Honors Muscle and Nervous Tissue
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Muscle Tissue
is contractile; can shorten and thicken making making movement possible. Muscle fibers are the cells that make up muscle tissue.
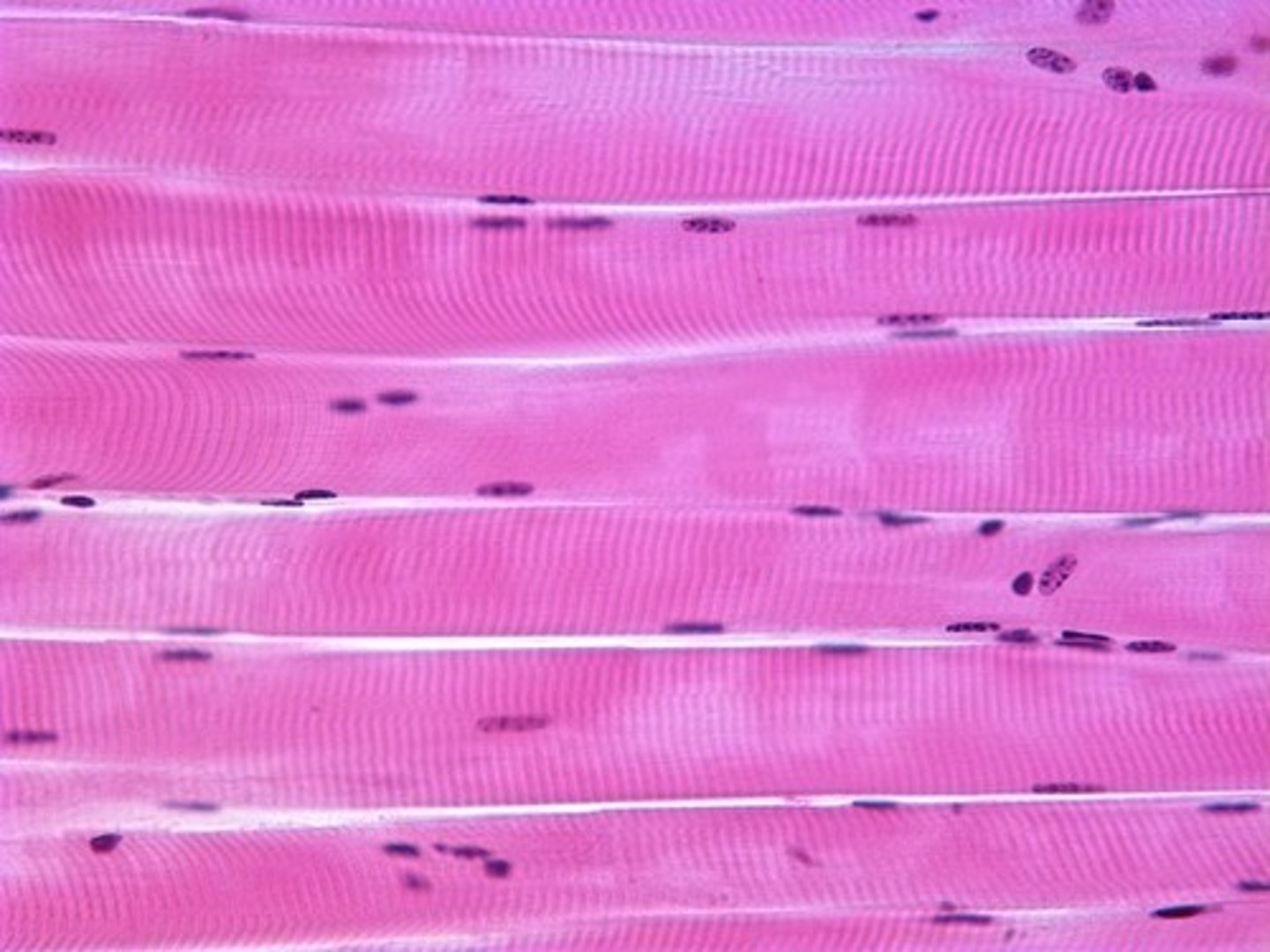
skeletal muscle tissue
forms muscle that attaches to bone, constitutes 40% of human body weight, multiple nuclei per cell, striated or banded due to alternating light and dark contractile proteins
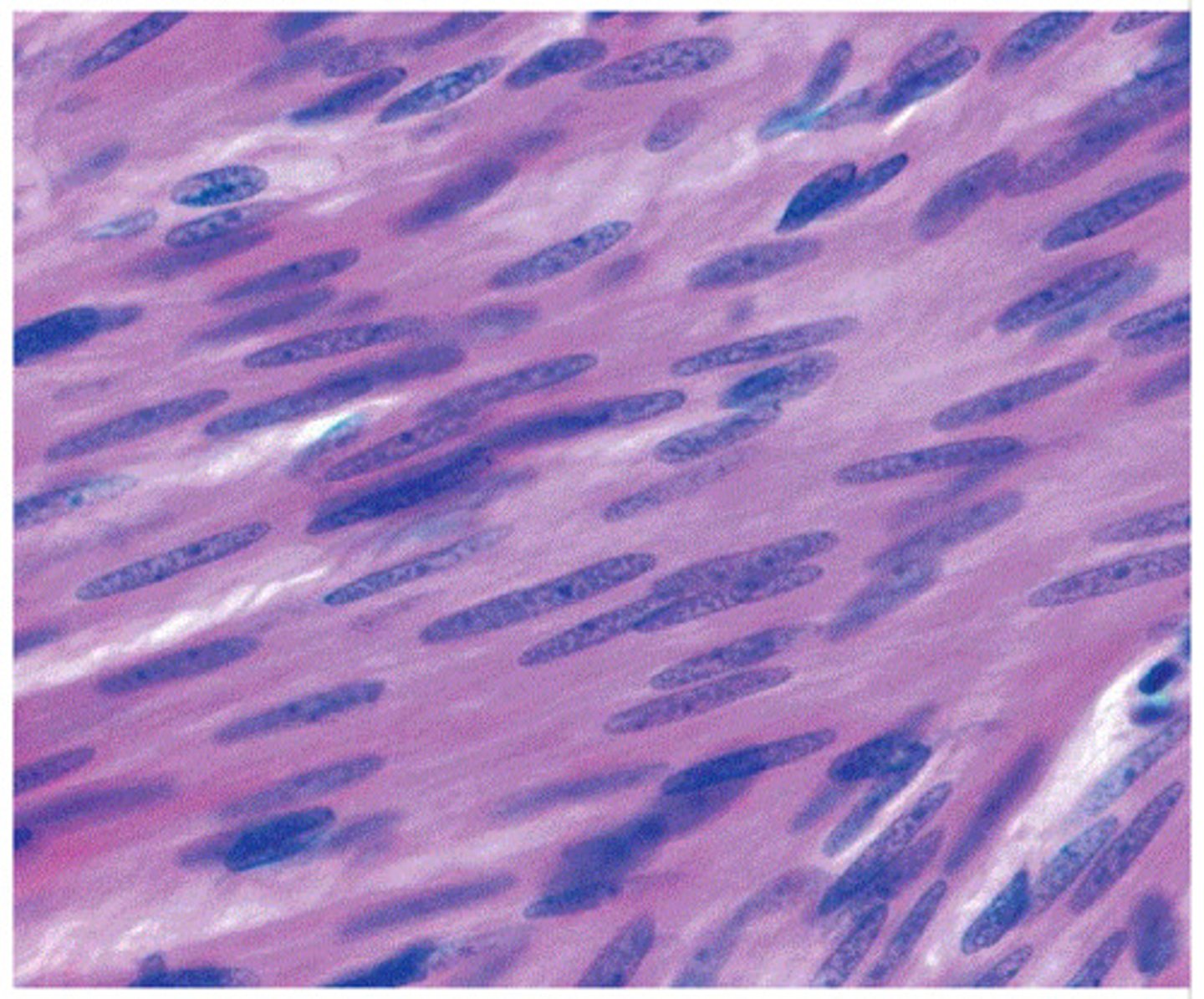
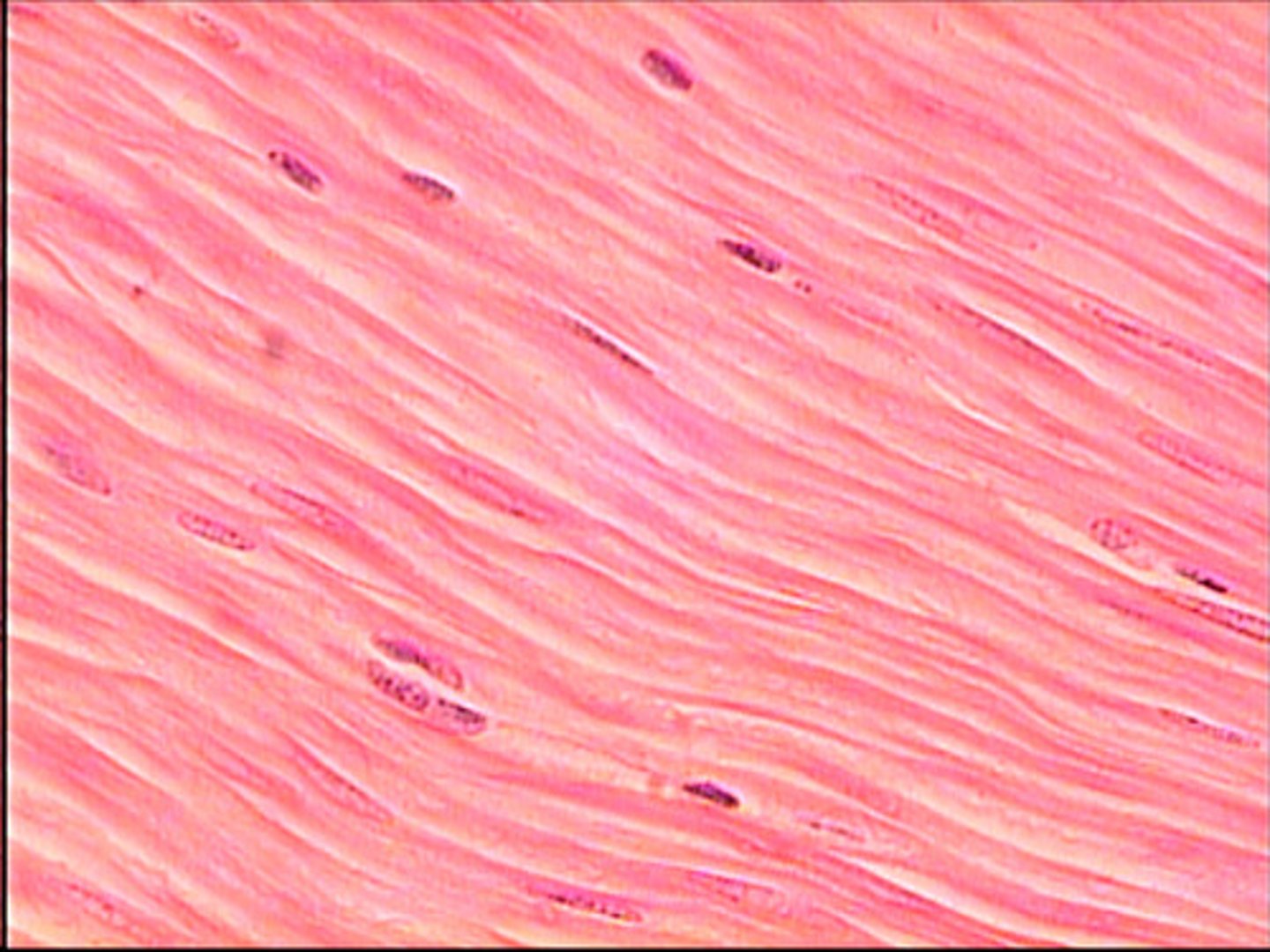
smooth muscle tissue
lacks striations, cells are shorter and tapered at each end, single nucleus, makes up walls of hollow organs such as stomach, intestines, bladder, uterus, blood vessels; involuntary
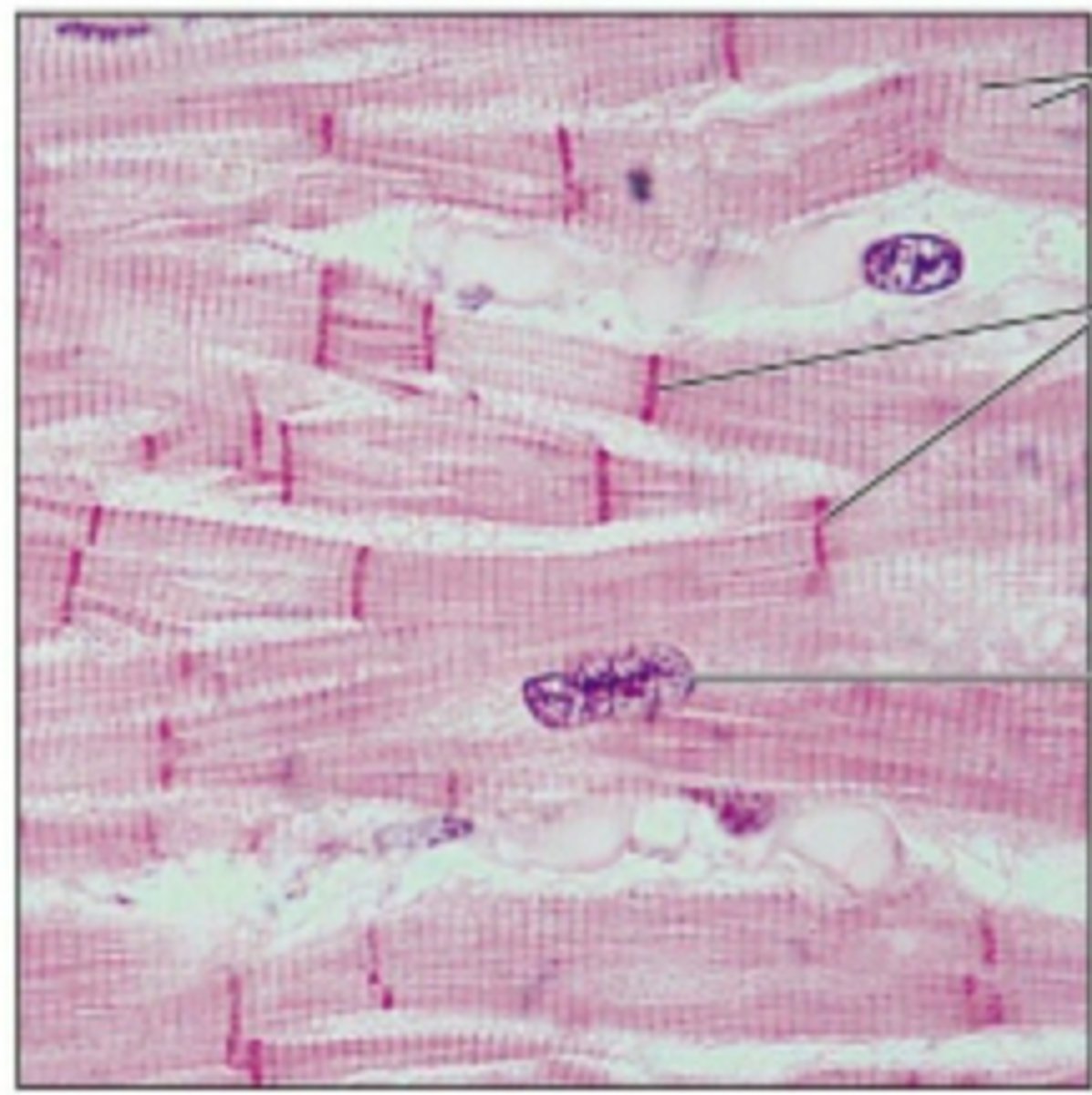
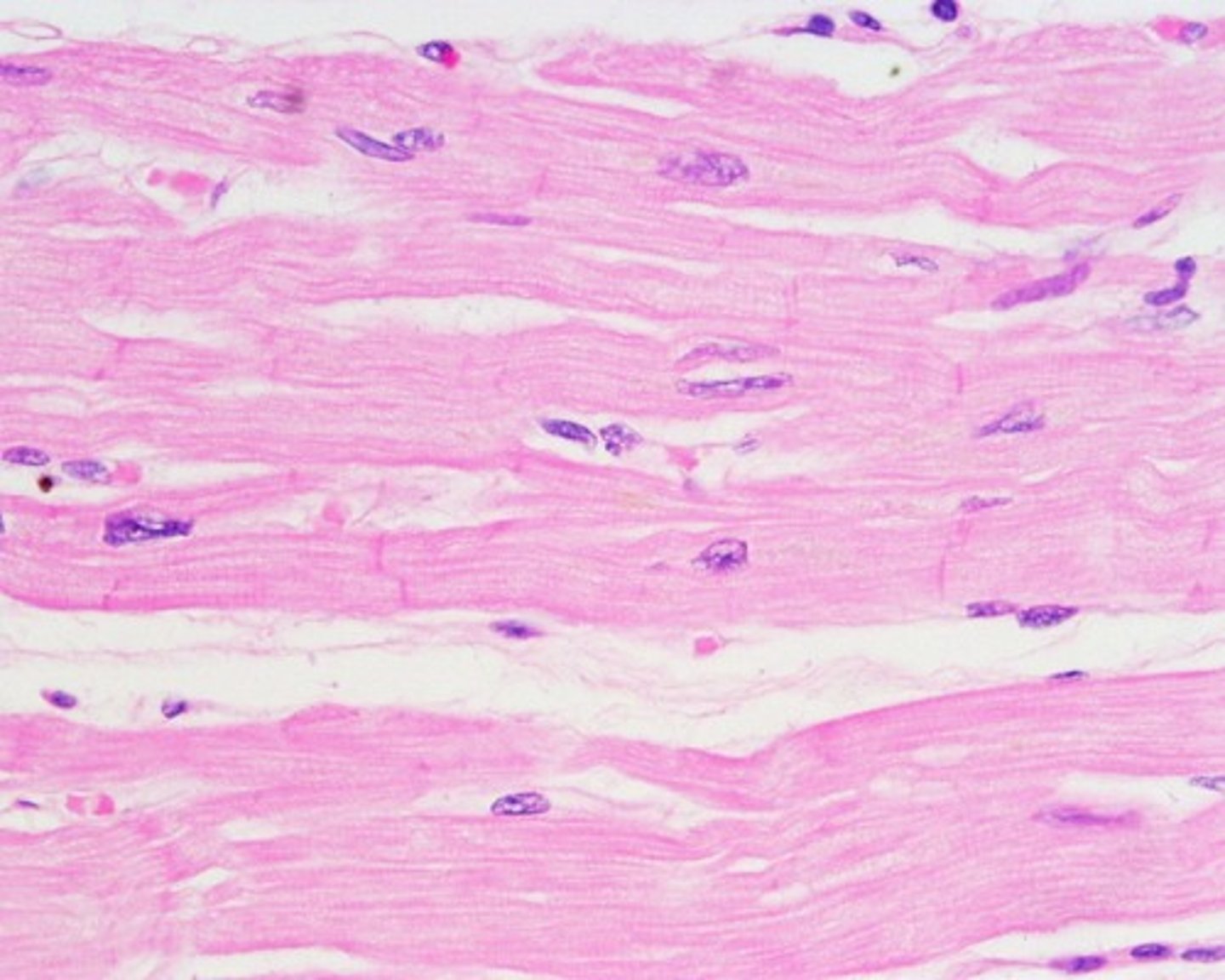
cardiac muscle tissue
only found in heart, responsible for pumping blood, cells are striated and branched, single nucleus, joined end to end by intercalated disks which contain gap junctions (type of intercellular connection)
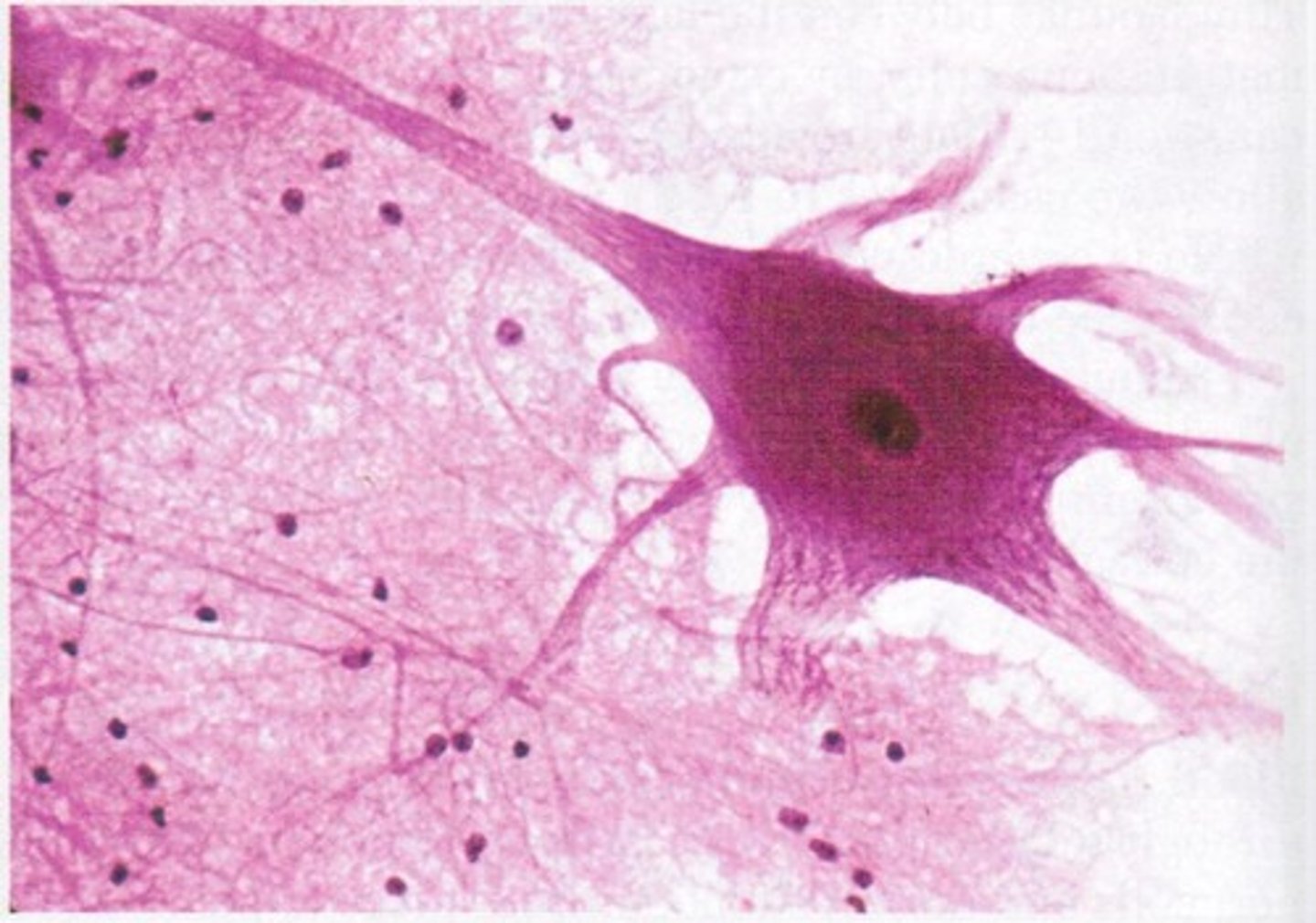
nervous tissue
found in brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, communicates with each other and other tissues by sending electrical signals called action potentials
neurons
cells of nervous tissue
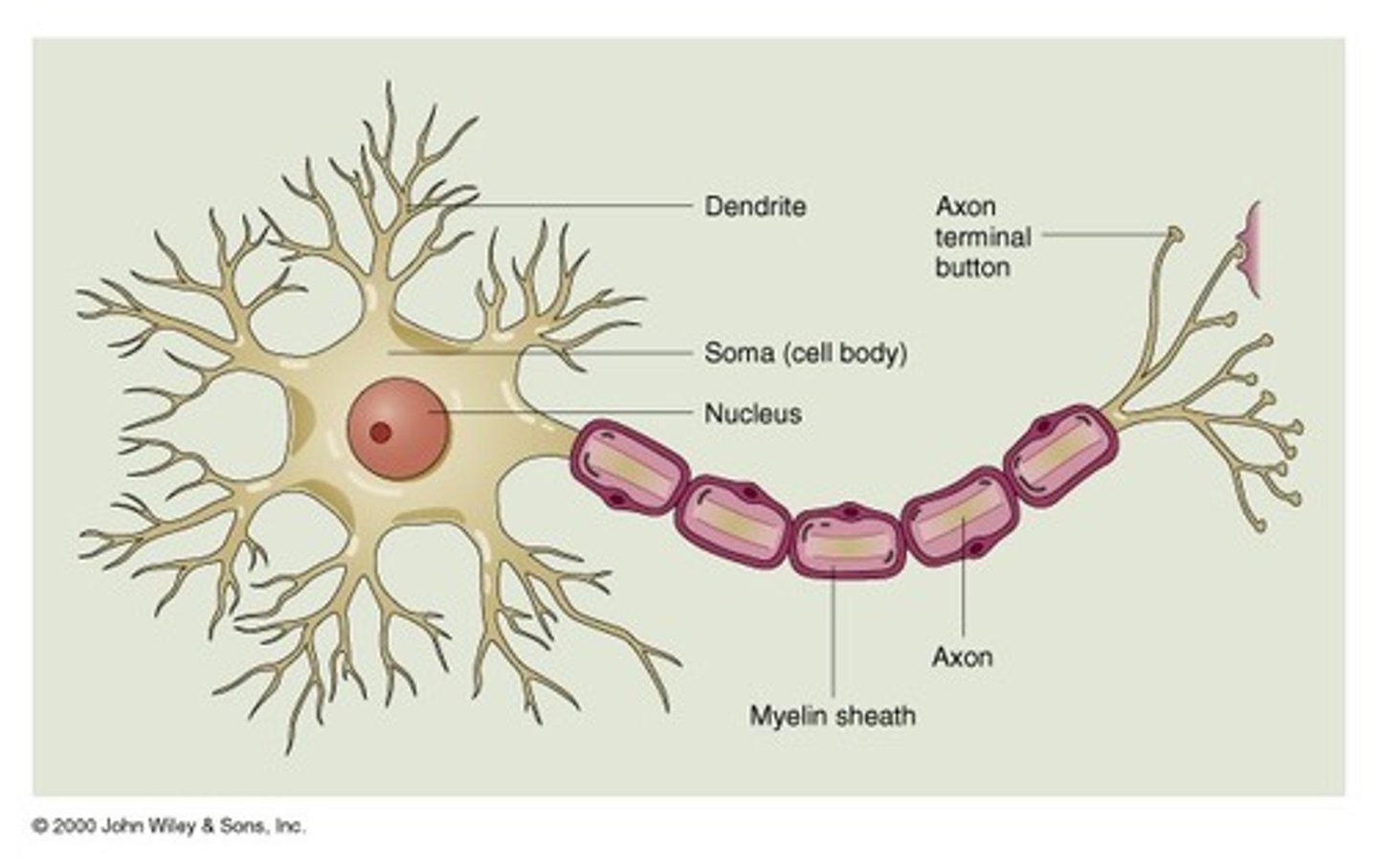
3 parts of neuron
cell body, axon, dendrites
cell body (soma)
contains the nucleus
axon
conducts action potentials away from cell body
dendrites
receive action potentials and conduct them toward the cell body (usually multiple in neuron)
neuroglia
are the support cells of the nervous system; nourish, protect, and insulate the neurons
which types of muscle tissue are involuntary?
cardiac and smooth muscle tissue
which type of muscle tissue is voluntary?
skeletal muscle tissue
nervous muscle tissue picture
skeletal muscle tissue picture
cardiac muscle tissue picture
smooth muscle tissue picture
Muscle Tissue
Tissue made of cells capable of contracting and provides movement
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Voluntary muscle pulls on bones and causes body movements.

Cardiac Muscle Tissue
specialized muscle tissue found only in the heart
Smooth Muscle Tissue
In the walls of internal organs; usually involuntarily controlled
Striated
striped
voluntary muscle
controlled by the conscious mind
involuntary muscle
muscle that responds automatically to brain signals but cannot be consciously controlled
nervous tissue
Tissue that senses stimuli and transmits signals
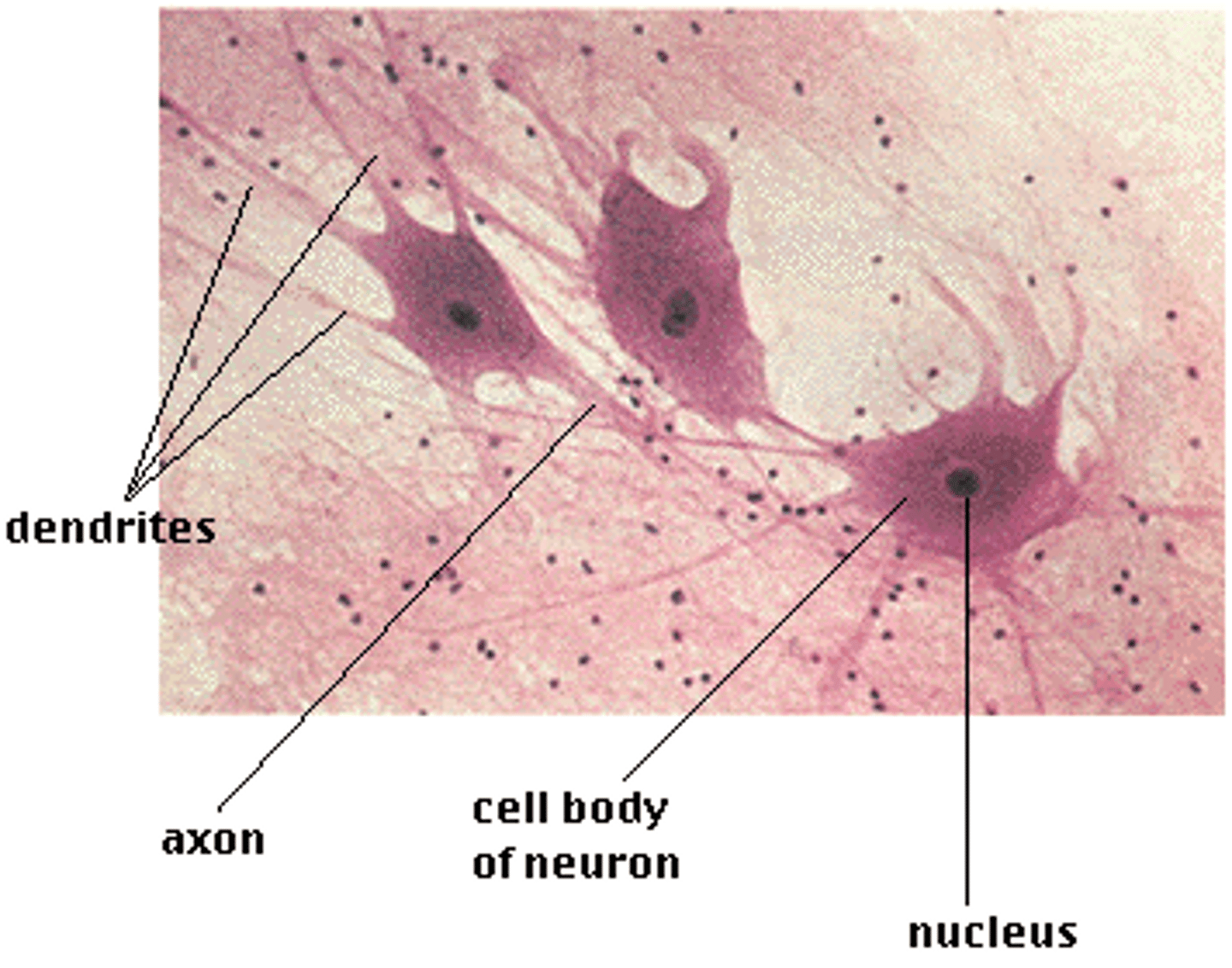
Neurons
Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information.
neuroglial cells
provide physical support, protection, and nutrients for neurons
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
Axons
a part of a neuron that carries impulses away from the cell body