central retinal vein occlusion
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
how many branches does the central retinal vein have?
4
what happens when there is a thrombus in the central retinal vein?
causes blood drainage problems from the whole retina
what is the classic presentation of central retinal vein occlusion?
profound, sudden, painless loss of vision
what are the 2 classifications of central retinal vein occlusion?
non-ischaemic (75%) and ischaemic (25%)
what is non-ischaemic cvro?
- venous stasis retinopathy where the optic nerve exits the globe
- leads to mild-moderate vision loss
how does the stasis of blood in non-ischaemic cvro affect the intravascular pressure?
increases intravascular pressure
what does increased intravascular pressure lead to?
- dilated tortuous veins
- flame and blot haemorrhage
- cotton wool spots
- hard exudates
- abnormal leakage of fluid from vessels - retinal oedema
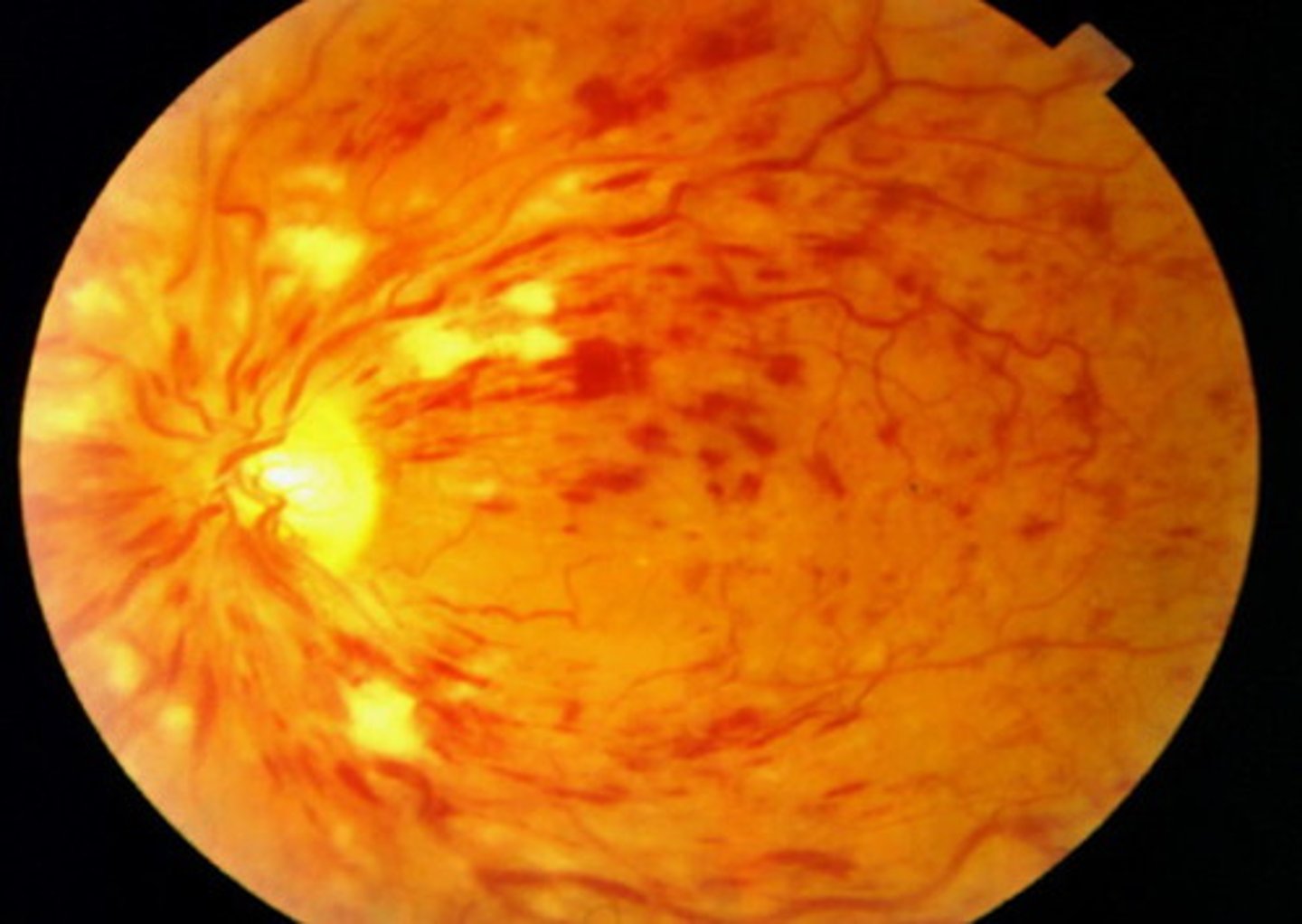
what is another term used to describe the fundus in CRVO?
blood and thunder - stormy sunset (not pizza pie like cytomegalovirus retinitis)
what is ischaemic crvo?
haemorrhagic retinopathy - leading to severe vision loss
at what ages is crvo most likely?
> 80 y/o
is cvro more common than central retinal artery occlusion?
yes, much more common
what are the differences in clinical features between ischaemic and non-ischaemic crvo?
non - subacute
isch - sudden
non - no afferent pupillary defects
isch - afferent pupillary defects present
what is the general presentation of CRVO?
painless blurred vision/vision loss
what conditions cause crvo?
- hypercoagulable/prothrombotic states
- ocular disease
what are examples of hypercoagulable/prothrombotic states?
- polycythaemia vera
- sickle cell disease
- OCP use
what are examples of ocular disease?
- glaucoma
- vasculitis
how can glaucoma cause ocular disease?
increased IOP can compress CRV
what are the risk factors for crvo?
- htn
- atherosclerosis
- DM
- smoking
- SLE
what are the investigations for crvo?
fundus examination:
- flame and blot haemorrhages
- optic disc oedema
- macular oedema
how would you differentiate between ischaemic and non-ischaemic cvro?
fluorescin angiogram
what is the management for crvo?
- anti-VEGF injection
- for macular oedema - intravitreal dexamethasone implants
- for neovasculatisation - laser photocoagulation