Lecture 8 (Fractures & CT)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What does bone resorption look like?
How long after fx is it first seen?
Decreased Density (Darker)
Seen Within 1 Week
What fx type may disappear with time?
How long would that take?
Stress / March Fractures
Disappears 10 Days Post
What elements are examined for fractures?
“S DAT ASS”
Site (Location)
Direction (Angle + Path)
Alignment (Can It Reform)
Type (Complete vs Not)
Associated Abnormalities (Dislocation)
Special Fractures (Weird Ones)
Special Types (Stress vs Disease)
What is Hills-Sachs vs Bankhart?
H-S: Posterolateral Humeral Head
Bankhart: Anteroinferior Glenoid
What is a Chauffeur’s Fracture?
Distal Radial Fx + Ulnar Styloid Fx
What is the difference between a Bennet Fracture and a Boxer’s Fracture?
Bennet: 1st Metacarpal
Boxer’s: 4th / 5th Metacarpal
What is a Chance Fracture?
Upper Lumbar Fracture (Normally L2)
What is used to assess Pediatric Fractures?
What are the grades given?
Salter-Harris Classification
I - Growth Plate Only
II - Growth Plate + Metaphysis
III - Growth Plate + Epiphysis
IV - Vertical (II + III Combined)
V - Crushed [Squished]
![<ul><li><p><strong>Salter-Harris Classification</strong></p><ul><li><p><strong>I -</strong> Growth Plate Only</p></li><li><p><strong>II -</strong> Growth Plate + Metaphysis</p></li><li><p><strong>III -</strong> Growth Plate + Epiphysis</p></li><li><p><strong>IV -</strong> Vertical (II + III Combined)</p></li><li><p><strong>V -</strong> Crushed [Squished]</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/062a1c50-7b7a-4b8b-ba98-e5ac0edaa7ad.png)
How long does bone typically take to heal?
1 - 3 Months
How long does cartilage typically take to heal?
2 Months - 2 Years
How long does tendinitis typically take to heal?
3 - 7 Weeks
How long does tendon laceration typically take to heal?
1 - 6 Months
How long does Grade III Muscle Injury & Grade II Ligamentous Injury take to heal?
1 - 6 Months
What are the stages of bone healing?
When does each one occur?
What processes are occurring?
Inflammatory: 1 - 2 Weeks
Bone Resorption (1 Week)
1st Cloudy Callus (2 Weeks)
Reparative: 2 Weeks - 6 Months
Callus Increases (6-12 Weeks)
Callus Calcifies (3-6 Months)
Remodeling: 6 - 12 Months
What is required for Primary Bone Healing?
“DONOR”
Direct Contact Between Segments
ORIF w/ Atraumatic Technique
New Bone Grows Directly Over Old
Osteoclastic Resorption → Osteoblastic Deposition
Rigid Internal Fixation w/ No Movement
What is Secondary Bone Healing?
Mineralization w/ Callus Formation
What terms are used for Primary vs Secondary bone healing?
Primary: Stress Bearing
Secondary: Stress Sharing
What is a Cortical Screw?
What are some characteristics?
For: Bone-Bone or Bone-Metal
Full Thread, Small Flutes
Non-Compressive
What is a Cancellous Screw?
What are some characteristics?
For: Bone-Bone Only
Half-Thread, Large Flutes
Compressive
What is a Canulated Screw?
What are some characteristics?
For: Guiding Larger Screws
Half-Thread, Hallow
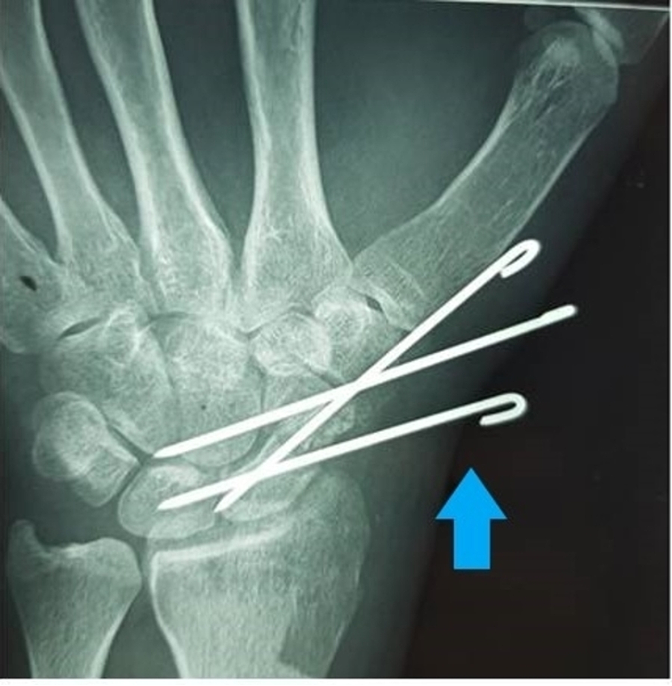
What are Kirschner Wires?
Fracture Stabilizers (For Hands & Feet)
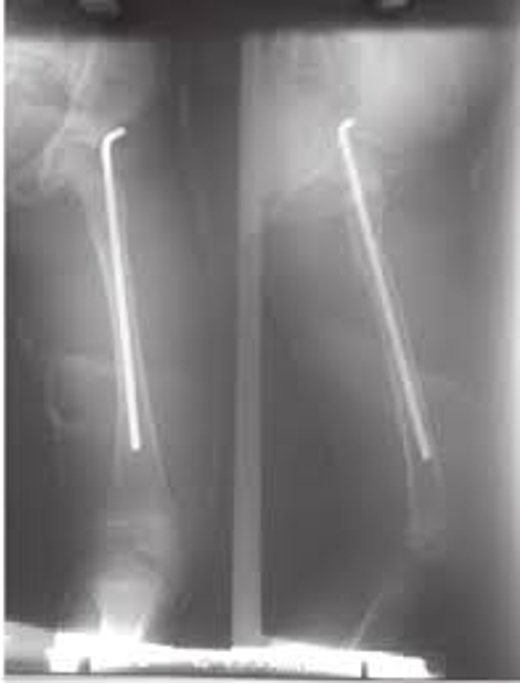
What are Steinmann Pins?
Fracture Stabilizers (For Pediatric Femurs)
What is a CT Scan best for?
“TITS”
Trauma Detection
Identifying Hemorrhages
Tumor Diagnosis
Spinal Alignment
What path does a CT Scan take?
How big is a typical slice?
Spiral (Around Patient)
7 - 10 mm
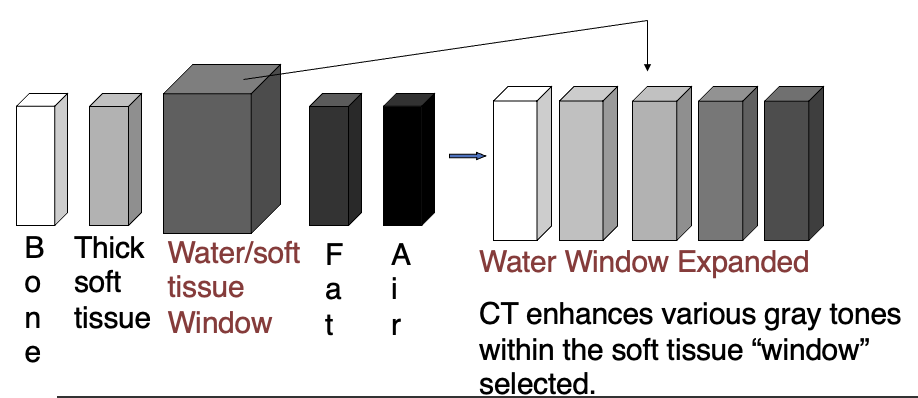
What is a CT Scan Window?
Settings That Adjust Visibility (Gray Scale Change)
This Also Specifies The Range Observed
How much more radiation dosage is in a chest CT (vs plain film)?
How many years of background radiation is this equal to?
400x More (0.02 → 8.0)
Roughly 4 Years Radiation