bio 7 skeleton
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
Axial Skeleton
Central part of the skeleton, includes skull and spine.
Long Bones
Greater length than width, includes humerus.
Short Bones
Cube-shaped, nearly equal length and width.
Flat Bones
Thin bones, protect organs and provide muscle attachment.
Irregular Bones
Irregularly shaped, includes vertebrae.
Sesamoid Bones
Seed-shaped bones, develop in tendons.
Sutural Bones
Small bones located in cranial sutures.
Diaphysis
Long bone shaft, contains medullary cavity.
Epiphysis
Ends of long bones, covered with articular cartilage.
Compact Bone
Dense bone tissue, forms outer layer.
Spongy Bone
Lightweight bone tissue, found inside bones.
Bone Surface Markings
Structural features adapted for specific functions.

Depressions
Surface markings that allow passage of tissues.

Openings
Holes in bones for nerves and blood vessels.

Fissure
Narrow opening between bones for vessels/nerves.
Foramen
Round opening for passage of blood vessels/nerves.

Fossa
Shallow depression in a bone.

Sulcus
Groove or furrow in a bone.

Meatus
Canal-like passageway in a bone.

Cranial Bones
Eight bones forming the skull's protective case.

Facial Bones
Fourteen bones forming the face structure.

Process
Outgrowths forming joints or attachment points.
Condyle
Large rounded projection with smooth articular surface.

Facet
Smooth, flat, slightly concave articular surface.

Head of bone
Rounded articular projection on neck of bone.

Crest
Prominent ridge or elongated projection on bone.

Line
Long, narrow ridge or border on bone.
Spinous process
Sharp, slender projection on vertebrae.

Tubercle
Variably sized rounded projection on bone.

Superior orbital fissure
Passageway for blood vessels and nerves.

Jugular foramen
Opening for jugular vein passage.

Foramen magnum
Large opening for spinal cord entry.

Mandibular fossa
Depression for mandible articulation.

External acoustic meatus
Passageway for sound to the inner ear.

Medial condyle
Inner rounded projection of femur.

Lateral condyle
Outer rounded projection of femur.

Greater trochanter
Large projection on femur for muscle attachment.

Lesser trochanter
Smaller projection on femur for muscle attachment.

Iliac crest
Top ridge of the hip bone.

Linea
Long, narrow ridge less prominent than a crest.

Appendicular skeleton
Comprises 126 bones, including limbs and girdles.

Cranial cavity
Contains 8 bones of the skull.

Auditory ossicles
6 small bones in the ear.

Vertebral column
26 vertebrae forming the spine.

Thorax
1 sternum and 24 ribs.
Pectoral girdles
4 bones connecting arms to the body.

Pelvic girdle
2 bones connecting legs to the body.

Frontal bone
Forms forehead and roofs of orbits.
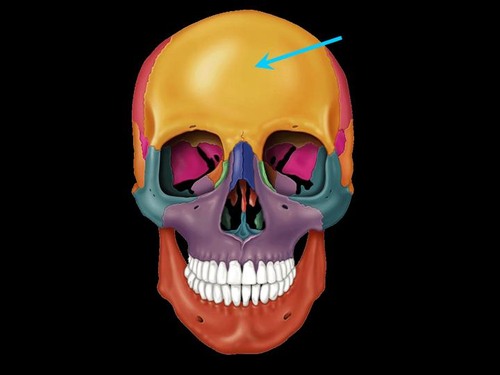
Frontal squama
Scalelike plate forming the forehead.

Supraorbital notch
Thickened frontal bone, brow line.

Supraorbital foramen
Passage for supraorbital nerve/artery.

Parietal bones
Form sides and roof of cranial cavity.

Temporal bones
Form inferior and lateral cranial aspects.

Zygomatic process
Part of the zygomatic arch from temporal bone.

Mastoid process
Attachment point for neck muscles.

Occipital bone
Contains foramen magnum for spinal cord.

Occipital condyles
Articulate with atlas, forming atlanto-occipital joint.

Sphenoid bone
Articulates with all cranial bones, keystone.

Optic canal
Passage for optic nerve.

Ethmoid bone
Delicate bone forming nasal cavity support.

Cribriform plate
Perforated plate for olfactory nerve passage.

Crista galli
Attachment point for brain membranes.

Perpendicular plate
Forms superior nasal septum portion.

Superior nasal concha
Scroll-like process, increases air surface area.

Middle nasal concha
Turbinates that warm and moisten air.

Non-paired facial bones
Includes vomer and mandible.

Coronal suture
Joint between frontal and parietal bones.

Parietal bone
Bone forming the side and roof of the skull.

Supraorbital margin
Upper edge of the eye socket.

Squamous suture
Joint between temporal and parietal bones.

Temporal bone
Bone forming the sides and base of the skull.

Orbit
Bony cavity containing the eye.

Nasal bone
Forms the bridge of the nose.

Inferior orbital fissure
Opening between the maxilla and sphenoid.

Palatine bone
Forms the posterior part of the hard palate.
Lacrimal bone
Smallest facial bone, contains lacrimal fossa.

Zygomaticofacial foramen
Opening for zygomatic nerve to the face.

Infraorbital foramen
Opening for infraorbital nerve below the orbit.

Zygomatic bone
Forms the cheekbone and lateral orbit.

Maxilla
Upper jawbone, forms part of the orbit.

Perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
Forms part of the nasal septum.

Alveolar process of maxilla
Contains sockets for upper teeth.

Inferior nasal concha bone
Separate bone that increases nasal cavity surface.

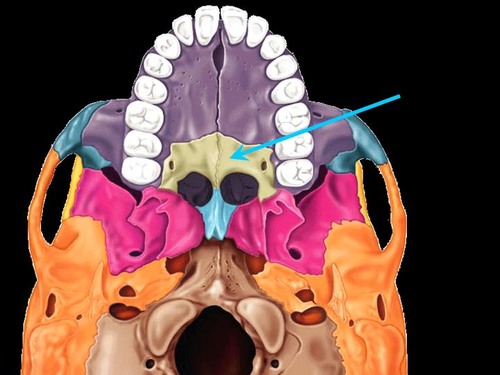
Vomer
Forms inferior part of the nasal septum.

Alveolar process of mandible
Contains sockets for lower teeth.

Mental foramen
Opening for nerves in the mandible.

Mandible
Lower jawbone, largest facial bone.

Nasal septum
Divides nasal cavity into left and right.

Septal cartilage
Cartilage forming the anterior part of the nasal septum.

Temporomandibular joint
Joint between temporal bone and mandible.

Ethmoid
Bone contributing to nasal cavity and orbits.

Orbits
Bony cavities containing the eyes.

Sagittal suture
Joint uniting the two parietal bones.

Lambdoid suture
Joint uniting parietal and occipital bones.

Paranasal sinuses
Air-filled spaces in skull bones.

Functions of sinuses
Lighten skull, resonate voice, moisten air.

Fontanels
Soft spots on an infant's skull.
Anterior fontanel
Soft spot at the front of the skull.

Posterior
Soft spot at the back of the skull.
