Micturition
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What muscle makes up the wall of the bladder itself?
Detrusor muscle
What tissue composes the internal “sphincter” of the neck of the bladder?
Smooth muscle and elastic tissue
Not a true anatomical sphincter, but stretching of the bladder muscle puts tension at the neck, contracting it and blocking it off
What tissue composes the external sphincter of the bladder/urethra?
skeletal muscle
True anatomical sphincter
The bladder is under _____, _______ and _________ nervous control.
somatic, parasympathetic, sympathetic
What nerve runs to the external sphincter of the bladder?
Pudendal Nerve
Containing both somatic sensory and motor nerves
Acts on the skeletal muscle of external sphincter, giving voluntary control
What sympathetic nerve runs to the smooth muscle (detrusor muscle) of the bladder?
Hypogastric nerves (Sympathetic nervous system)
Sympathetic chain - pre-ganglion fibers make contact with post-ganglionic fibers at level of caudal mesenteric ganglion (Hypogastric nerves)
Influence smooth muscle at neck of the bladder (Internal sphincter)
What parasympathetic nerve runs to the smooth muscle (detrusor muscle) of the bladder?
Long preganglion fibers synapse with short post-ganglion fibers (In end organ)
Afferent Fibers - Information into CNS
Efferent Fibers - Information out of CNS (Pelvic N.)
Information transmitted from the nerves in the bladder can be integrated in the _____ ______ where ____ ______ of ______ can be sensed.
sensory cortex, pain awareness, distension
What are the three processes the bladder needs to do?
Prevent urine escape (during bladder filling)
Allow urine Storage
Allow micturition-voiding
Describe the physiological mechanisms in place that prevent the escape of urine during bladder filling.
Internal Sphincter
Tension passively exerted by elastic elements in the neck of the bladder as bladder stretches, brings about blockage of the internal sphincter
Not true anatomical sphincter (Involuntary control)
External Sphincter
Stimulate pudendal nerve, which stimulates skeletal muscle in external sphincter, contracts urethalis muscle which prevents urine flow
True sphincter (voluntary control)
What physiological mechanisms are in place to allow the storage of urine?
Detrusor must RELAX
Sphincter must CONTRACT
Hypogastric Nerve is critical
Excitation of sympathetic nervous system causes - relaxation of detrusor muscle (Inhibiting Muscle - inhibitory receptors) and contraction of smooth muscle at internal sphincter (Create contraction - stimulatory receptors)
Internal sphincter passively occludes opening at bladder neck
Pelvic Nerve
If bladder is empty, afferent pelvic nerve fibers register low distension at S1-S3. Leads to inhibition of sacral spinal cord reflex by brain relfex center. (Inhibits parasympathetic nervous system)
Causes detrusor muscle to relax as bladder fills
Where do the sympathetic nerves innervating the bladder originate in dogs and cats?
L1-4 dogs
L2-5 cats
Where do the parasympathetic nerves innervating the bladder originate in dogs and cats?
Sacral Spinal Segments S1 - S3
What physiological mechanisms are in place to allow micturition or voiding to occur?
Bladder is distended, causing high activity in afferent fibers triggers the efferent parasympathetic nervous system, this causes contraction of the detrusor muscle of bladder
Stretch receptors inhibit activity at the hypogastric nerves, which prevent it from relaxing (Allow contraction)
Stretch receptors also inhibit activity of somatic pudendal nerves, urethral muscle relaxes and urethra opens
What does the voluntary control of the urethra or external sphincter allow for?
Allows for training, micturition permitted when appropriate, training/behavioral
What causes urinary retention?
Incomplete emptying (or voiding) of urine, with no obstruction of the urinary tract
What may cause urinary retention?
Trauma, pelvic nerve, spinal cord
Spinal disease
Slipped disc in recumbent patients
No exchange of information between bladder and brain
Chronic bladder distention
Electrolyte disturbances
Neuropathy, midbrain disorders
Dysautonomia
Excessive adrenal steroids (Cushing's disease)
What is urinary incontinence?
Involuntary loss of urine
What are some possible causes of urinary incontinence?
Possible causes:-
Age
Spay incontinence (Up to 80% bitches)
Diabetes
Kidney disease
Nerve damage/trauma (local spinal, brain)
Urinary tract (usually bladder) infections
Overactive bladder syndrome
Pressure on the bladder caused by a mass
REMINDER**
Describe the neurotransmitters and associated receptors for the parasympathetic, sympathetic and somatic nervous system.
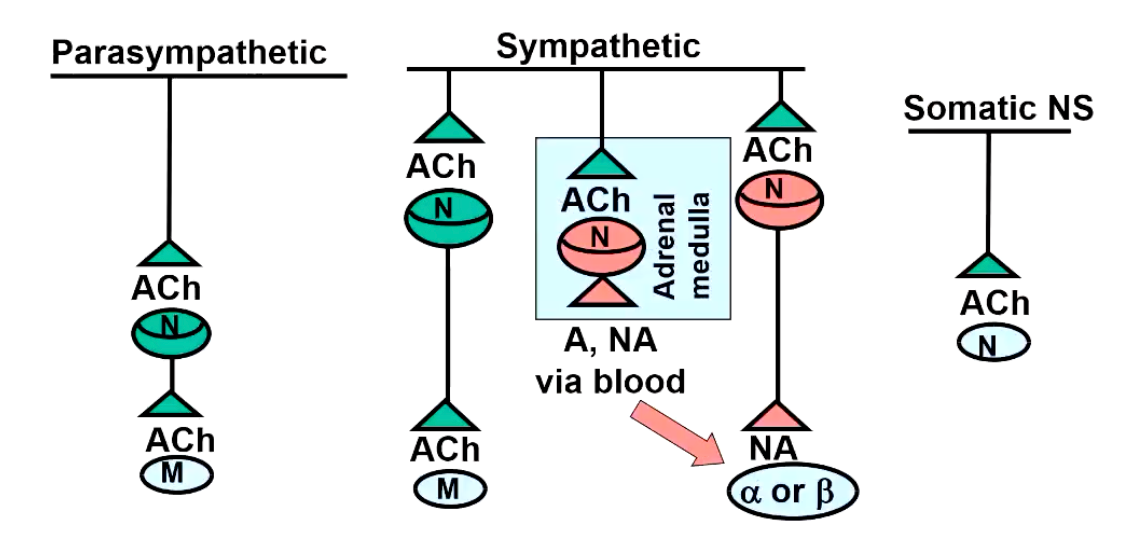
Adrenoreceptors all bind _______ or ______ as ___-_____ ______ _____.
____ or ____
adrenaline, noradrenaline, G-protein coupled receptors
Alpha, Beta
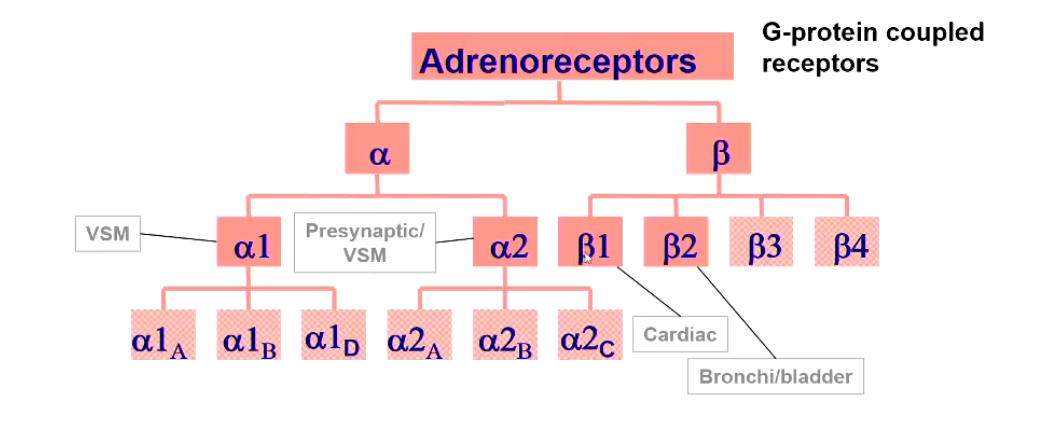
a1 adrenoreceptors are ______.
Which controls what?
stimulatory
Increase IP3 and DAG → Increased Calcium
Vasoconstriction of SM (Except in GI)
i.e. internal urinary sphincter
a2 adrenoreceptors are _______
Which controls what?
inhibitory
Decrease adenylyl cyclase → Decreased cAMP
Presynaptic inhibition, contraction of
B1 adrenoreceptors are ________
Which controls what?
stimulatory
Increase adenylyl cyclase → cAMP → Increased PKA → Increased calcium
Increase cardiac HR, Force, Conduction
B2 adrenoreceptors are ________
inhibitory
Increase or decrease cAMP
But cause relaxation of SM (e.g. detrusor bronchodilation, vasodilation in skeletal muscle)
REMINDER**
What can the parasympathetic actylcholine receptors be divided into?
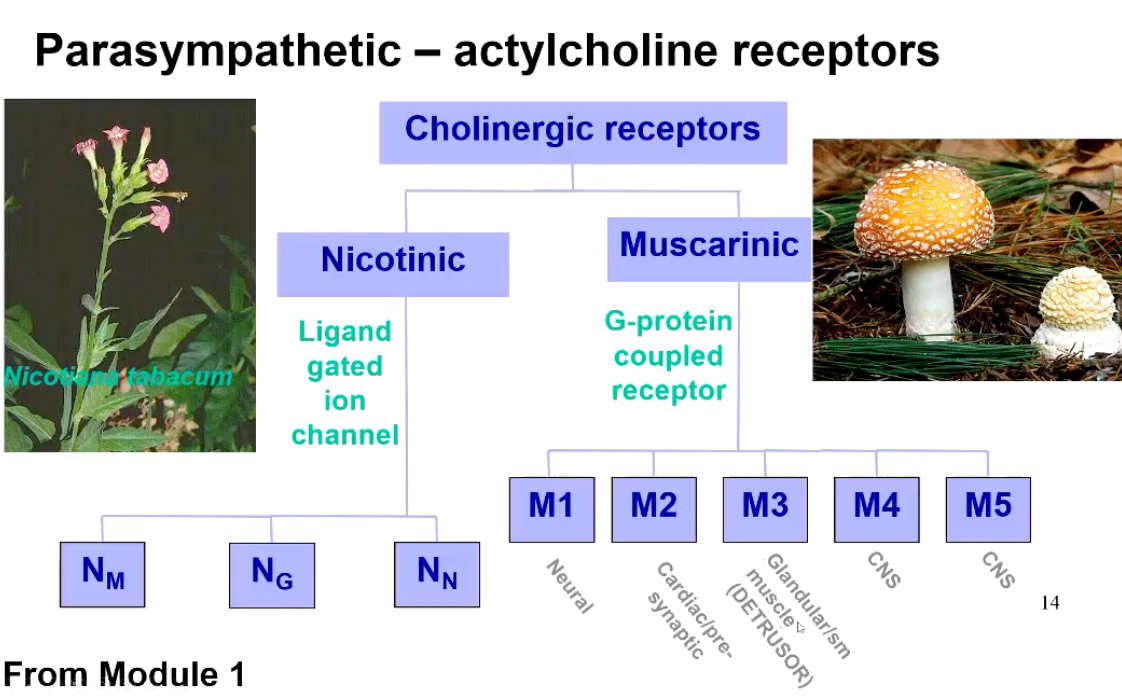
What are the ligand-gated ion channels composed of?
Pentameric structure
What happens when the nicotinic receptors in the PNS are stimulated?
What are the three types?
Increase permeability to Nat and K+ (stimulatory)
3 types
Skeletal muscle, Nu (a1)2ß1,0,8
Ganglia, Ng (a3)2(4)3 and a3,a5,a7,34, 37
The brain, NN. (a4)2(B2) 3 and (a7)5
Differentially sensitive to drugs!
Describe the five muscarinic receptors in the PNS.
M1 (neural), ganglia, CNS, gastric parietal cells; activate PLC leading to IP3 and DAG formation, + K+ conductance
M2 (cardiac), all areas of heart, also in the brain stem. Presynaptic inputs to peripheral and central neurones; inhibit adenylate cyclase and open K+ channels inhibiting Ca2+ channels
M3 (glandular/SM), smooth muscle and glandular tissue and the cerebral cortex; activate PLC. Also relaxation of vascular SM, due to NO
M4 (CNS), inhibit adenylate cyclase
M5 (CNS) activate PLC
Green - Stimulatory
Red - Inhibitory
Describe the distribution of muscarinic receptors in the urinary system.
M3 Receptors (Wall) + M2 Receptors (Wall and neck)
B2 Receptors (Wall and neck)
a1 Receptors (Neck of bladder)
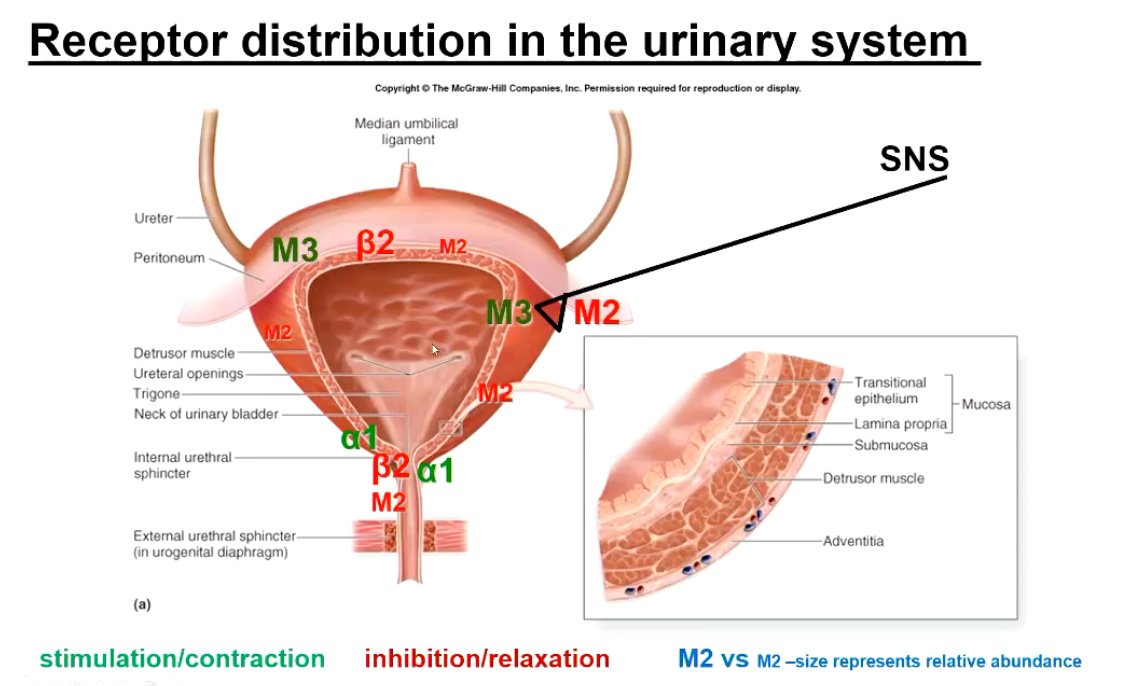
Describe the activity of receptors in the bladder during the filling / storage phase.
Sympathetic Dominance
STIMULATE a1 Receptors at neck of the bladder, contracting smooth muscle at internal sphincter
STIMULATE B2 Receptors in the detrusor muscle (Leading to relaxation of muscle)
Inhibits SNS → M2 → Relaxation
Describe the activity of receptors in the bladder during the micturition phase.
Parasympathetic Dominance
STIMULATE M3 and M2 Receptors
M3 - Stimulatory, contracts the Detrusor muscle
M2 - Inhibitory, relax internal sphincter, inhibits SNS
a1 adrenoceptor - inhibition, allowing sphincter to relax
Under or over activity of receptors in the smooth muscle may cause…
Disorders of storage - Urinary incontinence
Over-stimulation: Hypercontractile detrusor
Under-stimulation: Hypocontractile sphincter/urethra
Disorders of storage - Urinary retention
Over-stimulation: Hypercontractile Sphincter / urethra
Under-stimulation: Hypocontractile detrusor
Agonists and Antagonists can be ____ and ________.
Meaning?
specific, nonspecific
Specific - binds to one type of receptor
Non-specific - binds to multiple receptors
What are the direct acting agonists and antogonists?
• Agonists - Sympathomimetics, Parasympathomimetics
• Antagonists - Sympatholytics, Parasympatholytics
What are the indirect acting agonists and antogonists?
INDIRECT ACTING
• Sympathomimetics - displace NA
• Parasympathomimetics - ACHEs, displace ACh
What are common causes of situations where the detrusor is hypercontractile or spastic? (Too much voiding)
What drugs can be used? What is the aim of these drugs?
Common causes - bladder infections, neurogenic disorders
AIM: decrease detrusor activity - use antimuscarinic (Decrease M3 stimulation)
Non specific muscarinic antagonists
Oxybutalin, Propantheline, flavoxate, Atropine
What could be some potential issues of giving a non-specific muscarinic antagonist? (As in the case of detrusor hypercontractility).
Side effects reflect the systemic distribution of all muscarinic receptors.
LOW SALIVA, GI stasis, tachycardia, excitement, sedation, Increase in IOP, mydriasis, antispasmodic effects on GI tract.
What are common causes of destrusor atony? (Too little voiding)
What drugs can be used? What is the aim of these drugs?
What side effects might be produced?
Cause - Urinary retention, neurogenic disorders, overdistension
AIM - increase detrusor activity - cholinergic agonists (M3 Receptors)
Bethanechol, non specific muscarinic agonists (higher affinity for M3)
Oral administration of a non-specific drug, still can cause side effects
Gl stimulation, hypersalivation, defecation
Which animal is urethral sphincter incontinence common in?
How can it be treated?
What are potential side effects?
Common in spayed bitches - aetiology not full characterized
Steroids (Oestradiol) - common treatment, not directly ANS
AIM - increase sphincter tone - a1 agonists
Increase tone - improves continence
Oral Phenylpropanolamine (non specific alpha adrenergic agonists) and ephedrine (stimulates NA release, less predictable).
NOTE - systemic distribution, think about where else a1
adrenoreceptors are located within the body.
Hypertension, restlessness, TOP (contraindicated patient groups)
What are common causes urethral spasticity?
What drugs can be used? What is the aim of these drugs?
What side effects might be produced?
Cause - Infections, inflammatory neurological disorders, urethral obstruction, Bethanacol treatment
AIM - decrease sphincter tone - a1 adrenergic antagonist
Opens internal sphincter, allowing urination to occur
Can use Phenoxybenzamine (non selective a (a1>a2) IRREVERSIBLE)
Can cause: Hypotension, reflex tachycardia, TOP, Gl upset
Alternatively: Prazosin, terazosin (SELECTIVE a1 antagonist)
Can Cause: Hypotension, Gl upset