2.6 macro objectives and policies
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
conflicting macroeconomic objectives
-economic growth and inflation
-economic growth and reducing inequality
-economic growth and environmental protection
-economic growth and BoP equilibrium
-unemployment and inflation
when is there a conflict between economic growth and inflation
short run:
an increase in GDP will cause demand pull inflation due to an increase in AD
may worsen BoP, as demand for exports increases, but unemployment decreases
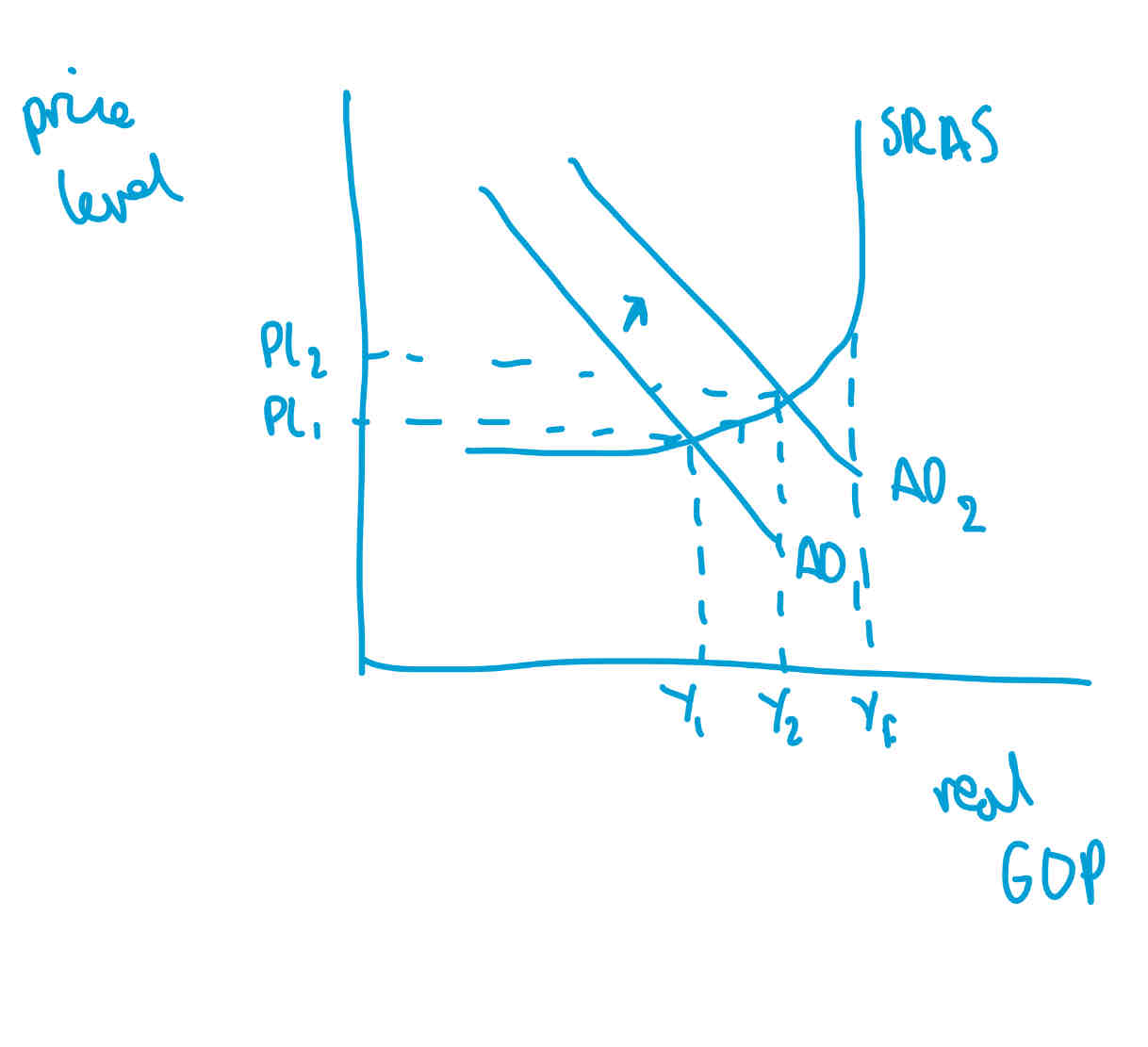
when is there not a conflict between economic growth and inflation (SR)
if inflation was already below 2%, then an increase would bring it closer to BoEs target
when is there not a conflict between economic growth and inflation (LR)
if an increase in real GDP happens without inflation, then the productive potential of the economy can increase, by improving quantity or quality of FoPs
if supply and demand increase at the same rate inflation wont happen
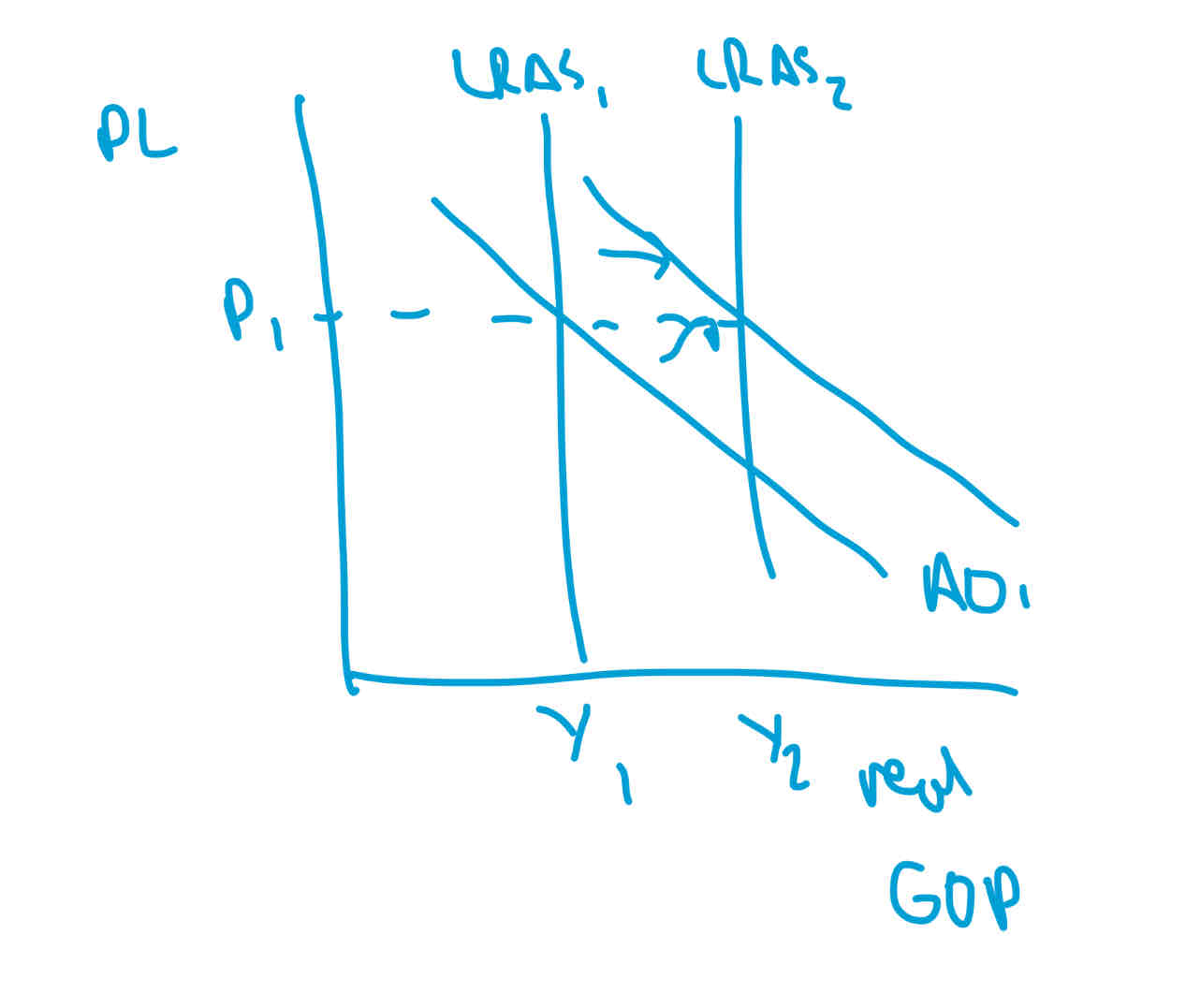
policies to reduce this conflict
-subsidise new technologies for firms
-policies to increase free trade of capital
-net immigration
-education/ training
-improve infrastrucutre
ways in which economic growth and reducing inequality don’t conflict
public services such as education, infrastructure and healthcare are improved
ways in which economic growth and reducing inequality conflict
short run growth increases inflation, which has the greatest effect on poorer people
privatisation of public services increases inequalities, as shareholders and senior executives benefit rather than workers
CEO to worker pay ratio has increased in the UK to 109 for FTSE 100 Jan 2024
diagram for conflict between economic growth and environmental protection
kuznets curve
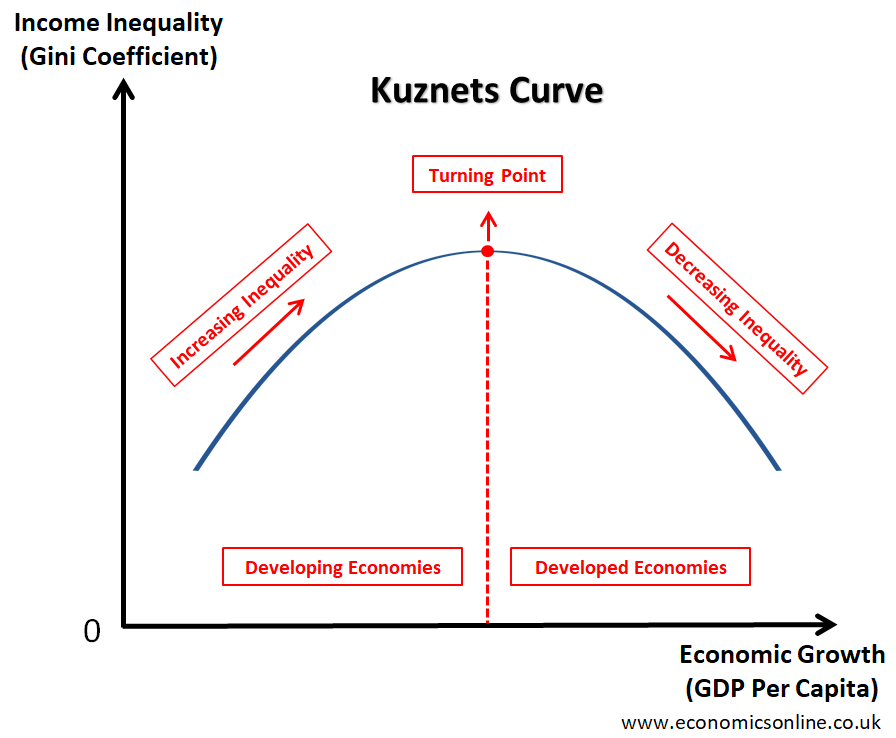
eval of kuznets curve
considers environmental degradation on a country scale, but post-industrial countries are likely shifting emissions abroad
why does economic growth and BoP conflict
as disposable income increases, demand for imports increases, increasing MPM, increasing current account deficit
why does economic growth and BoP not conflict
may lead to an increase in production and quality of UK goods, reducing the trade imbalance
Short run Philips curve
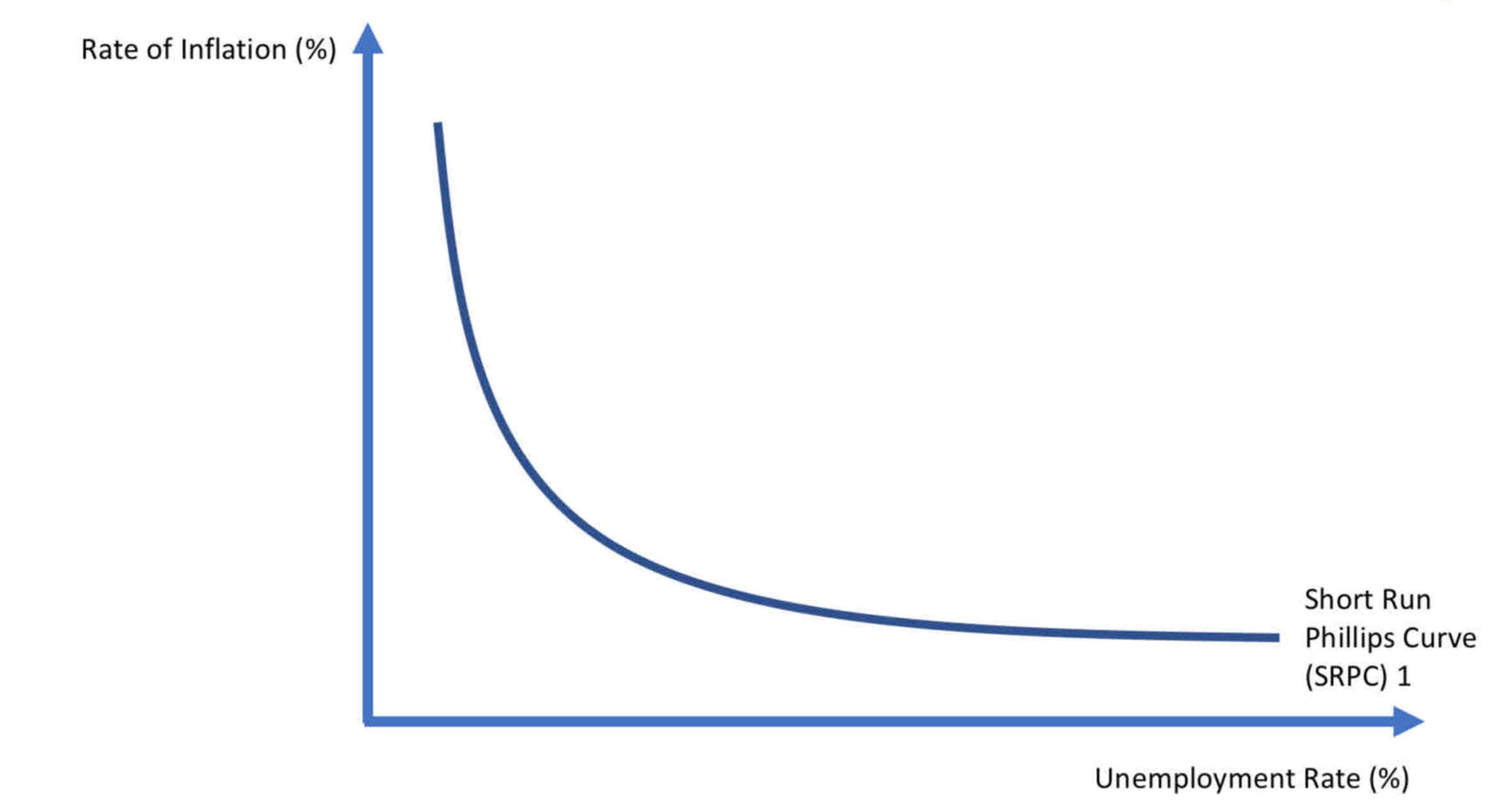
What is the Phillips curve
Possible inverse relationship between unemployment rate and rate of inflation
Explain the Phillips curve
An increase in government spending generates growth and increases the derived demand for labour
Unemployment falls
Firms must compete for fewer workers by raising nominal wages
Workers have greater bargaining power to demand nominal wage rises
Wage costs rise
Firms pass on the costs of increased wages to consumers, creating cost push inflation
a decrease in unemployment would increase consumption increasing AD
This would cause demand pull inflation
Example of when the Phillips Curve was not accurate
In the US in the 1970s which experiences high unemployment and high inflation at the same time due to high oil prices
Evaluation of the Phillips curve
-Stagflation: low growth, high unemployment, high inflation, eg in the 1970s due to high oil prices
Why are wages sticky down
Trade unions
Minimum wage
Efficiency wage hypothesis
Why is raising interest rates unpopular
Trade unions want lower interest rates for higher employment
Businesses want lower interest rates for investments
Government wants lower interest rates to reduce interest payments
Supply side policies
-funding for infrastructure
-funding for education
-relax migration
-trade deal with EU
Demand side policy
Fiscal or monetary
Example of monetary policy
Changes to interest rates of quantitative easing
Example of fiscal policy
Changes in tax rates of government spending
Does demand side or supply side generally lead to more conflicts
Demand side
Factors to consider with conflicting MEPOs
other MEPOs
Short run vs long run
Classical vs Keynesian
If there is spare capacity in the economy
How does raising interest rates impact AD
BoE raises interest rates
Banks raise interest rates
Borrowing is discouraged, saving is encouraged
Consumption decreases
Investment decreased
Mortgages are more expensive, so demand decreases, so house prices decrease
Investors move money to savings accounts, so share value decreases
Negative wealth affect, further decreases consumption
Hot money flows increase, due to high savings rate, worsening BoP