Honors Bio DNA Test
1/89
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What was Rosalind Franklin’s achivements?
She revealed the helical structure of DNA
What was Erwin Chargaff’s achivements?
Made the Chargaff’s Rules (A=T, C=G)
What were James Watson and Francis Crick’s achivements?
Constructed a model that showcased DNA's spiral form
What kind of macromolecule is DNA?
Nucleic Acid
What is the monomer of a Nucleic Acid?
Nucleotide
What are the three main components of a nucleotide?
A phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogen base
What are the 4 nitrogen bases?
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G)
What are the 2 Pyrimidines?
Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C)
What are the 2 Purines?
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
How many strands does DNA have?
2 strands
What sugar is DNA?
Deoxyribose
What is the Sugar-Phosphate Backbone (sides of DNA) made of?
phosphate groups and deoxyribose sugars
What bonds connect the phosphate groups and the deoxyribose sugars together, forming the Sugar-Phosphate Backbone?
Covalent bonds
What are the “rungs” of DNA made of?
Nitrogen bases
What bonds connect the nitrogen bases together, creating the rungs of the DNA?
Hydrogen Bonds
What does it mean that DNA runs “anitparallel”?
One strand runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction while the other runs int he 3’ to 5’ direction, making them create a double helix
What is chromatin?
Loosely packed DNA wrapped around a protein (found when the cell is NOT dividing)
What are Chromosomes?
Tightly compacted strands of DNA (found when a cell is DIVIDING)
What are Chromatids?
one of the two identical halves of a chromosome that has been replicated in preparation for cell division.
What is a gene?
The basic unit of heredity passed from parent to child.
Where does DNA replication take place in? (Eukaryotes)
Nucleus
When does DNA replication occur?
During the “S” phase of the Cell Cycle
What is “Semi-Conservative Replication”?
Making an identical copy of a double helix using only 1 side of the DNA molecule
What is the first step of DNA replication?
Helicase “unwounds/unzips” the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds between each nucleotide strand
Which enzyme “unzips” the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds beween each nucleotide strand?
Helicase
What is the second step of DNA replication?
RNA Primase creates short RNA sequences called primers that the DNA Polymerase uses to create each DNA template strand
Which enzyme creates short RNA sequences called “primers”?
RNA Primase
Which enzyme creates new DNA template strands after binding to the RNA primers by adding a complementary base nucleotide?
DNA Polymerase
DNA Polymerase can only bind to an available _________ group
OH-
In which direction does DNA Polymerase produce DNA in?
5’ to 3’
The strand of DNA that is created towards the “replication fork” is called the ________ ___________.
Leading Strand
The strand of DNA that is created “backwards” in short fragments is called the ______ __________.
Lagging Strand
What are Okazaki Fragments?
Short, discontinuous fragments created by DNA Polymerase in the Lagging Strand
What is the third step of DNA replication?
The short Okazaki Fragments get conneted together with a phosphate group by the enzyme called DNA Ligase.
Which enzyme connects the Okazaki Fragments with a phosphate group to complete the replication of DNA?
DNA Ligase
What are the end results of DNA replication?
2 new identical DNA strands (made up of ½ the original DNA strand and ½ of the newly synthesized strand)
Why do cells divide?
Cells divide to allow reproduction (single-celled organisms), growth and repairs, and for the production of sperm and egg cells
What are the 2 types of reproduction?
Asexual and Sexual
What is an example of asexual reproduction?
Vegetative Propagation (a cut piece of potato sprouting) and Budding (a small bud forming on the parent yeast cell and eventually splitting apart creating a new yeast cell)
What are the 2 types of cell division?
Mitosis and Meiosis
What is a Somatic Cell?
Any cell of a living organism other than a reproductive cell (goes through mitosis, has 46 chromosomes in humans)
What is a Gamete (Germ) Cell?
Sex cells/reproductive cells (the sperm and egg, has 23 chromosomes in humans)
What is the correct order of the cell cycle phases?
G0/G1 → S → G2 → M
What happens in the G1 phase?
The cell goes through rapid growth and performs its normal functions
What happens in the S phase?
The cell passes the “restriction point” of growth and begins to synthesise its DNA
What happens in the G2 phase?
All organelles are copied and the cell goes through more rapid growth and protein synthesis. All copied DNA is checked for errors here.
What is the G0 phase?
Cells that never move on to the S phase stay in the G1 phase until they die, which is known as the G0 phase.
What cells are in the G0 phase?
Brain cells, Heart cells and Neurons (cannot be repaired b/c they don’t go through cell division)
What is the order of the phases in the M phase?
Prophase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase → Cytokenisis
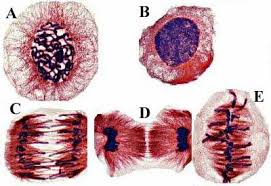
What phase is cell A in?
Prophase
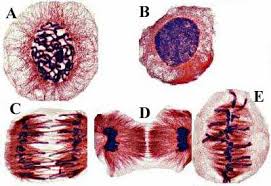
What phase is cell B in?
Interphase
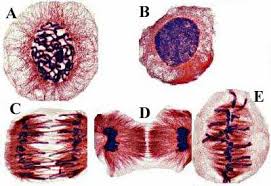
What phase is cell C in?
Anaphase
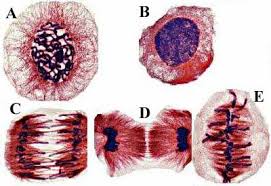
What phase is cell D in?
Telophase
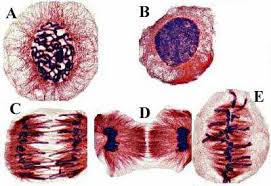
What phase is cell E in?
Metaphase
In which phase does the chromosomes in the cell double during Mitosis?
Anaphase
What happens in Prophase?
DNA condenses into chromosomes/sister chromatins
Centrioles move towards the poles of the cell (only in animal cells)
The nucleus/nuclear envelope disappears
What happens in Metaphase?
Microtubles (spindle fibers) from the centrioles connect to the kinetocore of each centromere
Chromosomes line up in the equator of the cell
What happens in Anaphase?
Spindle fibers shorten, pulling apart the centromeres at the kinetocore
Sister chromatins split and move towards the poles of the cell
This temporarily doubles the number of chromosomes
What happens in Telophase?
2 new nuclei (nucleus) begin to form
Chromosomes uncoil back into chromatin
A cleavage furrow begins to form
What is the centromere?
The “center” part of 2 sister chromatids that connects the 2 together
What is the kinetocore?
The part of the centromere where the spindle fibers connect to during Mitosis
What is a diploid cell?
A cell that has “paird chromosomes” (has 46 chromosomes in humans), all somadic cells are diploid cells
What is a haploid cell?
A cell that has a “single copy” of each chromosome type (Gametes/reproductive cells, has only 23 chromosomes)
What happens during cytokenesis in animal cells?
the plasma membrane of the parent cell pinches inward along the cell's equator until two daughter cells form
What happens during cytokenesis in plant cells?
the cytoplasm is partitioned by the construction of a new cell wall, the cell plate, inside the cell
Where do the spindle fibers come from in plant cells?
Cell wall
What is cancer (definition)?
The uncontrolled growth and division of somadic cells
What determines the type of cancer you get?
Where it originates from the body (ex: started from lungs → lung cancer)
How does cancer start?
Mutations that build up during the S-Phase that never get corrected deactivate the mechanisms that control its rate of cell division
What are the mechanisms of a cell that control the rate of cell division?
amount of nutrients/growth factors present
Density-Dependent Inhibition
Apotosis
What is Density-Dependent Inhibition?
Normal cells stop growing when they come in contact with another layer of cells (density)
What is Apotosis?
Pre-programmed cell death
What is Angiogenesis?
The process of cancer cells tricking the body into growing blood vessels to feed them
What are Tumors?
A mass of cancer cells
What are the 2 types of tumors?
Benign and Malignant
What is a Benign tumor?
A tumor that is NOT actively growing/spreading throughout the body
What is a Malignant tumor?
A tumor that can or is actively growin/spreading through the body
What is Metastasis?
The active spreading of cancer cells from 1 part of the body to another
What are some causes of cancer?
Genetic Predisposition
Country of Origin
Environmental factors
What are Preventable Cancers?
Types of cancers in which the chance of getting it can be reduced/avoided by lifestyle changes
What are Screenable cancers?
Cancers that can be detecte and treated early on
What is the surgical treatement for cancer?
The tumors/growths are surgically removed from the body
What is radiation therapy?
The cancer cells are exposed to radiation which messes up their DNA and kills them. However, this also kills healthy cells.
What is chemotherapy?
The use of drugs/chemicals to inhibit the growth/kill cancer cells
What is Hormone Therapy?
Treating cancer by reducing the chance cancer comes back/stopping or slowing its growth by using hormones.
What is Immunotherapy?
The usage of multiple different therapies to trigger the body’s immune system to detect adn destroy cancer cells on their own
What is a telomere?
A repeating strand of DNA at the end of a chromosome that acts like an “end cap”. It keeps chromosomes in order and protets them.
What happens to the telomere in a normal cell?
It shortens as the cell divides and eventually prevents the cell from dividing further
What do telomeres have to do with cancer cells?
The telomeres in cancer cells are constantly rebuilt, which enables the cancer cells to continue divide uncontrollably
What enzyme in cancer cells rebuild telomeres?
Telomerase