Exam 2 KIN223
1/271
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
272 Terms
Define Cytology
Study of cells
Describe the Light Microscope
2D image
Via visible light
Mag:40x,100x,1000x
Stained with colored dyes
Describe the Electron Microscope
Uses Electrons to illuminate
Stained with HEAVY metal
Describe the Transmission Electron microscope
2D image
Mag:5000x
Electron beam
Define the scanning electron
3D Image
Mag: 3000x
Which microscope has 2D images?
Light
Transmission
From smallest to largest what is the cell sizes? (HINT: REFENSES TO HUMAN HEIGHT/OSTRICH EGG)
Atom → Small molecules → Large macromolecules → ribosomes → viruses → Mitochondria → Red Blood cell → Most plant/animal cells → Human ooctye → Ostrich egg → some muscle and nerve cells → human height
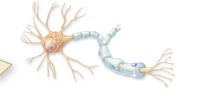
What are some irregular shaped cells?
Nerve cells

What are the biconcave disc shaped cells?
Red Blood cells

What are some cube shaped cells?
Kidney tubule cells
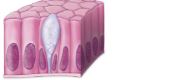
What are some Column shaped cells?
Intestinal lining cells

What are some spherical shaped cells?
Cartilage cells

What are some cylindrical shaped cells?
Skele muscle cells
What are the 3 common structures of a cell?
Plasma membrane
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
I create the outer, lining barrier that separated the internal contents of a cell
I can have modified extensions like Cilia, flagellum, microvilli
What am I?
Plasma membrane
I am the LARGEST structure
I am enclosed by a nuclear envelope
Inside: DNA (mostly) Nucleoplasm, dark staining body aka nucleolus
Nucleus
I am a general term for all cellular contents
I am located in between the nucleus and plasma membrane
I have 3 primary contents: Cystol, Organelles, Inclusions
Cytoplasm
Compare/contrast membrane bound organelles vs NON membrane bound organelles
Membrane- Enclosed, separates the organelles’ contents, includes the E.R, ex: golgi, lysosomes, peroxisomes, mitochondria
NON membrane- NOT enclosed, has: Proteins/ ribosomes, Within the cystol/external surface of E.R, ex: Centrsome, Proteasomes, cytoskeleton
What are some characteristics of inclusions?
NOT an organelle
Clusters of a single type of molecule
Ex: pigaments, nutrients stores
What are the cell functions?
Maintain integrity/shape of cells
Get nutrients and form chem. building blocks
get rid of waste
What are some of the lipid components of plasma membrane
Phospholipids
Cholesterol
Glycolipids
What is the Phospholipids’s function
Makes the phospholipid bilayer
Makes sure the cystol remains in the cell and interstitial fluid remains on the outside
What is the function of the cholesterol?
Strengthens the membrane/stabilize it at temp. extremes
What is the function of glycolipids
aka sugar antennae
Contribute to the glycocalyx
Where are integral proteins?
EMBEDDED within the phospholipid layer
Where are peripheral proteins?
NOT embedded within the lipid bilayer
Loosely attached
What are the 6 major roles by membrane proteins?
Transport proteins
Cell surface receptors
ID markers
Enzymes
Anchoring sites
Cell Adhesion Proteins
What are some of the different types of transport proteins?
Channels
Carrier proteins
Pumps
Symporters
Antiporters
In the anchoring site what is secured?
Secure the cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane
Define diffusion
Movement of ions/molecules down their concentration
Kinetic energy is random
Is dependent upon a concentration gradient
Spreads ions/molecules
If unopposed diffusion results in =
Which diffusion moves small/nonpolar?
Simple
Which diffusion moves charged ions/polar molecules
Facilitated
In simple diffusion describe the process
The movement does not need help
Movement is dependent on the concentration
Impaired respiratory/cardiovascular function can alter the gradient
Which diffusion needs a carrier?
Faciliated
What helps the facilitated diffusion?
Plasma membrane proteins
Describe the 2 types of facilitated diffusion?
Channel medicated diffusion: Small ions via channel leak (opened) or Gated channel (closed)
Carrier-mediated diffusion: movement of polar molecules, needs a carrier proteins, uniporter=one being transport
Define Osmosis
passive moment of water thru semipermeable
Passive transport
Water follows solutes
Define aquaporins
integral proteins that are water channels
Define Osmotic pressure
The pressure exerted by movement of water across semipermeable membrane due to diff in water concentration
Define hydrostatic pressure
Pressure exerted by fluid on the inside wall of its container
Define tonicity
Ability of solution to change the vol/pressure of the cell by osmosis
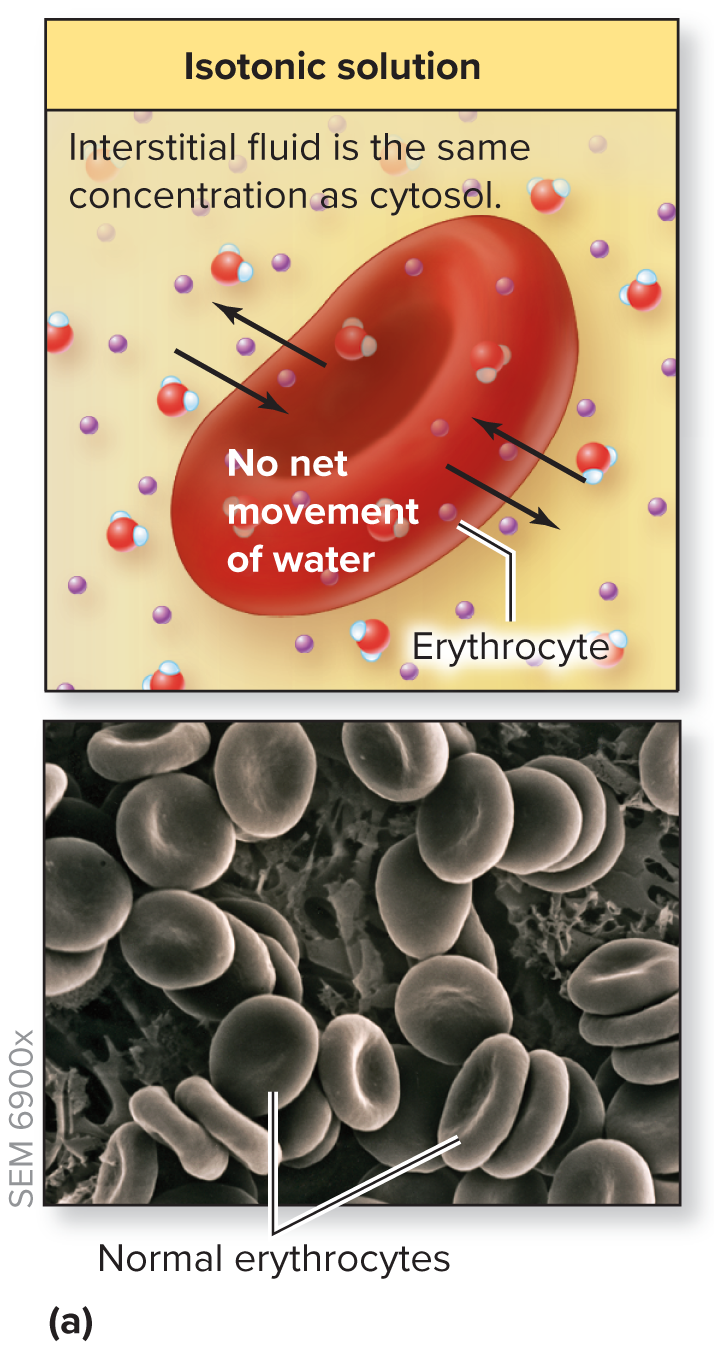
What happens to cell in a isotonic solution
Fluid stays the same
no movement
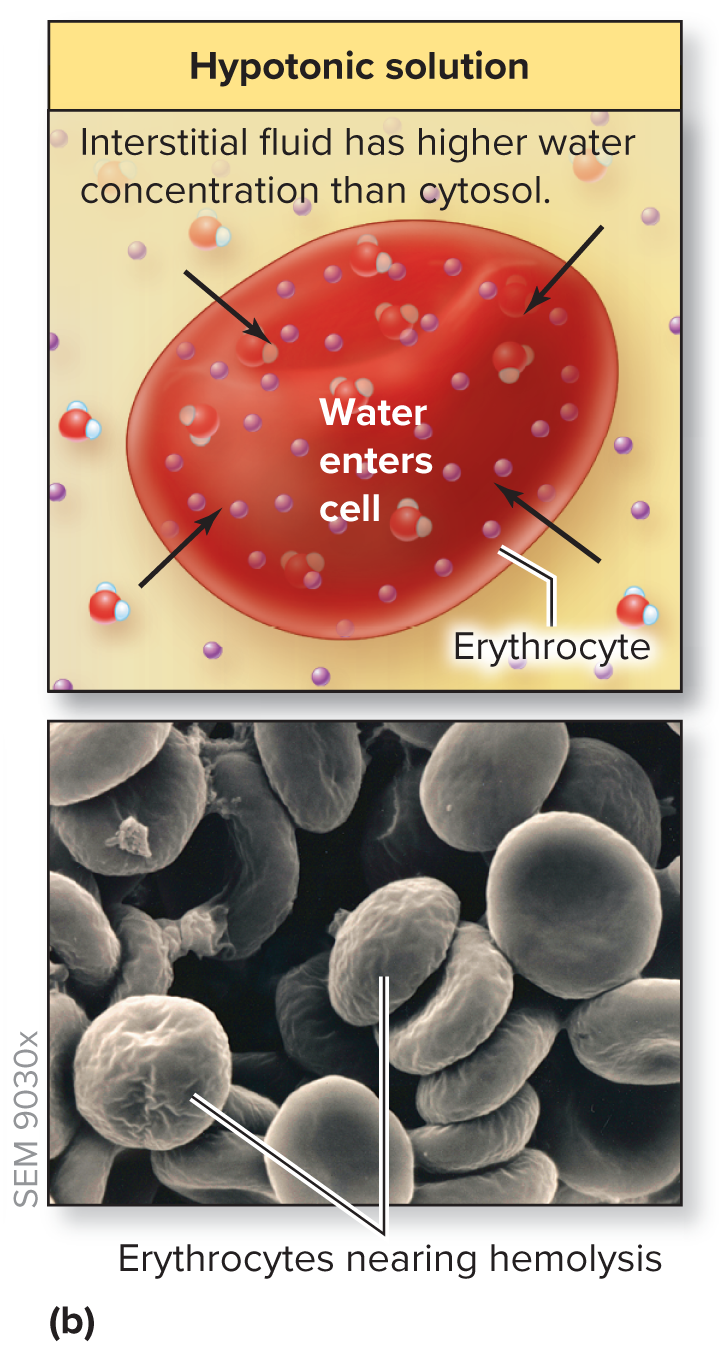
What happens in a hypotonic solution?
Water comes in the cell → hemolysis (CELL GROWS)
In: More concentration
Out: Less concentration
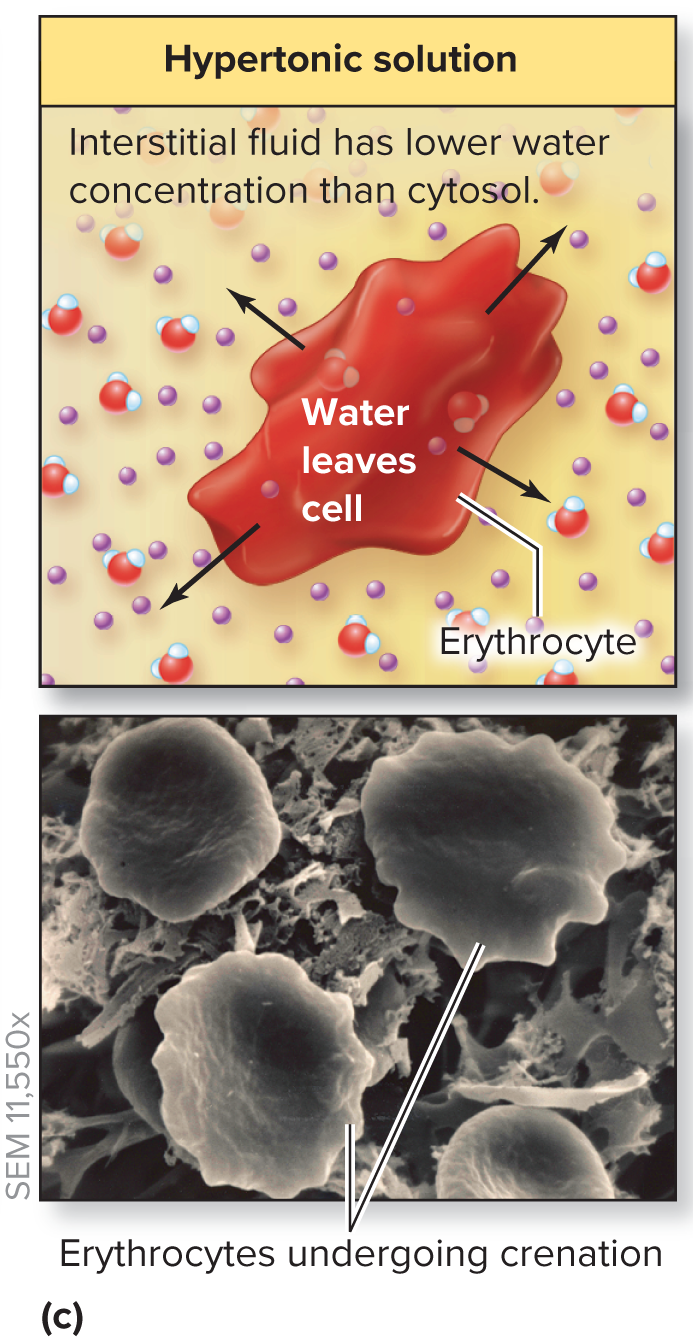
What happens in a hypertonic solution
Water leaves the cell → crenation (CELL SHRINKS)
In: LESS concertation
Out: MORE concentration
Compare and contrast Primary vs Secondary transport
Primary: Uses energy derived directly from breakdown of ATP, provides the phosphate group → change of protein shape and movement of solutes across membrane
Secondary: involves the movement of substance down the concentration gradient aka kinetic energy, symport-2 substance in same direction, antiport- 2 substances in opp direction
Define vesicular transport
Bulk transport
Uses a vesicle
Define exocytosis
Secreted from cell
Define endocytosis
Cellular uptake of large substances/large amounts of substances from external environment into cell
Which vesicular transport is used for uptake nutrients/extracellular debris for digestion, retrieval of membrane regions
Endocytosis
Which vesicular transport is use for large macromolecules
exocytosis
What are the 3 types of endocytosis
phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor mediated endocytosis
Define phagocytosis
Cellular eating
Define pinocytosis
Cell drinking
Receptor mediated
To bind molecules
Define membrane potential
Electrical charge difference shows protentional energy
Define resting membrane potential
When a cell is at rest
What are the cellular conditions for a resting membrane potential
Cell has an unequal distribution of ions/charged molecules
Cystol closes to contain K+ than the surrounding interstitial fluid
Relative amounts of post/neg charged are unequal distributed
More positive on the outside than the inside
Difference in charge are measured by electrodes
Explain the role of K+ concerning RMP
The most important
Loss of K+ = neg charged structure
Movement is opposed by the gradient
Positive charge repeals the movement
Neg charged attacks the K+
Movement is facilitated by the chem concentration but opposed by the electrical gradient
Explain the role of NA+
Sodium diffusion into the cell happens when K+ is lost
Dependent on the electrochemical gradient
The movement = inside being more positive
If Na+ moves in what happens to the K+?
K+ moves out
What is the primary function of the immune system?
Make contact with unhealthy cells and kill em
What is an example of a cell communication via direct contact?
egg + sperm
Why do we need direct contract for cell communication?
Replacing damaged tissues
Making a baby
What is involved for direction contract for our body cells to communicate with our immune cells?
Glycocalyx
How do cells know which are healthy vs unhealthy (involves direct contact)
By seeing if the same pattern of sugars of the glycocalyx are the same as the body cells
What are the 3 general mechanisms of a response to binding of a ligand with a receptor
Channel-linked receptors
Enzymatic receptors
G protein coupled receptors
Describe the Channel Linked receptor
Permits ion passage
Needed to start electrical changes to the resting membrane in the skeletal, cardiac, and nerve cells
Describe the enzymatic receptors
Work as a protein kinase enzymes and are started to directly phosphorylate other enzymes
Provides a mechanisms for modding enzymatic activity in response to external signals
Describe the G protein receptors
Involves protein kinase activation that are started indirectly from the g protein which serves as an intermediate molecule
what are the main functions of the membrane bound organelles of a cell?
Rough E.R
Smooth E.R
Golgi
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Mitochondria
Which organelles make up the endomembrane system? What is their function?
Rough E.R
Smooth E.R
Golgi
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Function: TRANSPORT
Describe the Endoplasmic reticulum aka E.R
An extensive and interconnected network
Varies in shape but has one continuous lumen
Is a point of attachment for both ribosomes and different types of enzymes
Describe the ROUGH E.R
Has a studded like texture because of the ribosomes
What is the ROUGH E.R’s function?
ALL ABOUT PROTEINS
Synthesis: Protein for secretion, incorporation into plasma membrane, and as enzymes within lysosomes
Processing molecules: Mods proteins and store proteins
Organelle formation: Helps make peroxisomes
Vesicle formation: Makes transport vesicles for shipping of proteins to golgi for more mods
Describe the SMOOTH E.R
No ribosomes
Looks just like the rough E,R but no studs
What does the SMOOTH E.R do
ALL ABOUT LIPIDS!
Synthesis: Lipid synthesis
Processing molecules: Carbohydrate metabolism
Detoxi: detox drugs, alcohols, poisons
Vesicle formation: Makes transport vesicles for shipment
Describe the Golgi
Looks like a pancake
Has transport vesicles outside of the pancake
What does the golgi do?
POST OFFICE
Synthesis: Forms proteoglycans
Processing molecules: Mods/stores proteins
Organelle Formation: Syntehsis digest enzymes for lysosomes
Vesicle formation: Creates secretory vesicles for delivering parts of the plasma membrane and letting the contents go from the cell via exocytosis
Describe the step by step process of synthesis, mods, shipping of proteins
(FIGURE 4.23)
Rough ER synthesizes with a protein that is let go in a transport vesicle
Vesicles from ROUGH go to Golgi
Vesicle combos with Golgi
Proteins are modded as they move thru the golgi
Modded proteins are packaged and released within the secretory vesicle
S.V merges with the plasma membrane to either insert molecules or release contents via exocytosis, they also provide digestive enzymes to lyosomes
What is the function of the Lysosomes
CLEAN UP CREW!
Digestion: Breaks down molecules via endocytosis, removing damaged organelles/cellular parts (autophagy), and breaking down cellular components following a cell death (autolysis)
Are small, membrane enclosed, spherical sacs
Has digestive enzymes that are immersed in acid fluid
what organelle is this?
Lyosomes
Are small, membrane enclosed, spherical sacs
Has over 50 different enzymes
Peroxisomes
What is the function of Peroxisomes
ALL ABOUT FATS
Digestion: Breaks down molecules via hydrogen peroxide produced during the process
Synthesis: Makes certain types of lipids (bile salts, plasmalogens)
Describe the mitochondria
Oblong shaped
Has a outer mitochondrial membrane
Matrix inside (Has small dna)
Has a cristae
Inner mitochondrial membrane
What is the function of the mitochondria?
POWERHOUSE
Energy Harvesting: Eats organic molecules to create ATP via aerobic cellular respiration
Also functions with cell death
What are the NON membrane-bound organelles? (All end with -Some the Threesome)
Ribosomes
Centrosome
Proteasomes
Describe the Ribosomes
Have protein and RNA
Has 3 hollow areas called the A,P, and E sites
They are puzzle
What does the ribosome do?
Protein synthesis: Bound ones are destined to be incorporated into the plasma membrane and are exported from the cell or housed within lysosomes, FREE ones are for use within cell
Is close to the nucleus
Has a pair of perpendicular oriented cylindrical surrounded by proteins
What organelle is it?
Centrosome
What are the main functions of the centrosome?
Synthesis: Organizes microtubules and supports their growth in NON diving cells
Cell division: Direct formation of spindle fibers in diving cells
A large barrel shaped protein
Located in the cystol and nucleus
Which organelle am i?
Proteasomes
What is the function of the proteasomes?
THE MANAGER
Protein digestion: Degrades proteins that are damaged/no longer needed
Quality assurance: Control the quality of exported cell proteins
What are the 3 separated types of protein molecules from the cytoskeleton?
microfilaments
Microtubules
Intermediate filaments
What is the function of the cytoskele?
MOVEMENT!
Structural support/organization: maintains cell shape and organizes organelles, stabilizes desmosome cell junctions
Cell division: Separates chromosomes during cell division, splits cell into 2 daughter cells
Movement: Starts cytoplasmic streaming,, a track for movement for organelles/vesicles, helps with muscle contraction
What am I? (Cilia, Flagella , Or micovilli)
I am small, hair-like, that extends from exposed surfaces of some cells
Contains: Supportive microtubule proteins
Enclosed by the plasma membrane
Found in LARGE numbers of certain cells
(Ex: Respiratory passageways)
Cilia
What am I? (Cilia, Flagella , Or micovilli)
Hair-like, LONGER/WIDER
Usually when present there is only ONE
Function: Helps propel an entire cell (EX SPERM)
Flagella
T/F
Movement of Cilia/Flagella occurs thru microtubules within their core, a process that needs energy via splitting of atp molecules
T
What am I? (Cilia, Flagella, Or microvilli)
Shorter/wider
DENSELY packed, lack powered movement
Supported by microfilaments
Provides a more extensive plasma membrane surface for more EFFICIENT membrane transport
Microvilli
Fill in the blanks
(Cilia, Flagella, Or microvill
Just like as not all cells have _____ not all cells have _____
Just like not all cells have CILIA not all cells have MICROVILL
What are the 3 types of membrane junctions?
Tight
Desmosomes
Gap