Thermodynamicsssssssssssssssssssssss
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is enthalpy change?
The heat energy transferred in a reaction at constant pressure
What is enthalpy change of formation?
The enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states, under standard conditions.
What is enthalpy change of atomisation?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous atoms is formed from the element in its standard state
What is first ionisation energy?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions is formed from 1 mole of gaseous atoms.
What is second ionisation energy?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous 2+ ions is formed from 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions.
What is the first electron affinity?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions is formed from 1 mole of gaseous atoms.
What is second electron affinity?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous 2- ions is formed from 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions.
What is bond enthalpy?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a particular covalent bond in the gaseous state is broken.
What is lattice enthalpy of formation?
The enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions under standard conditions
Why are lattice enthalpy of formation values always exothermic?
as energy is released when the oppositely charged ions come together to form the solid lattice
What is lattice enthalpy of dissociation?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is completely dissociated into its gaseous ions under standard conditions.
Why are lattice enthalpy of dissociation values always endothermic?
as energy must be supplied to overcome the electrostatic attractions between ions and separate them into the gas phase.
The more negative the lattice enthalpy of formation...
the stronger the ionic bonding in the compound.
The more positive the lattice enthalpy of dissociation...
the stronger the ionic bonding in the compound.
What does Hess' law state?
The overall enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the route taken
Why is there often a difference between theoretical and experimental lattice enthalpies?
Ion polarisation
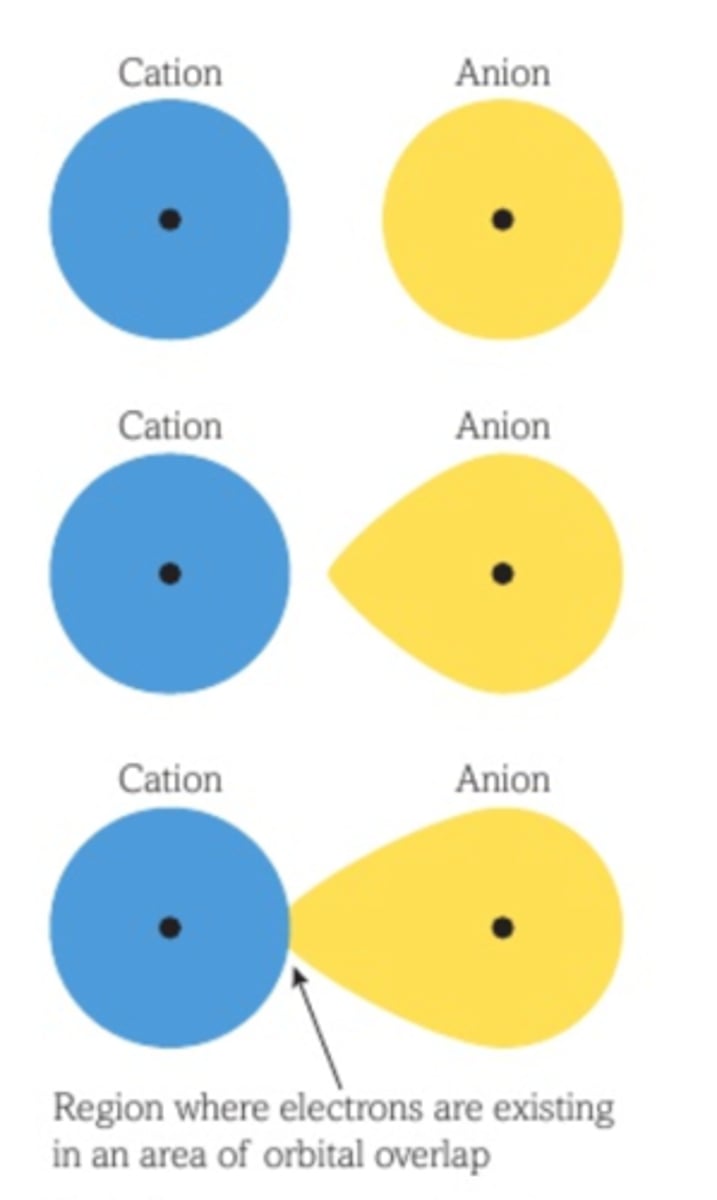
What does a large difference between theoretical and experimental lattice enthalpies signify?
stronger polarisation and more covalent character
Describe the perfect ionic model
assumes all ions are perfect spheres with evenly distributed charge

What factors affect lattice enthalpy?
ionic size and ionic charge
What is the enthalpy change of solution?
the enthalpy change when one mole of an ionic solid dissolves in water to form an infinitely dilute solution.
What is the enthalpy of solution a sum of?
the endothermic lattice breaking and exothermic enthalpy of hydration.
What is enthalpy change of hydration?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of aqueous ions is formed from 1 mole of gaseous ions.
Why is enthalpy of hydration always exothermic?
as energy is released when bonds are made between ions and water molecules
How can enthalpy change of solution be calculated?
Adding together lattice enthalpy and hydration enthalpy
What is entropy?
A measure of disorder or randomness.
What does entropy quantify?
the number of ways particles can be arranged
The higher the entropy...
the higher the level of disorder.
Is entropy positive or negative?
positive
What factors affect entropy?
Physical state, number of particles, and temperature.
How does physical state affect entropy?
The particles in a solid have much less freedom and disorder than those in a gas. Entropy increases across the physical states as follows:
(solid) < (liquid) < (gas)
How does the number of particles affect entropy?
more particles means more entropy
How does temperature affect entropy?
entropy increases as temperature increases
What is a feasible reaction?
One that can occur spontaneously without extra energy supplied
How can we calculate entropy change in a reaction?
using the formula:
ΔS = Sproducts - Sreactants
What is Gibbs free energy change?
represents the overall change in energy during a chemical reaction.
How can the feasibility of a chemical reaction under standard conditions be predicted?
To be feasible the Gibbs free energy change must be 0 or less.
What is the formula to calculate free energy change?
Gibbs free energy change = enthalpy change - (temperature x entropy change)
If ∆H is +ve and ∆S is -ve, will the reaction be feasible?
NO as ΔG is always positive
If ∆H is -ve and ∆S is +ve, will the reaction be feasible?
Yes as ΔG is always negative
If ∆H is -ve and ∆S is -ve, will the reaction be feasible?
Feasible below a certain temperature
If ∆H is +ve and ∆S is +ve, will the reaction be feasible?
Only feasible above a certain temperature
How can we calculate the temperature at which a reaction becomes feasible?
When ΔG = 0, divide enthalpy change by entropy change
What is k in a rate equation?
rate constant
What is the rate constant?
a proportionality constant that relates the rate of a reaction to the concentrations of the reactants at a specific temperature.
What does a larger k value indicate?
the faster the rate of reaction
What happens to the value of k if we increase the temperature exponentially?
increases
what are [A] and [B] in the rate equation?
concentrations of different reactants
What are m and n in the rate equation?
orders of reaction
what is meant by zero order reactant?
The rate is independent of the reactant concentration.
What is meant by a 'first order' reactant?
The rate is directly proportional to the reactant concentration.
What is meant by a 'second order' reactant?
The rate is proportional to the square of the reactant concentration.
What is the overall order of a reaction?
m+n