foot and ankle anatomy
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:52 PM on 12/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
1
New cards
proximal tibiofibular joint
type
type
plane gliding synovial joint surrounded by capsular ligament
2
New cards
distal tibiofibular joint
type
type
syndesmosis/ fibrous joint
3
New cards
syndesmosis defintion
2 bones held together by interosseous ligament
4
New cards
distal tibiofibular joint
importance
importance
stability of ankle reliant on the gripping of the talus by 2 malleoli
5
New cards
distal tibiofibular joint
talus socket area
talus socket area
the lower most part of the later deepens the tibial articular surface thus the socket for the talus
6
New cards
distal tibiofibular joint
shafts held together by
shafts held together by
interosseous membrane
7
New cards
what happens to fibula during dorsiflexion ?
slight lateral displacement due to wider anterior talus
8
New cards
tibia
weight bearing
weight bearing
main weight bearing bone
9
New cards
tibia
interior surface texture and why
interior surface texture and why
smooth for articulation with the superior surface of the body of the talus
10
New cards
fibula
weight-bearing %
weight-bearing %
17%
11
New cards
lateral malleolus (fibula)
function
function
serves as a site for ligament and muscle attachment
articulates with the tibia superiorly (superior tibiofibular joint) and inferiorly ( inferior tibiofibular joint)
articulates with the tibia superiorly (superior tibiofibular joint) and inferiorly ( inferior tibiofibular joint)
12
New cards
lateral malleolus (fibula)
palpation
palpation
easily palpated
13
New cards
ankle joint (talo-crural joint)
components
components
tibia
fibula
talus
fibula
talus
14
New cards
ankle joint (talo-crural joint)
tendon resembles
tendon resembles
mortise and tenon
15
New cards
ankle joint (talo-crural joint)
importance of mortise and tenon structure
importance of mortise and tenon structure
to prevent lateral or angular displacement due to medial and lateral malleoli
16
New cards
ankle joint (talo-crural joint)
type
type
synovial hinge joint
17
New cards
boney points of ankle and foot
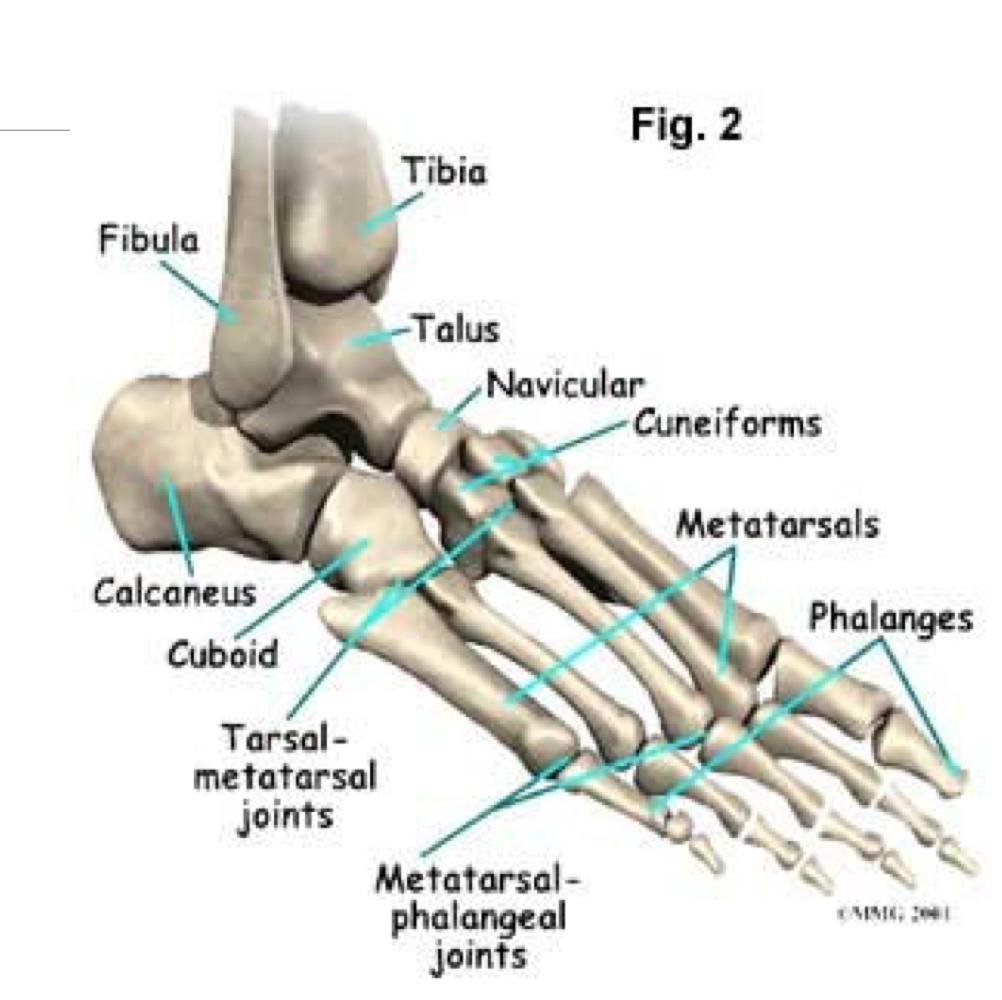
18
New cards
lateral ligaments
anterior talo fibular ligament (ATFL)
calcaneo fibular ligament (down and back) (CFL)
posterior talo fibular ligament (PTFL)
calcaneo fibular ligament (down and back) (CFL)
posterior talo fibular ligament (PTFL)
19
New cards
medial (deltoid) leigaments
posterior tibio talar ligament
anterior tibio talar ligament (forward and down)
tibio calcaneal ligament (down to sustentaculum tali)
tibio navicular ligament (down and forward)
anterior tibio talar ligament (forward and down)
tibio calcaneal ligament (down to sustentaculum tali)
tibio navicular ligament (down and forward)
20
New cards
the ankle joint
surface covered in
surface covered in
hyaline cartilage
21
New cards
the ankle joint
function of hyaline cartilage
function of hyaline cartilage
shock absorbing
lowers friction
hard wearing
lowers friction
hard wearing
22
New cards
the ankle joint
synovial fluid function
synovial fluid function
allows for smooth movement
provides nutrition
provides nutrition
23
New cards
the ankle joint
stability dependant on
stability dependant on
joint surface congruency
joint capsule and supporting ligaments
muscles around the joint
bony contours (concave surface of tib + convex surface of fib)
joint capsule and supporting ligaments
muscles around the joint
bony contours (concave surface of tib + convex surface of fib)
24
New cards
movements of the ankle joint
dorsiflexion
plantar flexion
plantar flexion
25
New cards
dorsi flexors
tibialis anterior
extensor digitorum longum
extensor hallucis longus
extensor digitorum longum
extensor hallucis longus
26
New cards
plantar flexion
gastrocnemius
soleus
plantaris
flexor digitorum longus
flexor hallucis longus
tibialis posterior
soleus
plantaris
flexor digitorum longus
flexor hallucis longus
tibialis posterior
27
New cards
talus
attachments
attachments
no muscle attachments
28
New cards
talus
position
position
between the malleoli of tibia and fibula
29
New cards
talus
articulation
articulation
with lower surface of tibia and fibula
30
New cards
sinus tarsi
what is it?
what is it?
a tunnel between talus and the calcaneus that contains structures that contribute to the stability of the ankle and to its propriocpetion
31
New cards
sinus tarsi
contains
contains
blood vessels
nerves
fat
ligamentous complex
nerves
fat
ligamentous complex
32
New cards
calcaneus
size comparison
size comparison
largest of tarsal bones
33
New cards
calcaneus
attachment
attachment
posterior surface is the attachment for the achilles tendon
34
New cards
sustentaculum tali
what is it ?
what is it ?
a horizontal shelf that arises from the anteromedial portion of the calcaneus.
35
New cards
sustentaculum tali
superior surface shape and articulation
superior surface shape and articulation
concave
articulates with the middle calcaneal surface of the talus
articulates with the middle calcaneal surface of the talus
36
New cards
sustentaculum tali
inferior surface groove purpose
inferior surface groove purpose
intended for tendon of flexor hallucis longus
37
New cards
navicular
location
location
medial side of foot
38
New cards
navicular
articulation (proximally, distally, and laterally )
articulation (proximally, distally, and laterally )
proximally with the talus
distally with the 3 cuneiform bones
laterally with the cuboid
distally with the 3 cuneiform bones
laterally with the cuboid
39
New cards
metatarsal phalangeal joints
type and description
type and description
condyloid joints
elliptical/round
elliptical/round
40
New cards
interphalangeal joints
type
type
hinge joints
41
New cards
interphalangeal joints
great toe
great toe
only 1 interphalangeal joint
42
New cards
interphalangeal joints
4 lateral toes
4 lateral toes
distal and proximal interphalangeal joints each
43
New cards
plantar calcaeonavicular ligament
type
type
spring ligament
44
New cards
plantar calcaeonavicular ligament
what and where
what and where
thick, broad fibrous band that is located on the bottom portion of the foot
45
New cards
plantar calcaeonavicular ligament
functions
functions
connects navicular bone's plantar surface with the sustentaculum of the calcaneus.
provides support to the head of talus
bears significant amount of body weight
provides support to the head of talus
bears significant amount of body weight
46
New cards
subtalar joint
importance
importance
maintain rear foot arthrokinematics
foot function in weight bearing particularly
foot function in weight bearing particularly
47
New cards
subtalar joint
type
type
synovial joint
48
New cards
subtalar joint
formed by
formed by
body of talus superiorly and body of calcaneus inferiorly
49
New cards
subtalar joint
communication
communication
doesnt communicate with any other and is surrounded by capsular ligament
50
New cards
subtalar joint
held by
held by
medial and lateral talocalcaneal ligaments
interosseous talocalcaneal ligament occupying sinus tarsi
cervical ligament attaching to neck of talus to upper surface of calcaneus
interosseous talocalcaneal ligament occupying sinus tarsi
cervical ligament attaching to neck of talus to upper surface of calcaneus
51
New cards
subtalar joint
movements
movements
inversion
eversion
eversion
52
New cards
subtalar joint
inversion muscles
inversion muscles
tibialis anterior
tibialis posterior
flexor digitorum longus
flexor hallucis longus
extensor hallucis longus
tibialis posterior
flexor digitorum longus
flexor hallucis longus
extensor hallucis longus
53
New cards
subtalar joint
inversion degrees of movement
inversion degrees of movement
20 degrees
54
New cards
subtalar joint
eversion muscles
eversion muscles
peroneus longus
peroneus brevis
extensor digitorum longus
peroneus brevis
extensor digitorum longus
55
New cards
subtalar joint
eversion degrees of movement
eversion degrees of movement
10 degrees
56
New cards
subtalar joint
nerve supply
nerve supply
branches of medial and lateral plantar nerves
57
New cards
transverse (mid-tarsal) joints
talo-navicular
calcaneo-cuboid
calcaneo-cuboid
58
New cards
talo navicular joint
type
type
ball and socket
59
New cards
calcaneo cuboid joint
type
type
saddle shaped synovial joint
60
New cards
transverse (mid-tarsal) joints
movements
movements
inversion and eversion
61
New cards
gastrocnemius
origin
origin
2 heads originate from the posterior surface of the medial and lateral condyles of femur
62
New cards
gastrocnemius
insertion
insertion
fuse together to insert into Achilles tendon which inserts into the posterior portion of the calcaneus
63
New cards
gastrocnemius
action
action
powerful plantar flexor of foot
64
New cards
soleus
origin
origin
2 heads originate form the proximal tibia and fibula
65
New cards
soleus
insertion
insertion
achilles tendon
66
New cards
soleus
actions
actions
powerful plantar flexor of foot
main role is postural
main role is postural
67
New cards
achilles tendon
what is it
what is it
the tendon through which gastrocnemius and soleus exert their force on the foot during the propulsive phase of walking, running, or jumping
68
New cards
achilles tendon
strength
strength
strongest tendon in the body
69
New cards
plantaris
origin
origin
lateral supracondylar line of the femur at a position slightly superior to the origin of the lateral head of gastrocnemius
70
New cards
plantaris
insertion
insertion
achilles tendon
71
New cards
plantaris
actions
actions
plantar flexion
72
New cards
flexor digitorum longus
origin
origin
arises back of the tibia below popliteus and medial to tib posterior
73
New cards
flexor digitorum longus
insertion
insertion
splits into 4 tendon attaches to tendon sheaths of the 4 toes
74
New cards
flexor digitorum longus
action
action
flexes the toes particularly distal phalanges
75
New cards
flexor digitorum brevis
origin
origin
calcaneal tuberosity
4 tendons perforated by flexor digitorum longus
4 tendons perforated by flexor digitorum longus
76
New cards
flexor digitorum brevis
insertion
insertion
side middle phalanx of 4 toes
77
New cards
flexor digitorum brevis
action
action
flexion of the toes
78
New cards
flexor hallucis longus
origin
origin
shaft of fibular below attachment of soleus
passes under sustentaculum tali
passes between 2 sesamoid bones of the head of 1st metatarsal
passes under sustentaculum tali
passes between 2 sesamoid bones of the head of 1st metatarsal
79
New cards
flexor hallucis longus
insertion
insertion
base distal phalanx great toe
80
New cards
flexor hallucis longus
action
action
flexor of great toe
81
New cards
flexor hallucis brevis
origin
origin
plantar surface lateral cuneiform/cuboid
82
New cards
flexor hallucis brevis
insertion
insertion
2 tendons into the proximal phalanx of the great toe
83
New cards
tibialis posterior
origin
origin
inner posterior borders of tibia and fibula
also attached to the interosseous membrane, which attaches to the tibia and fibula
also attached to the interosseous membrane, which attaches to the tibia and fibula
84
New cards
tibialis posterior
insertion
insertion
main portion inserts into the tuberosity of the navicular and the plantar surface of the medial cuneiform
pantar portion inserts into the bases of 2nd, 3rd, and 4th metatarsals , the intermediate and lateral cuneiforms, and the cuboid
pantar portion inserts into the bases of 2nd, 3rd, and 4th metatarsals , the intermediate and lateral cuneiforms, and the cuboid
85
New cards
tibialis posterior
actions
actions
inversion
assists in plantar flexion
supports medial longitudinal arch
assists in plantar flexion
supports medial longitudinal arch
86
New cards
tibialis anterior
origin
origin
upper 2/3rds of anterior lateral tibia
87
New cards
tibialis anterior
insertion
insertion
medial cuneiform base of 1st metatarsal
88
New cards
tibialis anterior
actions
actions
dorsiflexion
inversion
balance
controls placement of foot on the ground
inversion
balance
controls placement of foot on the ground
89
New cards
toe extensors
extensor digitorum longus
extensor digitorum brevis
extensor digitorum brevis
90
New cards
toe extensors
importance
importance
in running to ensure that great toe and foot clears the ground ready for the heel to be placed on the ground
91
New cards
extensor digitorum longus
origin
origin
arises upper 3/4s shaft of fibula
passes deep to extensor retinacula splits into 4 tendons
passes deep to extensor retinacula splits into 4 tendons
92
New cards
extensor digitorum longus
insertion
insertion
each tendon divides int o3, the central slip attaching base middle phalanx, other 2 unite to insert to base distal phalanx
93
New cards
extensor digitorum longus
action
action
toe extension
94
New cards
extensor hallucis longus
origin
origin
middle third shaft of fibula
tendon passes deep to extensor retinacula, traverses foot
tendon passes deep to extensor retinacula, traverses foot
95
New cards
extensor hallucis longus
insertion
insertion
base distal phalanx
96
New cards
extensor hallucis longus
action
action
great toe extensor
97
New cards
peroneus longus
origin
origin
proximal 2/3 lateral aspect of fibula
98
New cards
peroneus longus
insertion
insertion
base of 1st metatarsal and medial cuneiform
99
New cards
peroneus longus
nerve supply
nerve supply
superior peroneal
100
New cards
peroneus brevis
origin
origin
distal 2/3 lateral fibula