Art movements
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Abstract Expressionism
American art movement of the 1940s that emphasized form and color within a nonrepresentational framework. Jackson Pollock initiated the revolutionary technique of splattering the paint directly on canvas to achieve the subconscious interpretation of the artist's inner vision of reality.

Abstract Expressionism
Jackson Pollock
Willem de Kooning
Arshile Gorky
Hans Hofmann
Mark Rothko

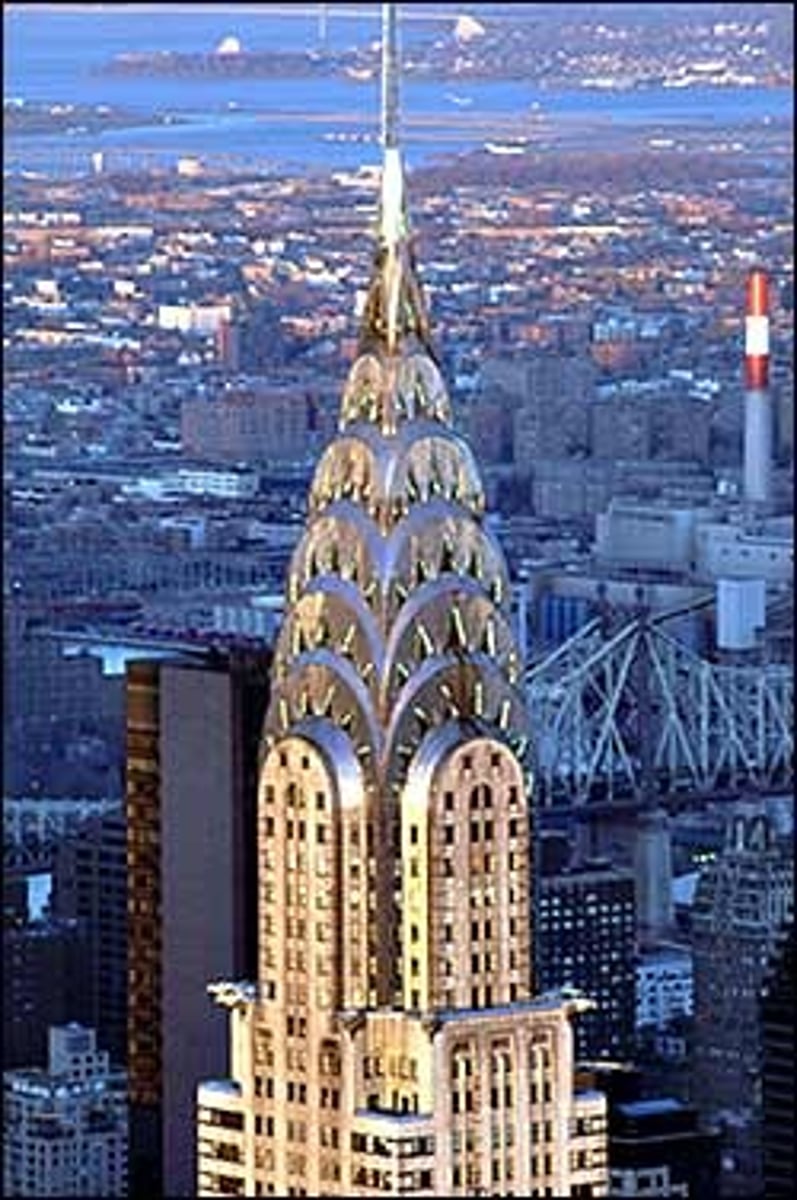
Art Deco
A 1920s style characterized by setbacks, zigzag forms, and the use of chrome and plastic ornamentation. New York's Chrysler Building is an architectural example of the style.

Art Nouveau
An 1890s style in architecture, graphic arts, and interior decoration characterized by writhing forms, curving lines, and asymmetrical organization. Some critics regard the style as the first stage of modern architecture. Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec is the best-known of its followers.

Ashcan School
A group of New York realist artists at the beginning of the twentieth century who rejected the formal subject matter of the academy and focused on gritty urban scenes and ordinary, even ugly, aspects of life.

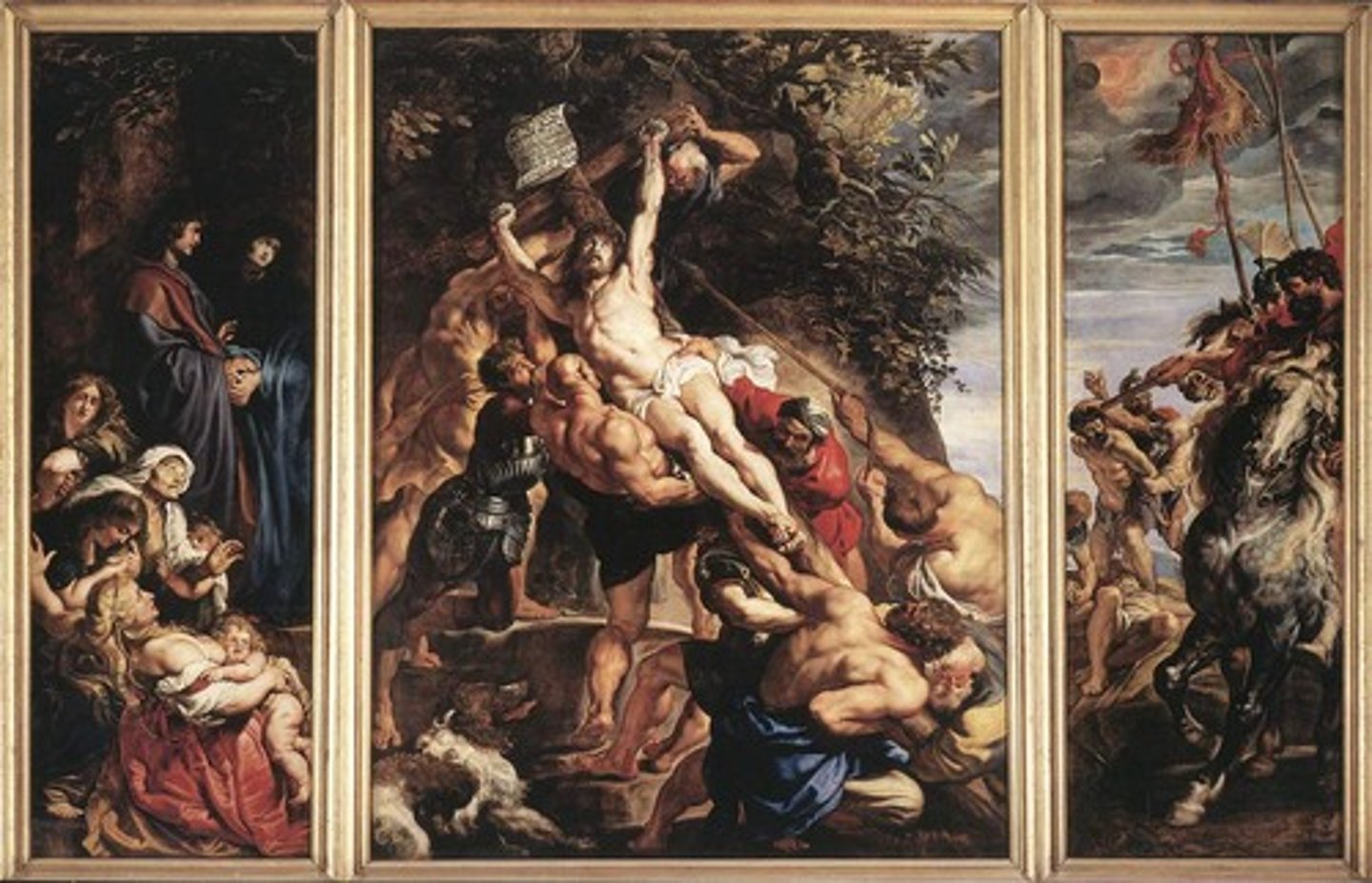
Baroque
European art and architecture of the 17th and 18th centuries. Giovanni Bernini, a major exponent of the style, believed in the union of the arts of architecture, painting, and sculpture to overwhelm the spectator with ornate and highly dramatized themes. Although the style originated in Rome as the instrument of the Church, it spread throughout Europe in such monumental creations as the Palace of Versailles.

Baroque
Rembrandt van Rijn
Caravaggio
Giovanni Bernini
Peter Paul Rubens
Diego Velázquez

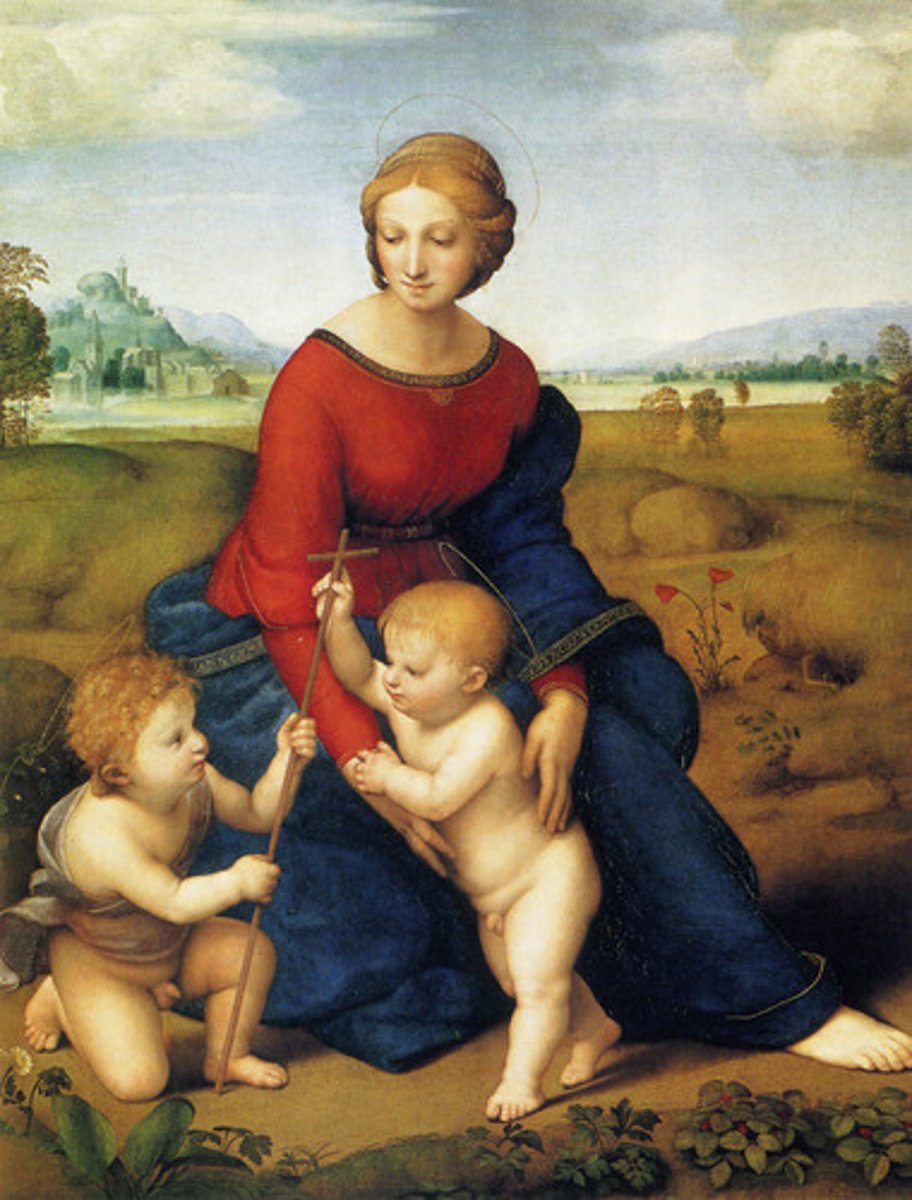
Classicism
A form of art derived from the study of Greek and Roman styles characterized by harmony, balance, and serenity. In contrast, the Romantic Movement gave free rein to the artist's imagination and to the love of the exotic.
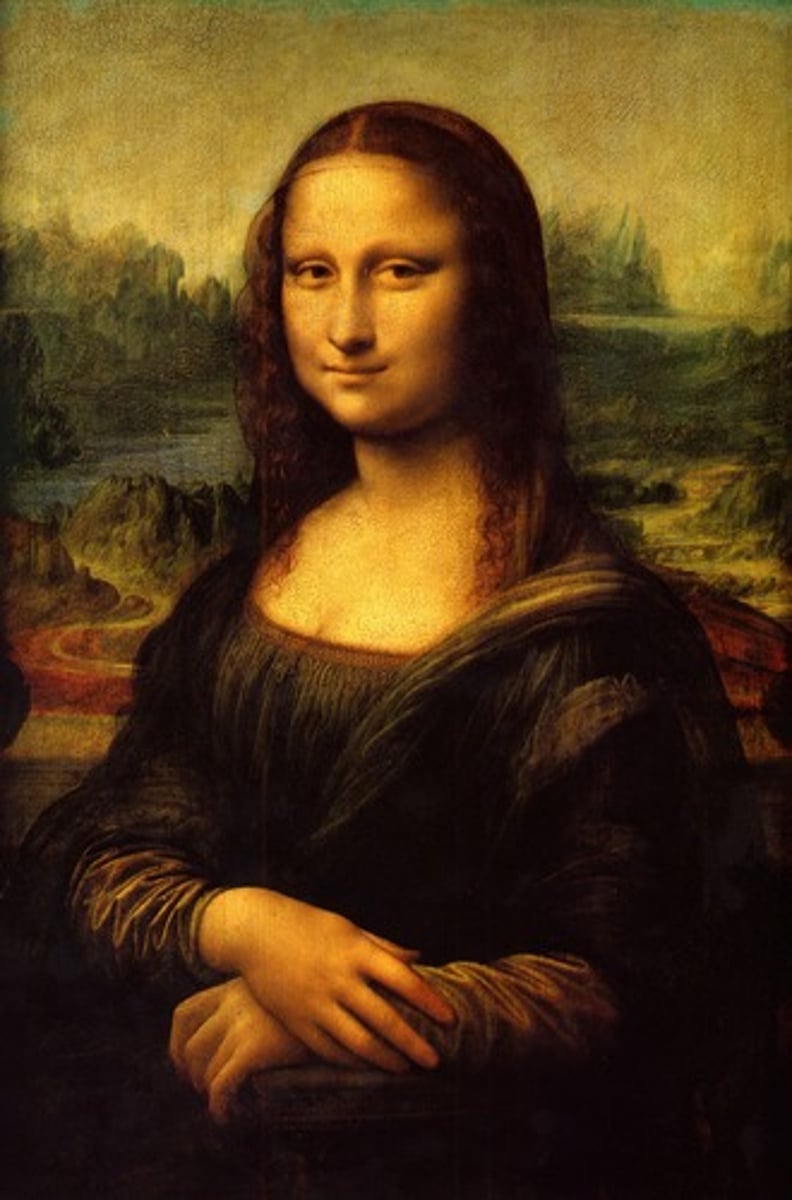

Classicism
Michelangelo
Raphael
Correggio
Mantegna
Anton Raffael Mengs
Johan Joachim Winckelman
most Renaissance artists

Constructivism
A form of sculpture using wood, metal, glass, and modern industrial materials expressing the technological society. The mobiles of Alexander Calder are examples of the movement.
Cubism
Early 20th-century French movement marked by a revolutionary departure from representational art. Pablo Picasso and Georges Bracque penetrated the surface of objects, stressing basic abstract geometric forms that presented the object from many angles simultaneously.
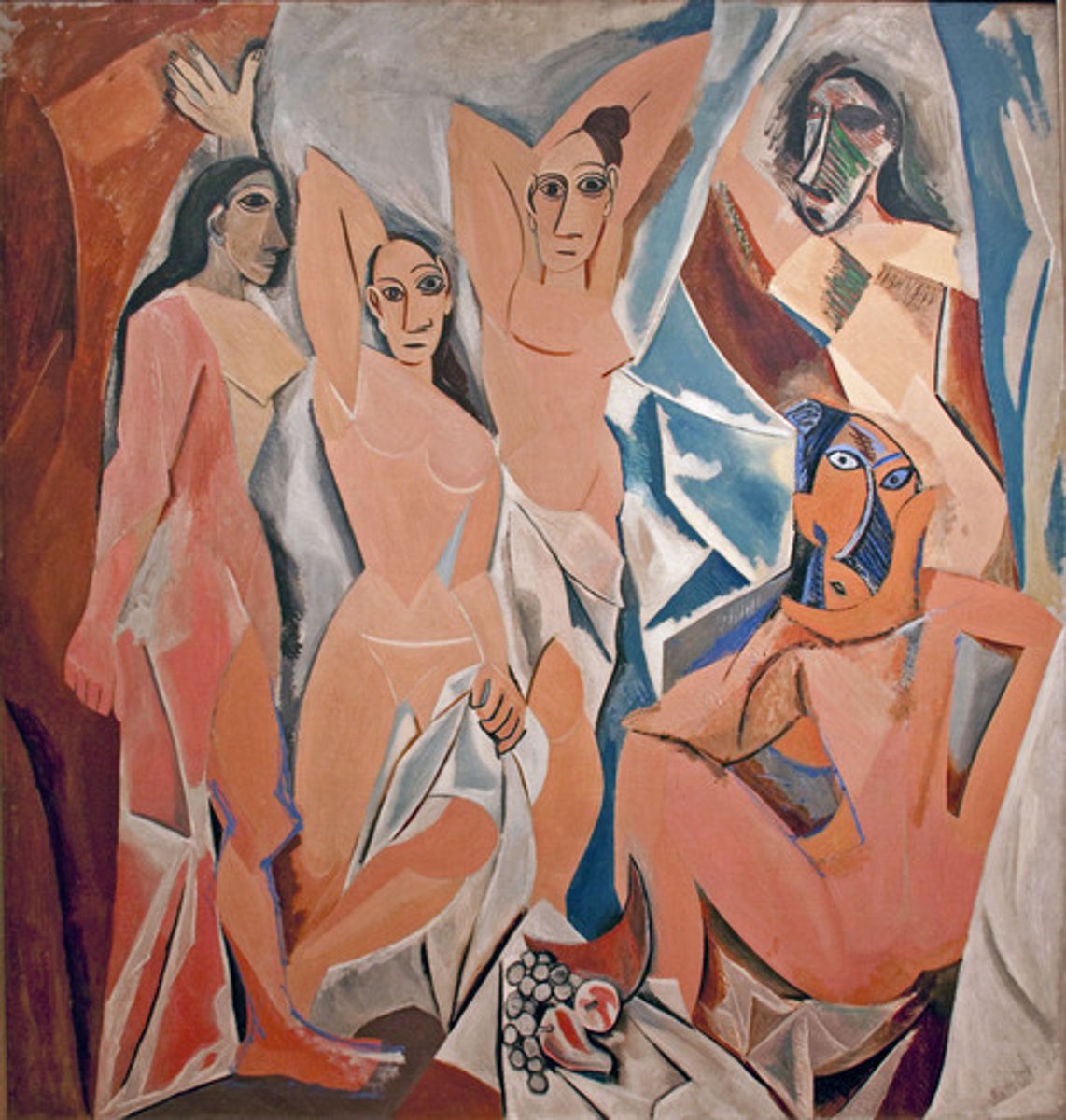
Cubism
Georges Braque
Pablo Picasso
Paul Cézanne
Jean Metzinger
Albert Gleizes

Dada
A product of the turbulent and cynical post-World War I period, this anti-art movement extolled the irrational, the absurd, the nihilistic, and the nonsensical.

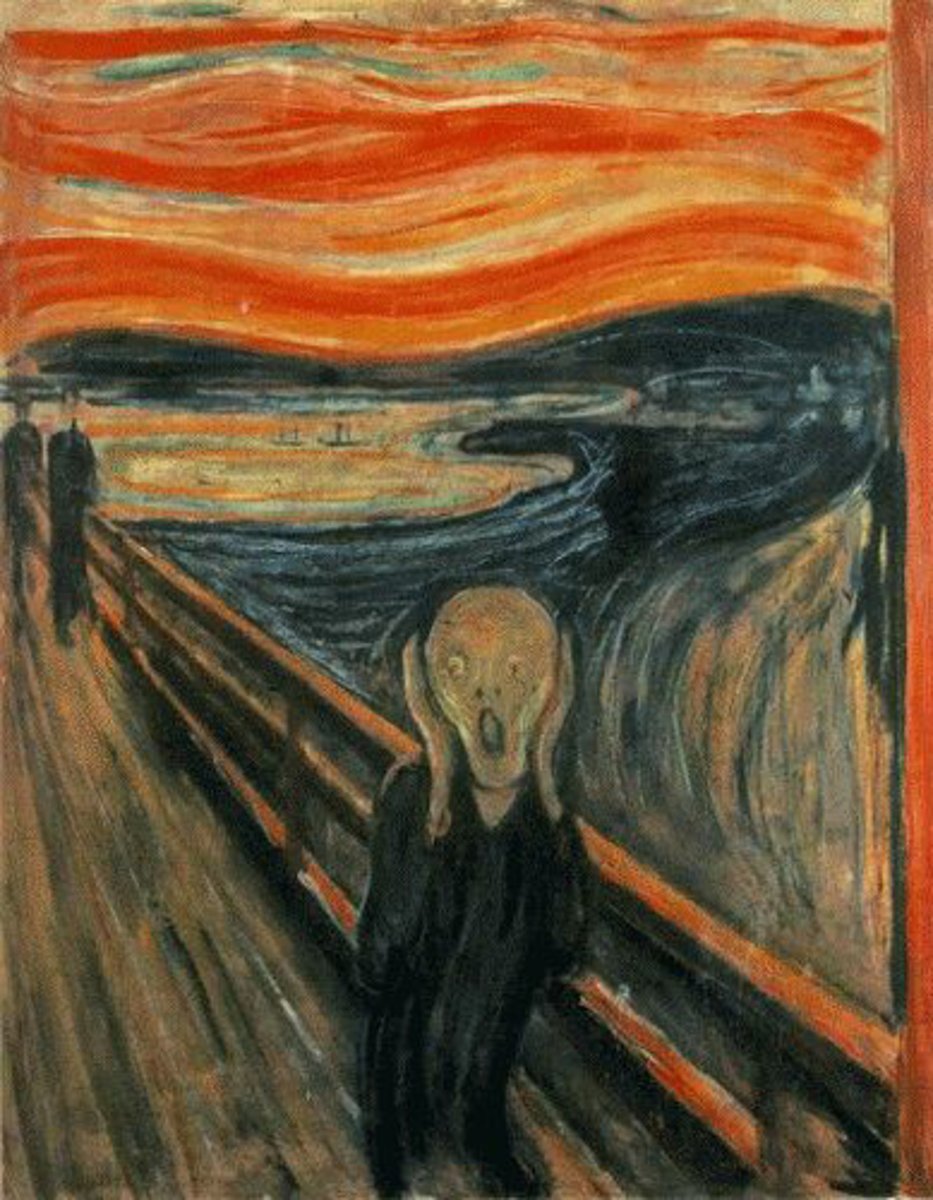
Expressionism
A 20th-century European art movement that stresses the expression of emotion and the inner vision of the artist rather than the exact representation of nature. Distorted lines and shapes and exaggerated colors are used for emotional impact. Vincent Van Gogh is regarded as the precursor of this movement.
Expressionism artists
Edvard Munch
Ernst Ludwig Kirchner
Franz Marc
El Greco
Wassily Kandinsky

Impressionism
Late 19th-century French school dedicated to defining transitory visual impressions painted directly from nature, with light and color of primary importance. If the atmosphere changed, a totally different picture would emerge. Claude Monet and Camille Pissarro were leaders of the movement.

Impressionism
Claude Monet
Camille Pissarro
Edgar Degas
Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Mary Cassatt
Eduoard Manet

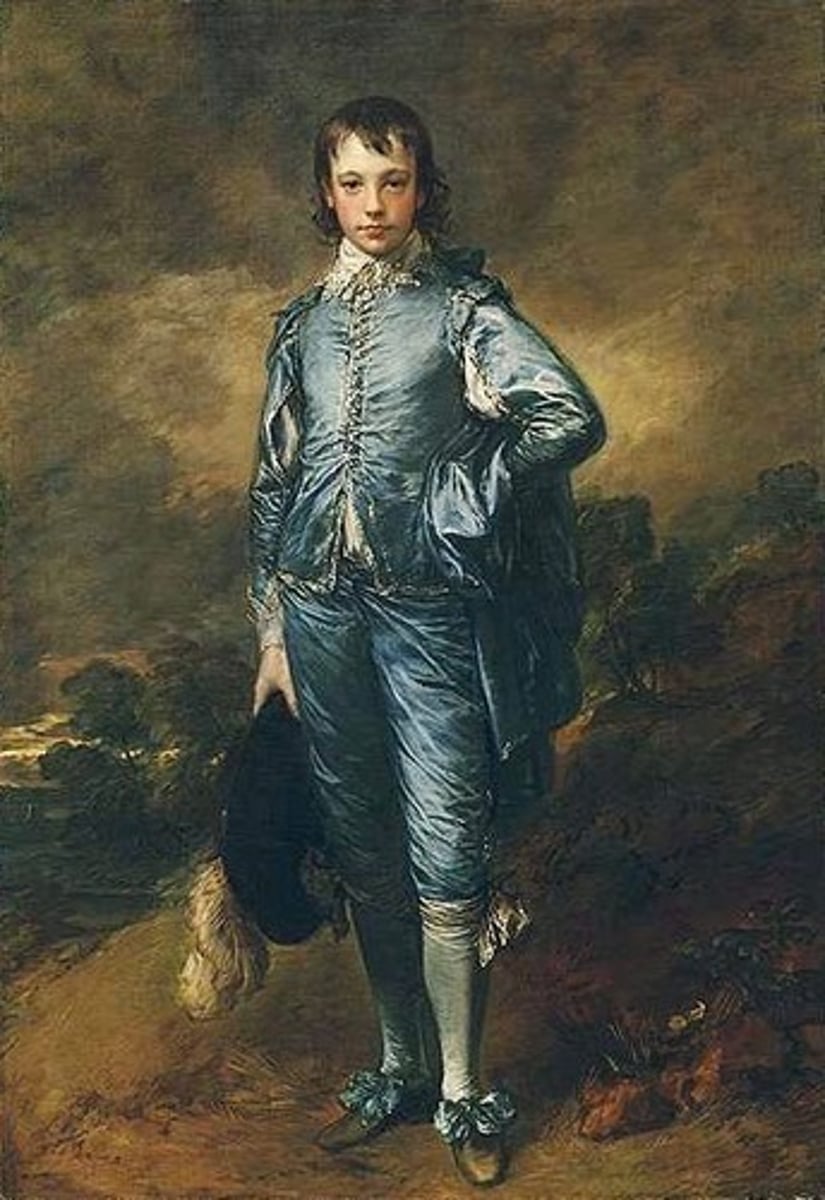
Neoclassicism
An 18th-century reaction to the excesses of Baroque and Rococo, this European art movement tried to recreate the art of Greece and Rome by imitating the ancient classics both in style and subject matter.
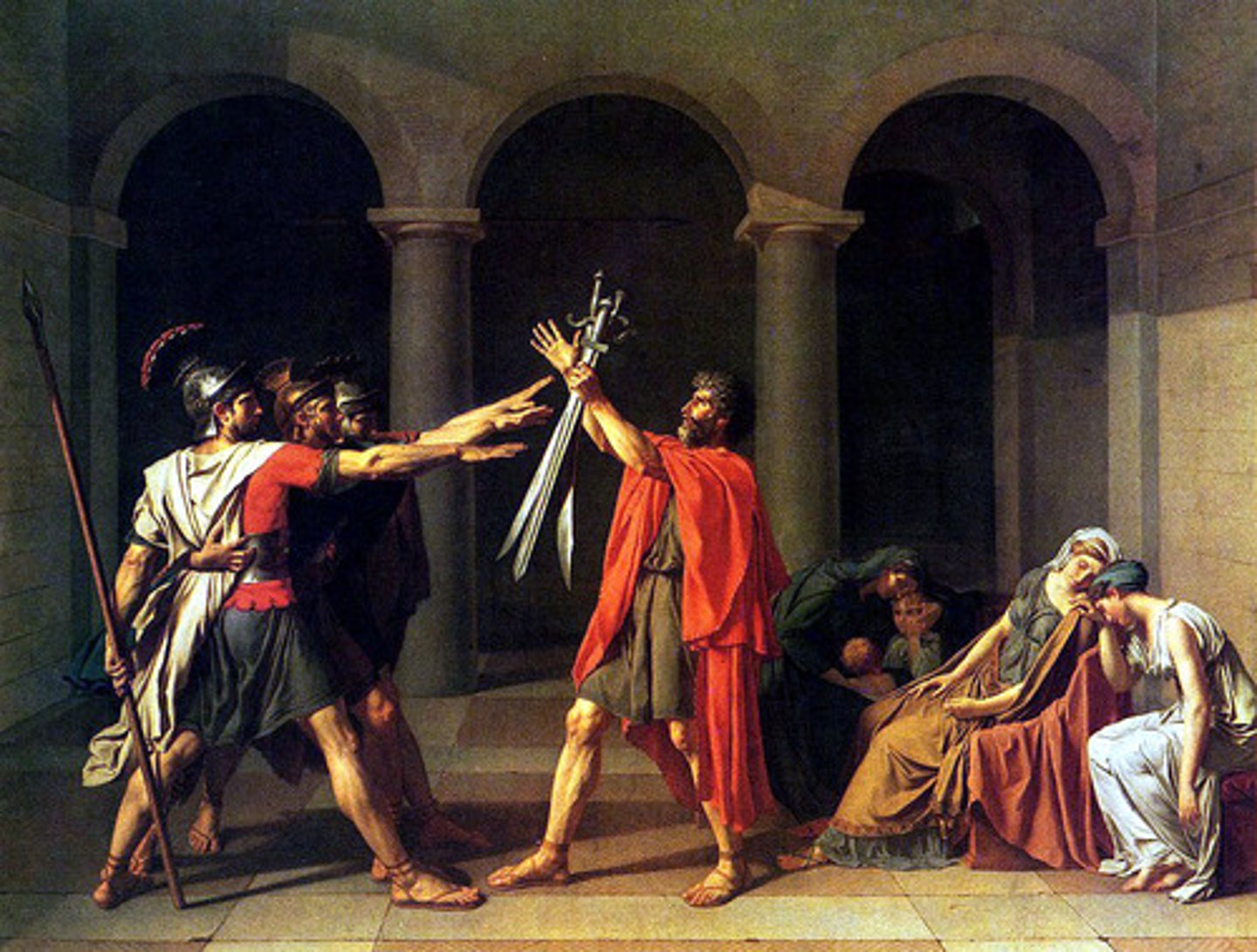

Neoclassicism
Jacques-Louis David
Sir Henry Raeburn
Sir Joshua Reynolds
Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres
Thomas Gainsborough
Antonio Canova
Arnold Bocklin

Pop Art
In this return to representational art, the artist returns to the world of tangible objects in a reaction against abstraction. Materials are drawn from the everyday world of popular culture—comic strips, canned goods, and science fiction.
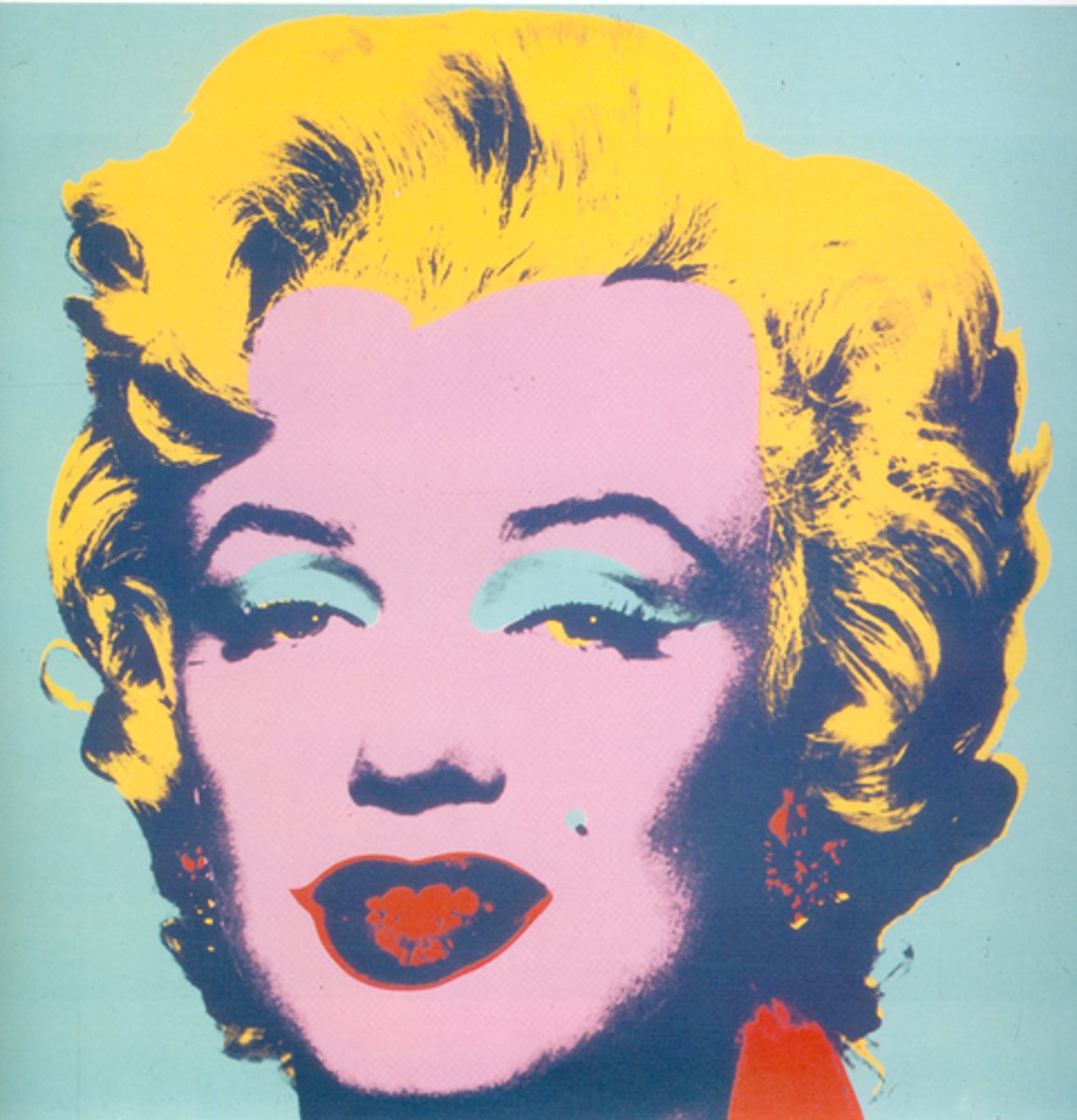

Pop art
Richard Hamilton
Roy Lichtenstein
Robert Rauschenberg
Andy Warhol
David Hockney
Jeff Koons
Claes Oldenburg
Tom Wesselmann

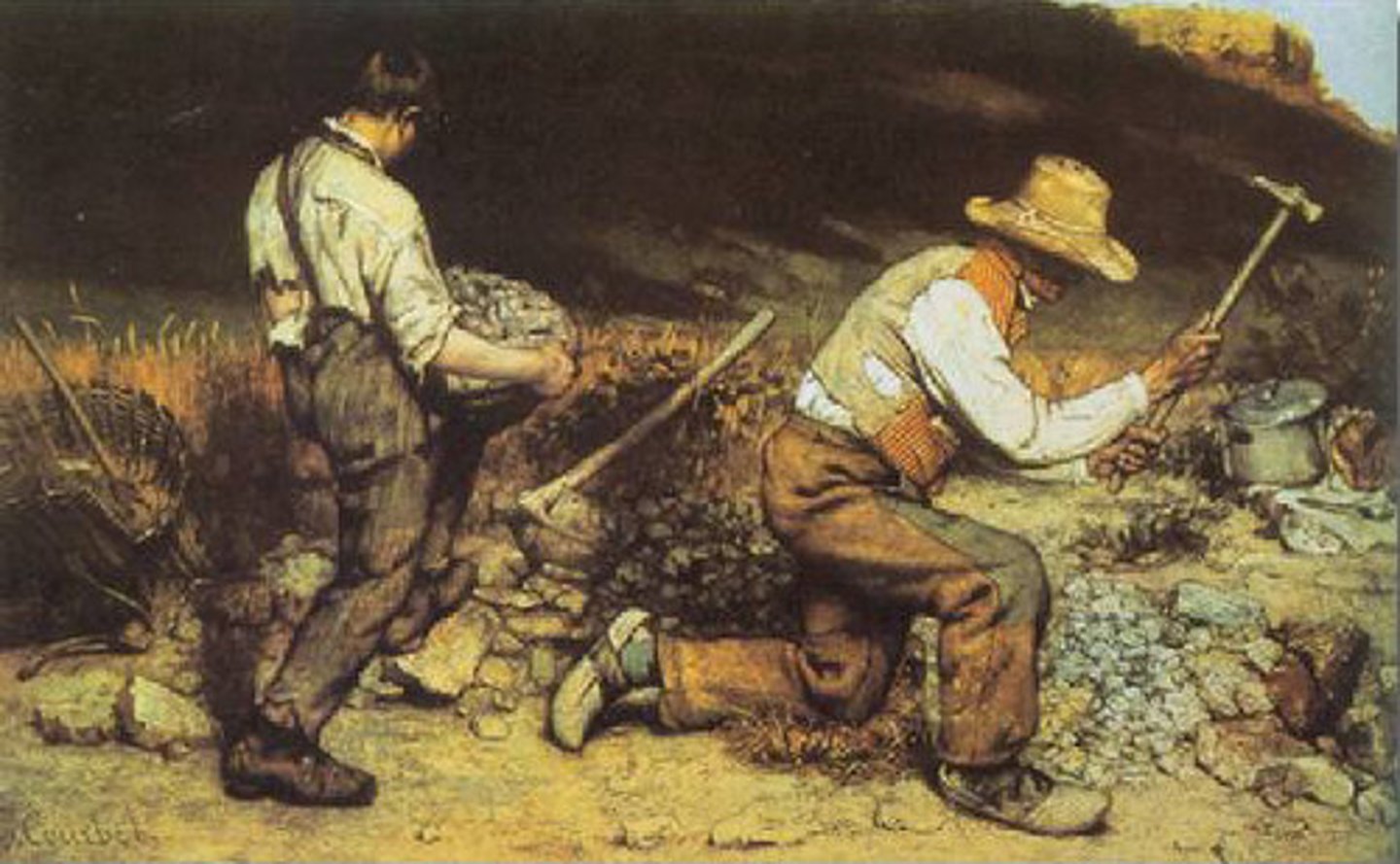
Realism
A development in mid-19th-century France lead by Gustave Courbet. Its aim was to depict the customs, ideas, and appearances of the time using scenes from everyday life. Americans in this movement included J A Whistler and John Singer Sargeant.

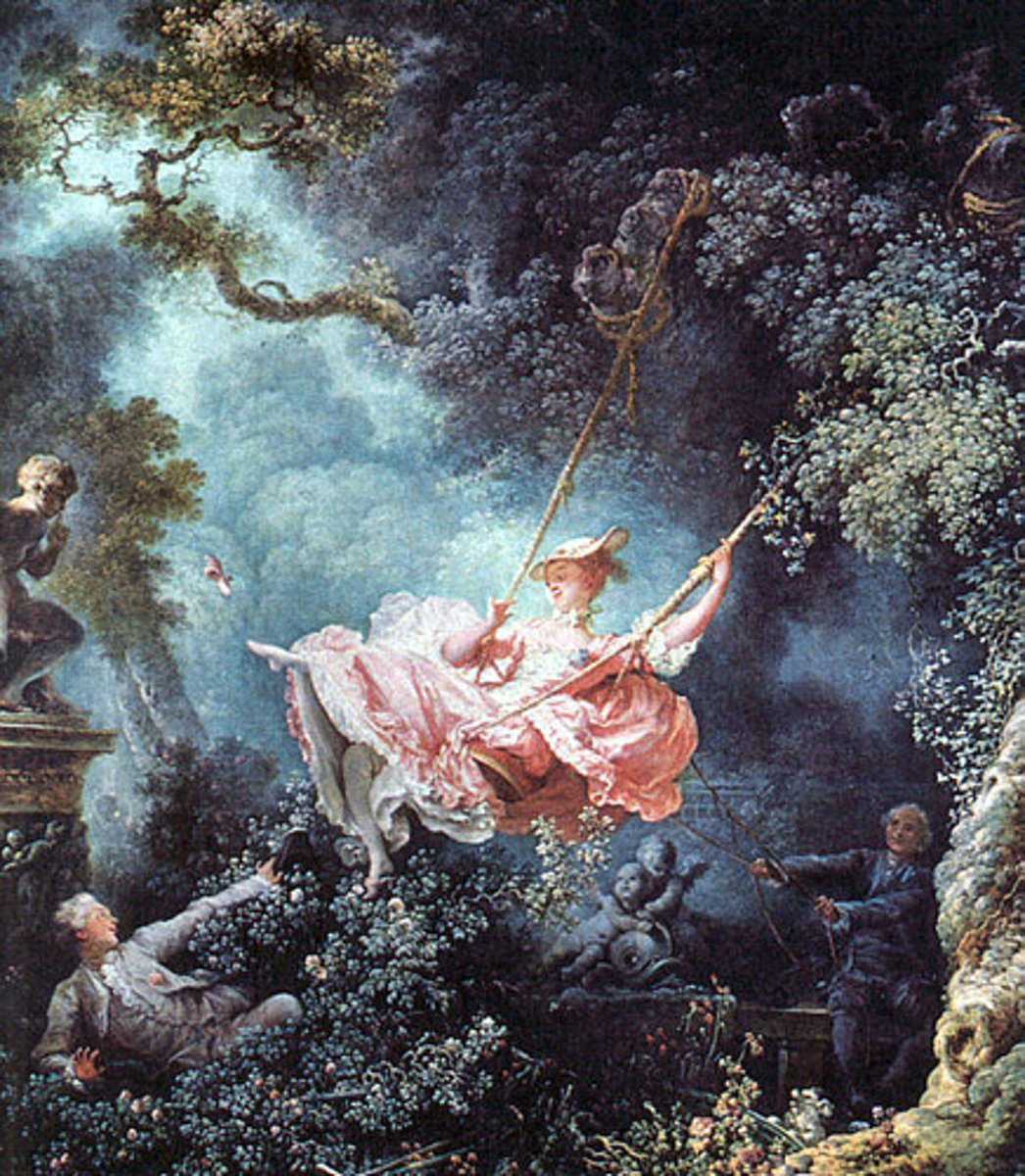
Rococo
A French style of interior decoration developed during the reign of Louis XV consisting mainly of asymmetrical arrangements of curves in paneling, porcelain, and gold and silver objects. The characteristics of ornate curves, prettiness, and gaiety can also be found in the painting and sculpture of the period.

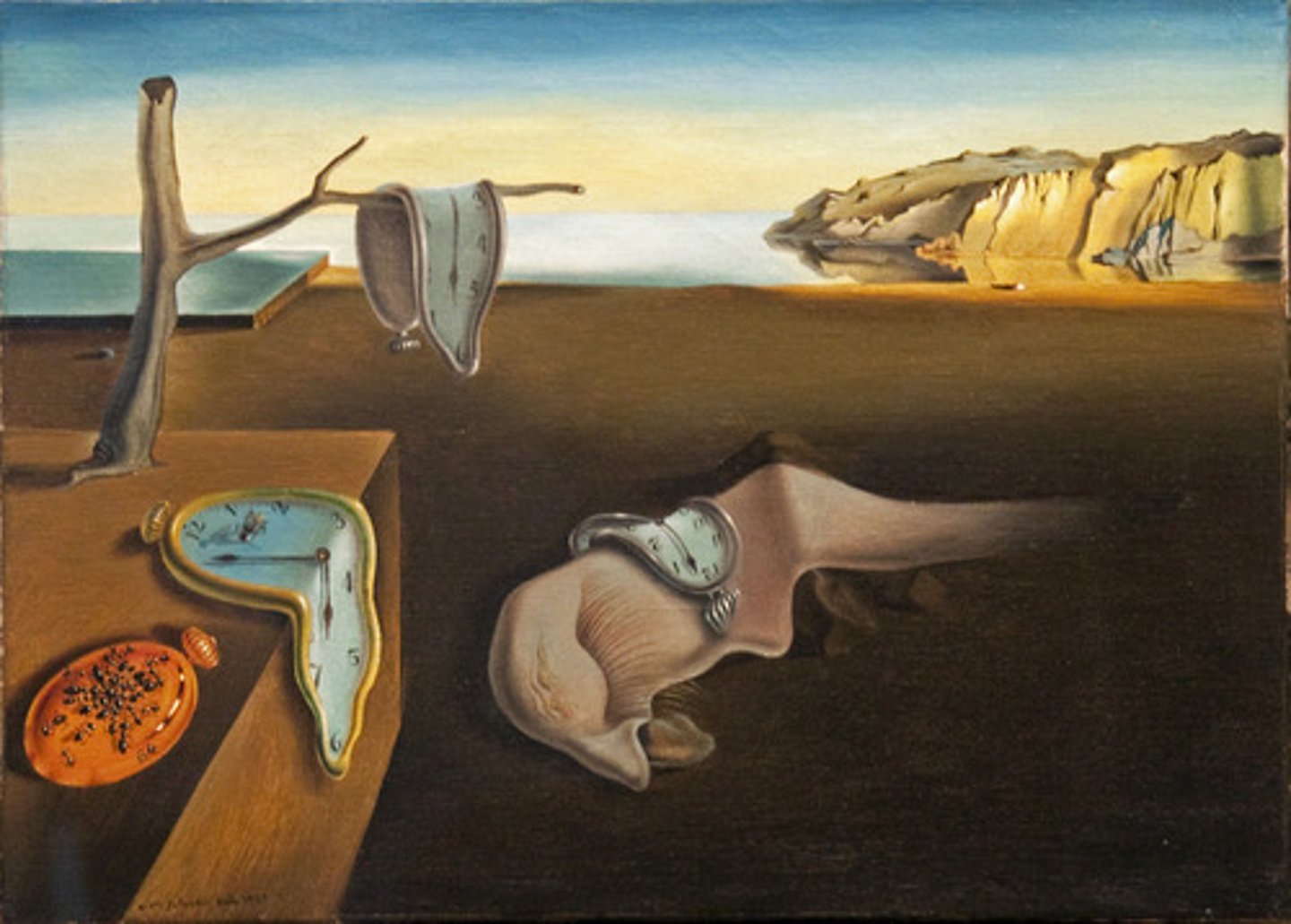
Surrealism
A further development of Collage, Cubism, and Dada, this 20th-century movement stresses the weird, the fantastic, and the dreamworld of the subconscious.

Surrealism
Marcel Duchamp
Georgia O'Keeffe
Max Ernst
Sir Henry Moore
Rene Magritte
Joan Miro
Salvador Dali
Pablo Picasso
Man Ray
Dorothea Tanning
MC Escher

Symbolism
As part of a general European movement in the latter part of the 19th century, it was closely allied with Symbolism in literature. It marked a turning away from painting by observation to transforming fact into a symbol of inner experience. Paul Gauguin and Gustav Klimt were practitioners.
