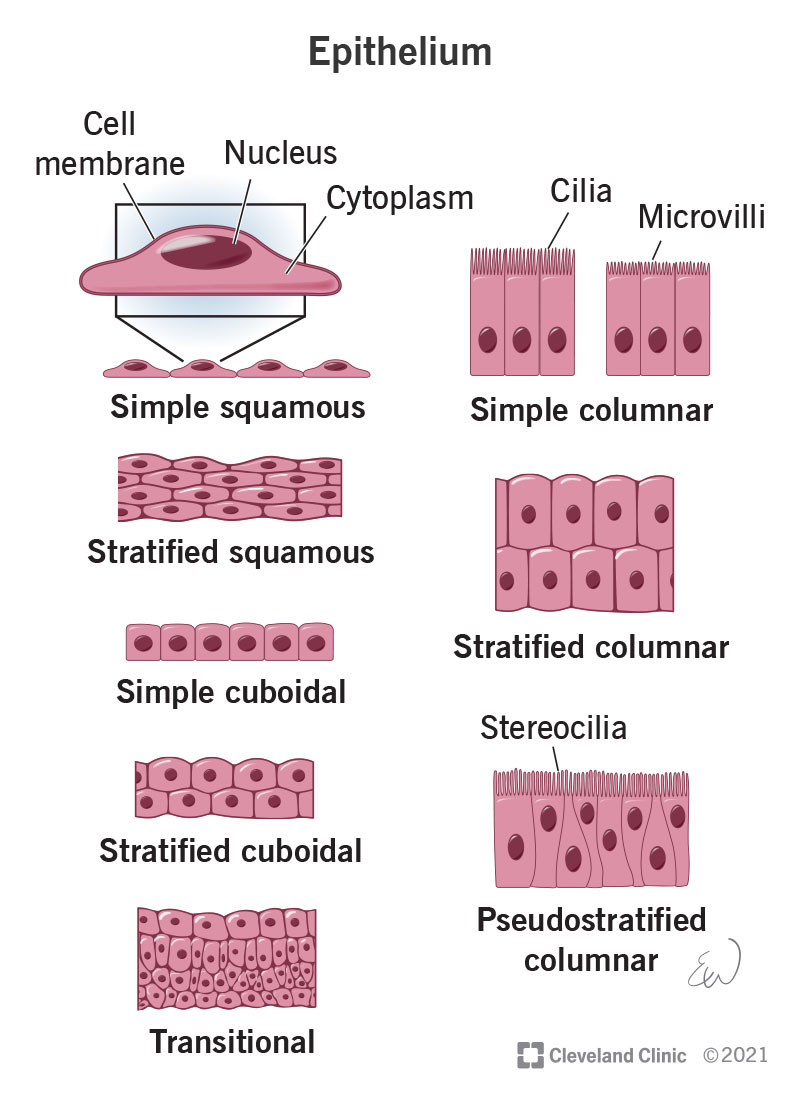
Stratified epithelium
Many layers of epithelial cells.
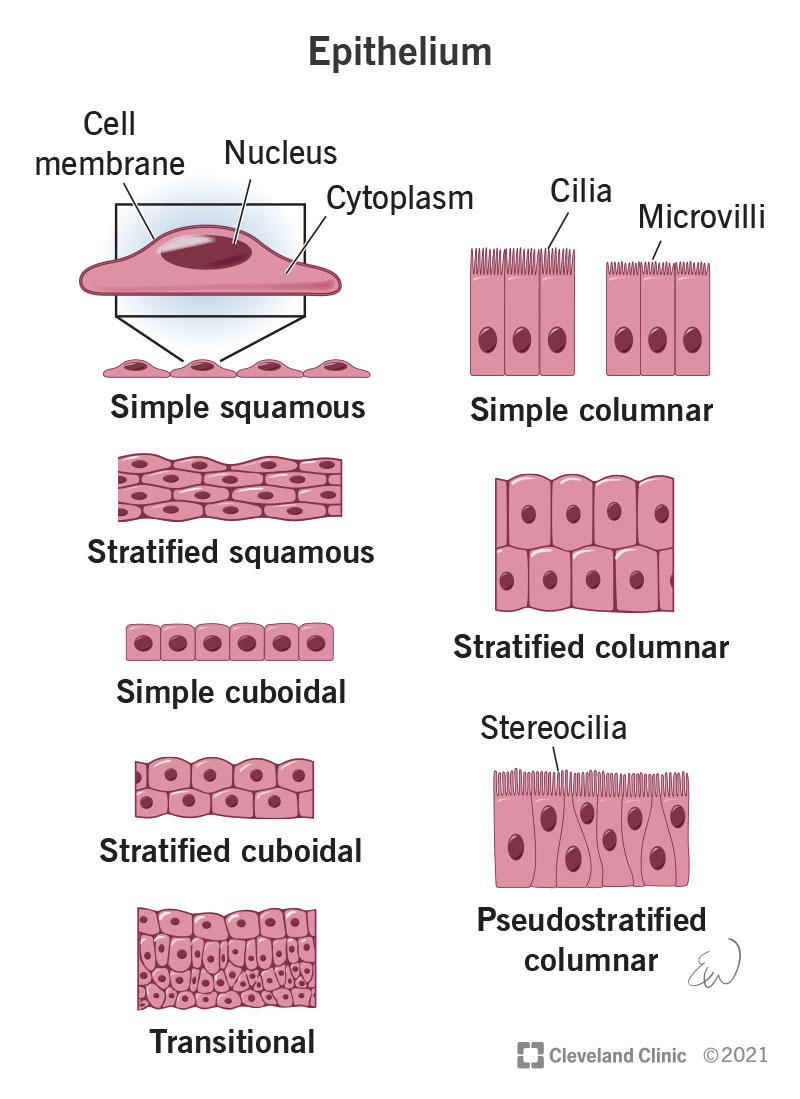
Cilia
Hair-like projections on some epithelial cells that move substances like mucus.
Simple squamous epithelium
One layer of flat cells; allows diffusion.
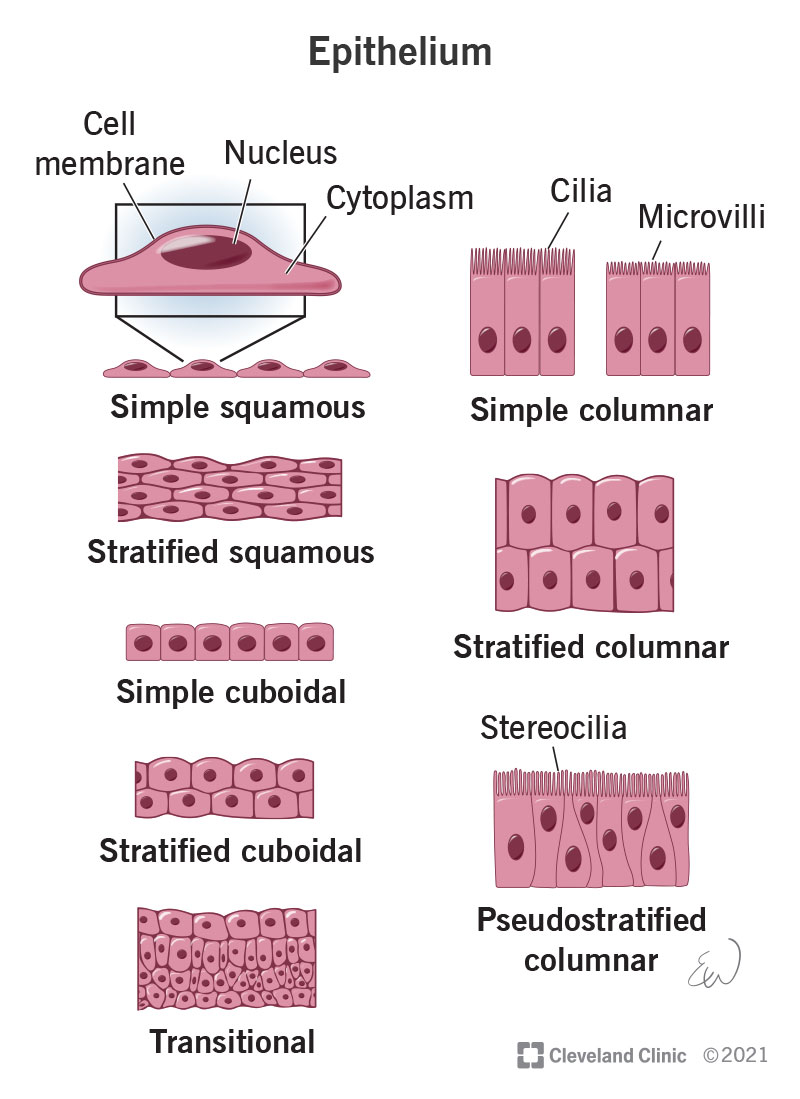
Simple cuboidal epithelium
One layer of cube-shaped cells; suited for secretion and absorption.
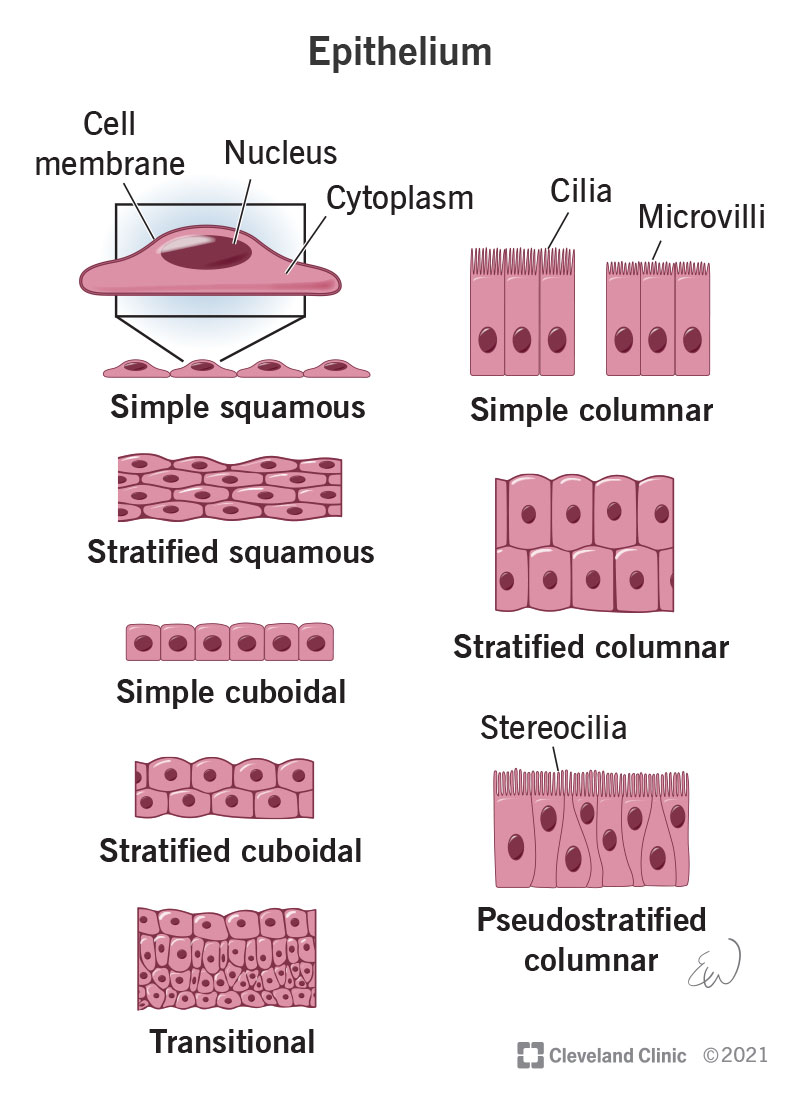
Simple columnar epithelium
One layer of tall cells; good for absorption and secretion.
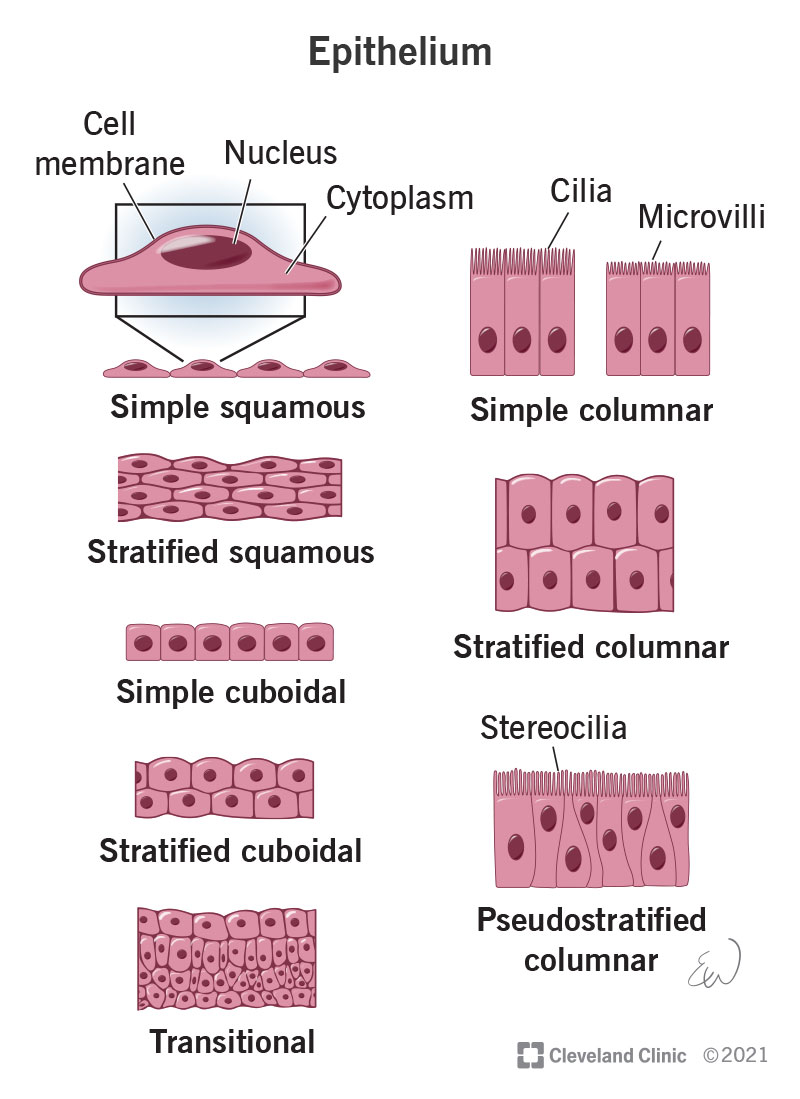
Stratified squamous epithelium
Multiple layers of flat cells; provides protection.
Neuron
Nerve cell that transmits electrical signals.
Glial cell
Supportive cells that nourish and protect neurons.
Cell body
The central part of a neuron containing the nucleus (soma).
Dendrites
Branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons.
Axon
Long projection that transmits impulses away from the cell body.
Axon terminal
End of an axon where it forms synapses with other cells.
Nervous tissue role
Transmits electrical signals and controls the body.
nervous tissue
Throughout the entire body.
Cartilage locations
Found in the ears, nose, and between bones.
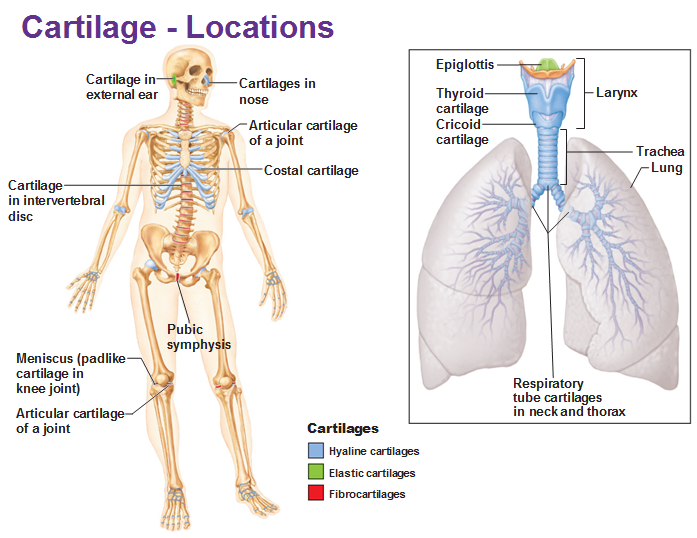
Long bones function
Used as levers in movement to facilitate locomotion.