cell biology - unit I
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 1-7: Proteins, DNA, Gene expression
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are cells?
The fundamental structural and functional units of life.
According to Koshland (2002), what are the seven pillars of life?
Program
Improvisation
Compartmentalization
Energy
Regeneration
Adaptability
Seclusion.
What does “Program” mean in the context of life?
An organized plan encoded in DNA that directs cellular structure and function.
What is meant by “Improvisation” in evolution?
Genetic variation through mutation plus natural selection allows organisms to adapt over phylogenetic time.
Why is compartmentalization essential for life?
Membranes confine biochemical reactions to specific spaces, increasing efficiency and regulation.
What defines life as an energy system?
Life is an open system that metabolizes energy efficiently and parsimoniously.
What is regeneration in cells?
Continuous transport of materials, resynthesis of components, cell division, and reproduction.
How does adaptability differ from improvisation?
Adaptability is rapid (behavioral or physiological), while improvisation occurs over evolutionary time.
What does seclusion refer to?
High specificity in biochemical interactions (e.g., enzyme-substrate, DNA base pairing).
What defines a prokaryotic cell?
A cell lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (e.g., bacteria, archaea).
What defines a eukaryotic cell?
A cell containing a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
What is a key evolutionary advantage of eukaryotic cells?
Compartmentalization allows specialization and complex regulation.
What is the function of the nucleus?
Stores genetic information and is the site of DNA replication and transcription.
What is the function of rough ER?
Protein synthesis for secretion, membranes, and organelles.
What is the function of smooth ER?
Lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage.
What is the main role of the Golgi apparatus?
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for delivery.
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
ATP production via oxidative phosphorylation.
Where are chloroplasts found and what do they do?
In plants and algae; they perform photosynthesis.
What is the function of lysosomes?
Degradation of macromolecules via acidic hydrolases.
What do peroxisomes do?
Carry out oxidation reactions, including detoxification and fatty acid breakdown.
What are the three major cytoskeletal elements?
Actin filaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments.
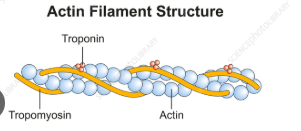
What is the main function of actin filaments?
Cell shape, movement, and muscle contraction.
Actin like active
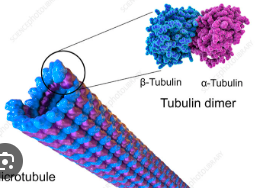
What are microtubules involved in?
Intracellular transport, mitotic spindle formation, and cilia/flagella structure.
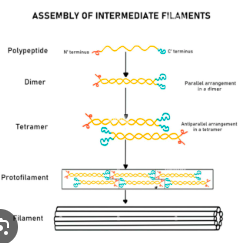
What is the role of intermediate filaments?
Mechanical strength and resistance to stress. Like support beams.
What is the cytosol?
The aqueous interior of the cell where many metabolic reactions occur.
Difference between cytosol and cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is a cup of bubble tea. Cytosol is the tea in bubble tea, organelles are like boba
What is a model organism?
A species studied intensively to understand biological processes applicable to other organisms.
Why are model organisms useful?
They share conserved cellular mechanisms and are experimentally accessible.
Why are proteins considered the most diverse macromolecules?
Because different amino acid sequences can fold into an enormous variety of 3D structures.
What determines a protein’s function?
Its three-dimensional folded shape.
What are the common structural features of all amino acids?
Central α-carbon bonded to an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen, and R group.
What stereoisomer of amino acids is found in proteins?
L-amino acids. (L for living)
What charges do amino acids carry at physiological pH (~7)?
Amino group: positive; carboxyl group: negative.
Which amino acids are polar charged?
Asp, Glu (negative); Arg, Lys, His (positive).
Why are polar charged amino acids especially important?
They largely determine the overall charge of a protein, affecting folding and function
Which amino acids are polar uncharged?
Asn, Gln, Ser, Thr, Tyr.
Which amino acids are nonpolar?
Ala, Gly, Val, Leu, Ile, Pro, Phe, Met, Trp, Cys.
Why is glycine special?
Its small size allows tight packing and flexibility; can act as a hinge.
What structural effect does proline have?
Introduces a kink or bend in the polypeptide backbone.
Why is cysteine unique?
Can form disulfide bonds, the only covalent bonds linking parts of a polypeptide or subunits.
How is a peptide bond formed?
By a condensation (dehydration) reaction on the ribosome.
Why is the peptide bond rigid?
Partial double-bond character due to electron resonance.
What parts of the polypeptide are flexible?
Bonds around the α-carbon, allowing R group movement.
What is a peptide?
A polymer of ~2–50 amino acids.
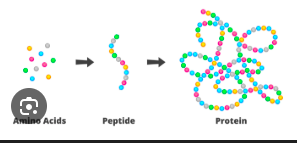
What is a polypeptide?
A longer amino acid chain with one free amino and one free carboxyl end.
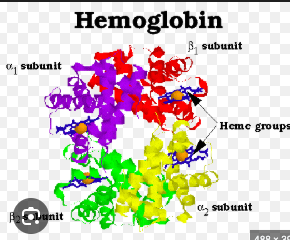
What is a multimeric protein?
A protein composed of multiple polypeptide subunits.
What types of bonds stabilize protein structure?
Covalent (disulfide) and noncovalent (ionic, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals, hydrophobic interactions).
Where are hydrophobic amino acids usually located in folded proteins?
In the interior, away from water.
Where are polar and charged amino acids usually found?
On the protein surface interacting with water.
Why do secondary structures form early during folding?
They allow the polar backbone to exist within the hydrophobic protein core.
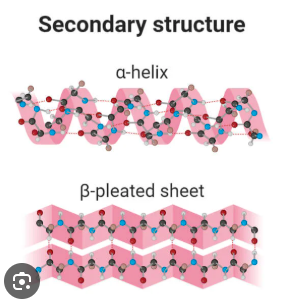
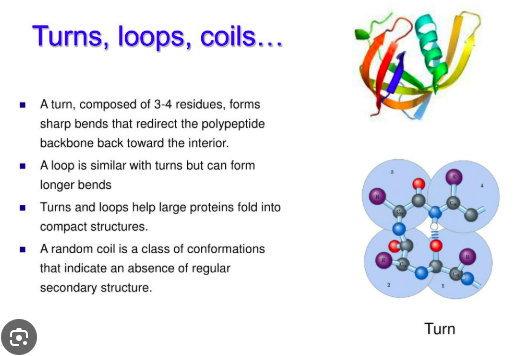
Where are loops or random coils usually located?
On the surface of proteins.