Week 10: elimination, nutrition, and dehydration
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Bowel elimination
passage and dispelling of stool through the intestinal tract by means of intestinal smooth muscle contraction
Urinary elimination
passage of urine out of the urinary tract through the urinary sphincter and urethra
Functional problems
passage of urine out of the urinary tract
through the urinary sphincter and urethra
Clinical manifestations of constipation
**infrequent and difficult passage of stool
-Two or fewer defections per week
-History of excessive stool retention or retentive posturing
-History of painful or hard bowel movements
-Presence of a large fecal mass in the rectum
-Large diameter stools
-At least one episode of incontinence after the acquisition of toileting skills
-History of large diameter stools (that may obstruct the toilet)
Constipation risk factors
-Limited daily fluid intake
-Sedentary lifestyle
-Poor fiber intake
-Consumption of foods known to cause hard stools
-Excessive dairy products
Other causes of constipation
-Lead poisoning
-Underactive thyroid function
-Celiac disease
-Abnormal calcium levels
Toddler/preschool triggers for constipation
-Learning to control body function
-Transition to cow’s milk
-Withholding behaviors
School age triggers for constipation
-Diet
-Toileting habits
-Activity
-Abuse
-Changes to routine
Withholding/retentive behaviors
Voluntary contraction of external sphincter “holding it in”
Causes of retentive behaviors
-he or she is afraid of the toilet
-doesn't want to take a break from play.
-uncomfortable using public toilets.
-Painful bowel movements caused by large, hard stools also may lead to withholding
-If it hurts to poop, your child may try to avoid a repeat of the distressing experience
Identifying retentive behavior
-Crossed legs(scissoring)
-Tiptoe with legs stiff
-On hands and knees
-Sitting on heel
-Potty dance
-Lifting off the toilet seat
-Stiff posture with legs locked (salute)
-Sitting on coccyx with legs in stiff posture
Health history Qs for constipation
-When was their last bowel movement?
-Describe the stool?
-How often do they usually stool in a week?
-Does it hurt to defecate?
-Is the stool large or hard?
-Any small lose stools or stains in underpants?
Physical exam for constipation
-Ausculate hyper or hypo depending on where you listen
-Palpate – may feel firm fecal mass
-Assess pain
Encopresis
-Abnormal elimination pattern characterized by the recurrent soiling or passage of stool at inappropriate times by a child who should have achieved bowel continence
-Liquid stool leaking around a large/hard/impacted stool mass
-Seen in chronic constipation
-As common as 1 in 100 kids
1st line constipation treatment
-↑ Fluids
-↑ fiber
-Age + 5 = grams of fiber needed per day
-Many children do not even meet the minimum
-Dietary modifications:
→ Infants: 2 oz pear, apple, prune juice
→ Increase physical activity and fluid intake
→ Remove constipating foods
Follow up treatment for constipation
-Next: Medications which increase water release into colon or soften stool
→ Miralax, Docusate sodium, Sennakot
-Clean out
→ Enemas: work on lower part of colon to release hard stool
-“jump start” – help get things moving as medications and 1st line treatments take time to work
-Laxatives
Laxatives
-Increase peristalsis: Bisacodyl – use short term only!
-Quicker effect than stool softeners
-Long term use can lead to dependence
Education for pt and family on constipation
School age kids
-anatomy of GI tract
-Talk with the older child about barriers to going to the bathroom
Families:
-physiology of bowel movements
-Stretching of rectum and colon
Constipation medication education
-purposes and dose adjustment
-length of treatment
Collaboration for constipation
-School notes to ensure they have access to the bathroom or a private toilet
-GI psychologists
Constipation behavioral modification
-Interrupt the withholding behaviors
-Encourage toilet sitting after meals and at scheduled times
-Toilet sits for 5-10 minutes after all meals
-Feet supported on step stool “squatty potty”
-Develop potty box with toys for potty sits for younger kids
-Age-appropriate incentives
Expected time for constipation resolution
-The longer the problem ~ the longer the treatment
-Minimum of 2-6 months of aggressive therapy
-If dependent on laxatives, 1-4 months to wean off
-Poor adherence with treatment recommendations will prolong therapy
-Even after problem is resolved there is 50% chance of reoccurrence in 1st year
-This can become an ongoing problem & consistency is required to prevent reocurrence
Enuresis
-Repeated involuntary voiding by a child old enough that bladder control is expected/after mastery of toilet training
-Bedwetting!
-Night (nocturnal) vs day (diurnal)
Primary enuresis
-Never dry
-Related to maturational delay, small functional bladder capacity
Secondary enuresis
-Dry for 6 months then bedwetting starts
-Related to stress, infection, sleep disorders
-Example: 10 year old boy starts wetting the bed (was potty trained since 3)
Enuresis treatment options
-Limit fluid in evening
-Toileting right before bed
-Avoid caffeine
-Avoid constipation
-Bladder exercises
-Timed voids
-Enuresis alarm
-Reward system
-Medications
Medications for enuresis
-Desmopressin (anti-diuretic)
-Oxybutynin (anti-spasmodic)
GER
-Defined as the passive backward flow of gastric contents upward into the esophagus that can occur with or without regurgitation or vomiting
-Considered a normal, physiological process – but can become problematic
-Effortless, painless spitting often within 40 minutes of eating
-GERD occurs when there is tissue damage from GER
Causes of GER
-Short and narrow esophagus
-Weak esophageal sphincter that does not close adequately
-Delayed gastric emptying time
-May progress to tissue damage from low pH of gastric acid
GER/GERD risk factors
-Prematurity
-Delayed maturation of lower esophageal neuromuscular function
Clinical GERD features for infants
-Feeding refusal
-Recurrent vomiting
-Poor weight gain (FTT)
-Irritability
-Sleep disturbances
-Respiratory symptoms
Clinical GERD features for older child and adolescents
-Abdominal pain/heartburn
-Recurrent vomiting
-Dysphagia
Airway irritation:
→ Asthma
→ Recurrent pneumonia
→ Upper airway symptoms (chronic cough; hoarse voice)
GERD resolution
Most instances resolve on own within 1 year
Non pharm interventions for GERD
-Smaller more frequent meals
-Position during/post feeding
-Avoidance of foods that cause reflux
Surgical interventions for GERD
-If tissue damage continues in severe GERD
-Nissen Fundoplication – wraps stomach around distal esophagus, decreases reflux
Medication for GERD
-Antacids
-Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
→ Omeprazole (Prilosec)
→ Lansoprazole (Prevacid)
-Histamine 2 (H2) Receptor Antagonists
→ Famotidine (Pepcid)
→ Cimetidine (Tagamet)
→ Ranitidine (Zantac)
Obstructive disorders
-Pyloric Stenosis
-Intussusception
Pyloric stenosis
-Hypertrophic obstruction of the circular muscle of the pyloric canal
-Blocks gastric emptying
-Often occurs in young infants in first few weeks-months
Pyloric stenosis etiology
exact cause unknown, possibly hereditary but no known risk
factors
Pyloric stenosis clinical manifestations
-Projectile vomiting
→ During/after feedings (even up to a few hours)
→ Not “happy spitters”
-Visible peristalsis
→ Hyperactive bowel sounds
-Hungry after eating, irritable
-Fails to gain weight, dehydration
-Olive shaped mass in RUQ
Pyloric stenosis diagnosis
made w ultrasound
Pyloric stenosis surgical intervention
-Pyloromyotomy
-Usually 24 hour admit (day surgery)
Pyloromyotomy pre op goals
correct fluid deficits and any electrolyte imbalances
Pyloromyotomy post op considerations
-Focus on comfort after surgery
-Anxiety for the parents
-Monitor incision site for infection and healing
-Keep diaper away from incision
-Advance feedings as tolerated per provider orders
Pyloromyotomy post op education
-Call provider for fever/infection signs
-Keep area clean
-Instructions for feeding at home
→ baby should be eating at regular intervals to maintain hydration + meet nutritional needs
→ If not tolerating feedings, contact provider
→ Do not hold feedings, infant is at risk for dehydration!
Intussusception
-Form of intestinal obstruction
-A segment of bowel telescopes or invaginates into another segment
-Often the cause is unknown (Could be due to lymphatic tissue)
-Most common site is at ileocecal valve
-Usually occurs between 5 months & 3 years
Intussusception manifestations
-Sudden onset of cramping abdominal pain
-Vomiting
-Inconsolable crying
-Drawing up the knees to the chest
-Hyperactive peristalsis – proximal bowel
-Hypoactive/overly inactive peristalsis – distal bowel
-Classic triad
Classic triad
-Abdominal pain
-Abdominal mass (sausage shaped)
-Bloody-like, mucousy stools (currant jelly-like stools)
Intussusception management
-May resolve spontaneously
-May resolve with contrast enema (Air or barium)
-May need surgical intervention:
→ reduce the invagination (telescoping)
→ possibly resect any areas of ischemia/necrosis
Intussusception nursing considerations
-Watch stools closely
→ If a normal stool occurs before the surgery the intussusception may have reduced itself.
-Watch for sepsis, dehydration
-Treat pain
-NPO, IV Fluids
Inflammatory and infectious conditions
-Appendicitis
-Celiac disease
-UTI
Acute appendictis
**similar to adult, but some differences in pediatrics
-Obstruction of the lumen of the appendix by hardened fecal material (usually), foreign bodies, microorganisms, or parasites resulting in inflammation/infection
-Obstruction blocks outflow of mucus, pressure builds within lumen causing compression of the blood vessels, venous engorgement, eventual necrosis and rupture
Appendicitis diagnostic assessment
-Largely based on history and exam
-R/O other causes such as:
→ Other infection (UTI or STI)
→ Pregnancy
→ Constipation or Gastroenteritis
→ Testicular torsion or ovarian cyst
Appendicitis diagnostics
-CBC
→ Elevated WBC
→ Increased neutrophil count
-Elevated C-reactive protein
-Abdominal ultrasound or CT Scan
Appendicitis therapeutic management
Antibiotics with/without surgery
Remove appendix (appendectomy)
Ruptured appendix
Requires IV antibiotics post op
Monitor for peritonitis
Usually has a peritoneal drain
Prognosis – overall good with early recognition
Be aware of possible complications: peritonitis or perforation
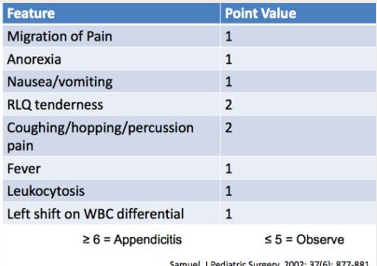
Pediatric Appendicitis Score (PAS)
Tool for clinical decision making:
Treat w/ abx and surgery
-Or-
Give antibiotics and observe
Post op care for appendectomy (same as adult care)
Maintain fluid balance
IV fluids until bowel function returns
Monitor for nausea
Advance diet as tolerated
Antibiotics & monitor for infection (especially if perforated)
Maintain skin integrity / incision site
Maintain airway clearance (incentive spirometer)
Assess for Bowel function (bowel sounds, flatus, stool)
Pain management
Pain management post appendectomy
Position: semi-Fowler or side-lying position on the right side
Medication
Splinting
Celiac disease
Autoimmune disorder
Not an allergy or an intolerance
A gluten-sensitive enteropathy
Immune-mediated inflammatory disease of the small intestine
caused by sensitivity to dietary gluten and related proteins
Intestinal lining is damaged
Cannot absorb nutrient as well
Complications: Leads to malabsorption and effects of being malnourished
Celiac risk factors
Genetic predisposition
First- and second-degree relatives of patients with celiac disease
People with…
Down Syndrome
Type 1 diabetes
Selective immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficiency
Autoimmune thyroiditis
Juvenile chronic arthritis
Classic manifestations of celiac
Chronic diarrhea
Steatorrhea (greasy/fatty, yellowish stool)
Abdominal distention
Bloating
Pain
Anemia
Growth delay
Atypical manifestations of celiac
tooth enamel defects
aphthous ulcers
Celiac crisis
Acute exacerbation due to exposure to gluten
Severe diarrhea
Dehydration
Metabolic acidosis
Electrolyte disturbances
Celiac diagnosis
72-hour fecal fat collection
Total IgA levels
commonly found in mucous membranes in respiratory & GI systems
Biopsy of mucosal tissue
Celiac treatment
Gluten Free Diet – life long
Referral to dietician
Financial burden
Adherence concerns
Cross contamination
‘cheating’
May need vitamin supplementation:
Fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E, & K)
Iron & folic acid
Examples of gluten
Wheat (and derivates)
Rye
Barley
Malt
Brewer’s yeast
Adult UTI review
Urine output: 30ml/hr MINIMUM
Normal Urinalysis Results:
pH 5 to 9
Specific gravity 1.005 to 1.030 (1.010-1.020)
Protein 0-8 mg/dl
Urobilinogen up to 1 mg/dl
Color: clear to pale yellow
Appearance: clear/translucent
NONE OF THE FOLLOWING Present:
Glucose RBC’s
Ketones Casts
Nitrates
WBC’s
Pediatric urine output differences
Determined by weight!
Newborn 2 ml/kg/hr
Child 0.5 to 1 ml/kg/hr
Adolescents 40-80 ml/hour
Pediatric bladder capacity differences
Average is 30 ml at birth
Grows until reaching adult capacity of 300-500mL
Bladder capacity (in Oz) = child’s age in years + 2
1 year old = 1 + 2 = 3oz (90mL)
Pediatric urethra differences
Shorter
risk for bacteria entering bladder
Pediatric renal function differences
Immature, infants do not concentrate urine
Glomerular filtration rate is slower in infant
Higher risk for dehydration
Risk factors for UTI
Urinary stasis
Poor hygiene
Irritated perineum
Uncircumcised penis (if not cleaned properly)
Constipation (prevents bladder from fully emptying)
Urinary tract anomalies
Urinary reflux (back flow, risk for upper UTI and renal damage)
Females (or person with vagina)
Female risk factors for UTI
Shorter urethra compared to males
Soaking in tub (bubble baths)
Staying in wet diapers, swimwear for a long time
sexually active adolescent females
provide education r/e urinating after sex, personal hygiene
Upper tract s/s of UTI
Fever
nausea/vomiting
flank pain (CVA tenderness)
general malaise
Lower tract s/s of UTI
Dysuria
frequency/urgency
incontinence
suprapubic pain
change in urine odor/color
Neonates s/s UTI
Fever
irritability
poor feeding
vomiting
diarrhea
FTT
jaundice
sepsis
UTI diagnostics
same as adult
Microscopic urinalysis / dipstick
Culture and sensitivity to determine best antibiotic treatment
Additional testing
Renal Ultrasound
After first febrile UTI
Assess for any damage
VCUG (voiding cystourethrogram)
If US abnormal Or reoccurrence of febrile UTI
Detect anatomical differences or retrograde flow
Pediatric urine collection
Clean Catch Urine preferred for older child
Catheterization or suprapubic needle aspiration for children <2 years old
Less risk of contamination from diaper contents
Different catheter sizes based on age/size
U-bag for collection from infant – child
Not recommended, error prone
Use of a bag for a sterile specimen has potential to yield a contaminated specimen.
UTI treatment
Anti-infective agents after urine culture and sensitivity
Screen for cause:
diagnostic tests
Treat underlying cause in addition to giving abx
Ensure Adequate fluid intake for age and weight
Flush the system.
UTI prevention and education
Wipe from front to back
No tight-fitting underwear
Cotton underwear
No bubble baths, bath oils, hot tubs, etc.
Encourage abstinence (-or- If sexually active female void before and after sex
Adequate hydration is key to prevention
Encourage frequent voiding, avoid holding it in
Probiotics:
some evidence may offer protection against recurring UTIs
Cranberry juice and supplement:
May help prevent UTI
Fluid imbalances
Extracellular fluid volume deficit (dehydration)
Extracellular fluid intravascular volume excess (fluid overload)
Interstitial fluid volume excess (edema)
Water toxicity
due to fluid shifts caused by electrolyte imbalance (namely hyponatremia)
causes intracellular edema & Cerebral edema = life threatening
Infants under 1 are at high risk for water toxicity due to their immature kidneys
Fluid status assessment Qs for caregivers
What intake has child taken?
Infants: crying tears, wet diapers (how many)
Behavior: tired versus listless
Breathing: faster? Working hard (retractions)?
Any Vomitting of Diarrhea? Are they able to keep fluids/food down?
How many wet diapers ( an infant should have 6-8 per day, fewer indicates dehydration)
Causes of dehydration
Vomiting and diarrhea
Fever
Wounds/Burns (insensible losses)
Tachypnea from respiratory distress can contribute
Dehydration r/t vomiting and diarrhea
most common viral causes: Rotavirus, Norovirus
Bacterial: Salmonella, Ecoli, Cdiff
Parasite: Giardia, Cryptosporidium
other: increased intracranial pressure, Toxins/Poisons, neuro and endocrine disorders
Infants: milk protein allergy, infections
Toddlers: infection, tumors, UC, celiac disease
School age: IBD, Appendix, Lactose intolerance, constipation, celiac disease
Dehydration assessment
Physical Exam:
Fontanel sunken
skin-dry, poor turgor, dry mucous membranes
fever, tachycardia,
low BP is a later and more severe sign
less active (lethargic)
more ill appearing
Labs: electrolytes, CBC-WBC, Stool Cx,
Treatment for moderate to severe dehydration
IVF- NS or LR bolus 20mg/kg then add K+ when voiding
Teaching points: hand washing, skin care and protection, prevention
Severity of clinical dehydration
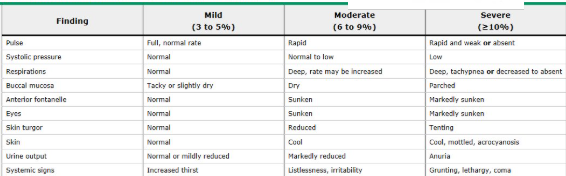
Moderate dehydration treatment
If unable to orally rehydrate after giving antiemetics, IVF will be needed
Antidiarrheals are not recommended – especially if it is due to an infectious cause!
Severe dehydration treatment
Admission to Hospital or Treatment in ED
Laboratory analysis to monitor electrolytes
Treatment for Moderate to severe Dehydration:
IVF- NS or LR bolus 20mg/kg then add K+ when voiding
1.5x Maintenance fluids
In addition to oral rehydration
Daily weights: accurate indicator of fluid status if you have a trend to follow
Careful I&O
Monitor vital signs (Pulse, Rate/quality of respirations,blood pressure (including orthostatic))
Nutrition health Hx
Current nutritional intake
Any recent changes?
Elimination
Physical Activity
Specifically for infants…
Gestational age/birth weight
Prematurity and LBW are risk factors for inadequate nutrition
Passage of first meconium stool within the first 24 hours?
Jaundice?
Nutrition red flags
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Spitting up
Fussy with feeds
Encopresis
Abdominal pain
Abdominal distention
GI Bleeding
Monitoring growth
Growth charts
Provide visual trend of growth over time
Track Height, Weight, Head circumference, BMI or Percentile for Weight to determine if over/under-nourished
Newborns diet patterns
Rapid physical, functional changes from growth & development
In first year, body weight triples
Full term, healthy baby should gain 25-35 gms/day during first months of life
Each baby’s feedings needs are unique
100cc/kg/day to be adequately hydrated
150cc/kg/day to grow (minimum 120)
Infants formula feeding
First few weeks: 2-3 oz every 3-4 hours
By 1 month: up to 4 oz, predictable schedule
By 6 months: 6-8 oz at each of 4 or 5 feedings per day
Max 32 oz of formula/24 hours
Different formulations to accommodate special dietary needs, and allergies
Infants breastfeedings
Smaller, more frequent feeds
8-12 times per day (Q3-4 hours)
Cluster feeding early in life
Will start to sleep through night and take larger PO intake during the day
Variance in length of feedings
Both AAP and WHO recommend exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months, followed by solid foods + complimentary BF through 2 years
Introduction of solids
introduce complementary foods at around 6 months of age
Assess an infant’s readiness to start foods
Good head control
Show eagerness to eat
Effectively move food from the spoon to the back of the mouth
No specific food order
Usually start with iron-fortified single grain cereal
No honey or cow’s milk until >12 months of age
Introduce new food every 2-3 days
Around 12 months, diet should be mostly solid food
About 1,000 calories/day (3meals + 2snacks per day)
Calorie needs
Based on age, gender, activity
Toddlers and young children eating patterns
Picky eating very common
Continue to offer a variety of healthy foods
May have to offer a new food more than 10 times
May not finish every meal or recommended portions in a single sitting
Small portions, offer snacks
Avoid a “liquid diet”
Limit juice intake or dilute
Recommended amounts of daily juice
Under 12 months – none
1-3 years – maximum 4 oz
4-6 – limit to 4-6oz
7 and up – limit to 8oz
Limit cow’s milk (based on age)
Whole milk until age 2 years
School aged child eating patterns
Encourage balanced diet with variety!
Teach healthy eating habits
Can assist with with meals
Shopping, Making simple dishes, preparing ingredients
Picky eating can persist
Very common with neurodivergence and sensory processing differences
Meal time is also about connection & is social in nature