Hydrocarbons 24
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What are hydrocarbons
organic compounds consisting only of carbon and hydrogen
What is hydrocarbons used for commonly and examples
Commonly used as fuels (e.g. methane, propane, octane), solvents, and raw materials for plastic production.
Examples: Methane (CH₄), Ethene (C₂H₄), Ethyne (C₂H₂), Benzene (C₆H₆)
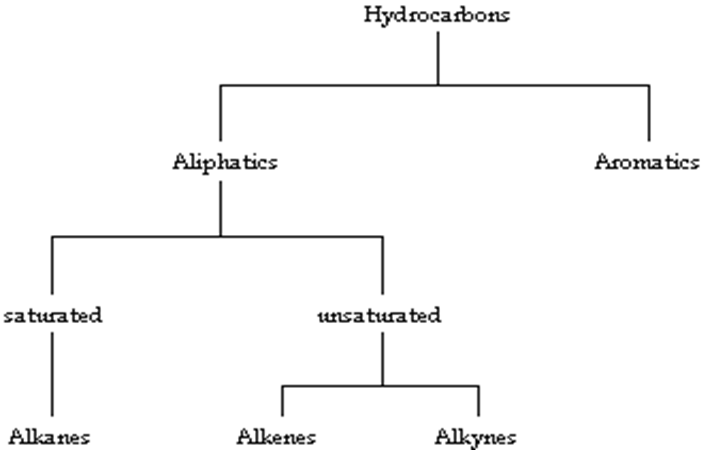
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons
1.Alkanes
Alkanes - saturated, single bonds only
Alkenes – unsaturated, one or more double bonds
Alkynes – unsaturated, one or more triple bonds
Aromatic hydrocarbon
contains a benzene ring
Saturated hydrocarbons
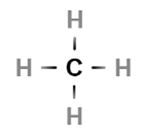
•: Only single bonds between carbon atoms (alkanes)
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons:

At least one double or triple bond (alkenes and alkynes)
Aromatic Hydrocarbons

Contain delocalised π electrons in a ring (e.g. benzene)
homologous series
w examples
•is a family of compounds with:
•The same general formula
•Similar chemical properties
•Gradual changes in physical properties (e.g. boiling point)
•Each member differs by a CH₂ unit
Alkanes: CH₄, C₂H₆, C₃H₈, C₄H₁₀
Trends in Physical Properties
•Boiling and melting points increase with molecular size.
•Straight-chain hydrocarbons have higher boiling points than branched ones (due to surface area).
•Aromatic hydrocarbons tend to have higher boiling points than aliphatic hydrocarbons of similar size
Uses of Hydrocarbons
•Fuels: methane, propane, octane
•Solvents: hexane, toluene
•Plastics: ethene (polyethylene), propene (polypropylene)
•Pharmaceuticals and dyes (aromatic hydrocarbons)
What are the four main types of hydrocarbons?
Alkanes: Saturated hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds between carbon atoms.
Alkenes: Unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one double bond between carbon atoms.
Alkynes: Unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one triple bond between carbon atoms.
Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Unsaturated, cyclic compounds that contain a special type of bonding called a delocalized pi-electron system. Benzene is the most common example.
Why are alkenes considered unsaturated?
Alkenes are considered unsaturated because they contain a carbon-carbon double bond 🔗. This double bond means that the carbon atoms are not bonded to the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms, unlike alkanes which are "saturated" with hydrogen atoms due to their single bonds. The double bond creates an opportunity for addition reactions where more atoms can be added to the molecule.
What distinguishes aromatic hydrocarbons from alkenes?
While both are unsaturated, the key difference lies in their structure and stability. Aromatic hydrocarbons are cyclic (ring-shaped) molecules with a special delocalized system of pi-electrons, which gives them exceptional stability. This stability makes them less reactive than alkenes and prone to substitution reactions rather than the addition reactions typical of alkenes. Alkenes, on the other hand, contain localized double bonds in a linear or branched chain, making them more reactive and readily able to undergo addition reactions where the double bond breaks to form new single bonds.
Name three everyday uses of hydrocarbons.
Fuels: Hydrocarbons are the primary components of fossil fuels like gasoline ⛽, diesel, natural gas, and propane, which are used to power vehicles, heat homes, and generate electricity.
Plastics and Polymers: Hydrocarbons serve as the raw materials for producing various plastics and polymers, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, which are used in countless products from bottles to synthetic fibers.
Lubricants: Heavier hydrocarbons, like those found in lubricating oils and motor oil, are used to reduce friction between moving parts in machinery and engines.