13.0 Circulatory System
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What is the layer that surrounds the heart
Pericardium (double layered sac)
Outerlayer = fibrous pericardium
Inner layer = serous pericardium
What is the prupose of the pericardium
Hold heart in place
Lubricate it
Protetion
How many chambers does the heart have and what separates them
Upper and lower chambers are separated by valves
Right and left side of the heart are separated by a septum
What are the upper (1,3) and lower (2,4) chambers of the heart claled
Upper = atria
Lower = ventricles
What is the right side of the heart and what does it carry?
Right atrium + ventricle = carries deoxygenated blood
What is the left side of the heart and what does it carry?
Left atrium + ventricle = carries oxygenated blood
Compare and contrast the pressures of ventricles and atria of the heart
Atria = Low pressure, sends blood to ventricles (not far)
Ventricles = high pressure, sends blood to lungs or systemic (far)
Valves of heart function
Prevent backflow of blood
Name all the valves in the heart that prevent backflow
Pulmonary valve
Tricuspid valve
Aortic Valve
Mitral Vavle
Where is the tricuspid valve located
Between right atrium and ventricle
Where is the pulmonary valve located
Right ventricle and pulmonary arteries
Where is the mitral valve located
Between left atrium and left ventricle
Where is the aortic valve located
Left ventricle and aorta
What distributes blood directly from the heart to the arteries of the body
Aorta
How many chambers in the following, fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals
Fishes = 2 (A + V)
Amphibians + Reptiles = 3 (2A + V)
Birds and mammals = 4 (2A + 2V)
What is the sequence of valves does blood flow as it flows through the heart
Tricuspid → pulmonary → mitral → Aortic
TPMA
Compare and contrast arteries and veins
Veins = carry. blood back to the heart (deoxygenated)
Arteries = carry blood away from the heart (oxygenated)
What is the goal of the pulmonary circulation
Goal is to get deoxygenated blood to the lungs then bring that freshly oxygenated blood back to the heart
Pulmonary circulation
Blood is pumped from the right ventricle to pulmonary arteries
Blood gets reoxygenated at the capillaries of the lungs
Blood travels back to the heart via pulmonay veins to the left atrium
Blood in the _____ has the lowest concentration of oxygen in the entire body
Pulmonary artery
Blood in the ____ has the highest concentration of oxygen in the entire body
Pulmonary veins
Why is the pulmonary circulation an exception to arteries and veins carrying certain types of blood
Normally, veins carry deoxygenated blood and arteries carry oxygenated
But its opposite for the pulmonary arteries (carry deoxygenated), and pulmonary vein (carry oxygenated)
Systemic circuit
Freshly oxygenated blood goes to left atria → left centricle → aorta → entire body → blood reaches capillaries dropping off O2 → veins carry blood back to superior and inferior vena cava → right atrium → right ventricle
What happens ot oxygen at the capillaries at the body’s tissues?
Oxygen is delivered from red blood cells to tissues, and blood becomes deoxygenated
In capillaries, What are delivered and transported back i
Nutrients + O2 are delivered
CO2 and waste are transported back
What are the phases of the cardiac cycle
Systole - heart contracts
Diastole - heart relaxes
What are the pacemaker cells of the heart
SA node in the right atrium - generates electricity to keep the heart beating
How are the cardiac muscles separated and what do they contain
Separated by intercalated dscs
Contain gap juncitons
Conduction pathway of the heart
SA node
AV node - WHERE delay occurs
Bundle of His - located between both lower ventricles
Purkinje fibers - Causes Both ventricles to contract together
Phases of cardiac cycle
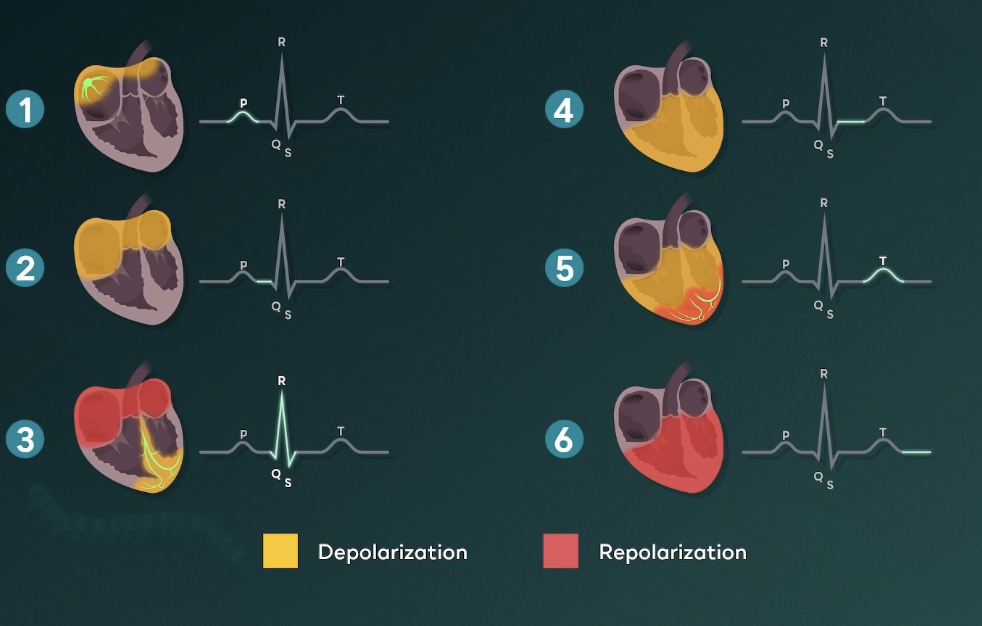
P wave = atria contraction
QRS complex = ventricles contraction/depolarization
T wave = ventricles repolarizing to prepare for another contraction `
In the cardiac cycle graph, why dont we see a bump when the atria repolarizes
Because that process is taken place at the same time when the ventricles are depolarizing
Cardiac output equation
CO = Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
CO - volume of blood moved by both ventricles each minute
SV - blood discharged from ventricles each contraction
HR - number of contractions per minute
Stroke volume formula
SV = End distolic volume (EDV) - End Sytolic Volume (ESV)
EDV = how much blood in the ventricles just before contraction
ESV = how much blood in the ventricles at the end of the contraction
Blood pressure formula
BP = Cardiac Output x Systemic vascular resistance
BP = pressure of circulating blood against the walls of vessels
SVR = resistance to the flow of blood (diameter, blood viscosity)
What are the four layers of arteries
Connective
Thick muscle layer
Elastic layer
Endothelium layer
Whay allows arterioles to regulate their diamter
Smooth muscle layer
What type of vessel is the smallest but has the greatest total surface area and cross sectional area
Capillaries
Name and compare the two pressures in vessels for capillary exchange
Hydrostatic pressure = pushing towards vessel walls. In capillaries causes fluid to flow out of vessel
Oncotic pressure = pressure of pushing inwards the vessels
What occurs at the arteriole end of the capillary?
Net filtration
Hydrostatic pressure high / Oncotoic pressure lower
What happens at the venous end of the capillary
Net reabsorption occurs
Hydrostatic pressure low / Oncoitic pressure stays the same
Precapillary sphincter
Rings of muscle that control blood flow (by contracting and relaxing)
Constrict = less nutrients and oxygen to tissues
Relax = more nutrients and oxygen to tissues
What is the smallest vein component
Venules
Veins layers
Connective tissue
Muscle (thin)
Elastic layer
Endothelium
Where does a fetus get its oxygen from
placenta
Ductus venosus; what is it, what it connects, what is its function
In fetuses, and connects the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava
A shunt that bypasses the liver in the fetus to deliver oxygenated blood
Foramen Ovale; what is it, what is its purpose; what does it bypass
A hole in the septum between the two atria that allows blood to flow form the right to left atrium
Bypasses the lungs and right ventricle so it can go to the body’s tissues faster since lungs arent functional yet
Ductus Arteriosus; what does it connect
Connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta
Similar to the foramen ovale
How are blood types catergorized
Your blood type is determined by the type of antigen you have
A antigen = blood type A
B antigen = blood type B
A + B antigen = blood type AB
O blood = Niether a and b antigen
Compare what would happen if we gave Type AB blood to someone who has Type O blood and vise versa
Donating typa AB to a Type O = immune response
Donating Type O to a Type AB = no immune response
What are the antibodies (not antigens) of each blood type
A = anti-B
B = anti-A
AB = none
O = anti-A and Anti-B
Rhesus Factor
Rh factor is another antigen on rbc
If present = + type
Lack = - type
Whats the TRUE universal blood type donor and recipient
O-
AB+ (have every type of antigen present in the RBC surface)
Which type of blood can only recieve blood from donors that share the same type
Type O blood
A father has blood type A and his father has type O blood, if the mother has blood type AB, what are the chances their child will have type B blood
set up punnet square
25%
Vasconstriction vs VASODILATION
VC = blood vessels constrict and increase pressure
VD = Widening of blood vessels and decreases pressure
Ways of controlling blood pressure
Direclty by changing the cardiac output and regulating hormones
Altering volume of blood in body (kidneys). More urine coming out = less blood volume. More urine held in = more blood volume
Order the blood pressure in our circulatory system
Arteries
Arterioles
Capillaries
Venules
Veins
Component of blood
55% liquid = called plasma
45% cellular componeents = red and white blood cells
Our blood is 55% plasma, what is the component of plasma
Aqueous mixture of;
Nutrients
Salts
Gases
Wastes
Hormones
Protines
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes
Erythrocytes = cells that carry oxygen and CO
Leukocytes (WBC) = iimmune cells that protect against pathogens
Thrombocytes = platelets
What is the most abundant cell type in blood
Erythrocytes
What molecules can bind to hemoglobin that we talked about
Oxygen
Carbo Dioxide
Carbon monoxide
What is a critical function of the bicarbonate buffering system
Keeps body to specific pH range
What happens when theres too much acid in the vlood
Bicarbonate buffering system combines acid with bicarbonate to from carbonic acid
What happens when theres too much base in the blood
Carbonic acid dissociates to neutralize it and forms bicarbonate
What is the major buffering system of the blood and where is it located in blood
Bicarbonate
Located in plasma = outside of the cells
What is the major buffering system INSIDE of the cells
Phosphate
Tight junctions act as the first barrier to prevent substance form crossing out of the blood to the ECS, what surrounds it
Astrocytes
When the platelets trigger the clotting cascade, what does this trigger
Triggers prothrombin (a zymogen) to be converted in its active form Thrombin
When thrombin is activated during a clotting cascade, what are its functions
Make more prothombin to make more thrombin
Convert fibrinogin to fibrin
What is the crucial last component of the clotting cascade
Fibrin = mesh of sticky protein strands that rap blood cells and platelets together to form a clot