Lecture 6 - Hemoglobin II
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Intersubunit contacts
a1-b1 and a2-b2 (strongest, cannot alter)
a1-b2 and a2-b1 (strong but CAN be altered, important)
a1-a2 and b1-b2 (few salt bridge contacts)
a1-b1 and a2-b2 contacts
35; VERY strong and cannot alter
a1-b2 and a2-b1 contacts
19; strong but CAN be altered (important for deoxy to oxy shift)
a1-a2 and b1-b2 contacts
Few salt bridges; weak, stabilize deoxy form
What occurs during the shift from deoxy to oxy Hb?
Change in quaternary structure: a1b1 dimer rotates relative to a2b2
Cavity in the middle of Hb
Water-filled; gets smaller after shift to oxy-Hb
What allows the a2-b2 dimer to rotate about a1-b1?
The flexible interactions between a1-b2 and a2-b1 contacts
Important Interactions
Hydrophobic effect, H-bond, and salt bridges between FG corners and C helices
NOTE that some interactions change and stay the same between deoxy and oxy Hb
Deoxy to oxy transition
O2 covalently binds to Fe on heme, requiring Hb to flatten heme
Flattening is the KEY to Hb cooperativity
Importance of heme flattening
Basis of cooperativity through a chain reaction for all four subunits
Process of Conformation Change
O2 binds to Heme Fe
Fe moves into the porphyrin plane with proximal His
F helix of b2 moves towards the porphyrin ring
b2 FG moves relative to a1C
Intersubunit H-bonds break/form
Salt bridges disrupt
What is required for all subunits to change conformation?
Deoxy to oxy shift must occur simultaneously at a1b2 and a2b1 interfaces because those interactions are flexible
Structural Changes Upon O2 Binding
Quaternary structure change
All 4 hemes adopt R (oxy, high affinity) state
MUST exist this way, not just 1 heme (positive cooperativity)
What two forms can Hb exist in?
T or R
T = deoxy
R = oxy
Which subunits communicate → R state?
a1 → b1
a1 → b2
b1 → a2
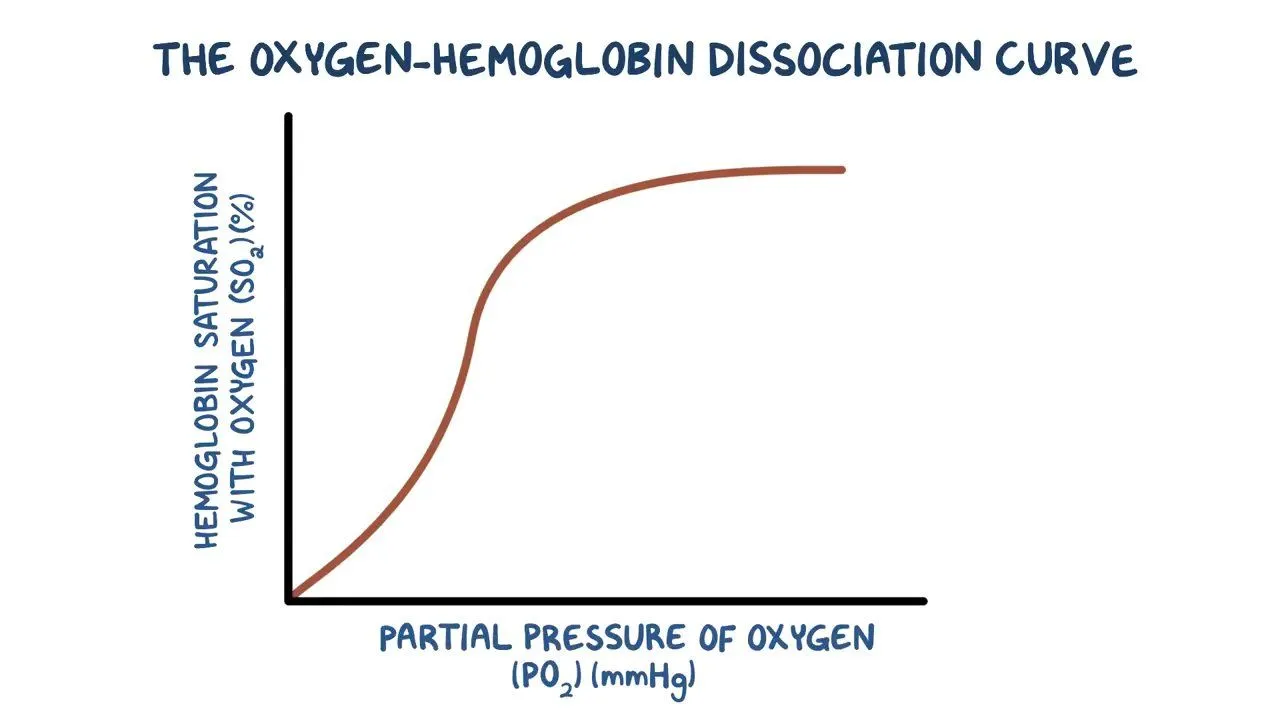
Sigmoidal Curve related to conformational changes
De-oxy state: all subunits in T state, low affinity
One molecule of O2 binds, inducing change in all others
Other 3 binding sites occupied
Fully in R state, high affinity
In what two ways in Hb regulated?
Heterotropically (by CO2 and 2,3-BPG)
Homotropically (by O2)
What is heterotrophic regulation?
Protein is regulated by something it doesn’t usually bind
Hb’s heterotrophic regulators
2,3-BPG
CO2
CO2 Regulation of Hb (Bohr effect)
CO2 lowers pH, causing His to protonate, stabilizing deoxy form with a salt bridge
2,3-BPG Regulation of Hb
Fits into cavity of deoxy-Hb ONLY, stabilizing it with a salt bridge (low affinity for O2)
Fetal vs. Maternal Hb
Fetal Hb has higher affinity for oxygen because instead of having a Histidine, it has Serine so BPG has one less spot to bind and stabilize deoxy-Hb
Why would fetuses need higher affinity Hb?
They are competing for oxygen with mother
Sickle Cell Anemia Cause
Mutation in gene coding for Hb-b, instead of glutamate there is a valine (Polar charged → Nonpolar)
What does Glu → Val switch do?
Creates sticky patch and hydrophobic effect, causing fibers
What do fibers in Hb lead to?
Sickling of RBCs (wrong shape), cannot transport oxygen and causes pain due to getting stuck in vessels