Biology Revision
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/465
Last updated 10:25 PM on 11/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
466 Terms
1
New cards
CELLS (2)
2
New cards
8 Factors living things must fufill (MRSGREEN)
Movement
Respiration
Sensitivity
Growth
Reproduction
Equilibrium
Excretion
Nutrition
Respiration
Sensitivity
Growth
Reproduction
Equilibrium
Excretion
Nutrition
3
New cards
Cell theory
- all living things are made up of cells
- cells are the smallest and most basic unit of life
- all cells come from pre-exisiting cells
- cells are the smallest and most basic unit of life
- all cells come from pre-exisiting cells
4
New cards
What do both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells have
membrane
cytosol
ribosomes
DNA
cytosol
ribosomes
DNA
5
New cards
What type of DNA do prokaryotes have
Single loop of DNA (circular)
6
New cards
What type of DNA do eukaryotes have
Multiple strand of linear DNA
7
New cards
What is/Role of plasma membrane
controls what can and cannot enter the cell
8
New cards
What is/Role of cytosol
contains salts, nutrients, and molecules (its fluid)
9
New cards
What is/Role of cytoplasm
cytosol and all organelles (not nucleus) make the cytoplasm
10
New cards
What is/Role of nucleus
double membrane, protect and confine DNA which codes for proteins
11
New cards
What is/Role of nucleolus
Site of ribosome production
12
New cards
What is/Role of ribosomes
rRNA and proteins, subunits makes proteins
13
New cards
What is/Role of rough endoplasmic reticulum
Synthesises and modifies proteins
14
New cards
What is/Role of smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Production of lipids
15
New cards
What is/Role of Golgi apparatus
Protein sorting, modifying and packaging
16
New cards
What is/Role of lysosome
breaks down cell waste and toxins
17
New cards
What is/Role of mitochondria
2 membrane, site of aerobic cellular respiration, producing ATP
- contains its own DNA and ribosomes
- contains its own DNA and ribosomes
18
New cards
What is/Role of chloroplast
double membrane, site of photosynthesis, own DNA and ribosomes
19
New cards
What is/Role of Vacuole
water and solute storage, turgor pressure of cell
20
New cards
What is/Role of cell wall
sturdy border outside plasma membrane and provides strength and structure
21
New cards
What is/Role of vesicle
membrane bound sac that transports substances in/out of cell or stores them
22
New cards
What is/Role of cytoskeleton
Protein filament, maintaining shape and transporting vesicles around cell
23
New cards
Aerobic cellular respiration formula (worded and equation)
Glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water + energy
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP
24
New cards
Photosynthesis formula (worded and equation)
Carbon dioxide + water -> glucose + oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
25
New cards
What happens during photosynthesis and where does it occur
Occurs in chloroplasts
Green pigment chlorophyll in chloroplast absorbs light to energise reactions
Glucose produced is used to build cell walls and carry out metabolic reaction
Excessive glucose stored in seeds as starch
Green pigment chlorophyll in chloroplast absorbs light to energise reactions
Glucose produced is used to build cell walls and carry out metabolic reaction
Excessive glucose stored in seeds as starch
26
New cards
Benefits of having small cells
Material exchange can occur efficiently due to high surface area to volume ratio
Distance to travel within cell is smaller so transport of molecules is faster
Distance to travel within cell is smaller so transport of molecules is faster
27
New cards
Is a larger of smaller SA:V ratio more efficient and why
larger - more exposed area
28
New cards
MEMBRANE (3)
29
New cards
What is the plasma membrane made of and what does it do
Made of (phospho)lipids and is selectively permeable to seperate intra and extracellular environment
30
New cards
What does the phospholipid bilayer contain
Proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol
31
New cards
What is the Phospholipid head made of
Glycerol and phosphate group
32
New cards
What charge is the phospholipid head
negatively charged
33
New cards
Does the phospholipid head love or hate water (hydrophilic or phobic)
Hydrophilic - loves water - polar
34
New cards
What is the phospholipid tail made of
fatty acids
35
New cards
Does the phospholipid tail love or hate water (hydrophilic or phobic)
Hydrophobic - hates water - non-polar
36
New cards
What charge is the phospholipid tail
uncharged
37
New cards
Why are phospholipids stable
Because they are amphipathic - contain both hydrophobic and hydrophilic components
38
New cards
Functions of proteins in the membrane
Transport - channels and pumps control what enters/exits cell
Adhesion - Stick to other cells, extracellular matrix or cytoskeleton
Catalysis - speeds up chemical reaction with proteins (enzymes)
Communication - signals and regonise cells and molecules
Adhesion - Stick to other cells, extracellular matrix or cytoskeleton
Catalysis - speeds up chemical reaction with proteins (enzymes)
Communication - signals and regonise cells and molecules
39
New cards
Types of proteins and where are they in the membrane
Integral - permanent part of membrane
Transmembrane - Integral proteins which span entire bilayer
Peripheral - temporal attached to membrane
Transmembrane - Integral proteins which span entire bilayer
Peripheral - temporal attached to membrane
40
New cards
Structure of carbohydrates
In chains which extend outside of the cell
Rooted in membrane to lipids (glyco) or proteins (glyco)
Rooted in membrane to lipids (glyco) or proteins (glyco)
41
New cards
Function of carbohydrates
Signalling and Communication with cell
Recognition of self or non-self molecules
Recognition of self or non-self molecules
42
New cards
Cholesterol structure
Lipid steroid embedded between fatty acid tails of phospholipid bilayer in animal cells
43
New cards
Role of cholesterol
Regulates membrane fluidity
- If hot keeps molecules bound together (phospholipids)
- If cold disrupts fatty acid tails, stopping phospholipids from being a solid boundary
- If hot keeps molecules bound together (phospholipids)
- If cold disrupts fatty acid tails, stopping phospholipids from being a solid boundary
44
New cards
What does the fluid mosaic model explain
Molecules in membrane are not static/ not held in one place
Different molecules embedded in membrane
Moves laterally (side to side)
Different molecules embedded in membrane
Moves laterally (side to side)
45
New cards
What is diffusion
Movement of particles down a concentration gradient
- from area of high concentration to area of low concentration
- from area of high concentration to area of low concentration
46
New cards
What molecules can freely diffuse across the membrane
- non-polar
- uncharged
- hydrophobic
- small molecules (uncharged)
- uncharged
- hydrophobic
- small molecules (uncharged)
47
New cards
What leads to even particle distribution
Kinetic energy causes molecules to randomly move and bounce off each other, eventually leading to even particle distribution
- because of this higher temperatures = faster diffusion
- because of this higher temperatures = faster diffusion
48
New cards
What is a solute
thing being dissolved
49
New cards
What is a solvent
Thing being dissolved into
50
New cards
When is diffusion faster
When concentration gradient is steeper
51
New cards
What is facilitated diffusion and what does it allow
passive movement of molecules down the concentration gradient through a membrane bound protein (protein channel or carrier protein)
Allows larger/polar molecules to pass through membrane
STILL A PASSIVE PROCESS
Allows larger/polar molecules to pass through membrane
STILL A PASSIVE PROCESS
52
New cards
What is a protein channel
Pores/holes in the membrane which let specific substances through
53
New cards
What is a carrier protein/what does it do
Binds to substance being transported and undergoes conformational change to push substance down concentration gradient through membrane
- returns to its original shape once the molecule is transported
- returns to its original shape once the molecule is transported
54
New cards
What is Osmosis
Diffusion of water from area of low solute (high solvent) concentration to area of high solute (low solvent) concentration
55
New cards
Why can water diffuse through membrane if hydrophilic
Can diffuse because of their small size
56
New cards
What are protein channels for water called
Aquaporins
57
New cards
What is Hypertonic and the related movement of water
High solute concentration (water moves in)
58
New cards
What is Isotonic and the related movement of water
Equal solute concentration (no net movement of water)
59
New cards
What is Hypotonic and the related movement of water
Low solute concentration (water moves out)
60
New cards
What happens when animal cells fill with too much water (hypertonic)
Lysed - Too much water moves in and cell swells and bursts
61
New cards
What is active transport
Transporting substances across the membrane using energy
62
New cards
Does active transport go with or against the concentration gradient
Against
63
New cards
What does active transport require
Energy (ATP)
Membrane proteins - pumps and carriers
Membrane proteins - pumps and carriers
64
New cards
3 steps of active transport
- Binding - binds to specific protein pump
- Conformational change - energy released when bond is broken between 2nd and 3rd phosphate ions when ATP becomes ADP + P
- Release - pushed through protein and into other side of membrane
- Conformational change - energy released when bond is broken between 2nd and 3rd phosphate ions when ATP becomes ADP + P
- Release - pushed through protein and into other side of membrane
65
New cards
What is bulk transport
Movement of groups of molecules across plasma membrane using vesicles
66
New cards
What are the stages of Exocytosis
1. Vesicular transport - vesicle containing secretory products transported to plasma membrane
2. Fusion - membranes of vesicle and cell fuse
3. Release - Secretory products released from vesicle and leave cell
2. Fusion - membranes of vesicle and cell fuse
3. Release - Secretory products released from vesicle and leave cell
67
New cards
Why is Exocytosis possible
Because membrane is fluid and fuses with vesicle
When the vesicle fuses, it adds phospholipids and makes SA slightly bigger
When the vesicle fuses, it adds phospholipids and makes SA slightly bigger
68
New cards
What is Exocytosis
- contents of vesicle released from the cell
69
New cards
Why does the cell expand when exocytosis happens
Phospholipids are added to membrane
70
New cards
What is Endocytosis
- Transport into the cell
71
New cards
How is Endocytosis an effective defense mechanism
If invaded, a lysosome cans enter and digest invader
72
New cards
Endocytosis steps
1. Fold - membrane folds inwards and forms cavity that fills with extracellular fluid and target molecules
2. Trap - folds in on itself until 2 ends meet and fuse
3. Bud - Vesicle (endosome) pinches off from membrane
2. Trap - folds in on itself until 2 ends meet and fuse
3. Bud - Vesicle (endosome) pinches off from membrane
73
New cards
Why does the cell shrink when endocytosis happens
Phospholipids are removed from membrane
74
New cards
What is phagocytosis
Endocytosis of solid material or food particles
75
New cards
What is pinocytosis
Endocytosis of liquid or dissolved substances
76
New cards
CELL CYCLES (4)
77
New cards
Purpose of cell replication
- growth and development
- maintenance and repair
- reproduction
- maintenance and repair
- reproduction
78
New cards
What does binary fission result in
2 genetically identical copies of a cell
79
New cards
Binary fission steps
1. DNA unclouded and replicated
2. Cell elongates and DNA duplicate move to opposite sides
3. Cytokinesis - pinches inwards and creates a septum
4. New wall and membrane formed down middle
5. seperate and 2 genetically identical cells are formed
2. Cell elongates and DNA duplicate move to opposite sides
3. Cytokinesis - pinches inwards and creates a septum
4. New wall and membrane formed down middle
5. seperate and 2 genetically identical cells are formed
80
New cards
Why aren't plasmids evenly distributed during binary fission
plasmids replicate Independently therefore aren't distributed evenly
81
New cards
What happens during Interphase
Cell synthesises the DNA, proteins and organelles required for growth/replication
82
New cards
What form is DNA in during Interphase
chromatin threads not chromosomes
83
New cards
What happens in the G1 phase
- Increase in cytosol volume
- Synthesising proteins for DNA replication
- Replicating its organelles
At the end, cell either proceeds to S or exits cell cycle and enters G0 phase
- Synthesising proteins for DNA replication
- Replicating its organelles
At the end, cell either proceeds to S or exits cell cycle and enters G0 phase
84
New cards
What happens during G0 phase
- cells which don't need to replicate rest here
85
New cards
What is a Quiescent cell
A cell which is dormant and can re-enter the cell cycle
86
New cards
Terminally Differentiated
A cell which is fully specialised and no longer replicates - remains in G0 indefinitely
87
New cards
What happens during the S phase
replicates DNA
- 1 chromosome becomes 2 genetically identical sister chromatids
- centromere holds them together
- 1 chromosome becomes 2 genetically identical sister chromatids
- centromere holds them together
88
New cards
What happens during G2 phase
- increase of volume in cytosol
- synthesis proteins to prepare for mitosis
- synthesis proteins to prepare for mitosis
89
New cards
What are the 4 stages of Mitosis and in order
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
90
New cards
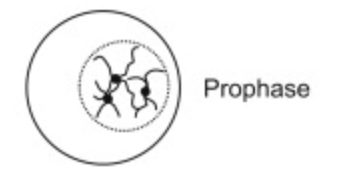
What happens at Prophase?
Condensation of chromatin so chromosomes become visible
Centrioles move to opposite poles
Spindle fibres begin to form
Nuclear membrane breaks down
Centrioles move to opposite poles
Spindle fibres begin to form
Nuclear membrane breaks down
91
New cards
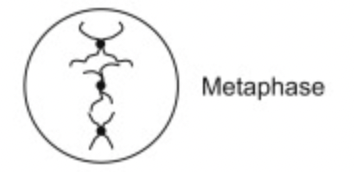
What happens at Metaphase?
- Spindle fibres are fully formed and attach to each chromosomes centromere
- The fibres guide chromosomes to line up at equator of cell
- The fibres guide chromosomes to line up at equator of cell
92
New cards
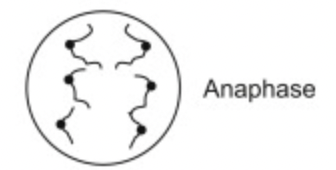
What happens at Anaphase?
- spindle fibres contract and splits centromere
- sister chromatids pulled to opposite ends of cell
- sister chromatids pulled to opposite ends of cell
93
New cards
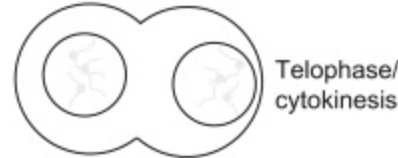
What happens at Telophase?
- spindle fibres disintegrate
- a cleavage furrow forms (animals)
- a cell plate forms (plants)
- a cleavage furrow forms (animals)
- a cell plate forms (plants)
94
New cards
What happens at Cytokinesis?
Cytoplasm divides and and organelles evenly distribute before separating into daughter cells
95
New cards
What happens at the G1 checkpoint?
Checks if
- Cell has grown to correct size
- DNA has been damaged
- If there is sufficient nutrients for mitosis
- Cell has grown to correct size
- DNA has been damaged
- If there is sufficient nutrients for mitosis
96
New cards
What happens at the G2 checkpoint?
checks if
- DNA replicated properly in S phase
- Cell has enough resources for mitosis
- DNA replicated properly in S phase
- Cell has enough resources for mitosis
97
New cards
What happens at the Metaphase checkpoint?
checks if
- Spindle fibres have formed and formed correctly
- Chromosomes are lined up in correct location
- Spindle fibres have formed and formed correctly
- Chromosomes are lined up in correct location
98
New cards
What are the 2 apoptotic pathways?
Mitochondrial (internal)
Death Receptor (external)
Death Receptor (external)
99
New cards
What detects internal damage in the mitochondrial pathway, and how does apoptosis then begin
Mitochondria - then releases cytochrome C to bind with proteins
100
New cards
What starts apoptosis in the death receptor pathway and what happens afterwards
Death signalling molecules are recognised by death receptor proteins on a cells surface (generally released by immune cells)
Molecules then bind to death receptor surface protein
Molecules then bind to death receptor surface protein