physio lab exam #1
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sinclair ccp anatomy and physio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
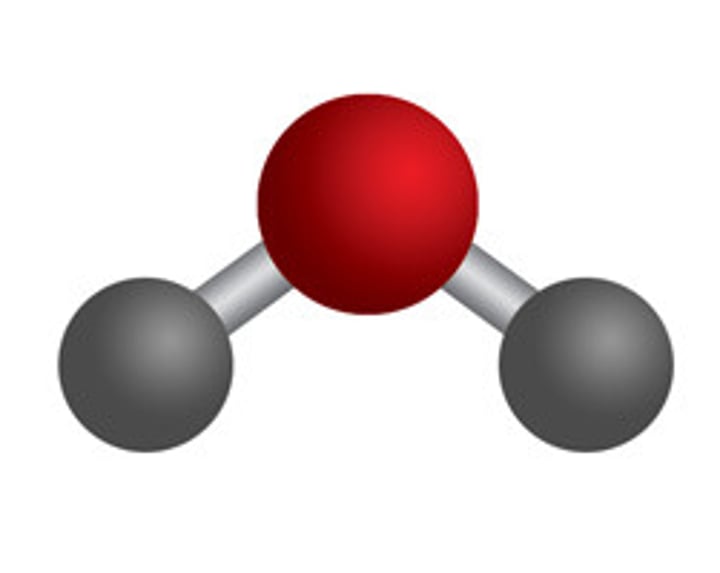
Methane (CH4)
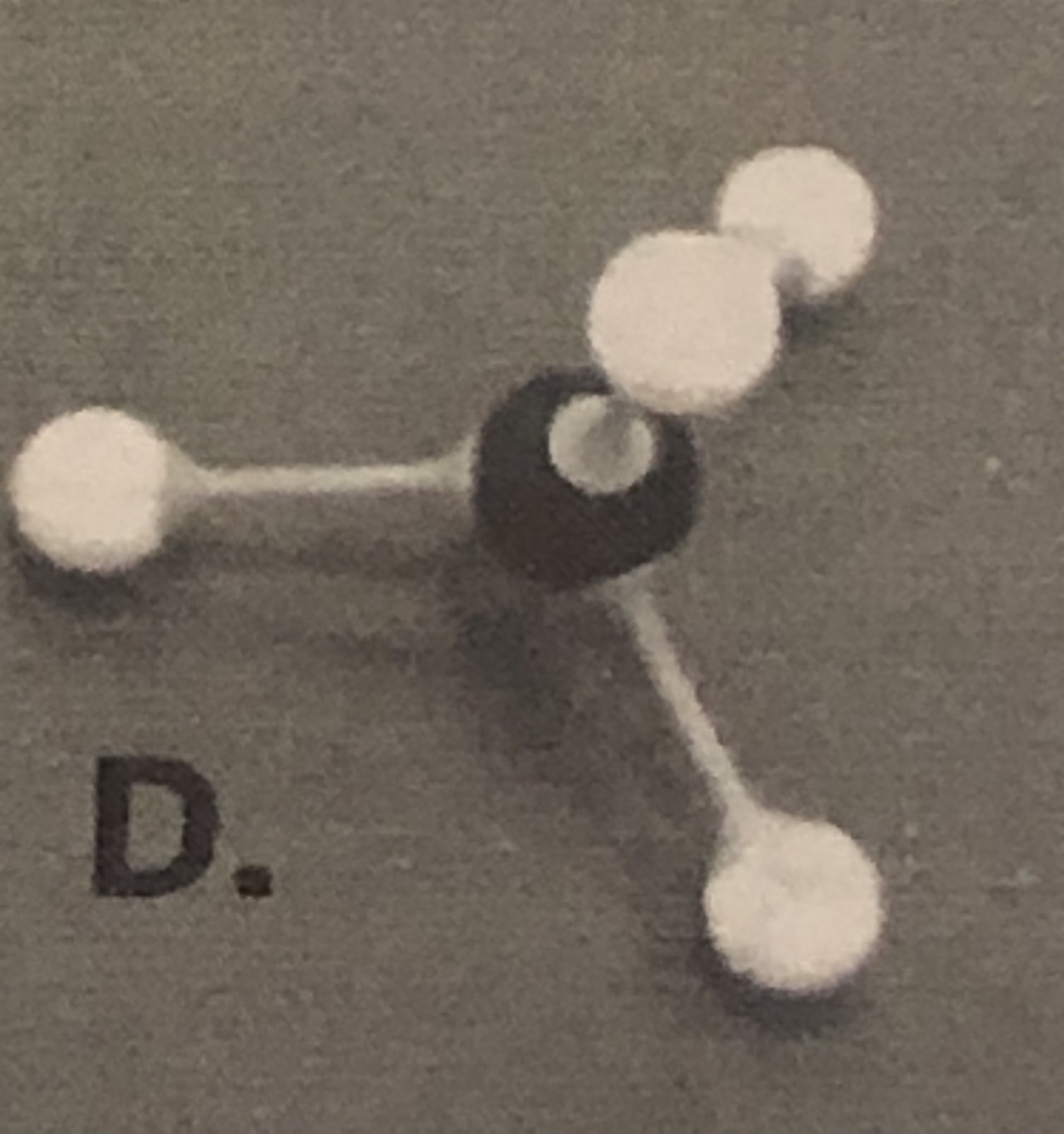
Glucose
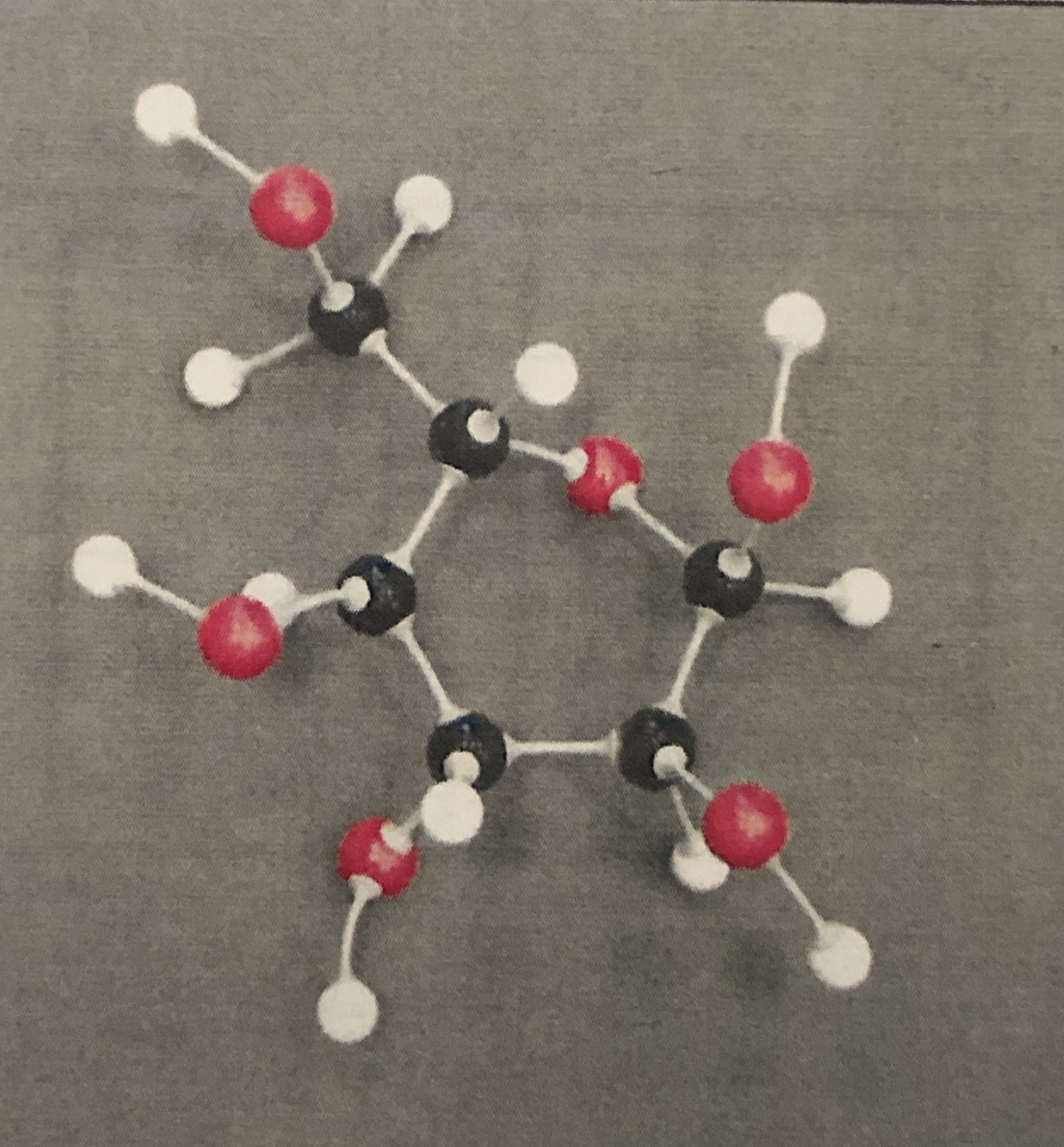
Glycerol
Saturated Fatty Acid
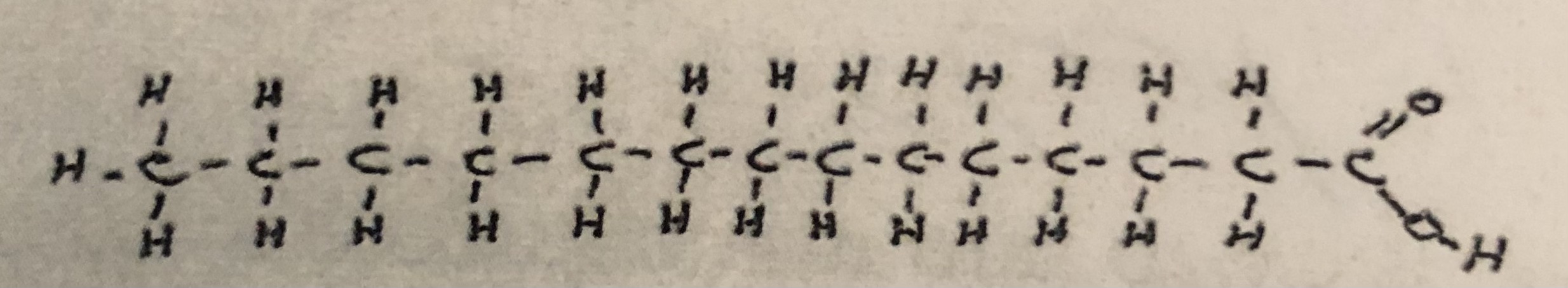
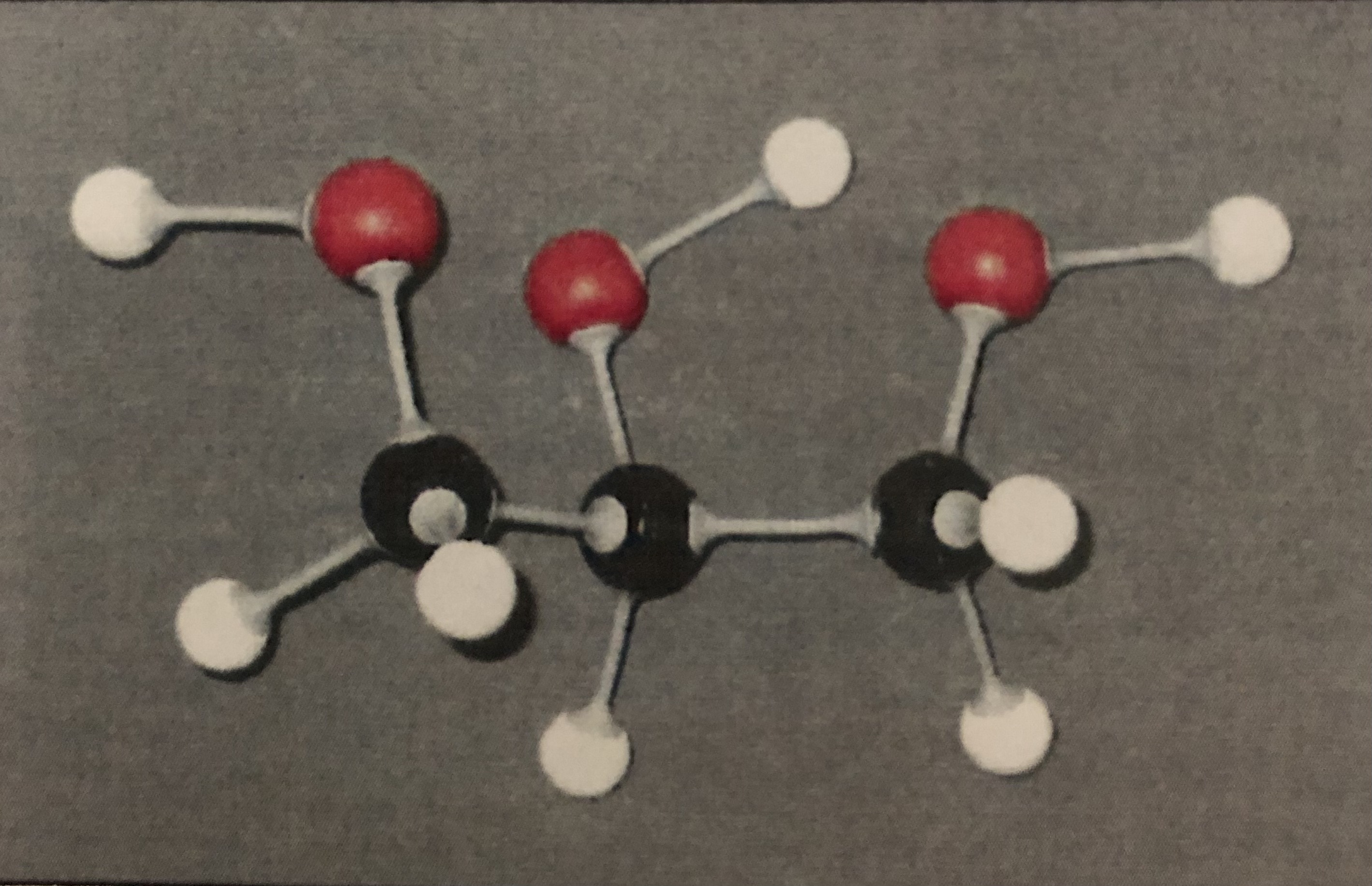
Monounsaturated Fatty Acid
Double bonded Carbon
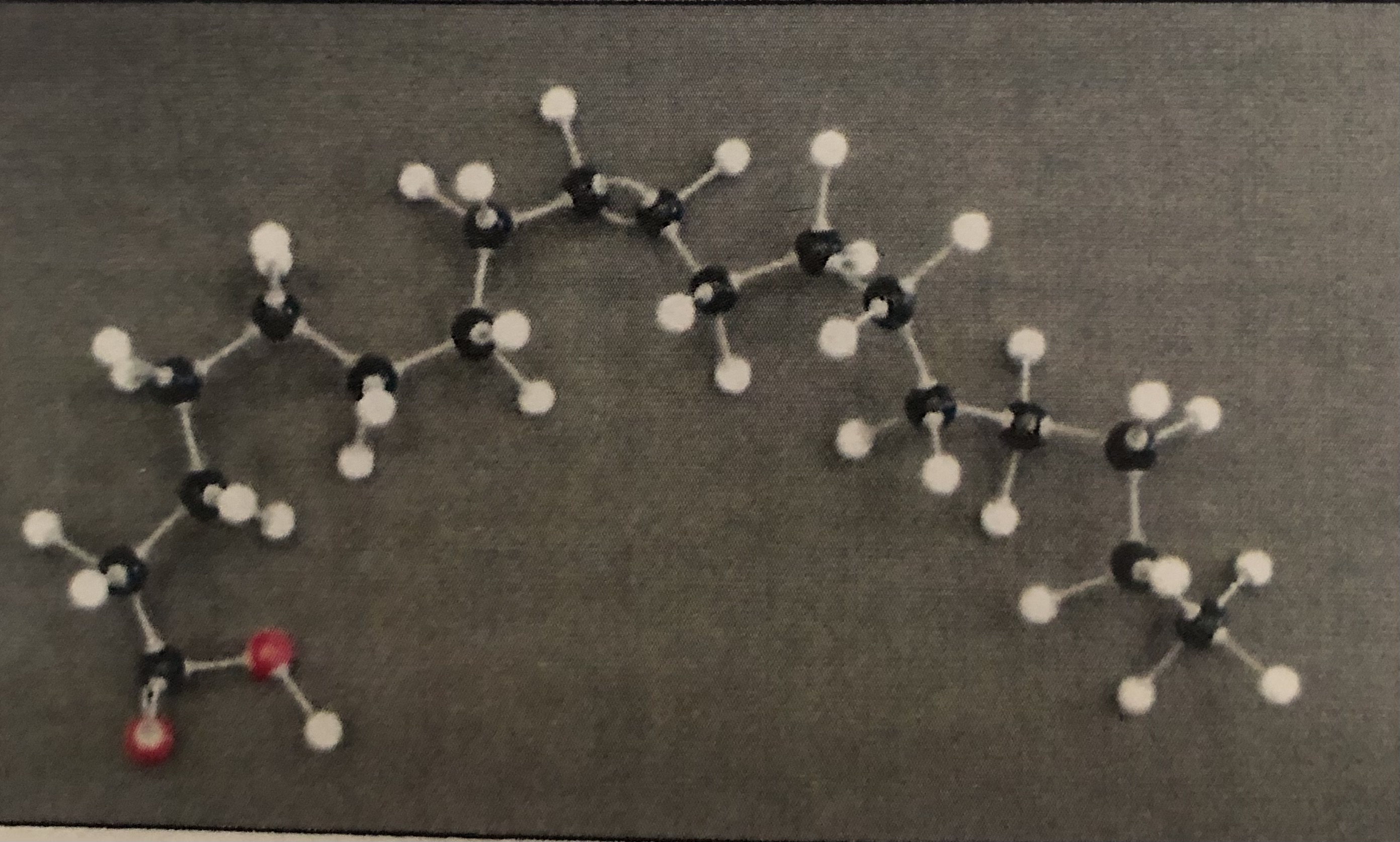
Triglyceride
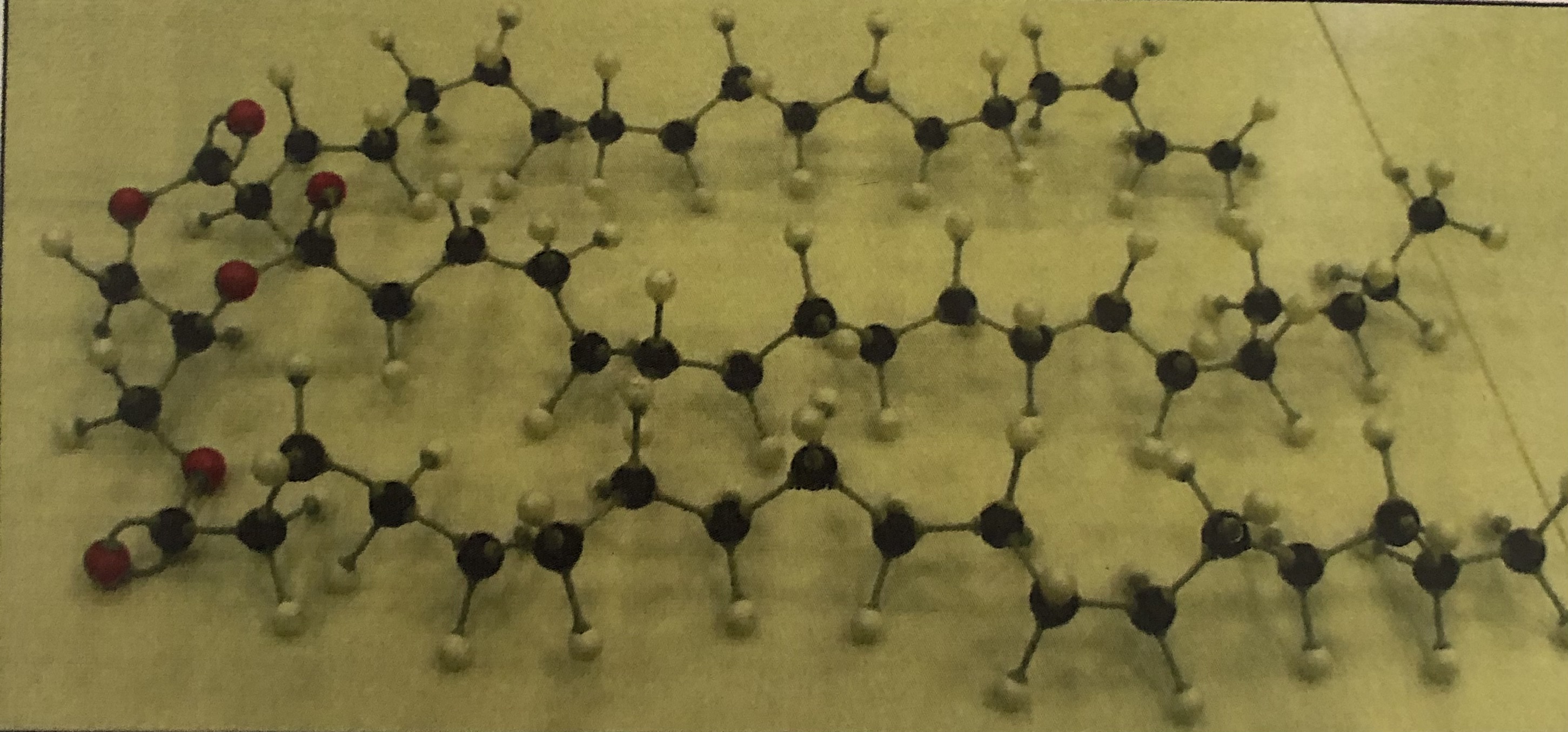

Steroid
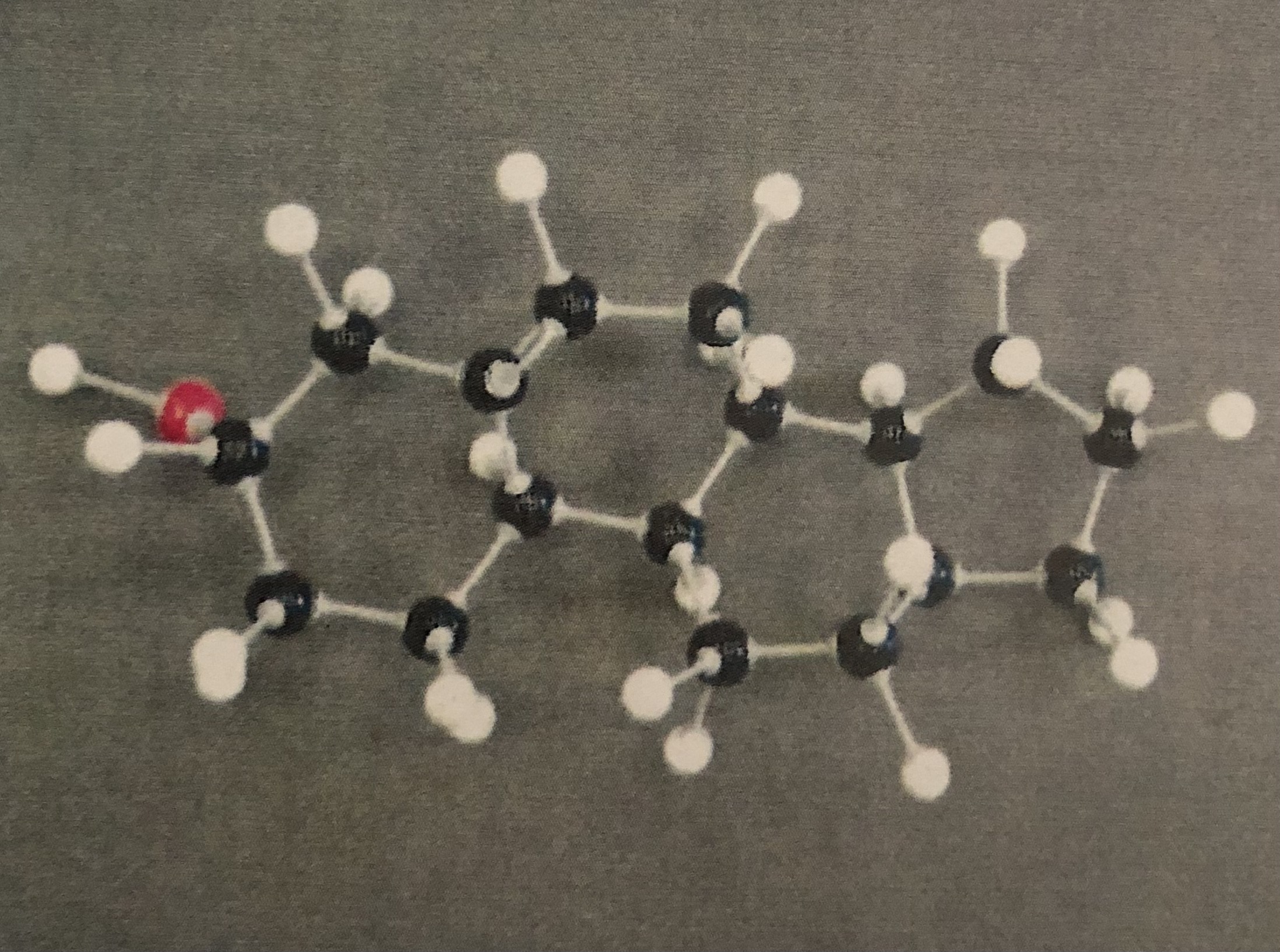
4 Carbon Rings
Glycerol
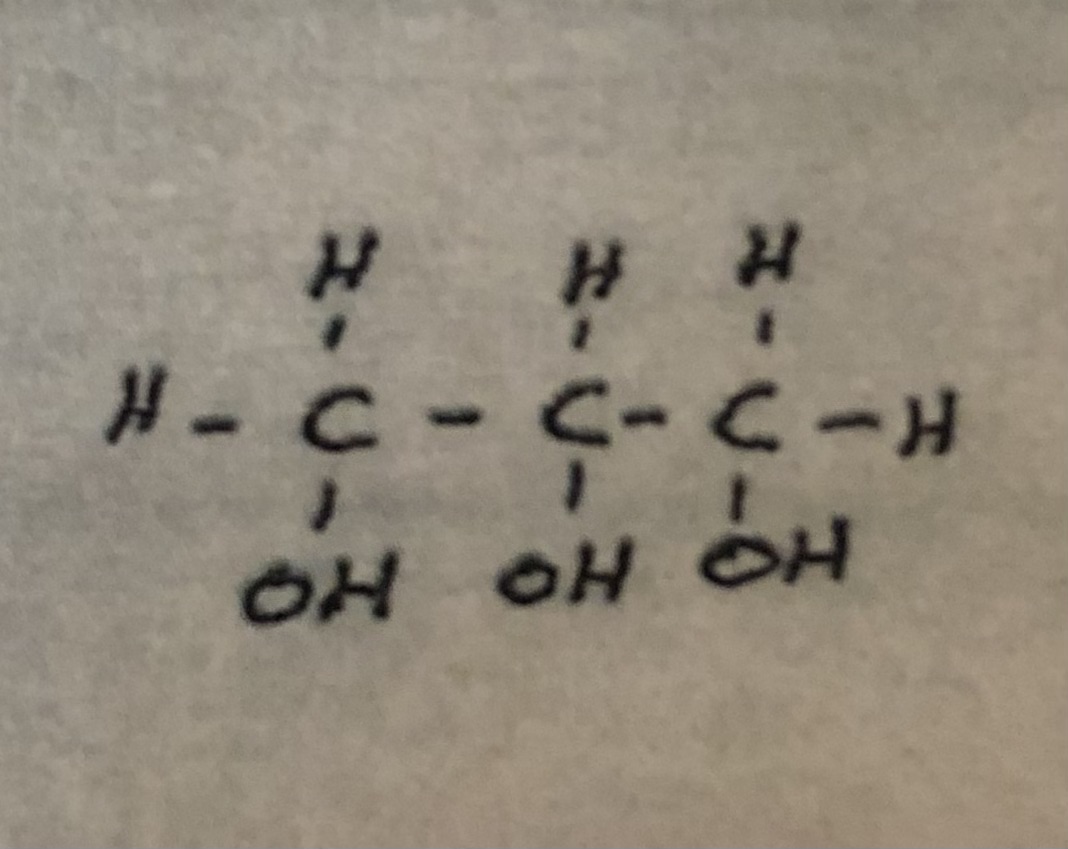
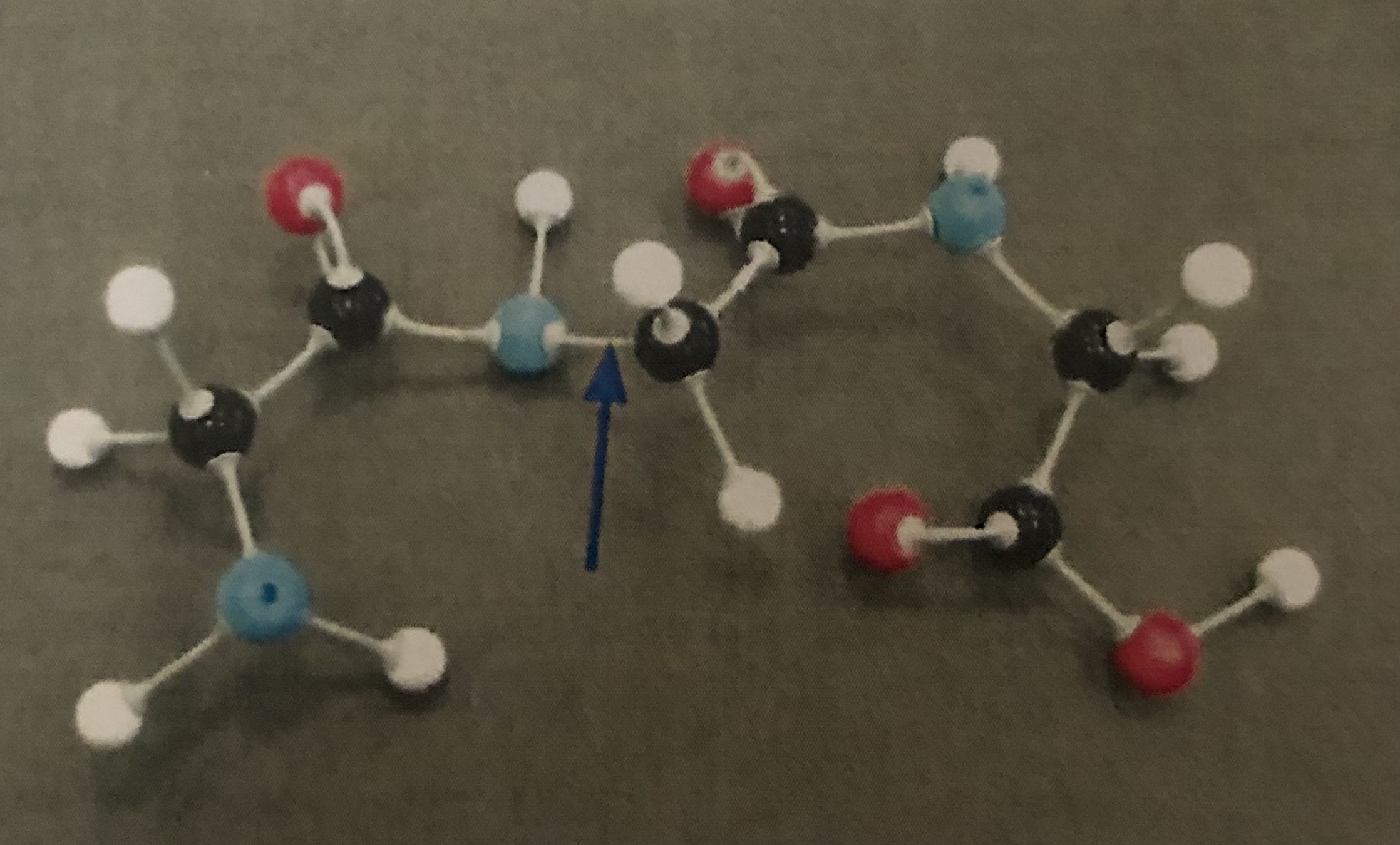
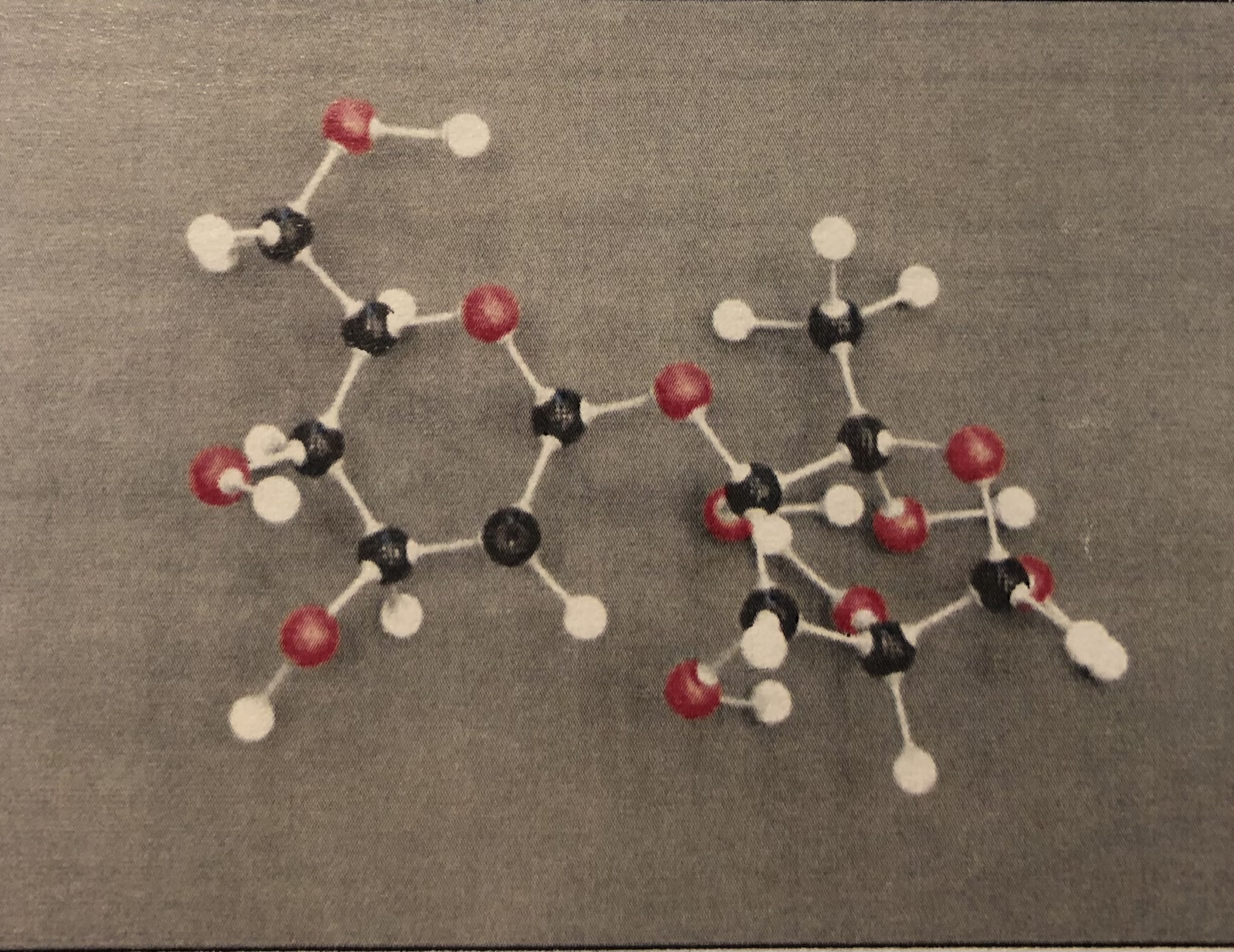
Dipeptide
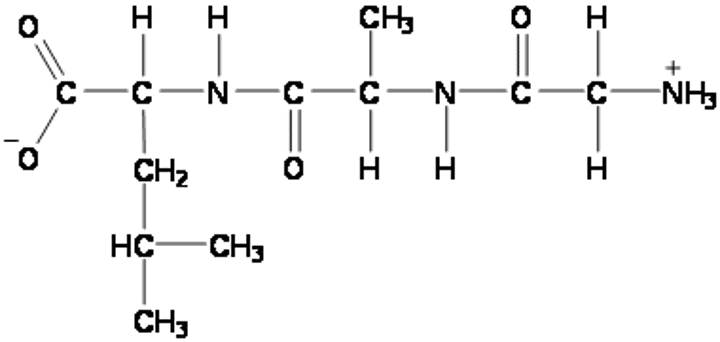
Tripeptide
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
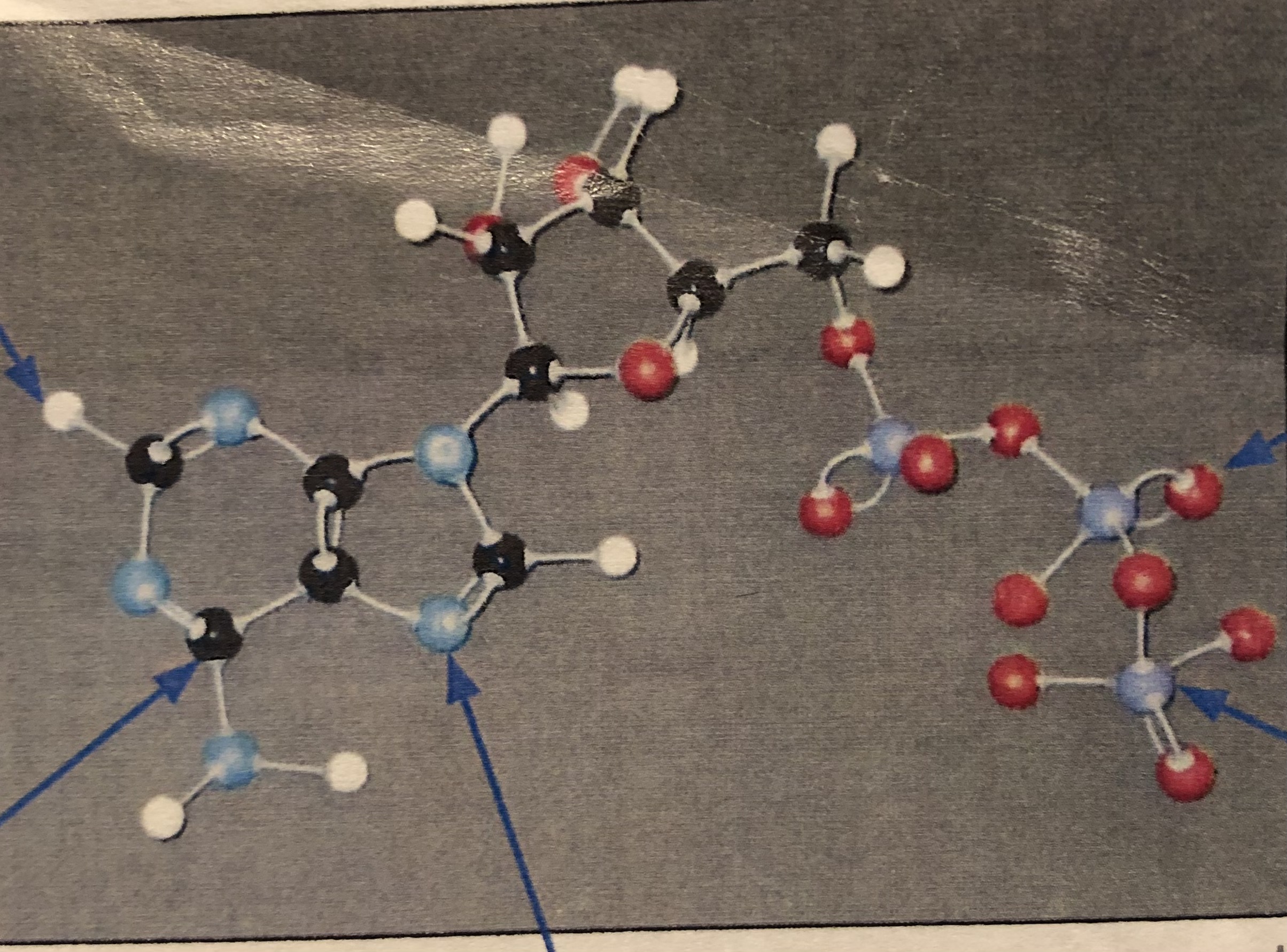
Maltose
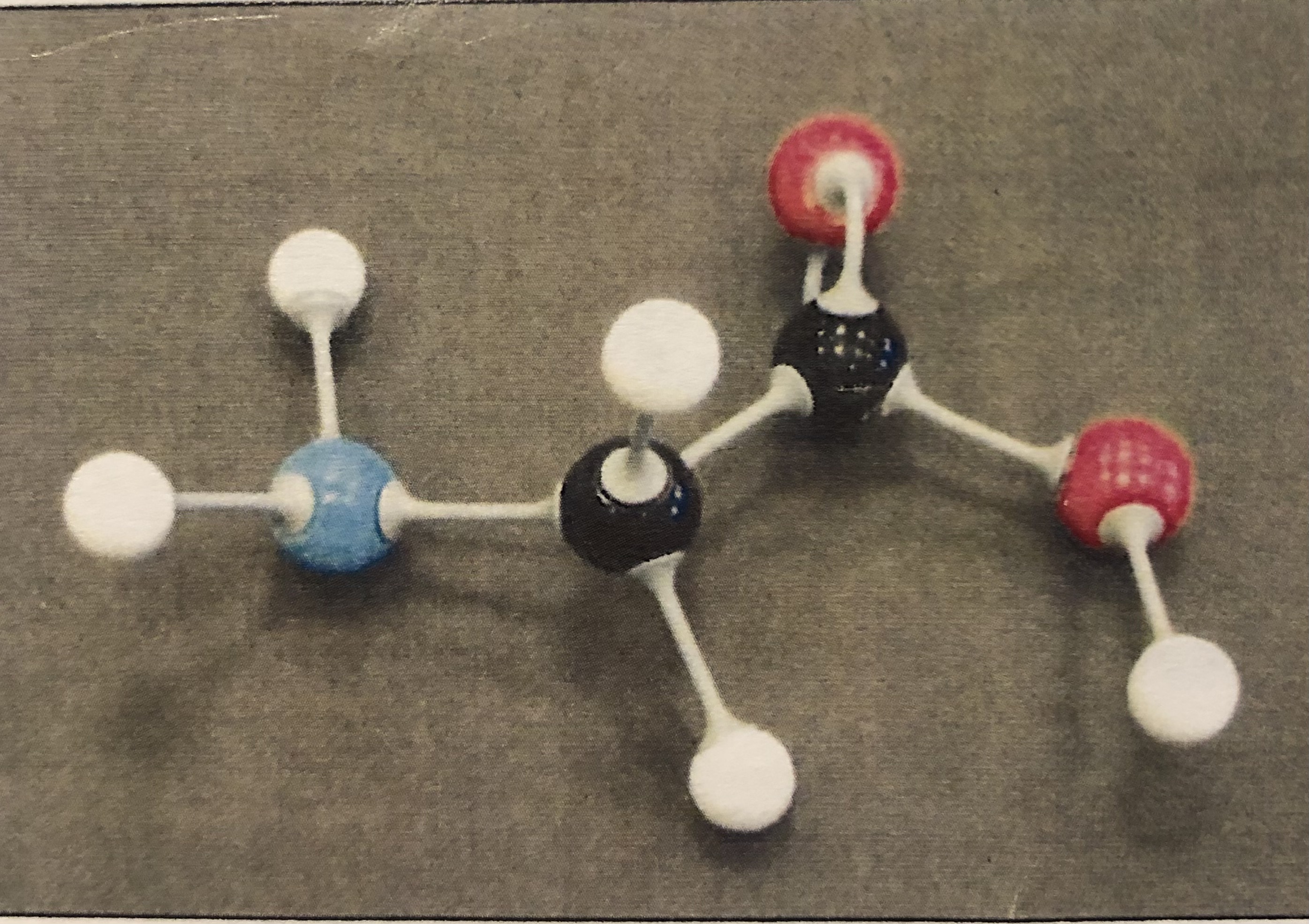
Amino Acid

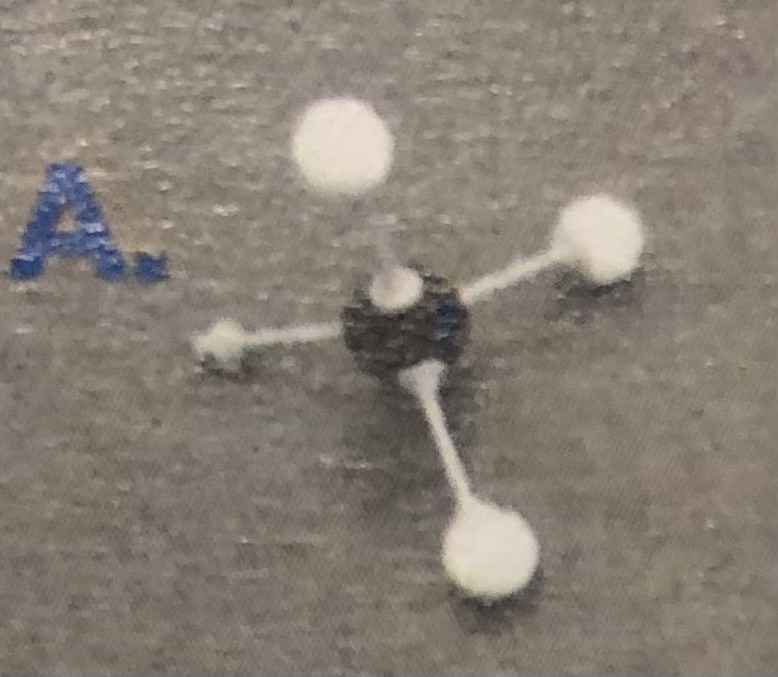
Hydroxyl group
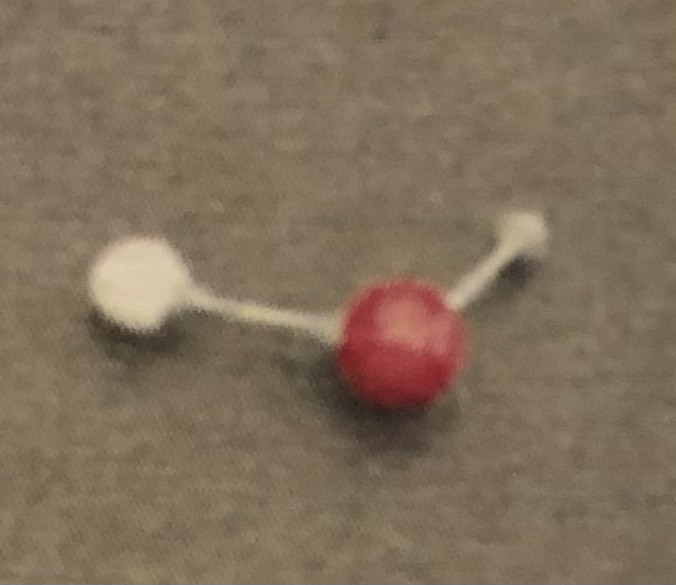

Carboxyl Group
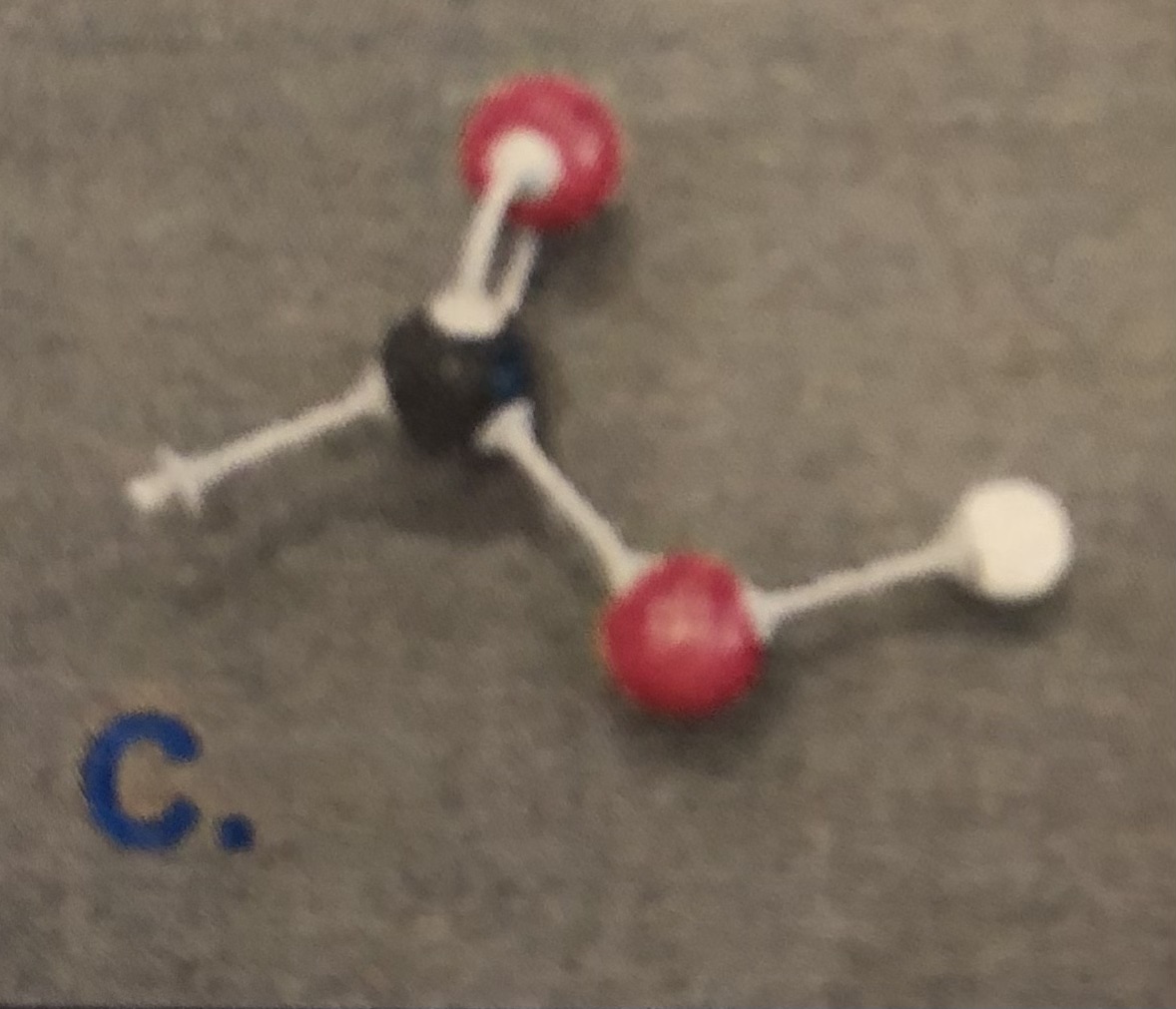

Amino Group
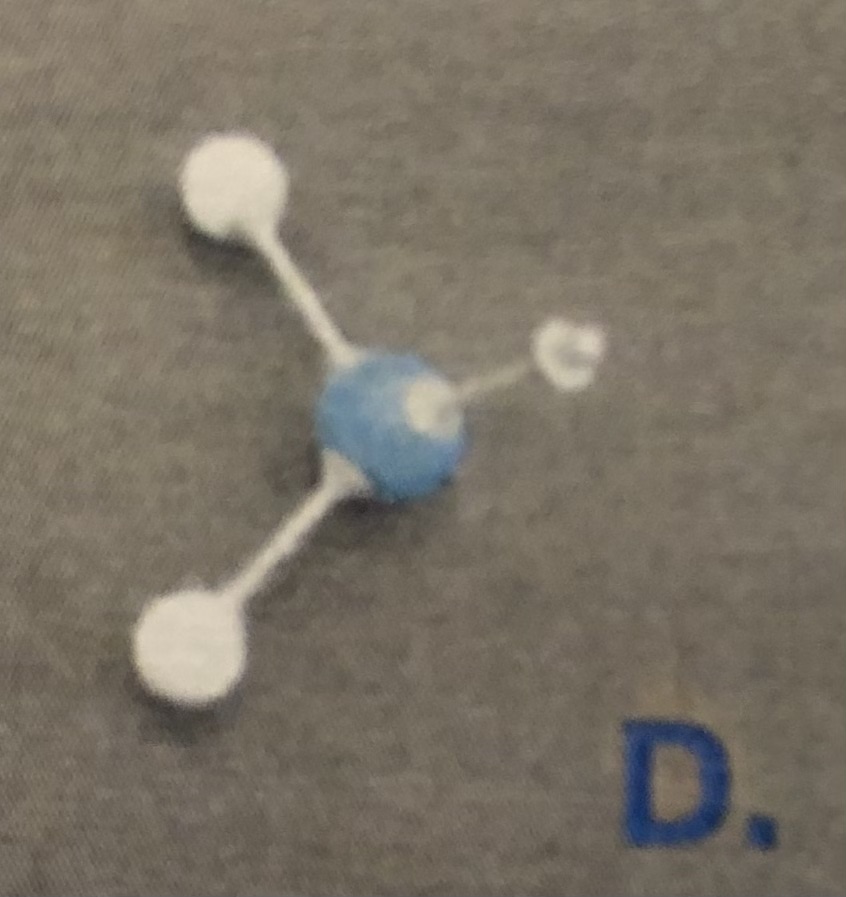
Methyl Group

Carbohydrates
contains the highest proportion of oxygen atoms
Amino Acids
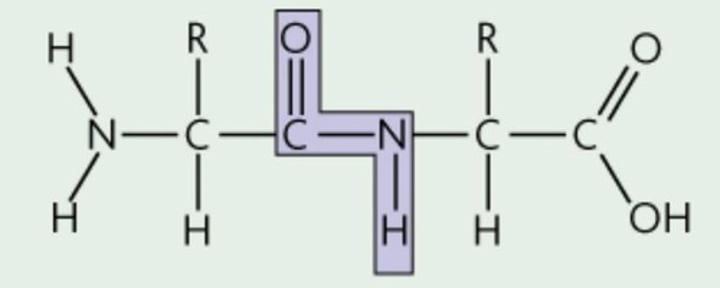
A peptide bond is formed when ___________ attach to each other by dehydration synthesis
Nitrogen connected to a carbon that is double bonded to oxygen
How would you recognize a peptide bond if you were asked to point out one?
Which element is found in amino acids which is not found in the carbohydrates, fatty aids, or steroids?
Nitrogen
CHO, 2:1 ratio of Hydrogen and Carbon
Name two properties that will help you correctly identify a carbohydrate
Carboxyl and Amino
Which two functional groups interact with each other to form a peptide bond.
Glucose, ATP, Steroid
Name three molecules seen in lab which contain rings in their structure
Glycerol, Fatty Acids, Amino Acids
Name three macromolecules that had linear structure
Has a ring composed of carbon and oxygen, classified as a carbohydrate
Properties of Maltose
Fatty acids, amino acids
Name two molecules that contain carbon-to-oxygen double bonds
Water
Which molecule is consumed in the chemical reaction when a dipeptide splits apart
unsaturated and saturated fatty acids
Which two macromolecules are composed of mostly carbon and hydrogen
frontal
forehead bone (1)
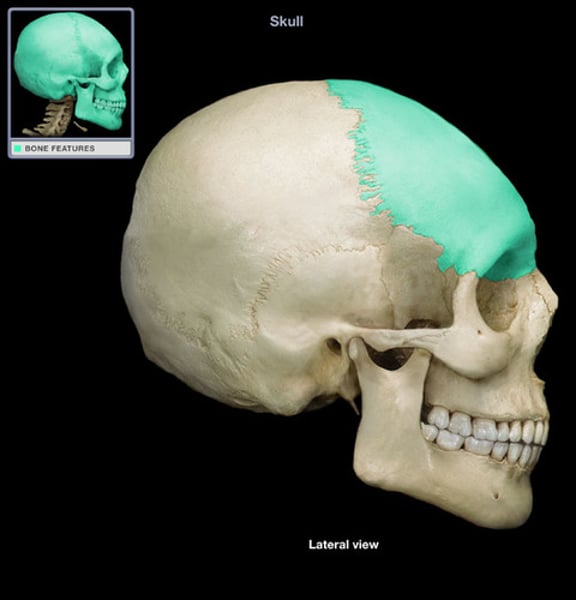
parietal
middle top of head (2)
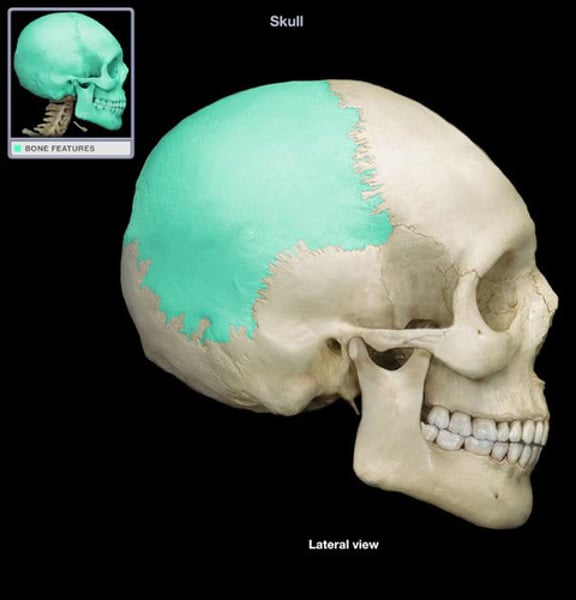
temporal
weird sides of skull (2)
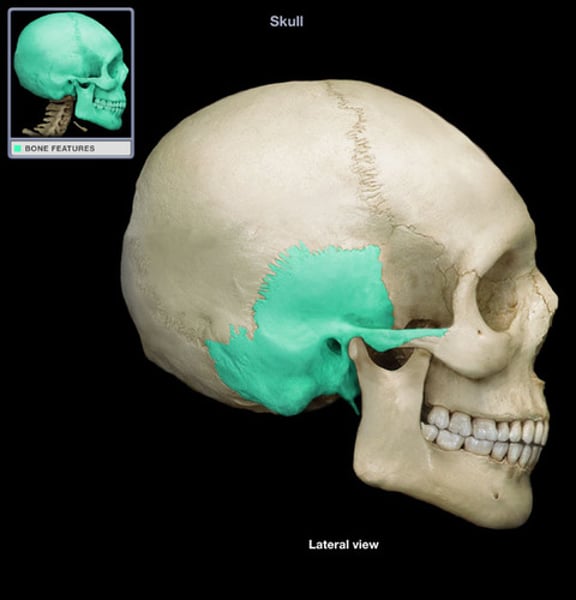
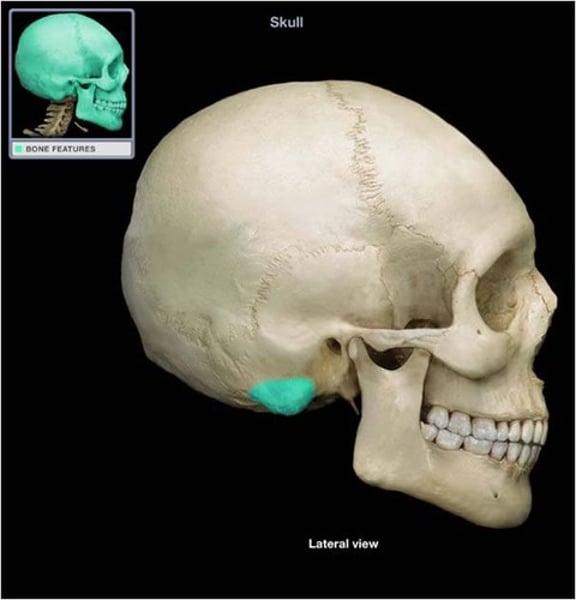
mastoid process
temporal bone,
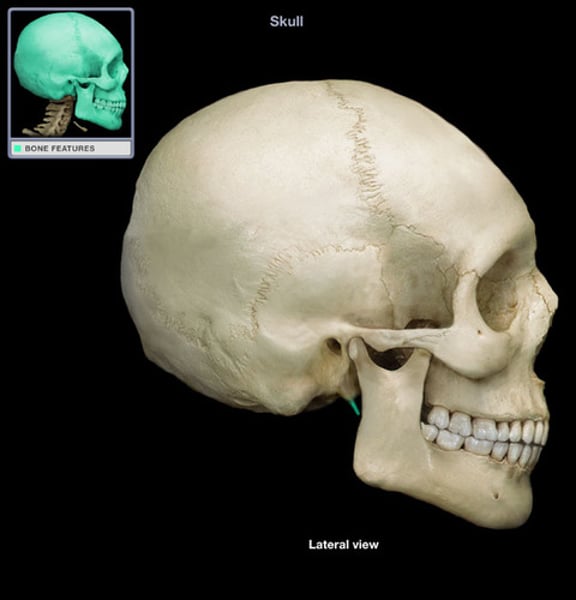
styloid process temporal bone
temporal bone
mandibular fossa
temporal bone
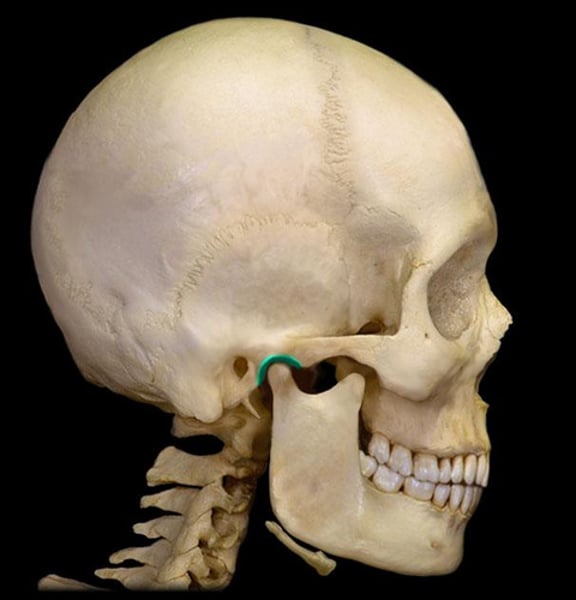
external acoustic meatus
temporal bone, ear canal
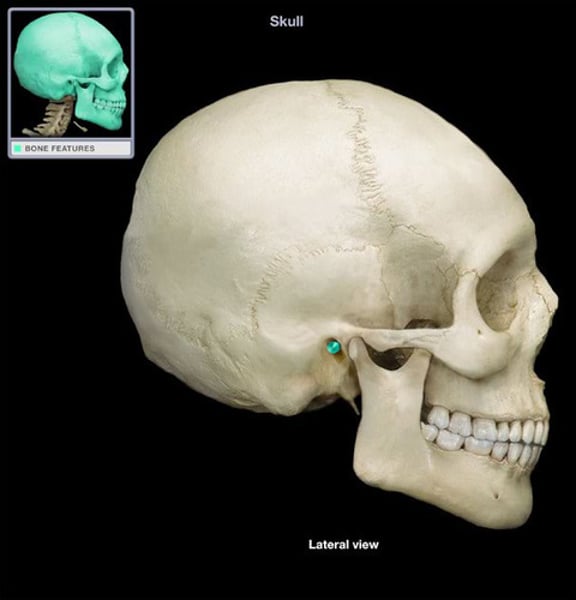
zygomatic process
temporal bone
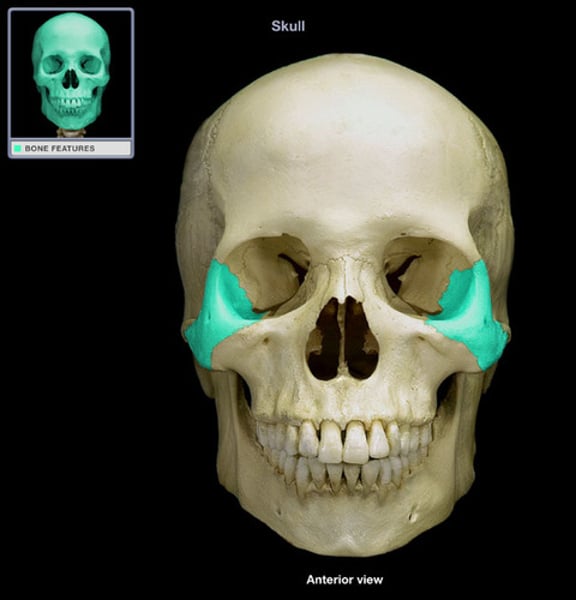
zygomatic
cheekbones (2)
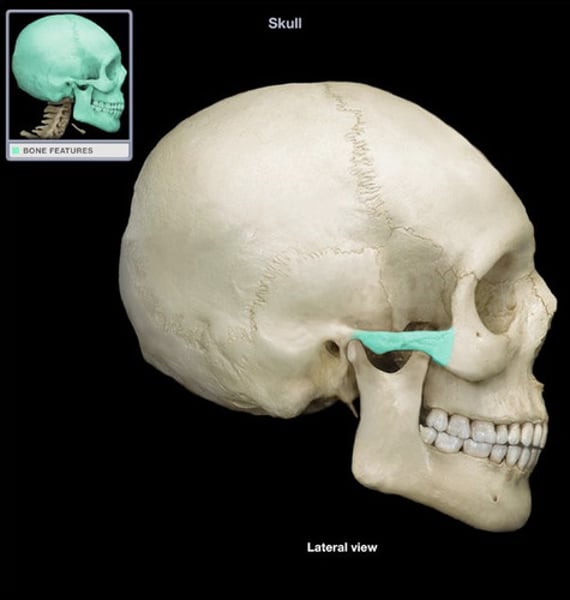
temporal process
zygomatic bone
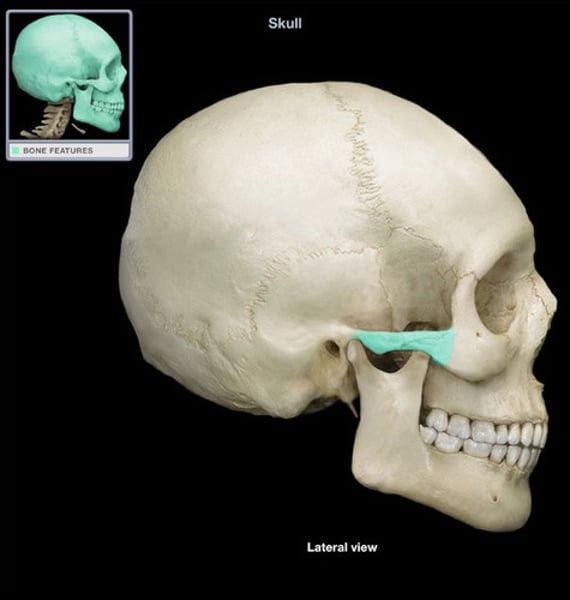
zygomatic arch
zygomatic bone
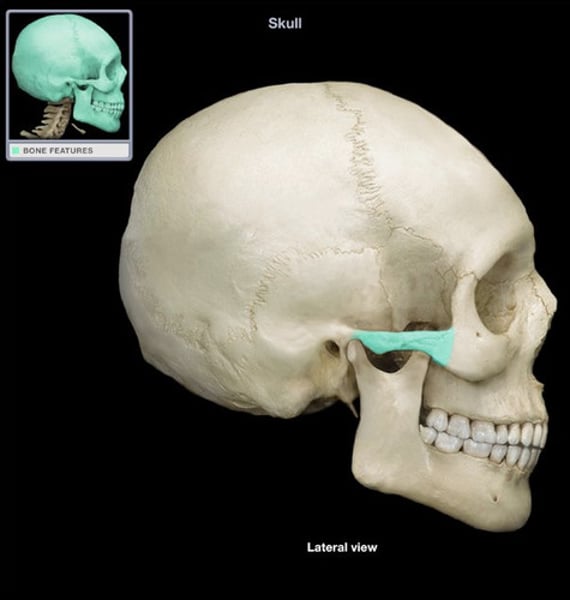
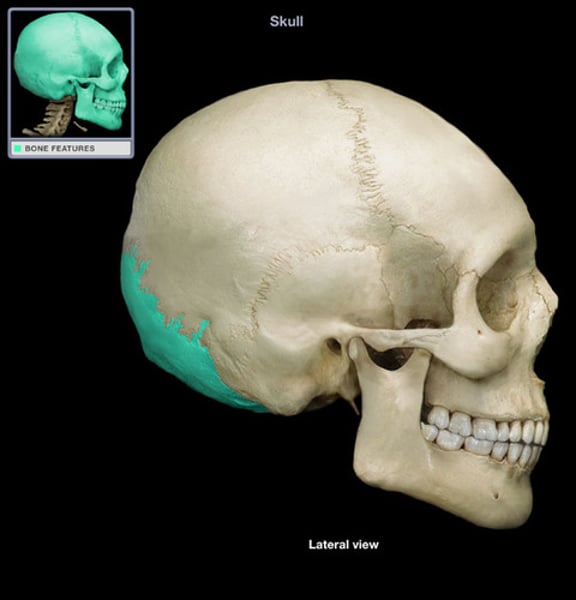
occipital
back of head (1)
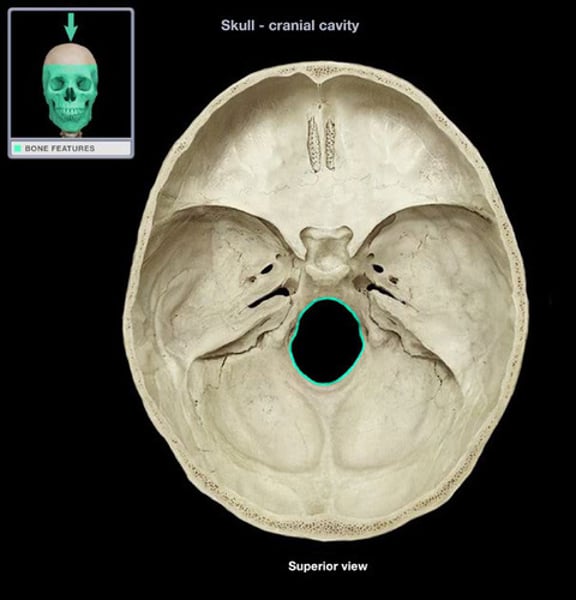
foramen magnum
occipital bone, massive hole for spinal cord
occipital condyles
occipital bone
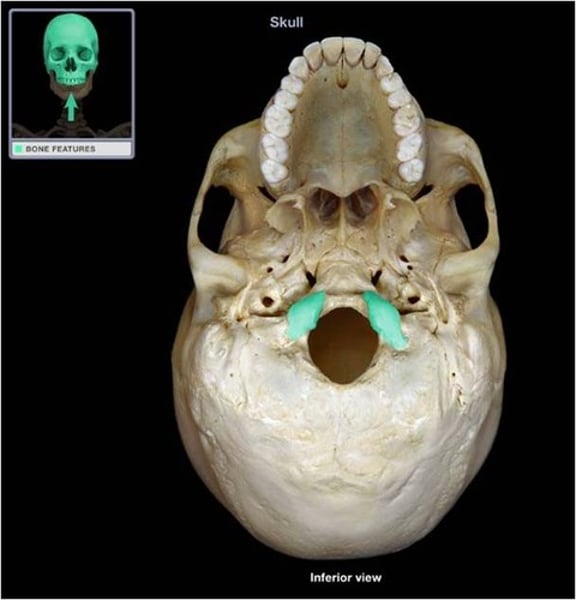
sphenoid
bat shaped bone forming part of the cranial floor (1)
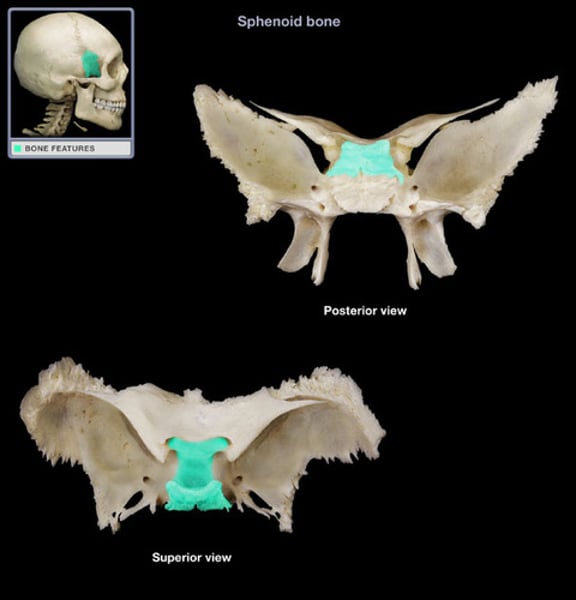
sella turcica
sphenoid bone, midline depression
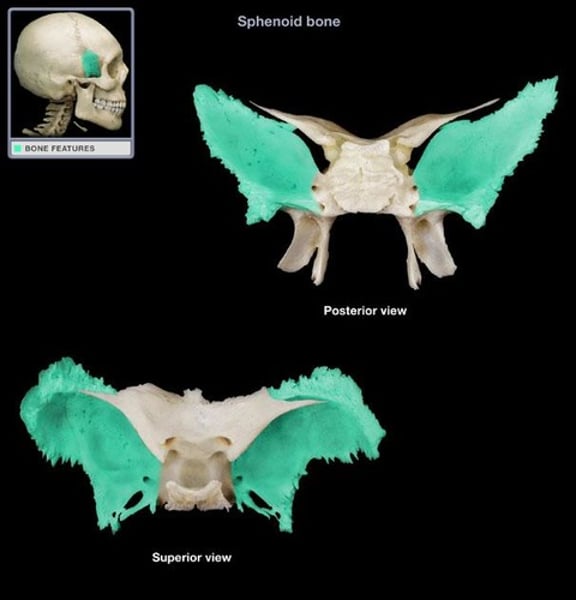
greater wing of sphenoid
bottom
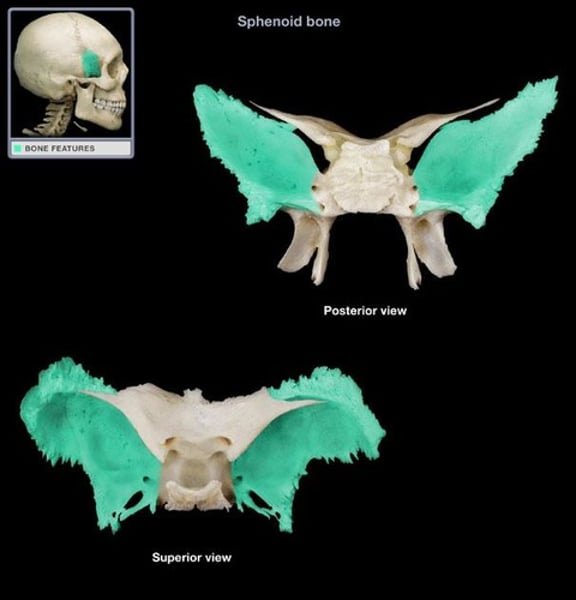
lesser wing of sphenoid
on top
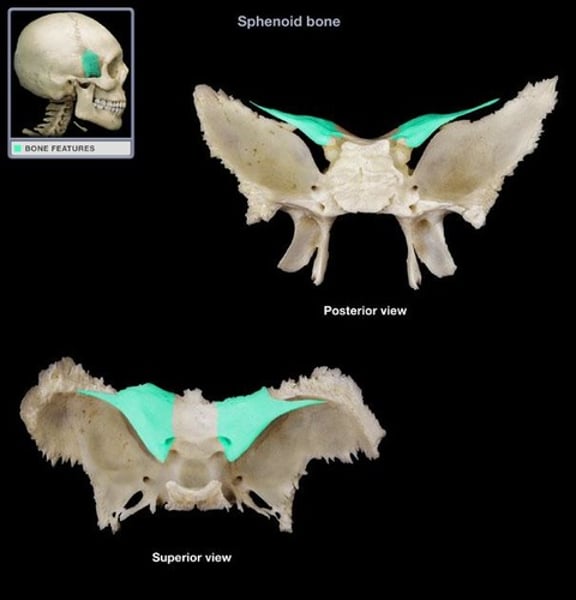
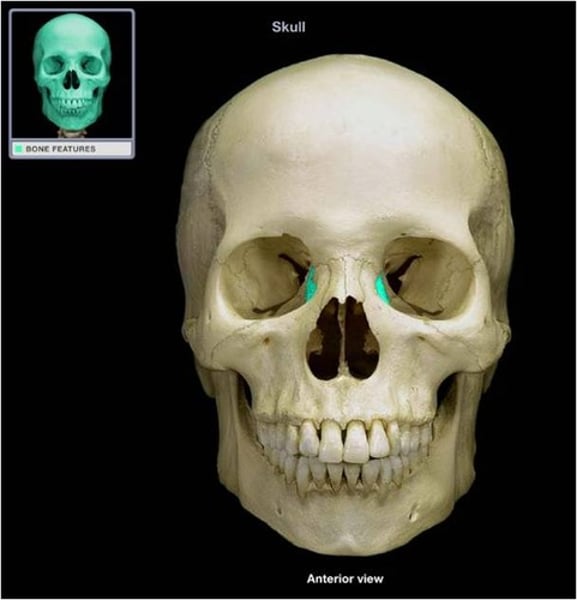
lacrimal
tear ducts (2)
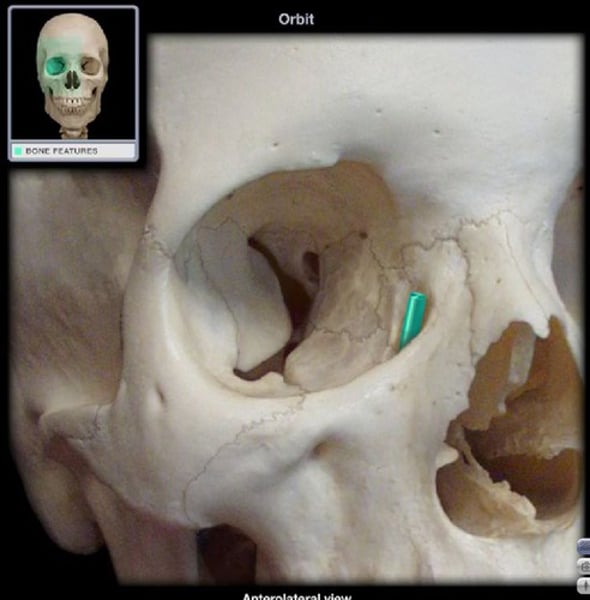
lacrimal fossa
lacrimal bone
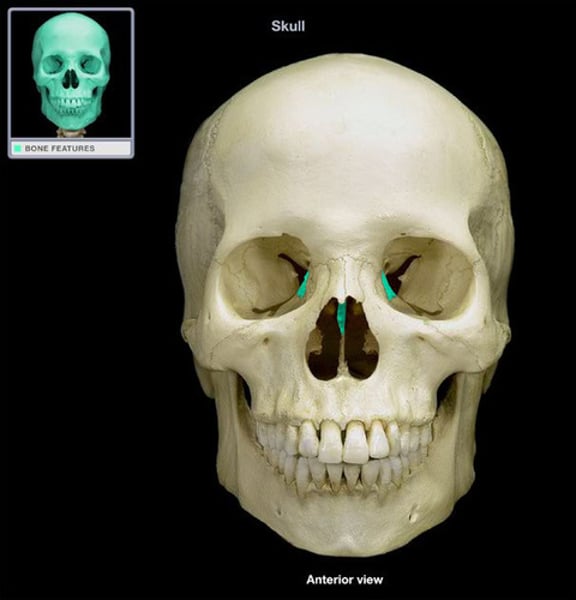
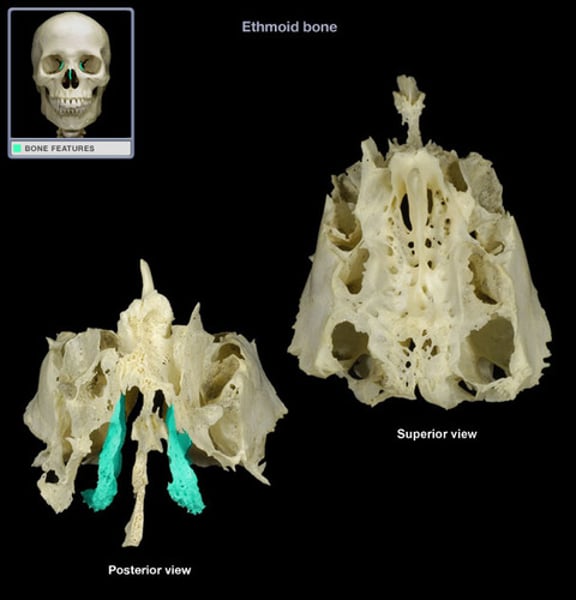
ethmoid
anterior to sphenoid, irregularly shaped (1)
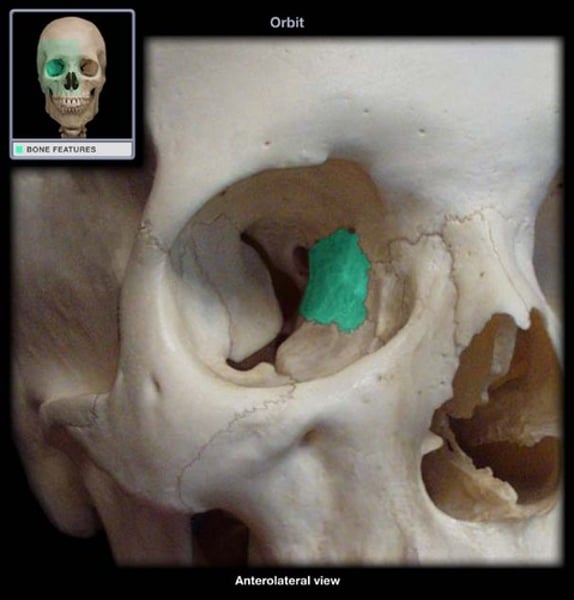
orbital plate
ethmoid bone, further back plate supporting eyes
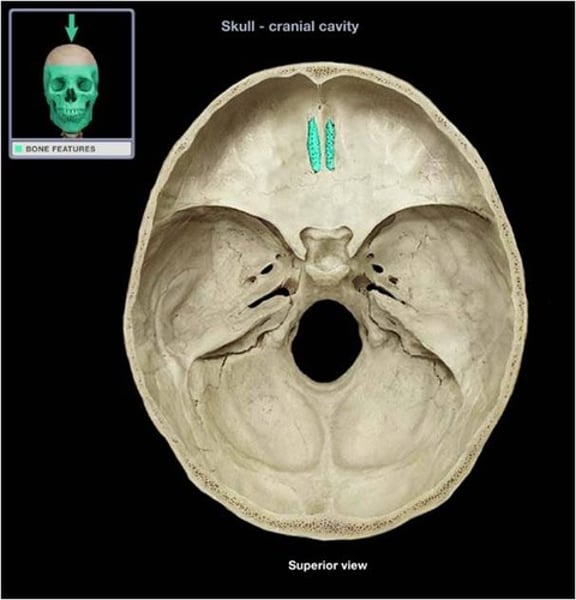
cribiform plate
ethmoid bone, top plate of the t
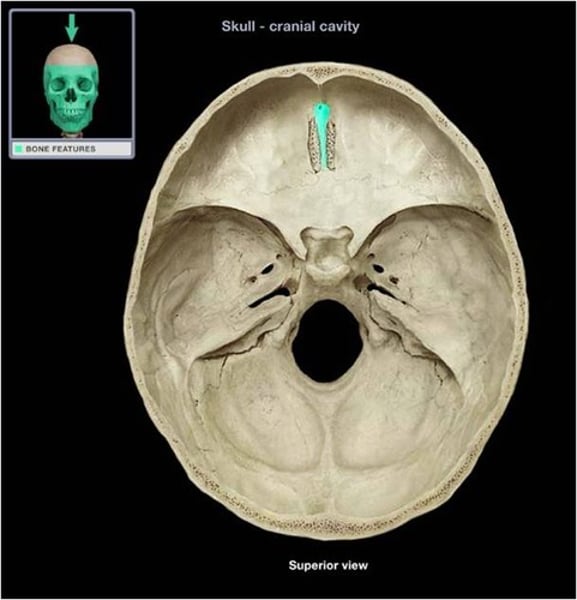
crista galli
ethmoid bone, the tip
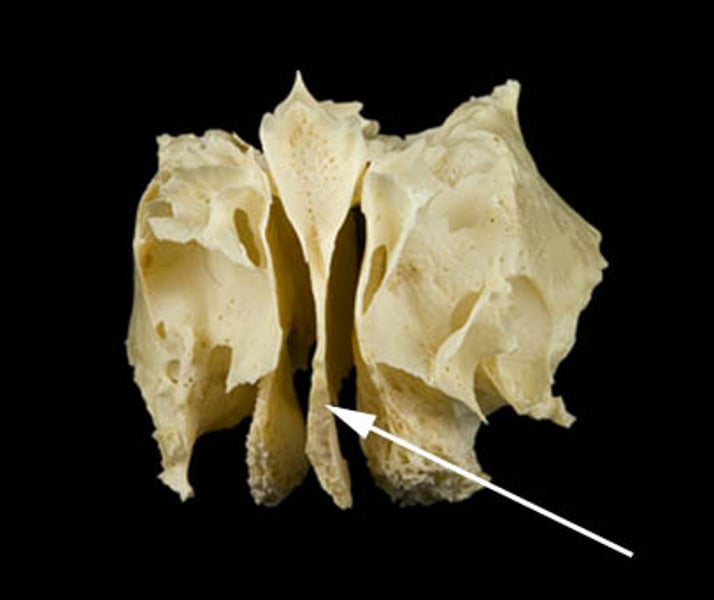
perpendicular plate
ethmoid bone, bottom, forms septum of nose
middle nasal conchae
ethmoid bone, stick out the bottom
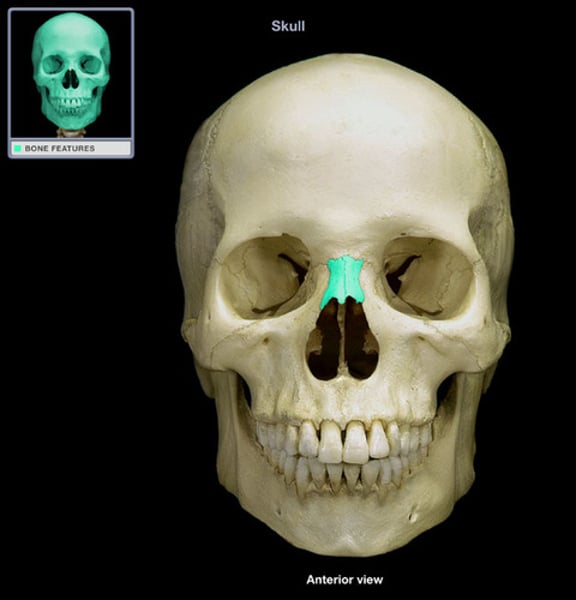
nasal
bridge of nose (2)
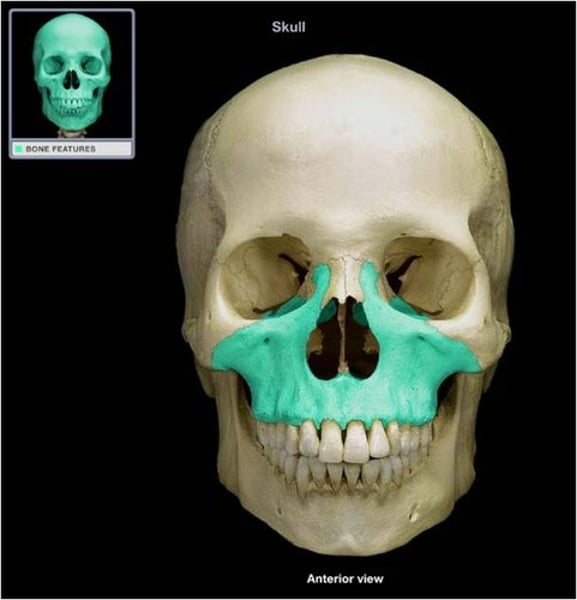
maxilla(e)
upper jaw (2)
mandible
lower jaw (2)
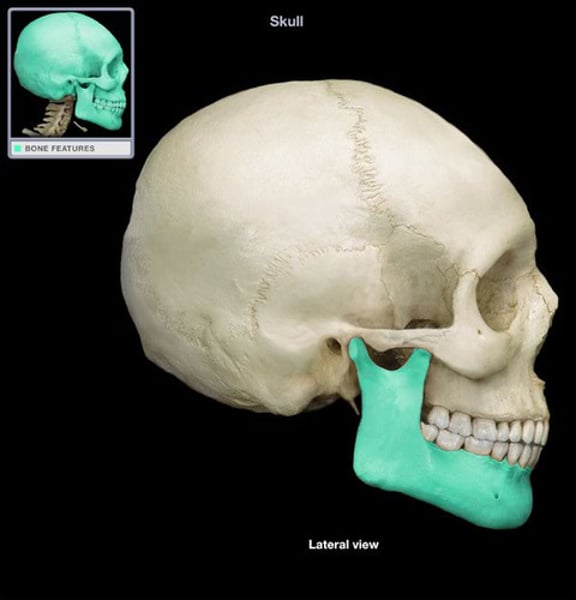
(mandibular) condyle
mandible bone
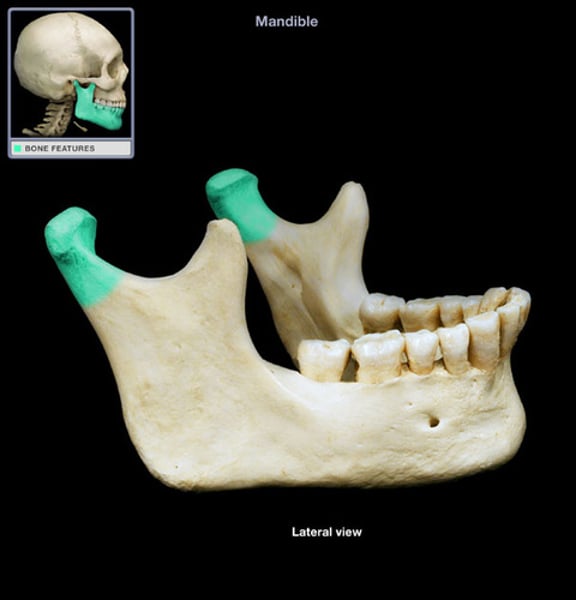
coronoid process
mandible bone
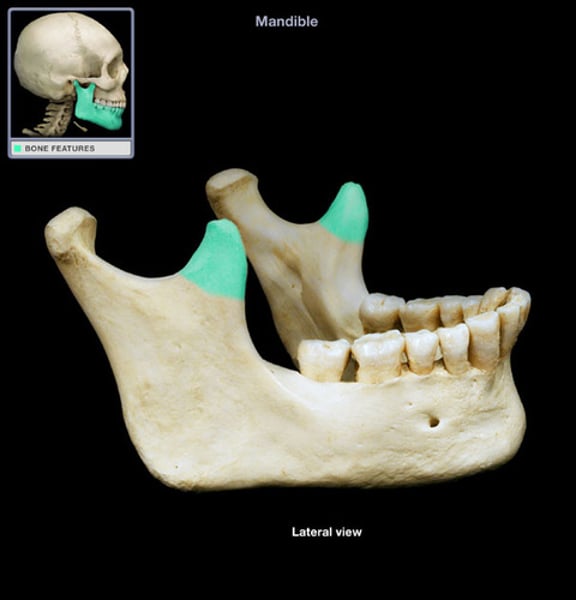
mental foramen
mandible bone, little holes
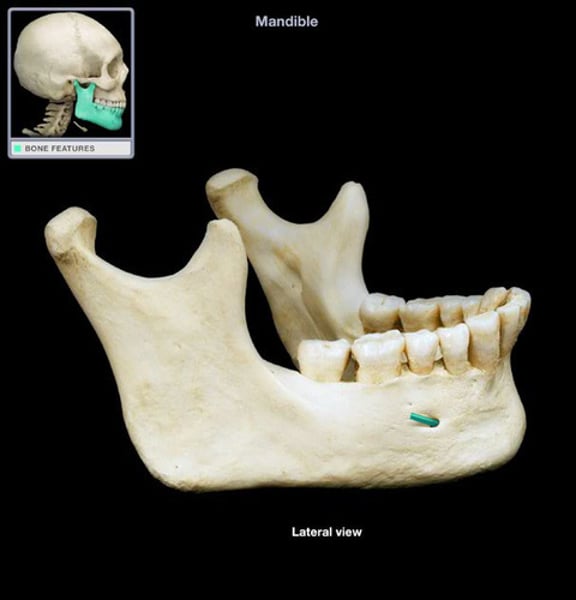
mandibular foramen
mandible bone, inner little holes
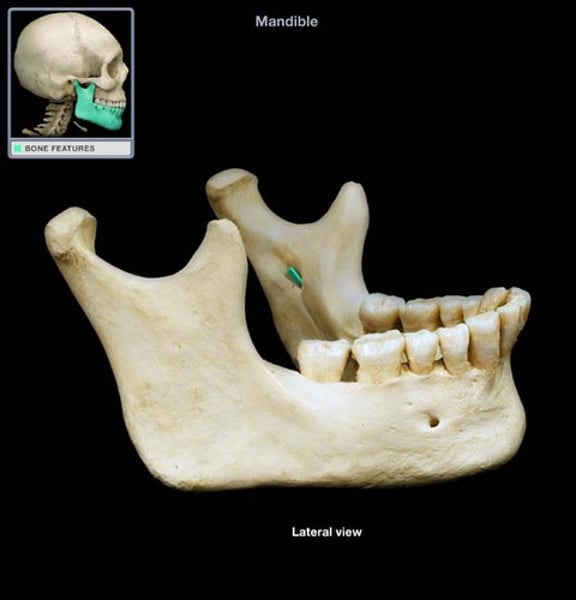
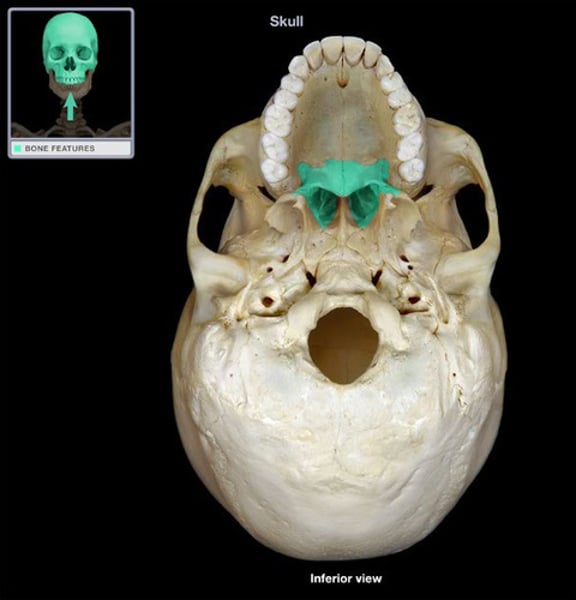
palatine
roof of the mouth (2)
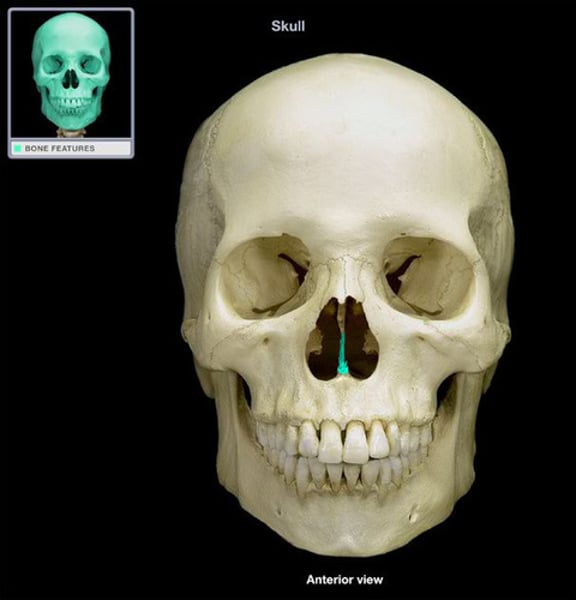
vomer
nasal septum, median line of nasal cavity (1)
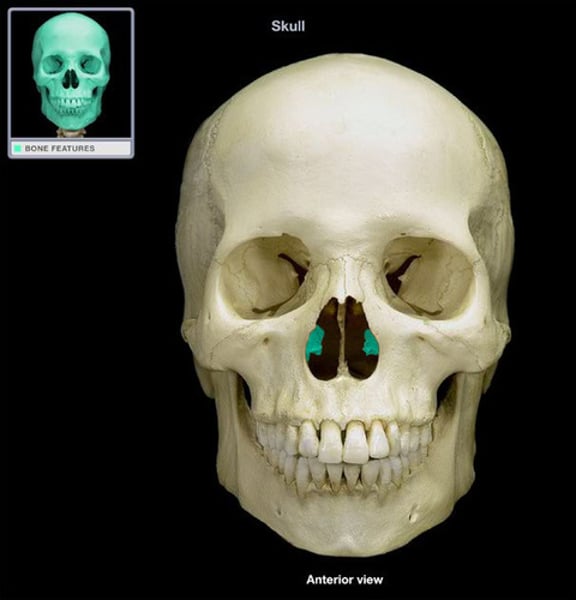
inferior nasal conchae
project from lateral walls of nasal cavity (2)
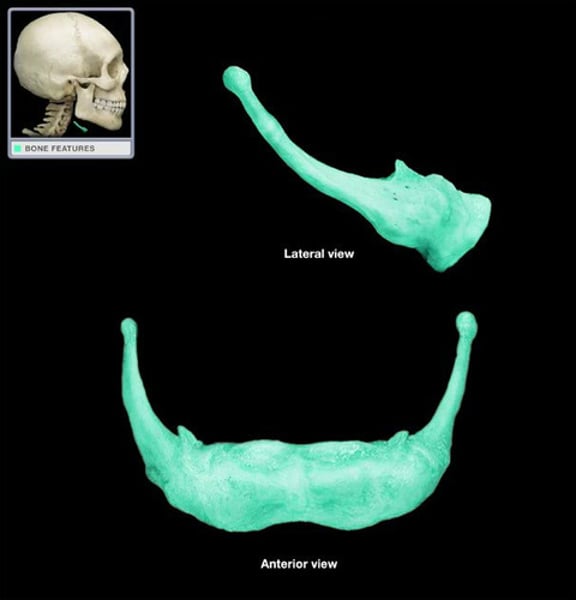
hyoid
u-shaped bone in the neck not connected to any other bones (1)
body (centrum)
vertebrae
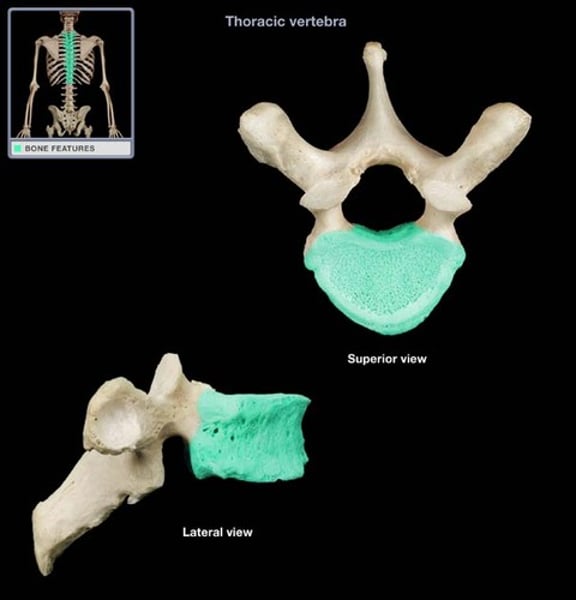
inferior articulating processes
vertebrae
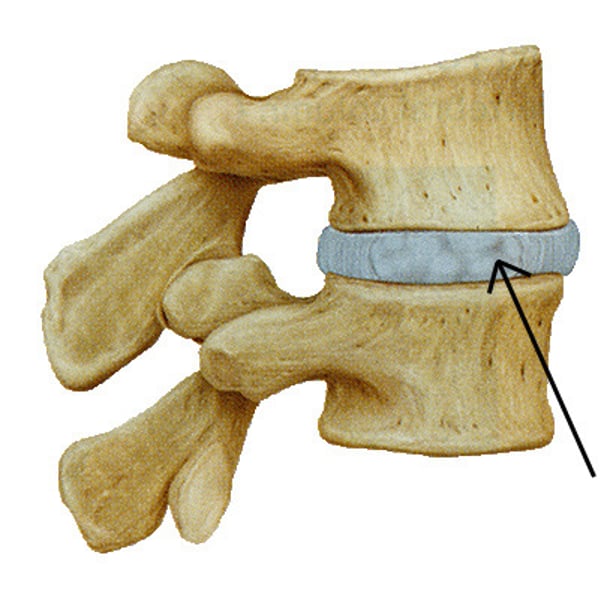
intervertebral discs
vertebrae, cartilage discs in between
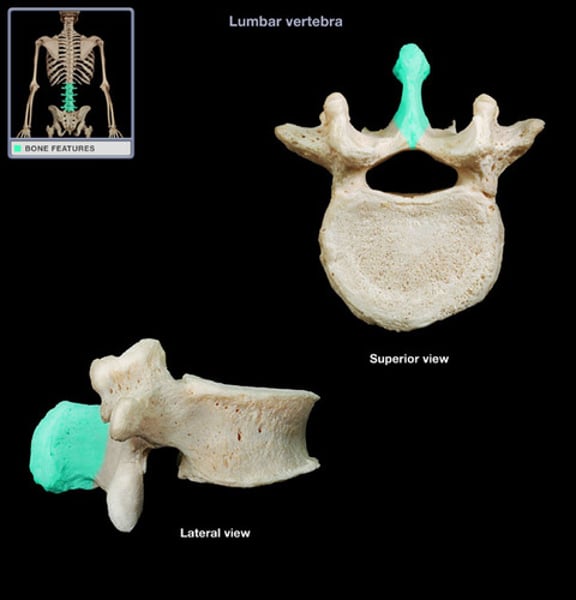
spinous process (dorsal spine)
vertebrae
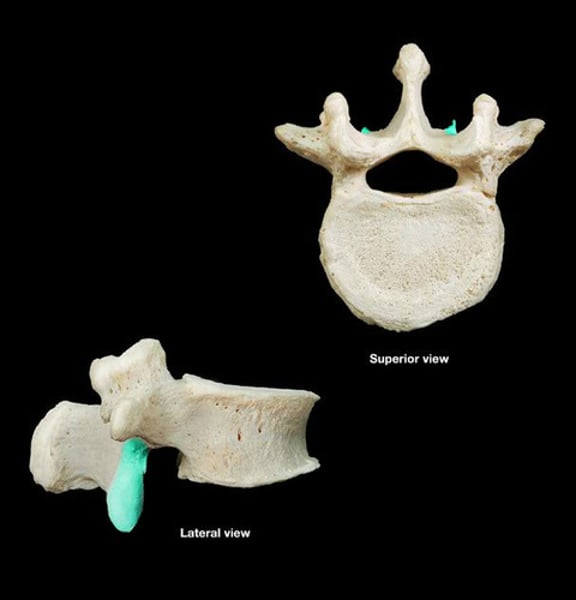
superior articulating processes
vertebrae
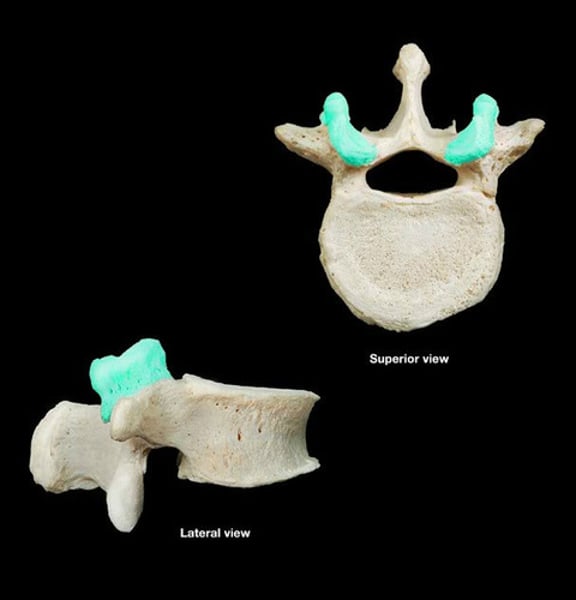
transverse processes
vertebrae
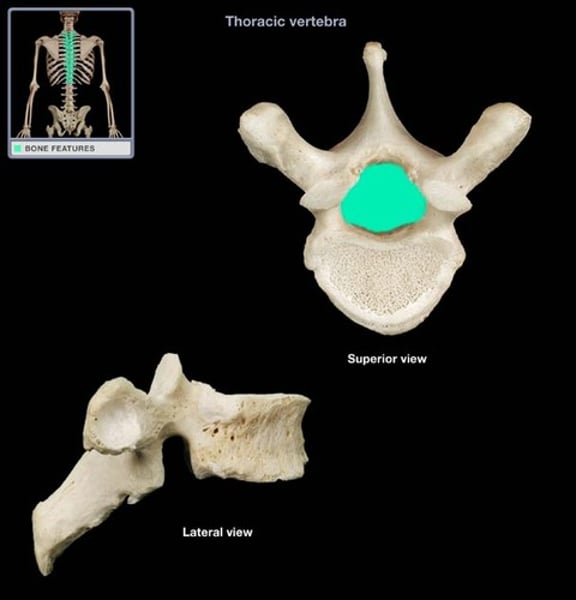
vertebral foramen
canal for spinal cord
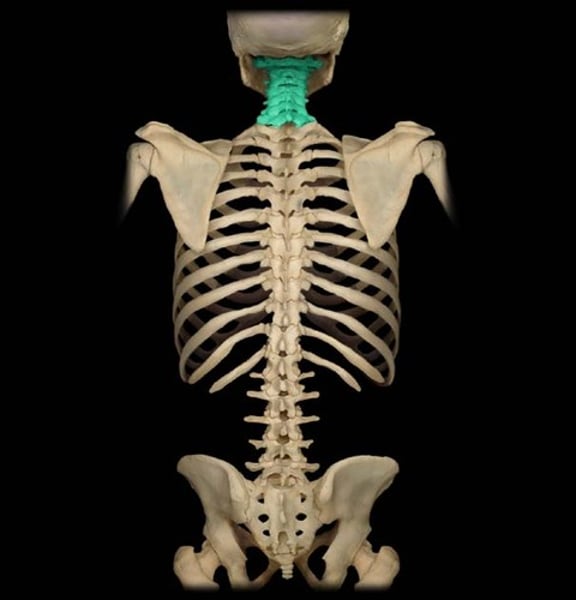
cervical vertebrae
neck (C1-C7)
atlas (C1)
first cervical vertebrae, sits on axis
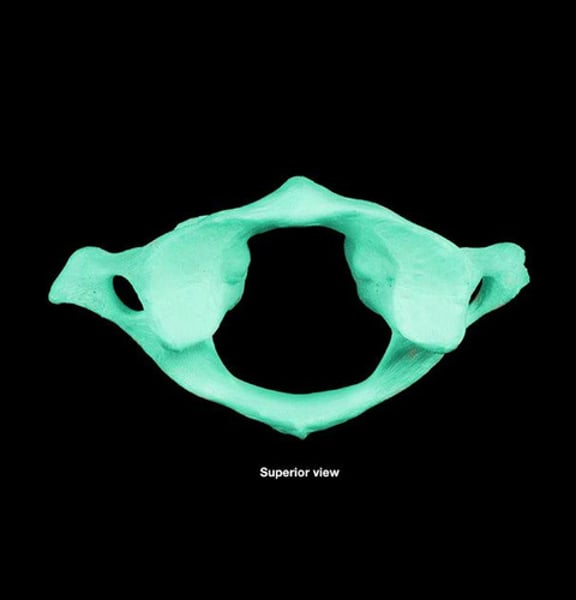
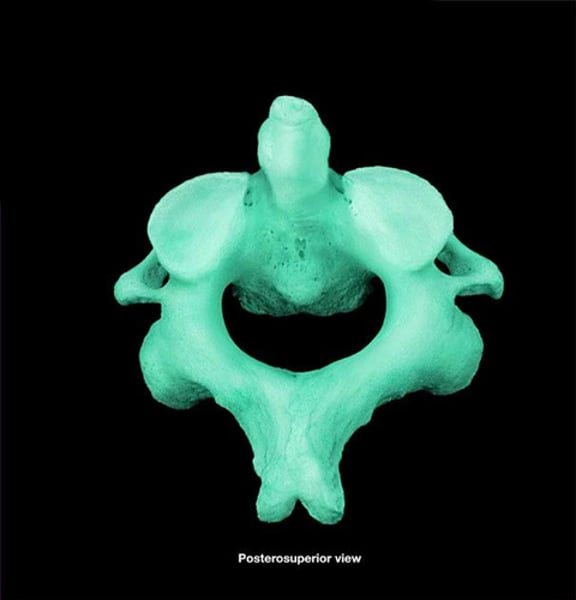
axis (C2)
second cervical vertebrae
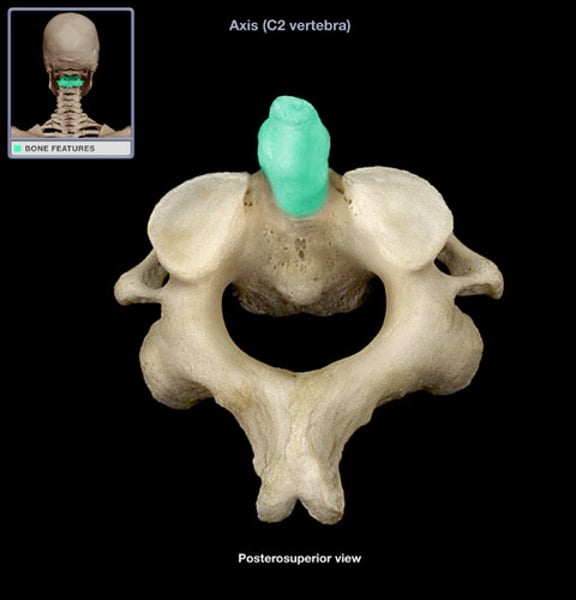
ontoid process/dens
axis (C2) lil nub
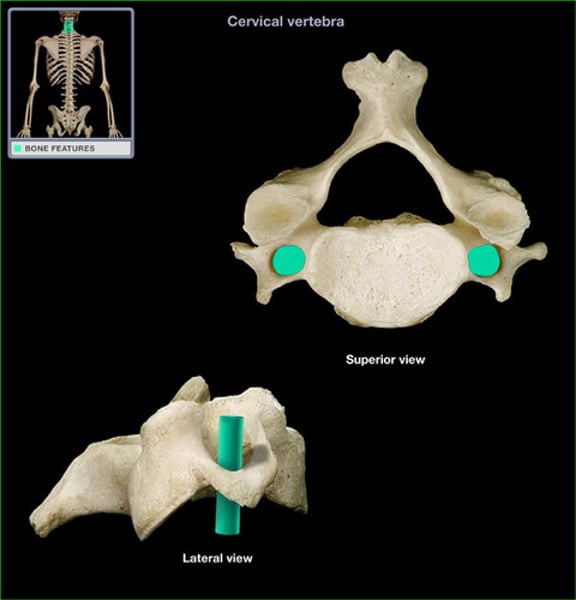
transverse foramen
cervical vertebrae only (for vertebral artery)
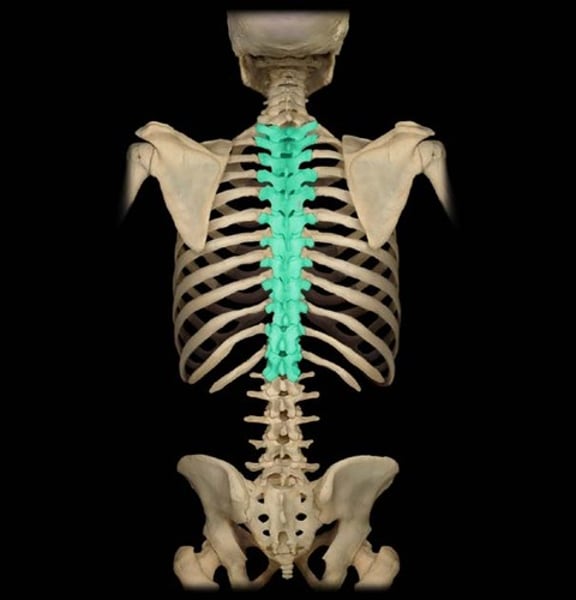
thoracic vertebrae
(T1-T12)
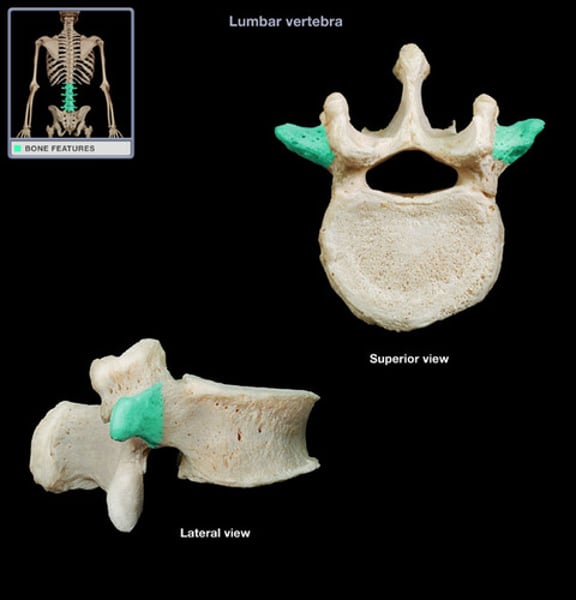
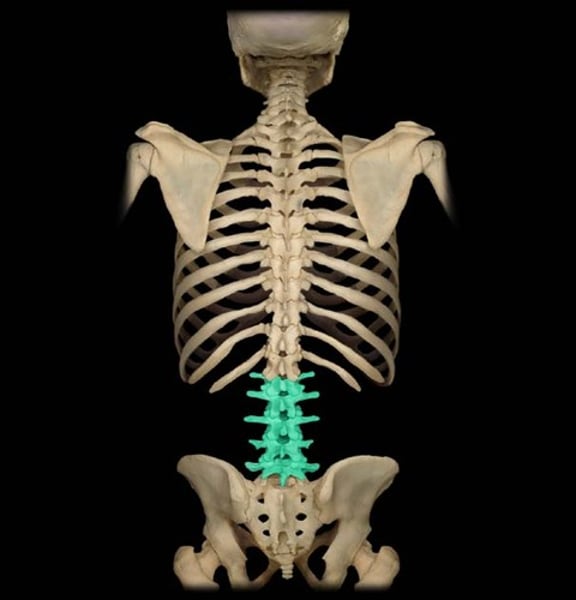
lumbar vertebrae
(L1-L5)
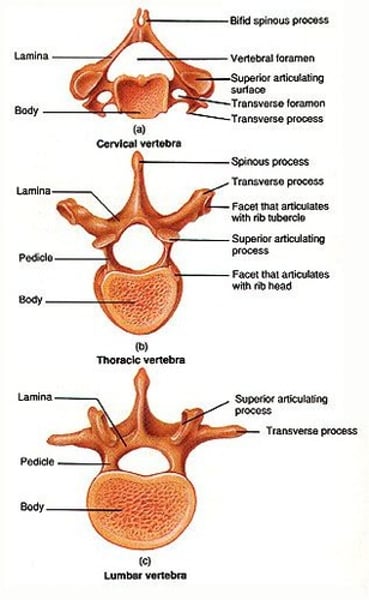
cervical vs thoracic vs lumbar vertebrae
amount of body weight each one supports
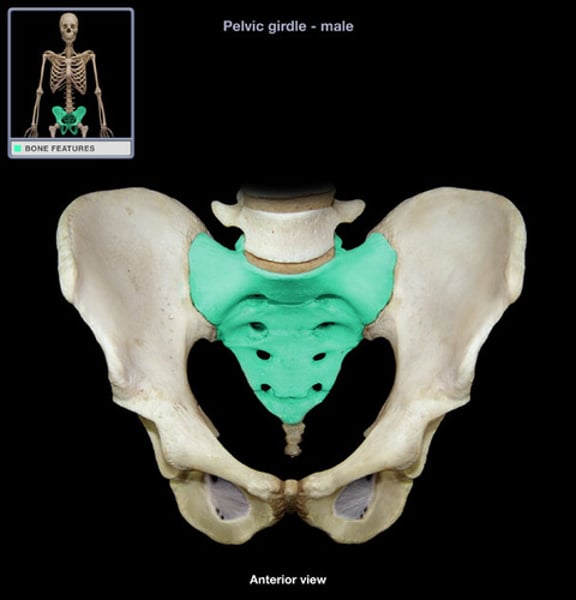
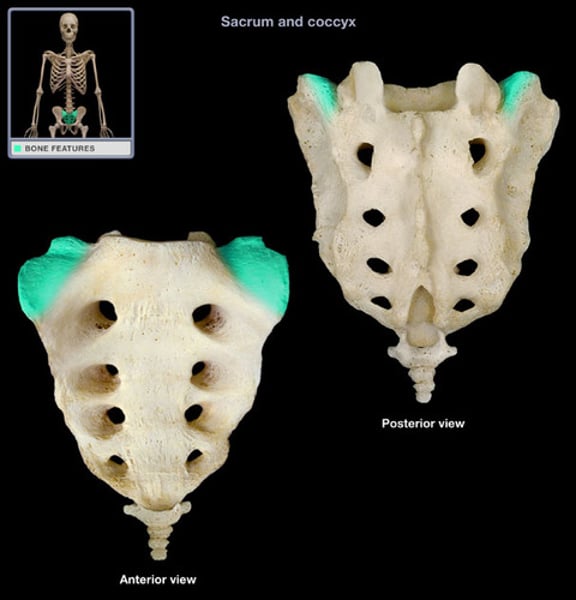
sacrum (sacral vertebrae)
5 fused vertebrae (1)
ala (wing)
sacrum, upper wing
sacral canal
sacrum, continuation of vertebral canal
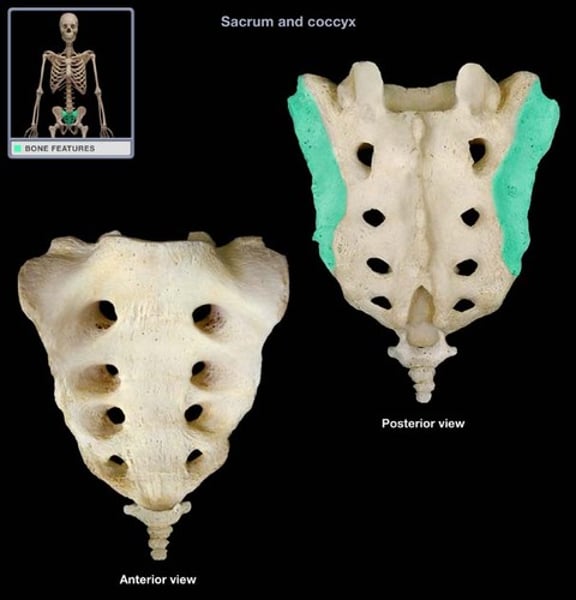
auricular surface
sacrum, articulates with pelvis
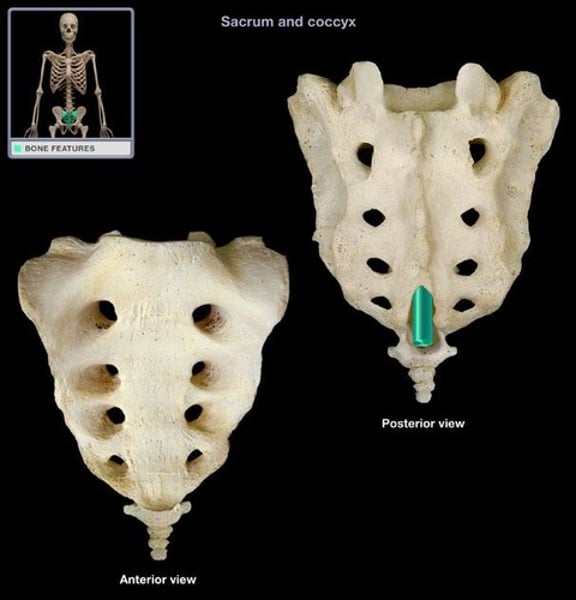
coccyx
tailbone (1)
sternum
breastbone (1)
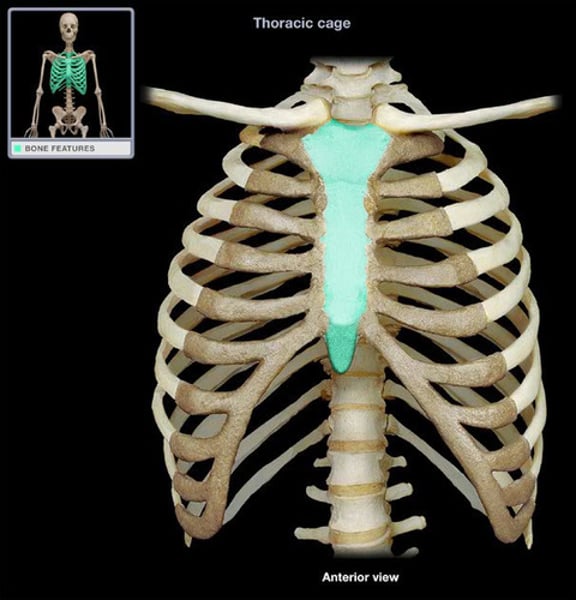
body
sternum, middle center
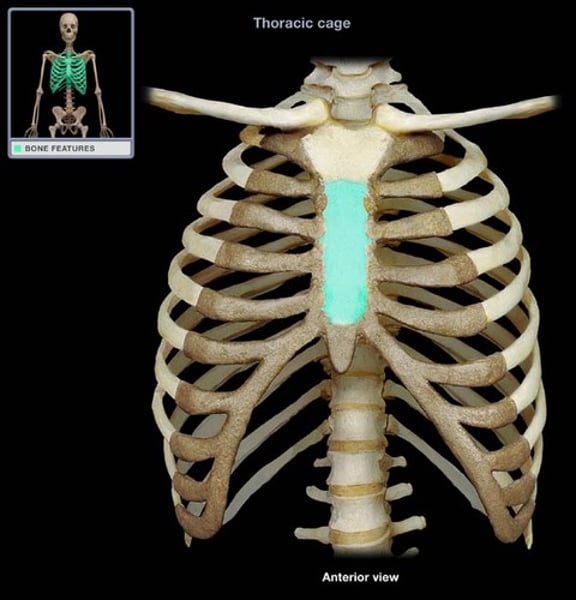
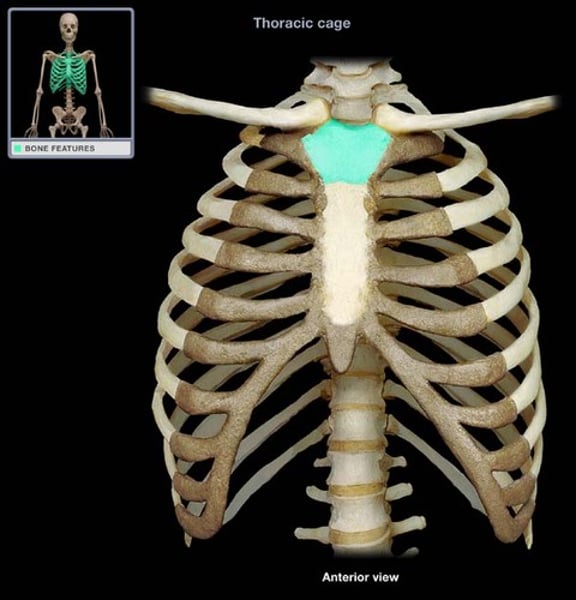
manubrium
sternum, upper part
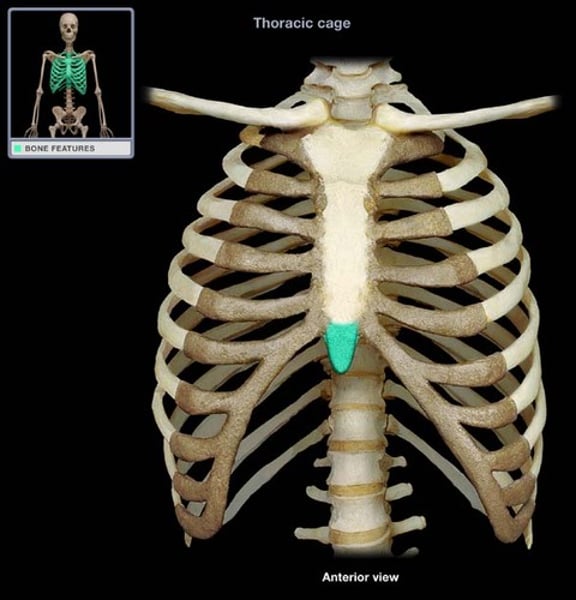
xiphoid process
sternum, lower portion
costal cartilage
connects ribs to sternum
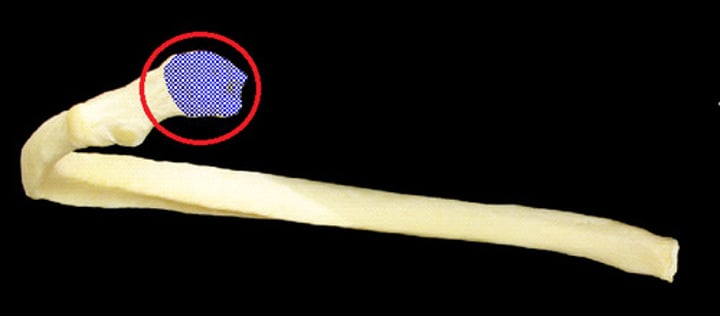
head of rib
rib where it attaches to vertebrae
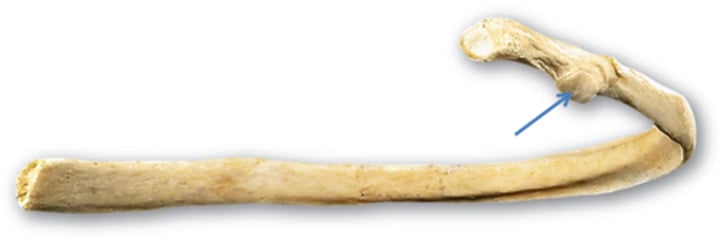
tubercle of rib
rib, articulates with transverse process
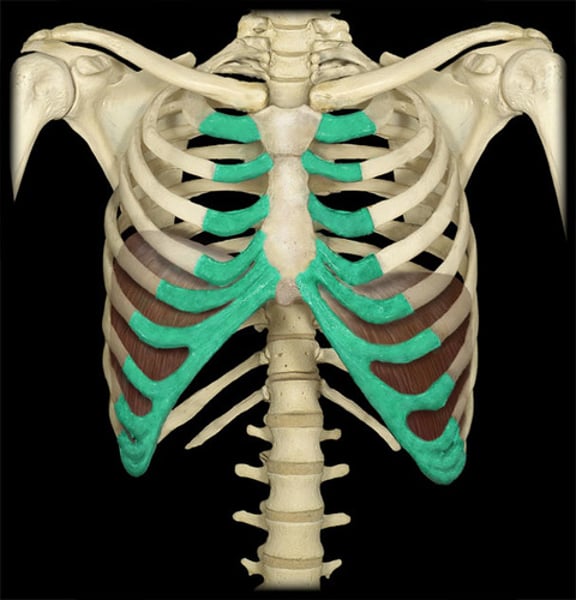
vertebrosternal ribs
true ribs (1-7)
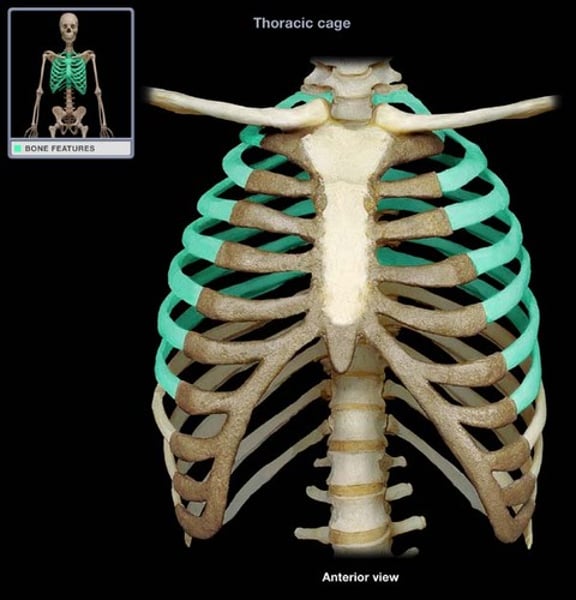
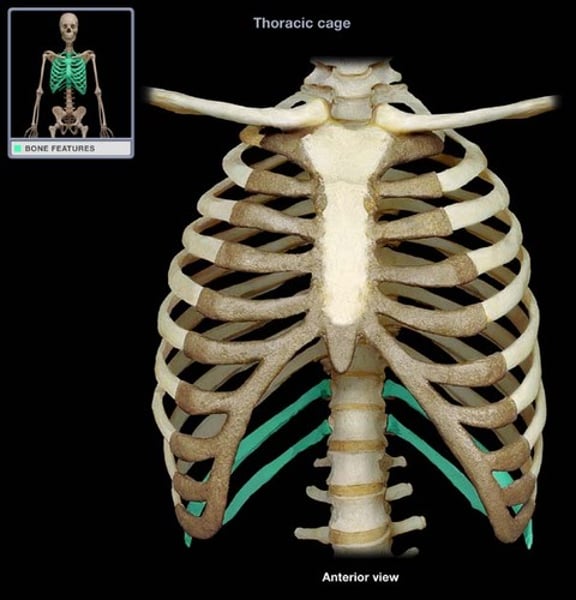
vertebrochondral ribs
false ribs (8-10)
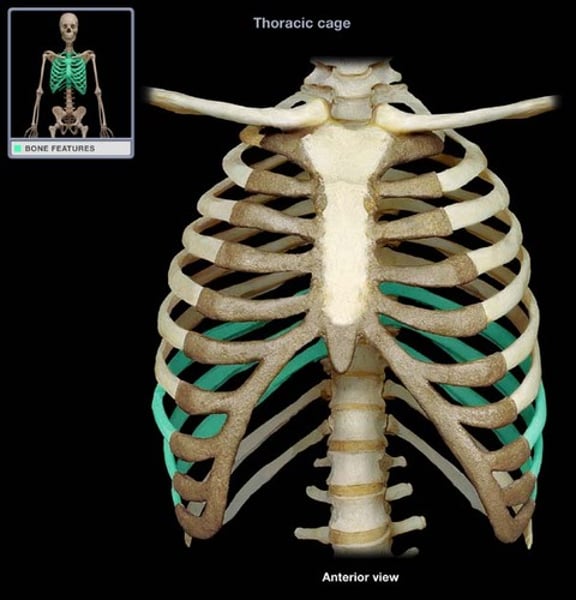
vertebral ribs
floating ribs (11-12)
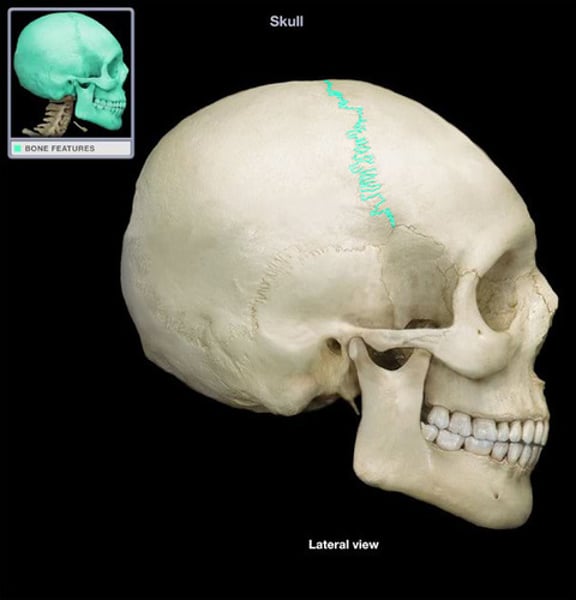
coronal suture
parietal and frontal
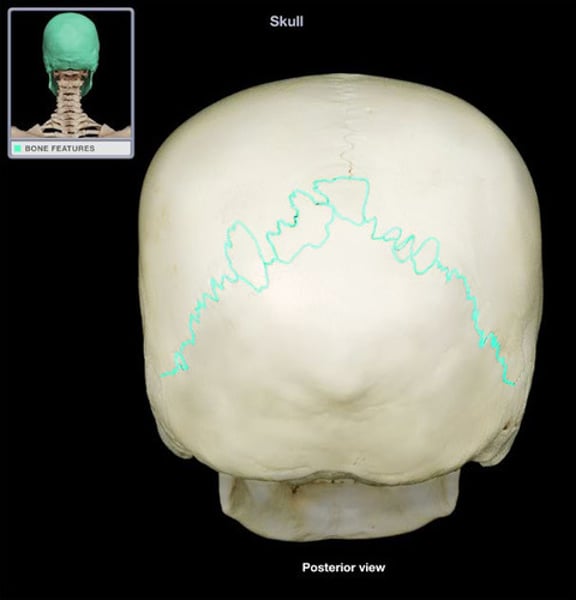
lambdoidal suture
parietal and occipital
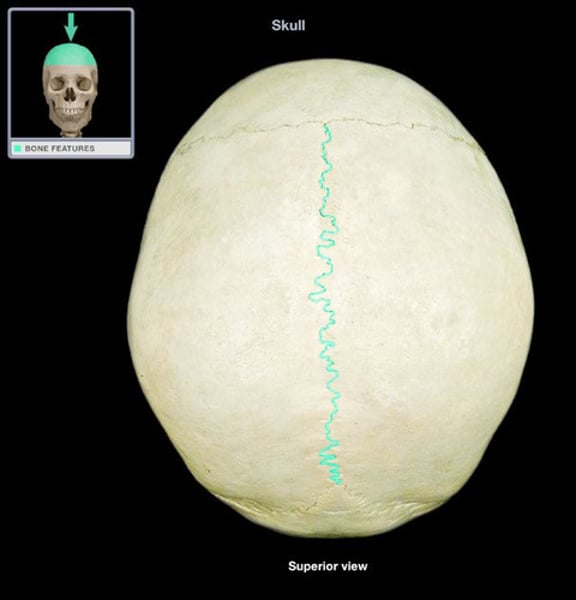
sagittal suture
parietal from parietal