IMOS Module 3 - Cermics/Glass Review
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UF IDS2935: Impacts of Material Science Quest Fall 2023
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Properties of Ceramics
inorganic, nonmetal solid
brittle
high melting point
poor conductor
waterproof
chemically resistant (iconic and colvalent bonds)
crystallinity
Crystallinity
varies from crystalline to semi-crystalline to amorphous
Crystalline v. Amorphous
crystalline: long-range structural order
amorphous: lacking long-range structural order (ex. oxides, borides, polymers, and metals)
Vitrification
transformation of atomic/molecular structure
requires >1200C (for clay)
Plasticity
water layers can slide pass each other
Properties of Glass
inorganic, nonmetallic solid
brittle
high melting point
poor conductor
stoff
waterproof
chemically resistant (ionic and colvalent bonds)
amorphous (no crystallinity)
Operational Sequence
accounting an accounting of a system's procedures for start-up and shut-down, response to varying conditions, and certain scheduled operations
Operational sequence v. entanglement
operation sequence: steps of a process to make a thing
entanglement: how things and people are dependent on each other
Flinknapping
controlled reduction of glass-like rock (ex. fluted Clovis points)
requires the right kind of rock
skills for applying controlled force
produce flakes and blades with/ sharp edges
an infinite variety of forms
Bifacial reduction
planned reduction of the core through successive function or applications
Clovis culture
after ice age
hunted mammoths as a community
fluting was a communal activity
raw materials were gathered from outside their territory
early cookware could insulate but not conduct (no boiling food)
wild grasses were the basis for early farming
Early glass
volcanic glass
does not need fire
used for spearpoints
Rupert drop
1625; will break at the tail but withstand blows on the opoosite end
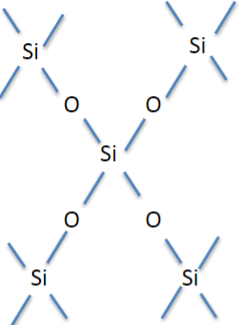
Silicon dioxide glass
amorphous solid
unstable
devitrification (crystallize with time)
melting poin at 1713C
Egyption glass (soda lime glass)
faience used Nile sediment Natron (NaCo3)
melts at 850C (lower melting point)
reacts with SiO2
Sodium silicate dissolves in water
added lime to strengthen the network (network former)
Roman glass
addition of MnO2 created clear, colorless glass
used as drinking vessels, windows, and mirrors
Chaine Operatoire
a tool used in anthropology to study the step-by-step production, use, and disposal of artifacts
Gorilla glass
substitue K for Na
Ceramics superhydrophonic coatings
Al2O3 nano particles
Corningware
resistant to cracking and chipping
will not break unless the coating has been tampered with
absorbs energy but high in tension (will explode when broken)
resistant from thermal shock
History of glass
used faience glazes and soda lime glass in Egypt
slump glass and new methods in Greece
glass blowing developed in Syria/Palestine
stained glass use in Europe
development of telescopes and microscopes revolutionized science
Jamestown’s first industry
development of fiber optics glass
Funcational ceramics
materials that can convert energy from one form to another or respond in unusual ways to external stimuli (ex. electroactive, multiferroic, piezoelectric)
“Cradle to Grave”
sustanibility and life cycle of materials