Intro, Reproductive Cycle, & Menstruation
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
What are the two types of women's health history?
gynecologic and obstetric Hx
These are part of what type of history?
◦GYN diseases and treatment
◦Sexually transmitted infections
◦Breast disease
◦Infertility
◦Urinary tract/bowel complaints
◦Personal hygiene
◦Health maintenance
◦Exposure to diethylstilbesterol (DES)
Last Pap and results, Regular breast exams, Mammogram, Colonoscopy, DEXA scan
gynecologic hisotory
What has to do with a risk for clear cell adenocarcinoma?
DES
What age should PAP smears be started?
21
What age should mammograms be started?
40
What age should a colonoscopy be started?
45
What age should a dexa scan be started?
65 or younger if risk factors
What is the average age for menopausal symptoms?
48-55yo (avg = 51)
What is the term for # of days between the first day of the first or second period?
cycle length
What is the term for # days of bleeding?
length of bleeding
What is the term for how may tampons/pads per x hours?
estimated blood loss
When asking about the last menstrual period, what do you need to know?
first day of bleeding
*ask “when was the first day of your last menstrual cycle?”
What characterizes menopause?
12 full months with no bleeding
What characterizes postmenopausal bleeding?
12 full months with no bleeding → bleeding (endometrial CA until proven otherwise!)
What is the average age for menarche?
9-16yo
What is the interval between period range?
24-32 days (average 28)
How long does bleeding typically last during menses?
3-7d
What is the term for menstruation that has never occurred?
primary amenorrhea
What is the term for menses has occurred at least once and has been absence for at least 6 months?
secondary amenorrhea
What is the term for:
absence of menstruation
amenorrhea
What is the term for:
scanty menstrual flow
oligomenorrhea
What is the term for:
excessive menstrual bleeding
menorrhagia
What is the term for:
bleeding between periods
metrorrhagia
What is the term for:
irregular or excessive bleeding other than during menstruation
menometorrhagia
What is the term for:
painful menstruation
dysmenorrhea
What is the term for:
the occurrence of menstrual cycles more frequently than normal
polymenorrhea
What are the 5 P's when obtaining a sexual history?
Partners: Number and gender
Pregnancy Prevention: TTC vs what is being used for prevention
Protection: STI protection, % time used
Practices: oral, anal, vaginal
Past: STIs (what, when, tx, current concerns)
What are 3 cases when to take a sexual history?
-all new pts
-pts present with a problem that is likely to be sexually related (ex: dysuria, urethral discharge)
-pt has medical or social problems that may lead to sexual difficulties (ex: HTN, DM, Divorce)
Explain the GTAL for obstetric Hx.
Gravidity total
Parity (TPAL)
Term, Preterm, Abortion/miscarriage, Living
What is the term for:
total # of pregnancies regardless of outcome
gravidity
What is the term for:
# of births after 20 wks
parity (TPAL)
Term, Preterm, Abortion/miscarriage, Living
What is the formula for expected date of delivery (EDD)-- Negele's Rule?
First date of LMP + 7 days - 3 months
What is the term that calculates the expected date of delivery?
Negele's rule
What are the three components for a women's health PE?
◦Breast exam
◦Abdominal exam
◦Pelvic exam
in the reproductive cycle, ovulation is _____ ___ menstrual bleeding, in a cyclic predictable fashion, if pregnancy does not occur
followed by
The duration of an adult reproductive cycle from the beginning of menses (day 1) to the beginning of next menses (day 1), averages ____ days.
28 days (+/- 7d)
The 3 phases of the reproductive cycle are referring to what?
status of the ovaries
What are the three phases referring to the ovary?
follicular, ovulation, luteal
What are the phases that refer to endometrium?
proliferative and secretory
What phase of the reproductive cycle remains relatively constant?
luteal phase
What phase of the reproductive cycle varies?
follicular phase
In the reproductive cycle, ovulation is _______ menstrual bleeding, in a cyclic predictable fashion, if pregnancy does not occur.
followed by
What phase of the reproductive cycle is described:
-Begins with onset of menses (1st day)
-Ends day of luteinizing hormone (LH) surge
-Lasts about 14 days
- Endometrium in proliferative phase
follicular
What stage of the repro cycle ENDS the day of LH surge?
follicular
What stage of the repro cycle does the LH surge START?
luteal
What phase is the endometrium when in the follicular phase of the repro cycle?
proliferative phase
What phase of the reproductive cycle is described:
-Occurs within 30-36 hours of LH surge
-Window to get pregnant and egg to be fertilized
ovulation
What phase in the repro cycle is the window for the egg to be fertilized?
ovulation
What phase of the reproductive cycle is described:
-Begins the day of LH surge
-Ends with onset of menses
-Lasts about 14 days
- Endometrium in secretory phase
luteal phase
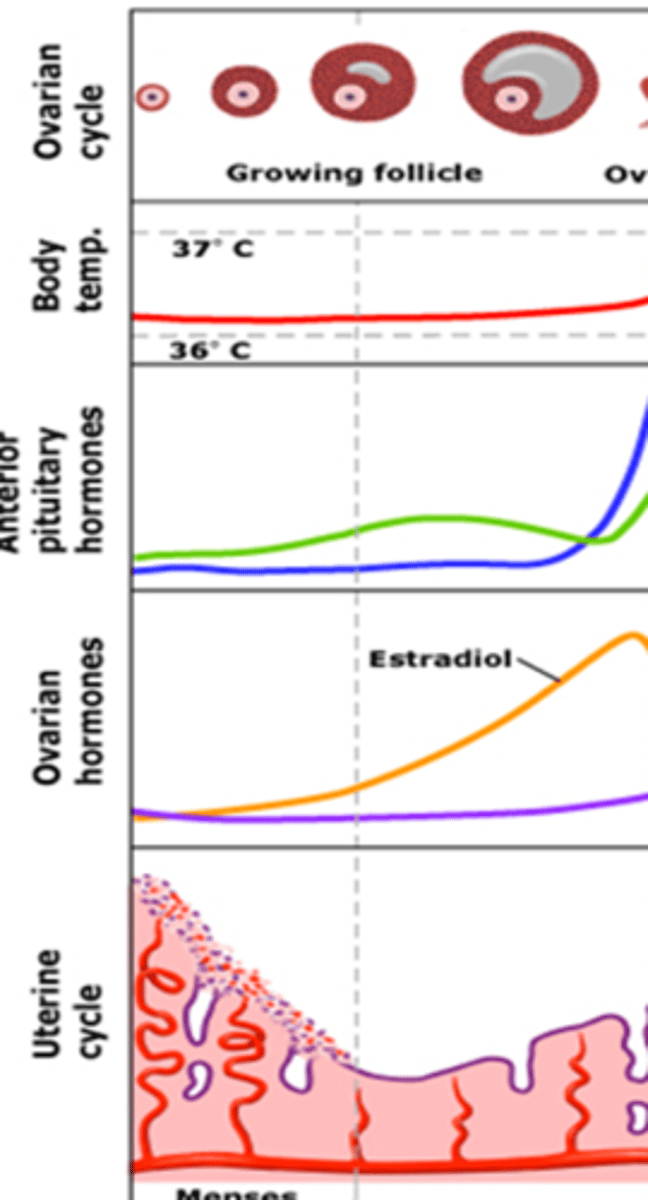
What stage of the repro cycle is shown and what endometrial phase ?
follicular phase
endometrium= proliferative phase
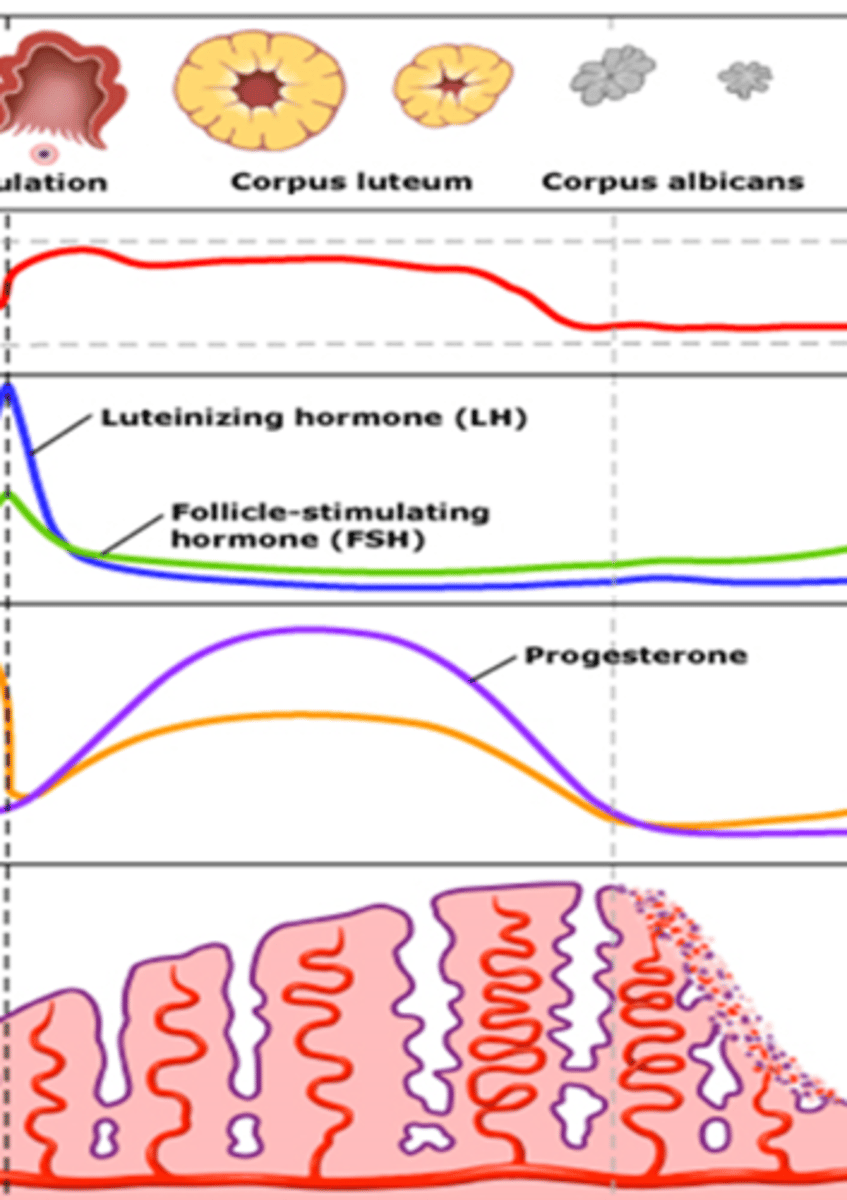
What stage of the repro cycle is shown?
luteal phase
endometrium= secretory phase
What phase is the endometrium when in the luteal phase of the repro cycle?
secretory
What 3 complexes regulate the reproductive cycle?
hypothalamus
pituitary
ovaries
Trace the pathway of regulation of hormones for the reproductive cycle.
Hypothalamus releases Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) -->
stimulates anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH -->
stimulates the ovaries to produce follicles (which release estrogen) & progesterone
What hormone released by the hypothalamus-- stimulates the gonadotropins in the ant. pituitary and is a pulse generator of the repro cycle?
GnRH
What two hormones are released from the ant pit in response to GnRH?
FSH and LH
What hormone is decreased during menopause?
estrogen
(FSH = elevated)
Trace Ovarian Follicle Development.
◦Ovary contains 1-2million follicles at birth
◦Each follicle contains an oocyte in the first stage of division
◦Every month the pituitary gland tells the ovaries to produce several fluid-filled cysts called follicles
◦As the follicles grow, they secrete estrogen
◦Estrogen works to thicken the wall of the uterus in preparation for pregnancy
◦On day seven of the cycle, the follicles stop growing except for one
--->This follicle continues to grow and to nourish a maturing egg (oocyte) within
What is needed to induce ovulation?
LH surge
In late follicular phase, _____ ______ from dominant follicle sends message to pituitary to stimulate mid-cycle LH surge, starting ovulation.
peak estradiol
What is a progesterone secreting ovarian cyst that develops due to a follicle leaving behind remnants?
corpus luteum
What can you check to confirm that ovulation has happened?
progesterone
What produces contractions of the uterine vasculature and musculature?
prostaglandins
What leads to menstrual cessation?
rising estrogen levels in early follicular phase
____ is high during the follicular phase and _____ is high during the luteal phase.
estrogen, progesterone
What is the term that means pain associated with ovulation?
Mittelschmerz
During conception the zygote secretes what hormone that sustains the corpus luteum for 6-7 wks?
hCG
During conception adequate _______ production by the corpus luteum is necessary to sustain early pregnancy.
progesterone
By 9-10 weeks the ______ assumes progesterone production.
placenta
When conception does not happen the CL stops producing progesterone and becomes a white fibrous steak within ovary called a ____ _____.
corpus albicans
What are some clinical manifestations of hormonal changes to:
breasts
breast tenderness or nodules
What are some clinical manifestations of hormonal changes to:
vaginal epithelium
variation in secretions
What are some clinical manifestations of hormonal changes to:
endocervix
variations in secretions
What are some clinical manifestations of hormonal changes to:
endometrium
proliferative or secretory on histologic eval
What are some clinical manifestations of hormonal changes to:
hypothalmus
basal body temperature changes
What phase of the endometrium has predominant estrogen switch to progesterone?
secretory phase
What is the only way to ID proliferative from secretory endometrium?
biopsy
The endocervix under estrogen influence secretes what?
thin, clear, watery mucus
What can you monitor to optimize timing of intercourse or to avoid conception?
cervical mucus
progesterone or estrogen:
influences ductal elements of the breast, nipple, and areola causing tenderness and fullness during luteal phase
progesterone
progesterone or estrogen:
aids in lubrication and growth of the vaginal epithelium
estrogen