MBG 2040 First Half of Semester
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:33 PM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
1
New cards
genes come in multiple forms called _______ and are located on __________
alleles (same gene w small differences in sequences of DNA bases)
chromosomes
chromosomes
2
New cards
gene
genetic factor (region of DNA) that helps determine a characteristic
3
New cards
locus
the specific site of an allele on its chromosome
4
New cards
genotype VS phenotype
set of alleles possessed by individual organism
manifestation of alleles
manifestation of alleles
5
New cards
heterozygote
possessing 2 different alleles at a locus
6
New cards
Mendel's Monohybrid cross
RR (dominant round) and rr (recessive wrinkled) produced: F1 generation of all Rr
-self fertilized F1 to produce F2 with (1/4 RR, 1/2 Rr, 1/4 rr) aka 3:1 ration of round to wrinkled
-self fertilized F1 to produce F2 with (1/4 RR, 1/2 Rr, 1/4 rr) aka 3:1 ration of round to wrinkled
7
New cards
dihybrid cross produces what ratio of F2 generation
9:3:3:1
8
New cards
if trait is rare and autosomal recessive, then ppl who marry in are _________-
homozygous for normal allele
9
New cards
mitosis
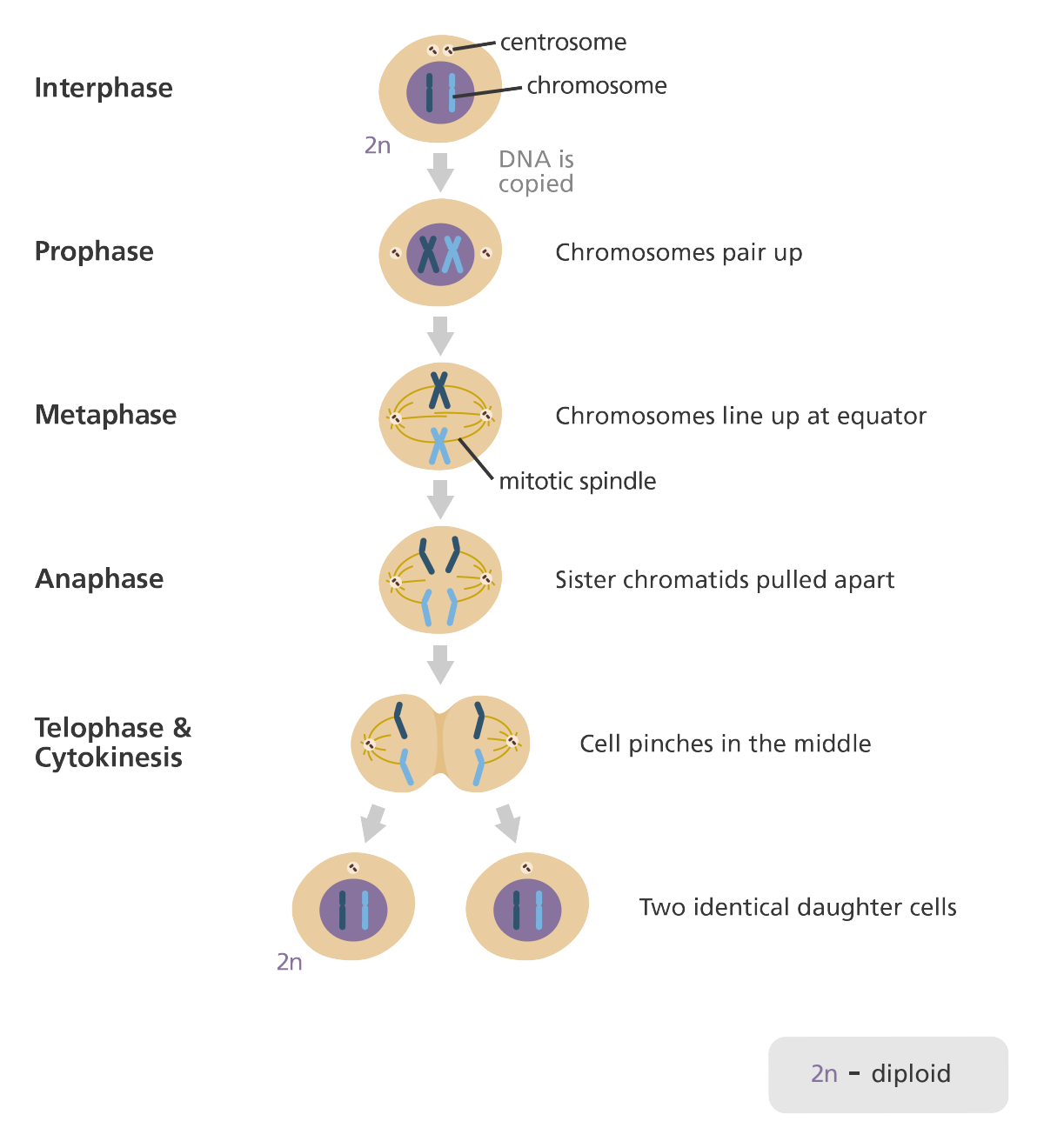
10
New cards
meoisis 1
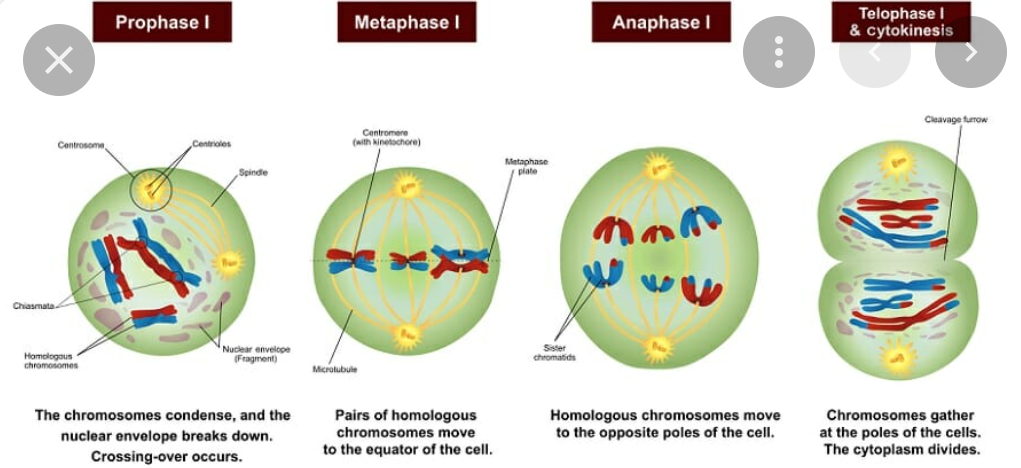
11
New cards
meiosis 2
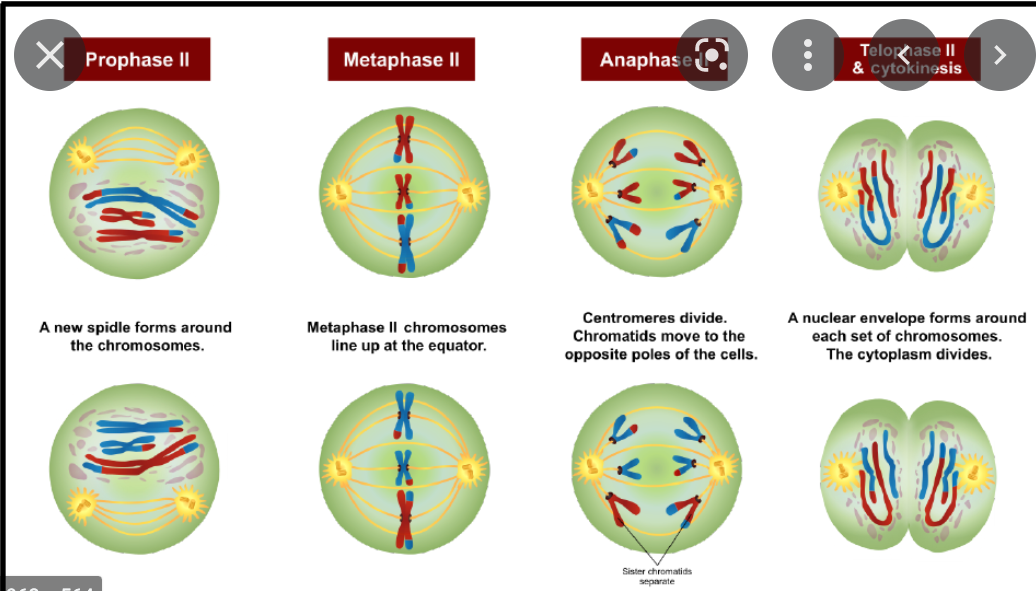
12
New cards
null/amorphic alleles
-nonfunctional protein is produced OR
-no protein is produced
-no protein is produced
13
New cards
hypomorphic allele
- poorly functioning protein is produced OR
- reduced amounts of a normally functioning protein is produced
- reduced amounts of a normally functioning protein is produced
14
New cards
multiplication rule
aa AND AA
multiply probs
multiply probs
15
New cards
addition rule
aa OR/ EITHER AA
add probs
add probs
16
New cards
dominant hypermorphic alleles
negative phenotypic consequences due to:
- *over-production* of a normal protein
- production of protein w/ *increased activity* levels
- *over-production* of a normal protein
- production of protein w/ *increased activity* levels
17
New cards
neomorphic alleles
negative phenotypic consequences due to:
- presence of an altered protein that has a new function
- altered protein interferes w/ the wildtype protein
- presence of an altered protein that has a new function
- altered protein interferes w/ the wildtype protein
18
New cards
For traits to be rare and dominant.. affected individuals are most likely _______________, why?
heterozygous.
BB is very rare bc even Bb x Bb crosses are rare bc Bb die very young therefore infrequent mating
BB is very rare bc even Bb x Bb crosses are rare bc Bb die very young therefore infrequent mating
19
New cards
complete dominance and complete recessiveness are extremes of a range
BB = Bb same
bb = different
bb = different
20
New cards
incomplete dominance
BB, Bb, bb all differ phenotypically
therefore, Bb is in between BB and bb (pink flower, in between white and red)
therefore, Bb is in between BB and bb (pink flower, in between white and red)
21
New cards
codominance
BB, Bb, bb are all different
Bb exhibit phenotypes of both homozygotes
white and red splotched flower
Bb exhibit phenotypes of both homozygotes
white and red splotched flower
22
New cards
individual (diploid)
only 2 alleles coexist in each cell
23
New cards
I^A encodes a transferase which adds ______________
acetylgalactosamine
24
New cards
I^B encodes a transferase which adds ______________
galactose
25
New cards
i encodes a ______________ transferase
non-functional
**no antigen
**no antigen
26
New cards
blood types
A: IAIA, IA,i
B: IBIB, IBi
O: ii
AB: IAIB
B: IBIB, IBi
O: ii
AB: IAIB
27
New cards
Type AB blood has ____________ alleles, so both galactose and acetylgalactosamine
codominant
both alleles are expressed
both alleles are expressed
28
New cards
wildtype allele
functional enzyme or other protein is produced
most common in nature
most common in nature
29
New cards
loss of function allele
enzyme or other protein is no longer being produced, is produced at lower levels, or is nonfunctional
30
New cards
haplosufficiency
often the wildtype allele is dominant over the loss of function allele
**half as much protein is synthesized yet this is often sufficient to achieve the wildtype phenotype
**half as much protein is synthesized yet this is often sufficient to achieve the wildtype phenotype
31
New cards
haploinsufficient
in heterozygote, half as much protein is synthesized and this is not sufficient for a normal phenotype
*dominant allele can be loss of function allele
*dominant allele can be loss of function allele
32
New cards
dominant alleles can be gain of function mutations, in which the mutant allele produces a protein that has increased (detrimental) function
eg. Huntington's disease
33
New cards
recessive lethal alleles
essential genes, when mutated, lead to a lethal phenotype
**death in homozygotes****
1/4 die.. therefore its 2/3 to 1/3 colour ratios
**death in homozygotes****
1/4 die.. therefore its 2/3 to 1/3 colour ratios
34
New cards
dominant lethal genes can be expressed in both _________________ and the _______________-
heterozygote
homozygote
Bb and BB lethal
bb= not lethal
homozygote
Bb and BB lethal
bb= not lethal
35
New cards
genes function to produce ________________-
polypeptides
36
New cards
wildtype allele produces a functional polypeptide ..... which then produces a _____________ phenotype
wild-type
37
New cards
recessive amorphic loss of function allele does not produce a functional polypeptide ....which then produces a _____________ phenotype... But since it is recessive, when paired w a wildtype allele, the phenotype is wildtype
severe mutant
38
New cards
recessive hypomorphic loss of function allele produces a partially functional polypeptide ....which then produces a _____________ phenotype...But since it is recessive, when paired w a wildtype allele, the phenotype is wildtype
mild mutant
39
New cards
dominant-negative allele produces a polypeptide that interferes w/ the wild-type polypeptide ....which then produces a _____________ phenotype...since it is dominant, when paired w a wildtype allele, the phenotype is mutant
severe mutant phenotype
40
New cards
penetrance
proportion of individual organisms having a particular genotype that expresses the expected phenotype-variation in the **population**
ex. how many ppl have brown hair in a city
ex. how many ppl have brown hair in a city
41
New cards
degree to which a phenotype is expressed (mild to severe); variation in the **individual**
expressivity
ex. the degree of brownness in the hair of the ppl in the city
ex. the degree of brownness in the hair of the ppl in the city
42
New cards
complete penetrance
100% expected phenotype (every hedgehog is brown)
43
New cards
incomplete penetrance
< 100% expected phenotype (some hedgehogs brown, some white(lack of brown entirely))
44
New cards
constant expressivity
every hedgehog is the exact same shade of brown
45
New cards
variable expressivity
range of phenotypes
all diff shades of brown
all diff shades of brown
46
New cards
all shades of brown, and also white hedgehogs
incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity
47
New cards
split hand foot syndrome
rare autosomal dominant disorder that shows variable expressivity
-missing one or more central digits in hand or foot
-missing one or more central digits in hand or foot
48
New cards
piebaldism
rare autosomal dominant disorder that shows variable expressivity
-absence of melanocytes in skin and hair
-absence of melanocytes in skin and hair
49
New cards
huntington disease
rare autosomal dominant disorder that shows variable expressivity in the time onset of the disease
-neuro degenerative - causes loss of muscle coordination, cognitive decline and dementia
-neuro degenerative - causes loss of muscle coordination, cognitive decline and dementia
50
New cards
what causes incomplete penetrance and expressivity
-effects of other genes
-environmental factors that can alter or completely suppress the effect of a particular gene (age, sex, temperature, chemicals)
-environmental factors that can alter or completely suppress the effect of a particular gene (age, sex, temperature, chemicals)
51
New cards
norm of reaction
range of phenotypes expressed by a single genotype under different environmental conditions
52
New cards
example of environmental effects on phenotype -
himalayan allele in rabbits produces dark fur at extremes of body bc it can only develop at low temps
himalayan allele in rabbits produces dark fur at extremes of body bc it can only develop at low temps
ex. siamese cat
53
New cards
a change in phenotype arising from environmental factors that mimic the effects of a mutation in a gene
ex. chemical can cause a limb to not develop in the womb like a rare dominant trait would
ex. chemical can cause a limb to not develop in the womb like a rare dominant trait would
phenocopy
54
New cards
mendel's 2nd principle: law of independent assortment
inheritance pattern of one trait will not affect the inheritance pattern of another trait
ex: round by yellow seeds
ex: round by yellow seeds
55
New cards
when there is two genes contributing to a single trait, and complete dominance occurs
use multiplication rule
9:3:3:1 ratio..... ex: recessiveness dilutes fur colour from black to brown to grey
9:3:3:1 ratio..... ex: recessiveness dilutes fur colour from black to brown to grey
56
New cards
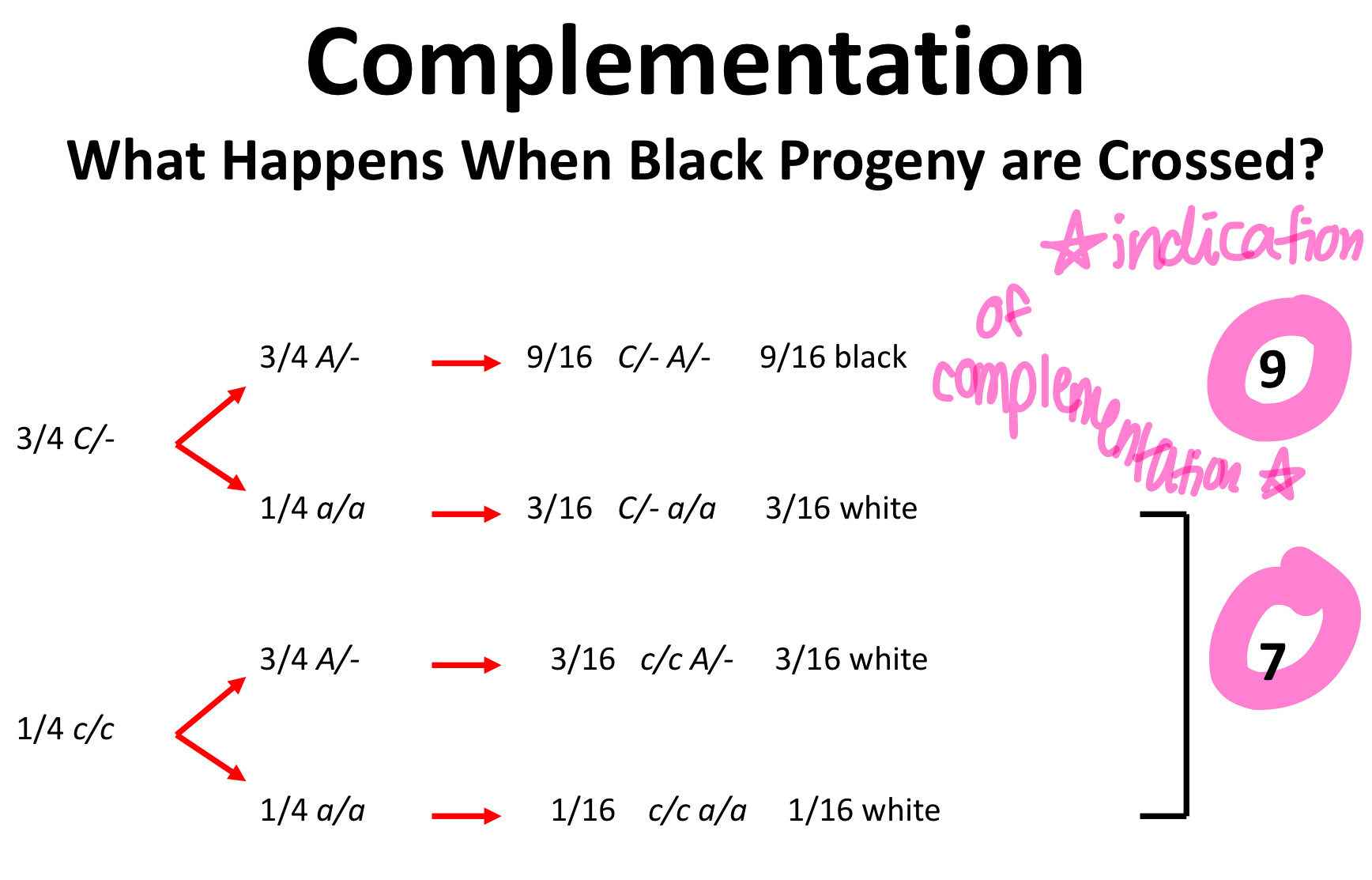
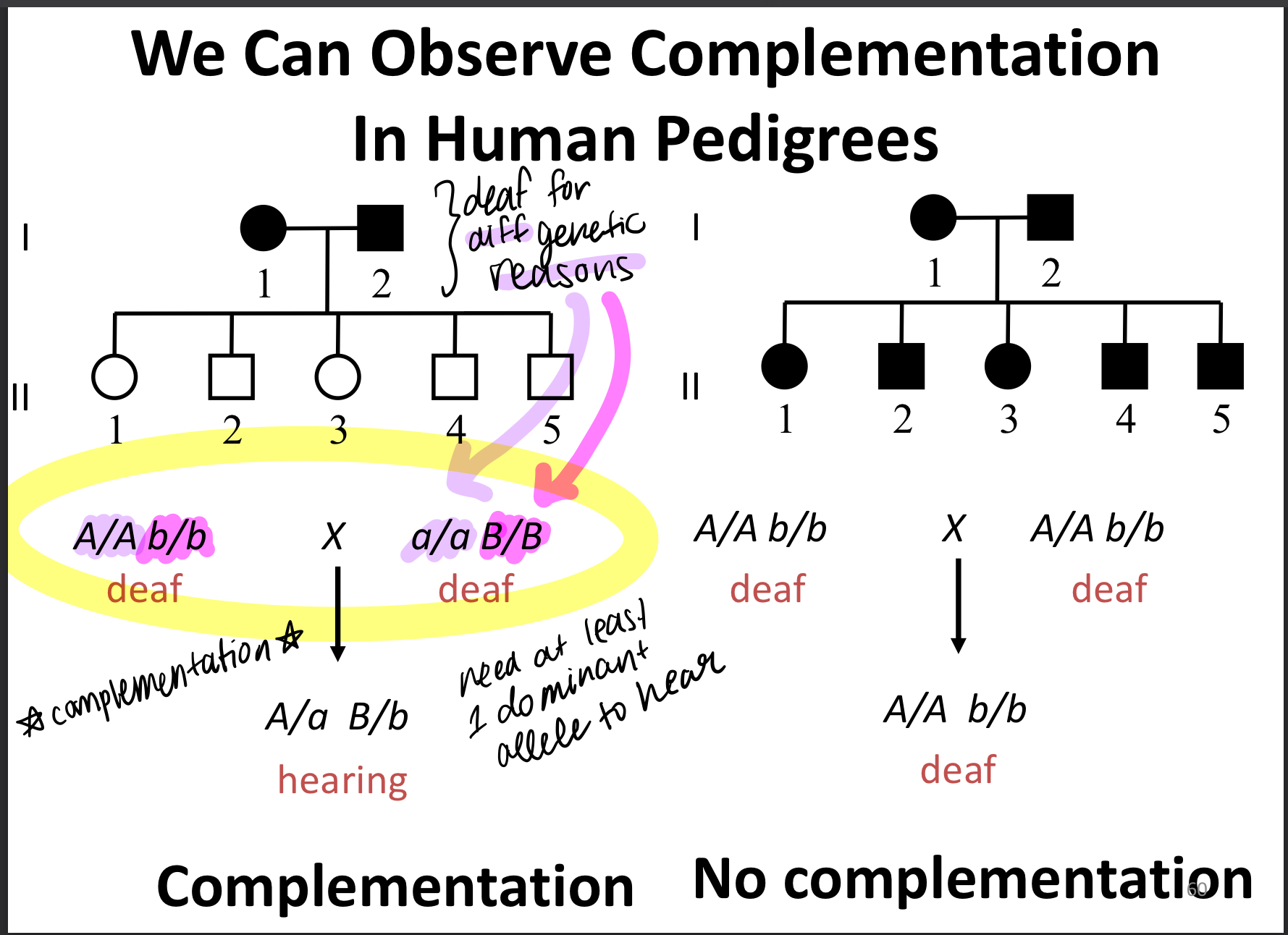
complementation
2 strains of an organism w/ different homozygous recessive mutations that produce the SAME phenotype, produce offspring of the wild-type phenotype when mated or crossed
-the other genome supplies the wild-type allele to "complement" the mutated allele
-the other genome supplies the wild-type allele to "complement" the mutated allele
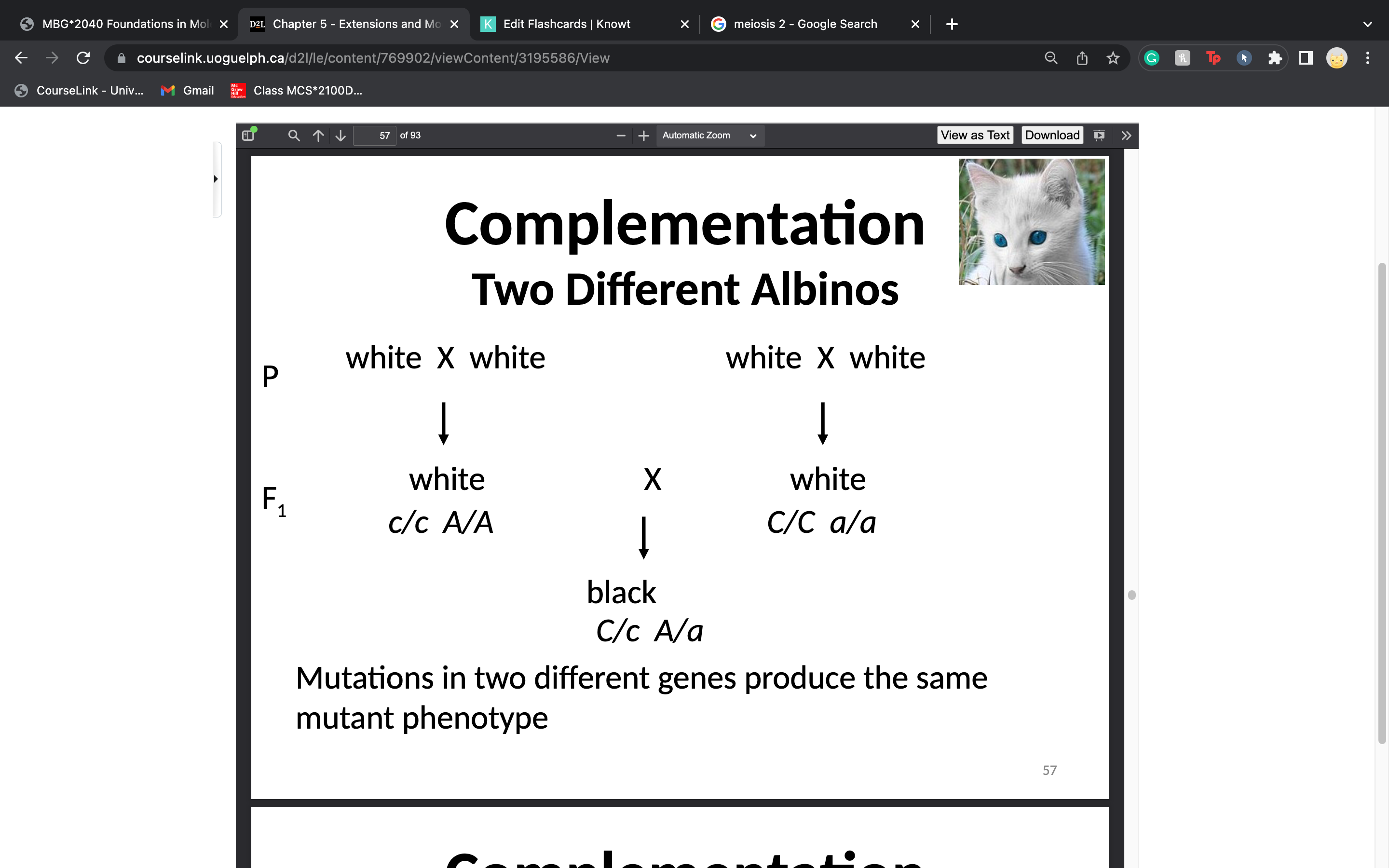
57
New cards
complementation will only occur is the mutations are in ________________
different genes
will not occur if the mutations are in the same gene!
will not occur if the mutations are in the same gene!
58
New cards
heterogenous trait
mutation in any one of a number of genes can give rise to the same phenotype
in yellow
in yellow
59
New cards
epistasis
masking of the expression of one gene by another, no new phenotypes are produced
**epistatic gene does the masking
**epistatic gene does the masking
60
New cards
T or F: the hypostatic gene is masked
true
61
New cards
recessive epistasis
ratio and purpose
ratio and purpose
F2 phenotypic ratio 9:3:4 recessive epistasis
-homozygous recessive at one gene pair mask expression from the other gene
**b/b does the masking
-homozygous recessive at one gene pair mask expression from the other gene
**b/b does the masking

62
New cards
dominant epistasis
ratio and purpose
ratio and purpose
one dominant allele at one gene masks expression from the other gene

63
New cards
summary of F2 ratios!! really important
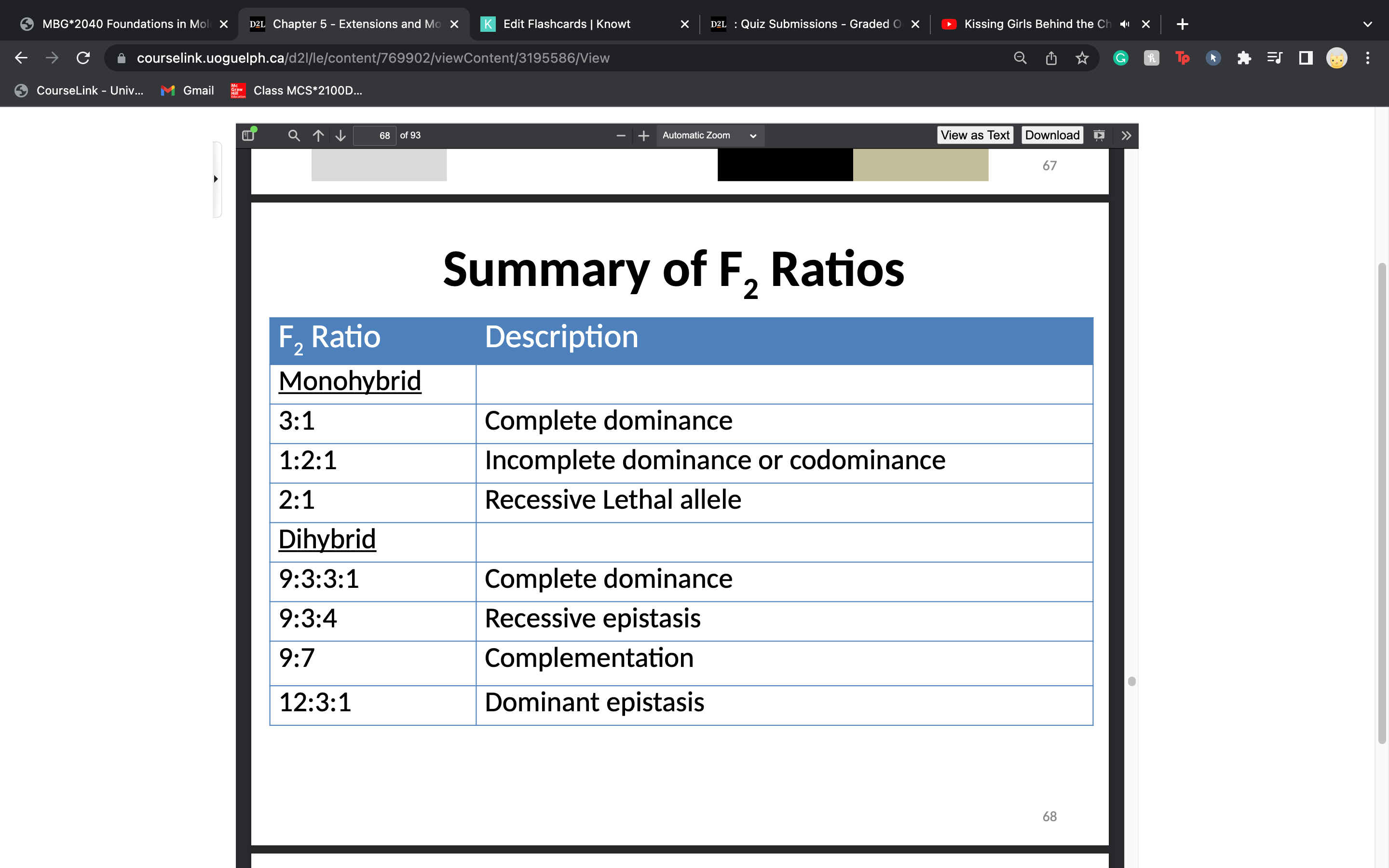
64
New cards
pleiotropy and examples
single gene affects two or more phenotypic traits
ex: sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis
ex: sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis
65
New cards
when 2 inbred lines are crossed, it leads to heterosis... whats this
hybrids are heterozygous for many genes... which have a ton more traits than the parents
66
New cards
Inbreeding increases the frequency of______________ and decreases the frequency of
heterozygotes
heterozygotes
homozygotes
67
New cards
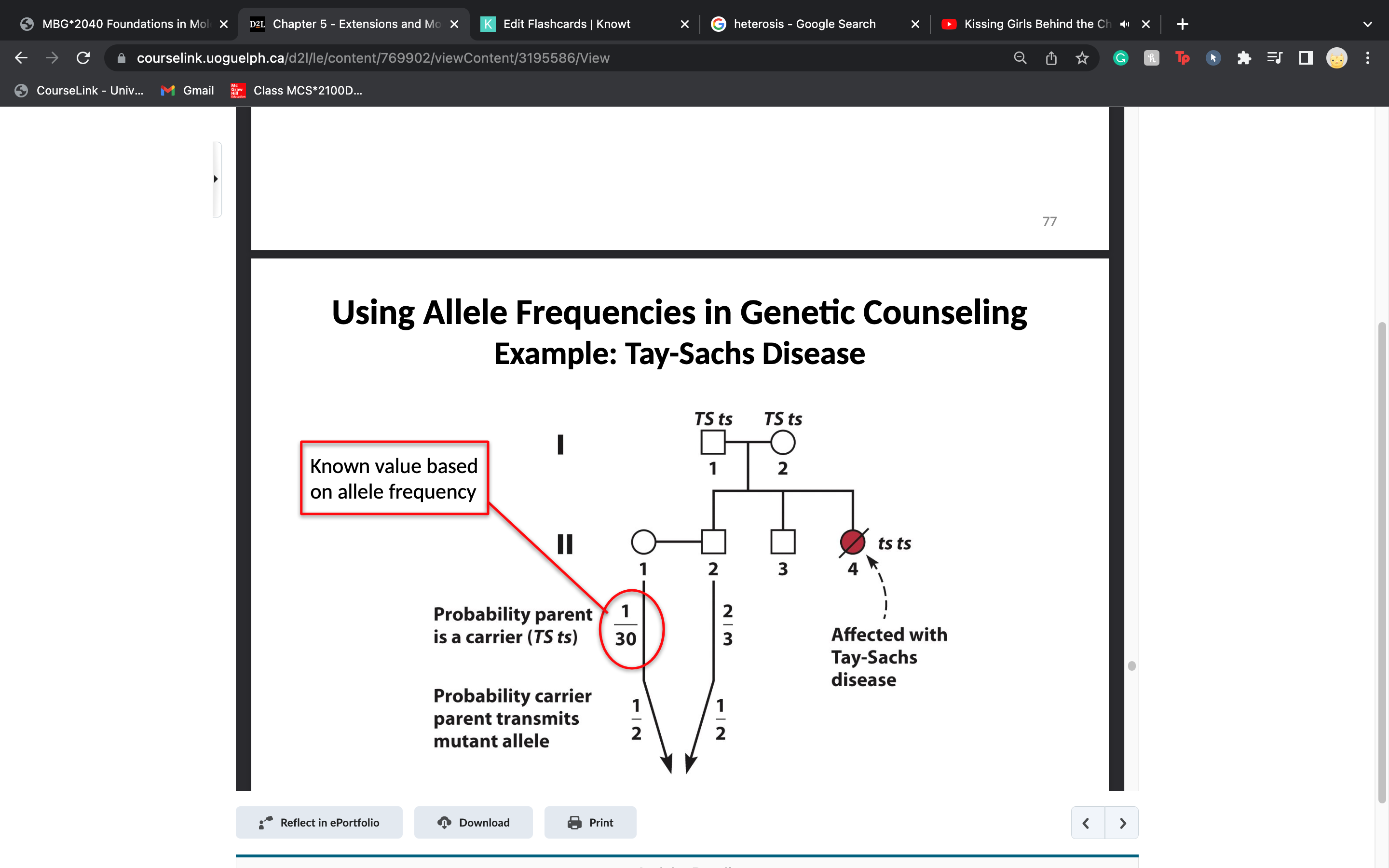
answer this
1/180... get 1/30 from hardy weinberg
pg. 78 of chapter 5 notes
pg. 78 of chapter 5 notes
68
New cards
what is the expected frequency of heterozygotes in a population with the allelic frequency x and y is in Hardy-Weinberg equation?
2xy
69
New cards
dosage compensation
way of equalizing gene expression in the face of different gene dosage
dosage compensation for X-linked genes is achieved by inactivating one of the two X chromosomes in females.
dosage compensation for X-linked genes is achieved by inactivating one of the two X chromosomes in females.
70
New cards
The X and Y chromosomes pair during meiosis, even
though they are not homologous (the genes located
on each are different). how does this happen
though they are not homologous (the genes located
on each are different). how does this happen
X and Y chromosomes are homologous only at pseudoautosomal regions, which are essential for the XY pairing
71
New cards
If a cell contains more than 2 X chromosomes, all but one of them are inactive
• X0 females have no Barr Bodies, XXY males have 1 Barr Body, XXX
females have 2 Barr Bodies
• Therefore, females are functionally hemizygous for X-linked genes at the cellular level
– Approximately 50% cells express one allele, and 50% cells will express the other allele
• X0 females have no Barr Bodies, XXY males have 1 Barr Body, XXX
females have 2 Barr Bodies
• Therefore, females are functionally hemizygous for X-linked genes at the cellular level
– Approximately 50% cells express one allele, and 50% cells will express the other allele
72
New cards
females that are heterozygous for X linked traits are __________
genetic mosaics
73
New cards
X inactivation
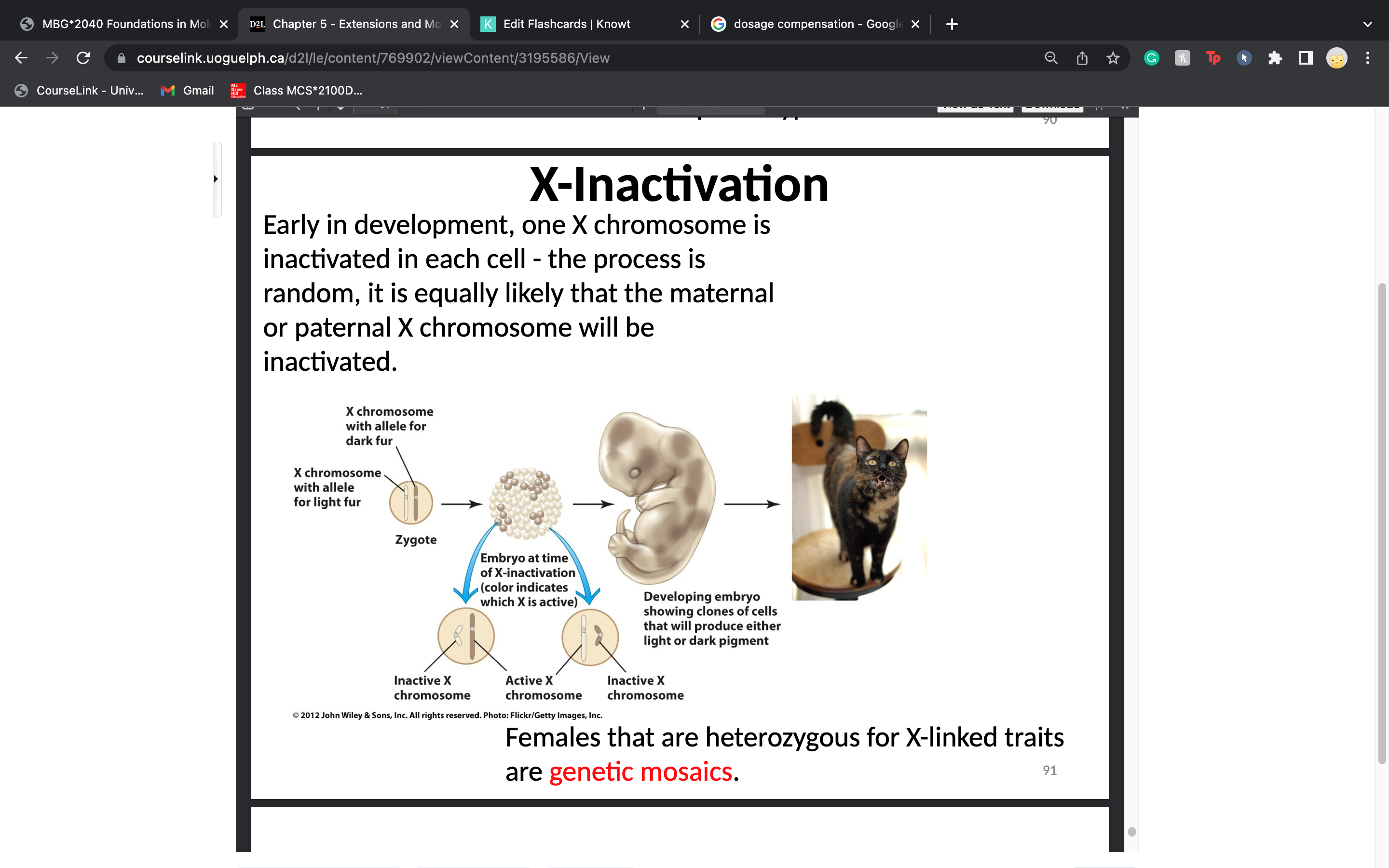
74
New cards
Explain calico cats
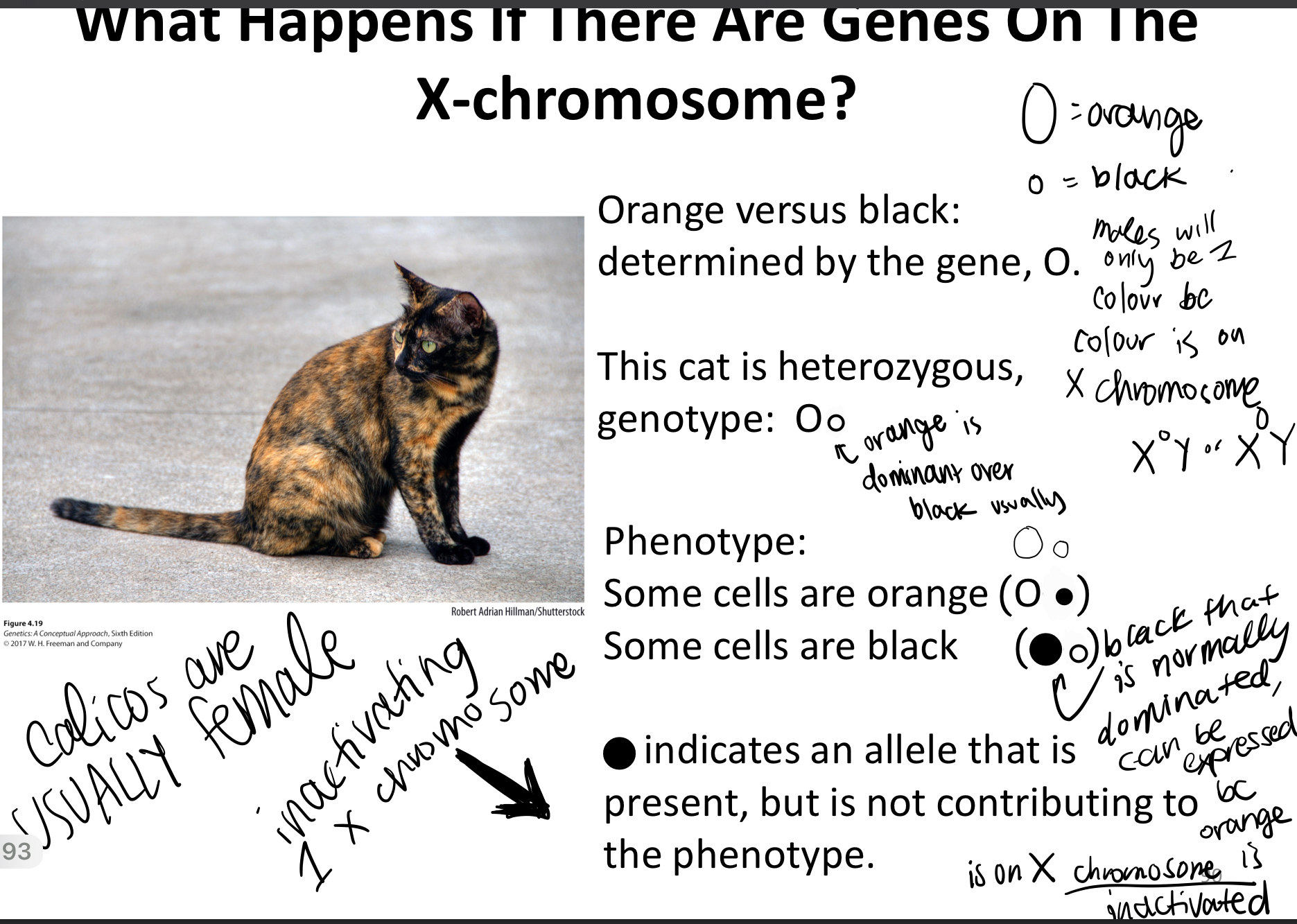
75
New cards
chromosome
76
New cards
sister chromatid
77
New cards
homologue
78
New cards
mitosis
79
New cards
meiosis
80
New cards
how do chromosomal nondisjunction events cause aneuploidy
81
New cards
how is polyploidy common in plants and rare in animals
30-35% of flowering plants are polyploids
animals: rare
animals: rare
82
New cards
monoploidy, what is it and what types of animals/insects are this
one set of chromosomes (Sterile)
1N
ants, bees, wasps MALES
1N
ants, bees, wasps MALES
83
New cards
diploid
2 sets of chromosomes
2N
2N
84
New cards
polyploidy
more than 2 sets of chromosomes (2 is normal)
ex: triploid banana 3N, tetraploid 4N
~usually sterile but can sometimes reproduce, like how 4N could theoretically reproduce if everything split up the exact same way (very small chance)
ex: triploid banana 3N, tetraploid 4N
~usually sterile but can sometimes reproduce, like how 4N could theoretically reproduce if everything split up the exact same way (very small chance)
85
New cards
autopolyploids
-are chromosomes identical?
-sterility?
-are chromosomes identical?
-sterility?
chromosome sets are identical (Ex: 4N= AAAA homologous groups are identical) (not getting alleles from diff parents to diversify aka... spontaneous doubling)
all chromosomes derived from same species (no crossing between ex: two plant species)
-MORE GROWTH (larger cells, larger plant)
-less seeds/STERILE
UNIVALENTS HAS TO EQUAL BIVALENTS
all chromosomes derived from same species (no crossing between ex: two plant species)
-MORE GROWTH (larger cells, larger plant)
-less seeds/STERILE
UNIVALENTS HAS TO EQUAL BIVALENTS
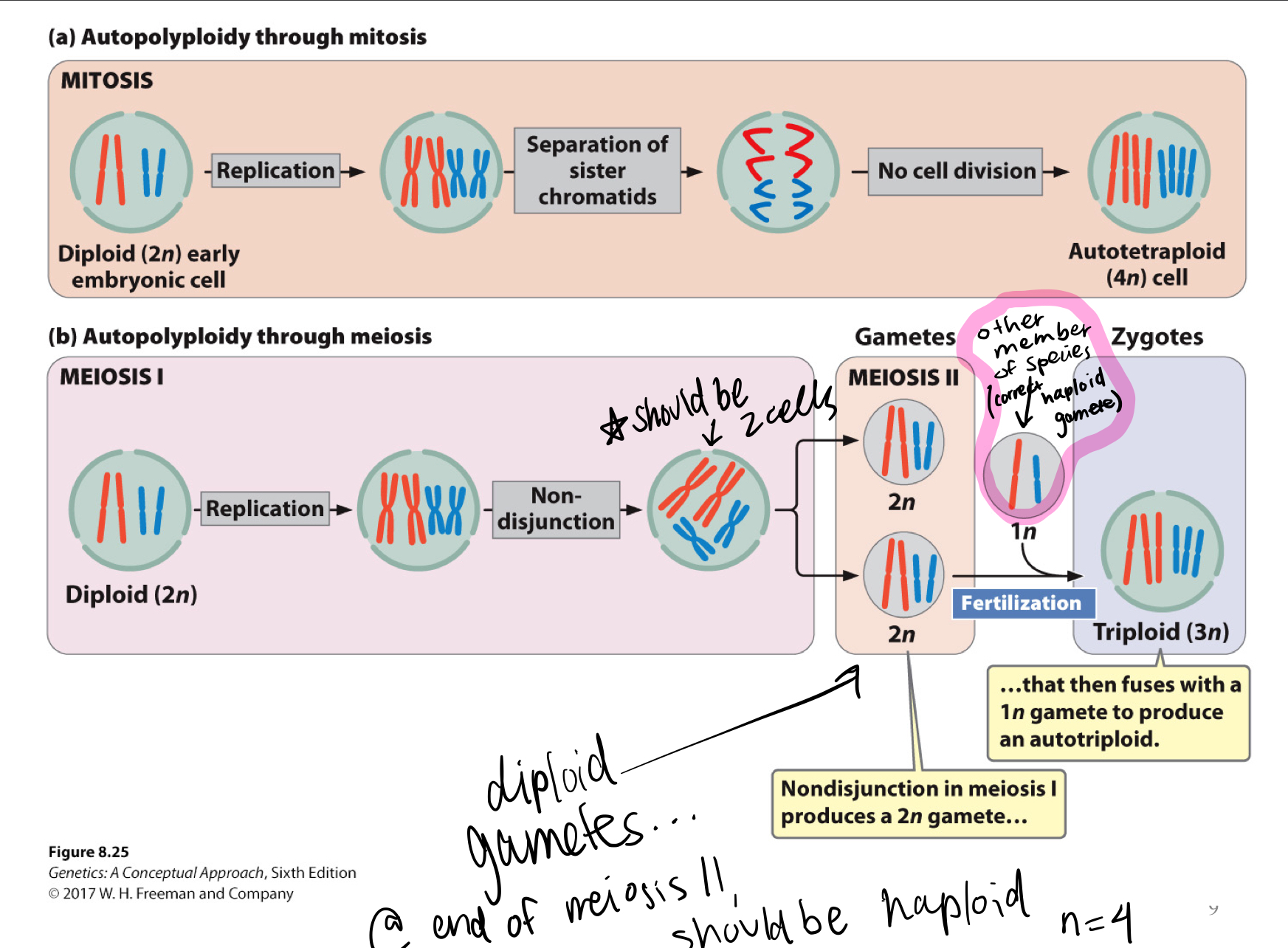
86
New cards
two types of 3N distribution.. what happens
Meiosis 1: (1 cell)
1) 1 bivalent and 1 univalent
2) 1 trivalent
1) 1 bivalent and 1 univalent
2) 1 trivalent
87
New cards
Demonstrate the paths of 3N in meiosis 1 and meiosis 2
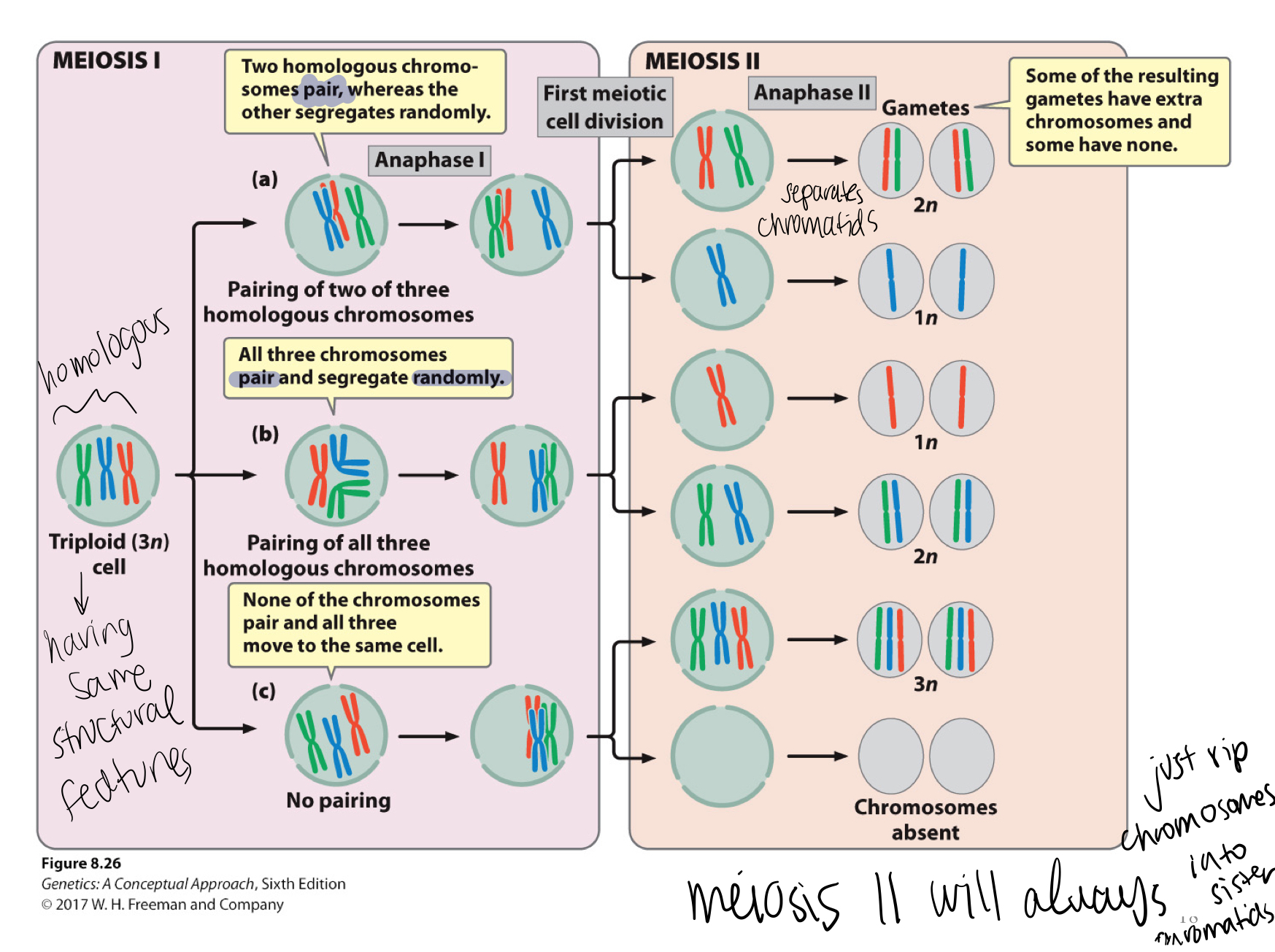
88
New cards
Allopolyploids
-cross between TWO species (related)
89
New cards
spontaneous doubling
restores fertility to sterile allopolyploids
A B ------> AA BB
2N--------> 4N
A B ------> AA BB
2N--------> 4N
90
New cards
aneuploidy
diploid genome which lacts a chromosome or has an extra chromosome
2N + 1 = trisomies
2N - 1 = monosomies
2N + 1 = trisomies
2N - 1 = monosomies
91
New cards
Turner syndrome and how it happens
X__
how it happens:
female but just one X chromosome, there is no other x chromosome to inactive like w normal females
-therefore there is no genetic leakage coming from the other inactivated X.. this leakage is important and is what makes normal females normal!
-only 45 chromosomes in total
how it happens:
female but just one X chromosome, there is no other x chromosome to inactive like w normal females
-therefore there is no genetic leakage coming from the other inactivated X.. this leakage is important and is what makes normal females normal!
-only 45 chromosomes in total
92
New cards
Klinefelter syndrome and how it happens
XXY
-nondisjunction in *meiosis 1* in the mother, put both chromosomes into the same gamete. meiosis 2 splits them up normally into 2 sister chromatids in each cell , leaving finished zygote cell with 2 X chromatids and 1 Y chromatid
-one of the Xs is inactivated, but not completely, there's some leakage, which affects male displaying traits
47 chromosomes in total
-nondisjunction in *meiosis 1* in the mother, put both chromosomes into the same gamete. meiosis 2 splits them up normally into 2 sister chromatids in each cell , leaving finished zygote cell with 2 X chromatids and 1 Y chromatid
-one of the Xs is inactivated, but not completely, there's some leakage, which affects male displaying traits
47 chromosomes in total
93
New cards
XYY male
how do you get TWO Ys
-in meiosis 1 when the X and Y separate, the chromosome is made up of 2 Y sister chromatids
**Non -disjunction in meiosis 2** both Y sister chromatids go into same gamete, therefore YY in one gamete instead of one Y in each
not much damage done by having 2 Ys
-in meiosis 1 when the X and Y separate, the chromosome is made up of 2 Y sister chromatids
**Non -disjunction in meiosis 2** both Y sister chromatids go into same gamete, therefore YY in one gamete instead of one Y in each
not much damage done by having 2 Ys
94
New cards
Triple X syndrome and how it happens
XXX
-in meiosis 1 when the X and Y separate, the chromosome is made up of 2 X sister chromatids
**Non -disjunction in meiosis 2** both X sister chromatids go into same gamete, therefore XX in one gamete instead of one X in each ***** CHECK THIS IDK IF ITS RIGHT***
two of the X's are inactivated, but not completely so there's too much X
-in meiosis 1 when the X and Y separate, the chromosome is made up of 2 X sister chromatids
**Non -disjunction in meiosis 2** both X sister chromatids go into same gamete, therefore XX in one gamete instead of one X in each ***** CHECK THIS IDK IF ITS RIGHT***
two of the X's are inactivated, but not completely so there's too much X
95
New cards
Down Syndrome
2N + 1
extra chromosome for the 21st chromosome
trisomy
extra chromosome for the 21st chromosome
trisomy
96
New cards
Patau Syndrome
2N + 1
extra chromosome on 13th chromosome
die before 2
extra chromosome on 13th chromosome
die before 2
97
New cards
Edward Syndrome
2N + 1
extra chromosome on 18th chromosome
die before 2
extra chromosome on 18th chromosome
die before 2
98
New cards
deletion/deficiency
missign chromosome segment
99
New cards
duplication
extra chromosome segment
100
New cards
hypoploidy
less genetic material such as a deletion of a chromosome segment or the loss of an entire chromosome