Lifestyle, Health and Risk
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Define causation.
When the change in one variable is responsible for a change in another variable
Define correlation.
When a change in one variable is accompanied by a change in the other.
Why is the difference between correlation and causation important?
Correlation does not mean causation. They may be a 3rd variable providing an impact.
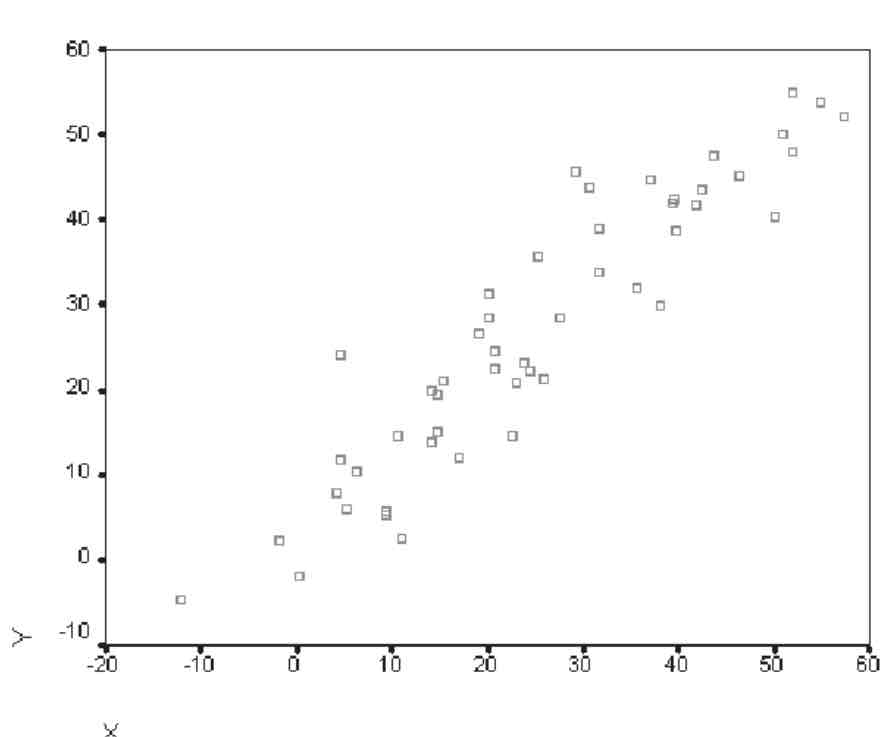
What does this graph show?
Positive correlation
How do hypertensives reduce the risk of CVD?
Decrease blood pressure so the endothelium is less likely to be damaged
How do anticoagulants reduce the risk of CVD?
Reduce blood clotting which reduces the risk of blood vessels being blocked by a clot
How do statins reduce the risk of CVD?
Decrease blood cholesterol levels which reduces risk of an atheroma forming
What are the risks of hypertensives?
Headaches
Drowsiness
Heart palpitations
Swelling of feet and ankles
Persistent cough
What are the risks of anticoagulants?
Rashes
Liver dysfunction
Stomach lining damage
Excessive bleeding in case of injury
What are the risks of statins?
Have to take them long term
Take a while to become effective
Muscle and joint pain
Liver damage
Neurological issues
What is an HDL?
High density lipoprotein
What is an LDL?
Low density lipoprotein
What is the proportion of protein in an HDL?
High
What is the proportion of protein in an LDL?
Low
What is the proportion of cholesterol in an HDL?
Low
What is the proportion of cholesterol in an LDL?
High
What is the type of fat that forms an HDL
Unsaturated
What is the type of fat that forms an LDL
Saturated
What is a lipoprotein?
A protein that transports cholesterol
What is cholesterol used for?
Cell membrane
Forming bile salts
Producing sex and growth hormones
How do LDLs work?
They bind to cell receptors. Cell receptors then become overloaded and cholesterol levels increase
How do HDLs work?
Transport cholesterol to the liver where it is then broken down. Blood cholesterol is lowered and fatty deposits are removed
What is the formula for BMI?
Body mass in kg / height in m²
Give the formula for waist to hip ratio
Waist circumference in cm / hip circumference in cm
Explain why waist to hip ratio is a better measure of obesity and heart disease risk.
Unlike BMI, waist to hip ratio takes into account lean mass and abdominal fat, which is associated with an increased risk of CVD
Explain why obesity increases the risk of CVD
Obesity associated with high blood pressure due to inactivity and bad diet. High blood pressure increases likelihood of endothelium damage which would then cause an inflammatory response. This would then lead to an Athenian which increases the risk of CVD
Explain what is meant by the term energy budget?
The balance between the energy taken in and the energy used during life processes
Describe the consequences of a lifestyle where there is an imbalance between energy taken in and energy used.
If more energy is taken in then used then the excess energy is stored and weight is gained.
If less energy is taken in then used then stored energy is used and weight is lost.
Describe consequences of a lifestyle where energy requirement is less than energy intake. Explain how this links to an increase in the risk of CVD.
Excess energy is stored in the body. This increases cholesterol and therefore blood pressure. This then increases the risk of the endothelium being damaged and causing an inflammatory response. An atheroma then forms which increases the likelihood of CVD
Define BMR
Basal metabolic rate
What is BMR?
The calories that you need each day depending on how much energy your body uses when it is completely at rest
What are the risk factors for CVD?
Smoking
Sex
Inactivity
Age
Diet
Genetics
What risk factors can be controlled?
Diet
Smoking
Inactivity
Which risk factors can’t be controlled?
Age
Genetics
Sex
Why is genetics a risk factor?
You can inherit certain alleles that increase cholesterol production or make you more susceptible to high blood pressure
How does Diet increase risk for CVD?
A diet high in saturated fats increases blood cholesterol levels which increases likelihood of atheroma
A diet high in salt increases blood pressure
How does inactivity increase risk of CVD?
Inactivity can increase blood pressure
How does smoking increase risk of CVD?
Nicotine makes platelets more sticky which increases the likelihood of a blood clot
Carbon monoxide bonds to haemoglobin which reduces oxygen being transported which then increases blood pressure
Reduces antioxidants in the blood which increase likelihood of the endothelium being damaged
How does sex increase the risk of CVD?
Men are at a greater risk due to lower oestrogen levels
How does oestrogen decrease risk of CVD?
Increase levels of HDLs which removes cholesterol circulating in the blood
What is a triglyceride?
A type of fat
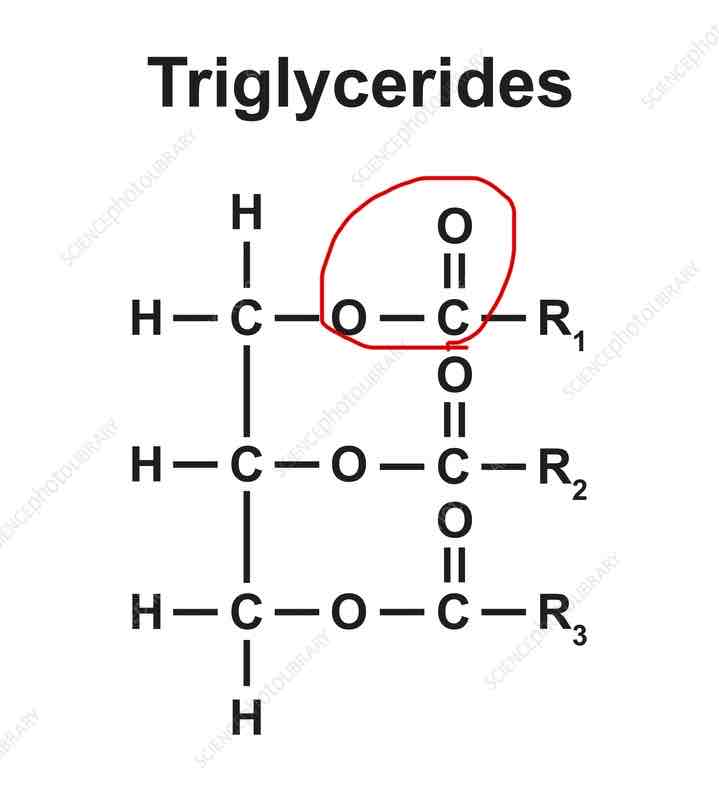
What is an ester bond?
A bond that forms when the hydroxyl group of the glycerol binds with the carboxyl group of the fatty acid.
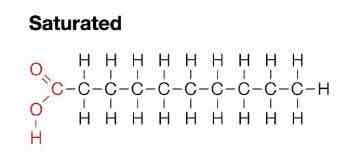
What is a saturated fat?
A fat with only single bonds between the carbons
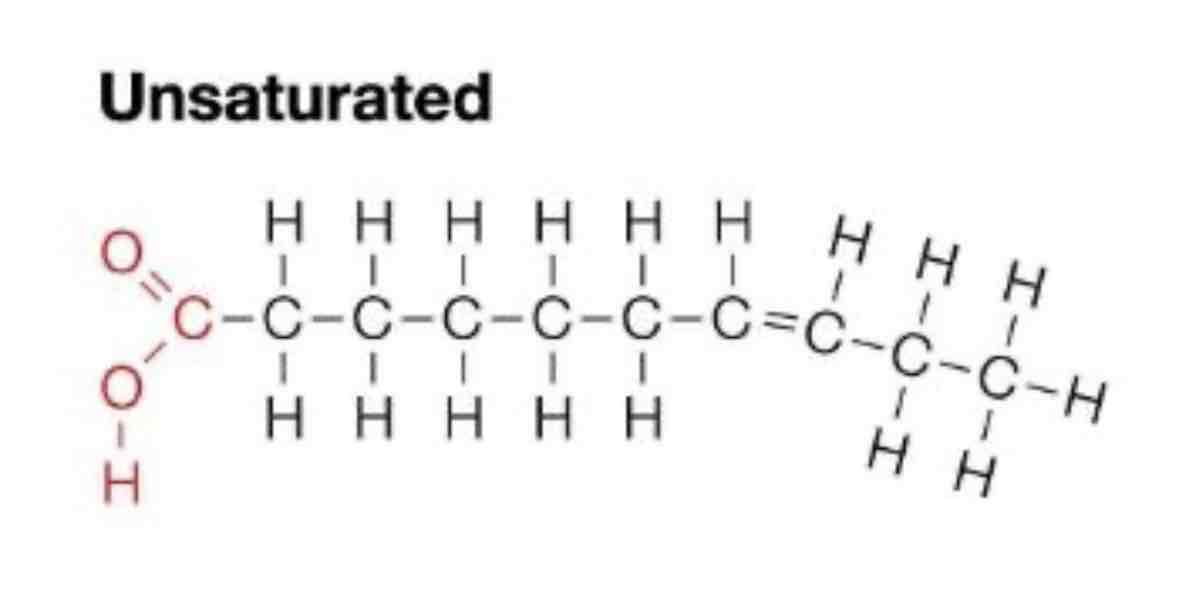
What is an unsaturated fat?
A fat with at least 1 double bond between the carbons
Draw the structure of an unsaturated fat.
.
Draw the structure of a saturated fat.
.
What does an ester bond look like?
.
Name the products of lipid breakdown
Glycerol and 3 fatty acids
How are triglycerides formed?
Condensation reaction
How are triglycerides broken down?
Hydrolysis reaction
Define glycosidic
A chemical bond, like a covalent bond, that connects a carbohydrate molecule to another group.
What is a condensation reaction?
Joining of molecules where hydroxide and hydrogen ions form water
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
The breaking down of molecules where water forms hydroxide and hydrogen ions
How do monosaccharides react to form disaccharides?
Condensation reaction
How do monosaccharides react to form polysaccharides? Specifically amylose and amylopectin.
By condensation reactions. They can form 1,4 glycosidic bonds or 1,6 glycosidic bonds.
How are polysaccharides/ disaccharides broken down into monosaccharides?
By hydrolysis reaction
What monosaccharides make up sucrose?
Glucose and fructose
What monosaccharides make up lactose?
Glucose and galactose
What monosaccharides make up maltose?
Glucose and glucose
How do two monosaccharides form 1,4 glycosidic bonds?
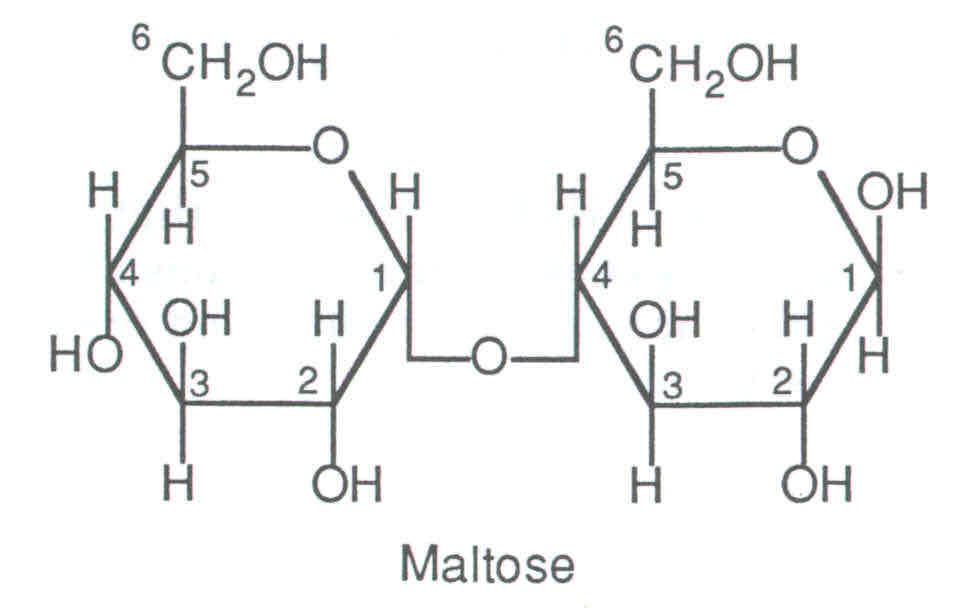
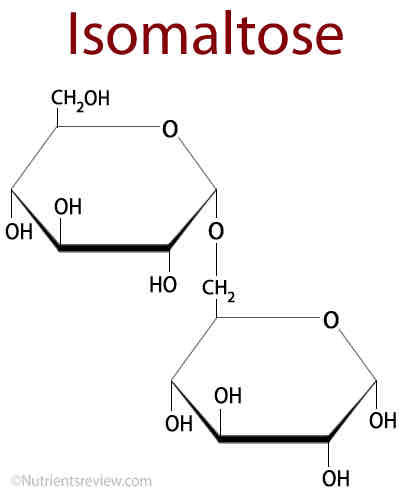
How do two monosaccharides form a 1,6 glycosidic bond?
What is a monosaccharide?
A simple carbohydrate
What is a disaccharide?
2 carbohydrate molecule
What is a polysaccharide?
More than 2 carbohydrate molecule
Define saccharide
A carbohydrate
What does alpha glucose look like?
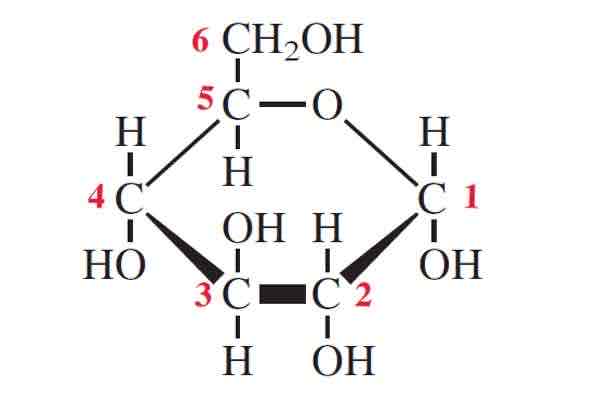
How does the structure and properties of starch make it a suitable storage molecule?
Amylose:
Polymer of alpha glucose
Has 1,4 glycosidic bonds
Straight chain molecule
Forms a helical structure
Efficient at storing lots of glucose
Insoluble
Does not effect the water concentration
Amylopectin:
Polymer of alpha glucose
1,4 and 1,6 bonds
Highly branched molecule
Many terminal glucose molecules. Makes it ideal for rapid hydrolysis to release glucose for respiration
Insoluble- no osmotic effect
Explain how the structure and properties of glycogen makes it a suitable storage molecule
Polymer of alpha glucose
1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
Highly branched
Rapid hydrolysis
Insoluble- no osmotic effect
Stored in muscles and liver
Why is it ethically acceptable to use invertebrates in research?
They don’t have a developed CNS so they are less susceptible to pain.
They are abundant.
What did you do to lessen the harm of the daphnia?
Use cotton wool to immobilise the r daphnia
Use a truncated pipette to avoid crushing it
Add pond water to the slide to avoid the daphnia suffocating
What could be a drawback of using Daphnia in experiments?
They may experience stress or pain during the experiment
Why may some people disagree with using daphnia?
They still feel pain
Independent Variable
A range of at least 5 caffeine concentrations
Dependent variable
The heart rate
How would you measure the dependent variable?
Count the beats in 15 seconds then multiply by 4 to get bpm
Control Variables
Daphnia- use the same daphnia
Temperature- carry out the practical in the same place. Use an LED lamp
Time- use the same time for the daphnia to acclimatise
What is the method?
Place a small piece of cotton wool in the slide
Place a daphnia on the cotton wool
Place under the microscope and count the times the heart beats in 15 seconds
Multiply by 4 to get bpm
Add a drop of caffeine solution to the daphnia
Leave for 2 minutes
Count the beats in 15 seconds. Multiply by 4 for bpm
Repeat with same caffeine solution and different daphnia 2 more times
Repeat with 4 more caffeine solutions if different concentrates
Why are daphnia suitable for the practical?
They have a translucent exoskeleton so the heartbeat can be seen and they don’t have a nervous system so won’t feel pain
How would you adapt this method to investigate the effects of the volume of caffeine on the heart rate of a glass frog?
Immobilise the frog on the slide
Measure the resting heart rate
Add the caffeine and leave for the acclimatisation period
Measure the heart rate with the effect of caffeine
Repeat with the same and different caffeine concentration solutions
Define risk
The possibility of something bad happening.
Define risk factor
Something that increases the risk
Explain why people’s perception of risk and actual risk factor differ.
Risk can be underestimated if the effects happen in the long term.
It can be overestimated if the risk is unfamiliar, out of our control or has severe consequences.
Define probability
The likelihood that something will happen
Explain how you can evaluate experimental design.
If the conclusion is supported by the features of a good experiment then the experiment is valid.
What are the features of a good study?
Representative sample
Controlling variables
Clear aim
Sample size
Valid and reliable results
How can you use standard deviation to state whether there is a significant difference between two mean values?
If the standard deviation between the values doesn’t overlap then there is a significant difference.
How can you ensure results are valid and reliable?
Repeat the study using the same method
Use a representative sample
Control variables that may influence the results
Describe the events in the blood clotting cascade.
Blood vessel wall damages
Platelets join to the damaged tissue and each other to form a platelet plug
Platelets produce thromboplastins
Thromboplastins convert prothrombin to thrombin with Ca2+ ions and vitamin K
Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrins
Fibrin produces a mesh that traps red blood cells and forms a clot
Explain how blood clotting can impact blood flow and respiring tissues.
Blood clot forms in blood
Narrows lumen of blood vessel
Restricts blood flow
Stops transport of oxygen downstream
Cells downstream don’t get oxygen
Cells can’t respire and die
Where is prothrombin produced?
In the liver.
What is required for thromboplastin to function?
Ca2+ and Vitamin K from the plasma.
Define fibrin.
Substance that traps red blood cells to form a clot.
Define fibrinogen.
Substance that is converted to fibrin.
What is the clotting cascade.
The process that forms a clot.
What is a heart attack?
Myocardial Infarction
When an artery is blocked or restricted and stops transport of oxygen to heart muscles.
Risk factors for atherosclerosis.
High blood pressure
Obesity
High blood cholesterol (dietary factors)
Smoking
Inactivity
Genetic inheritance
How does atherosclerosis develop?
Endothelium damaged by things such as high blood pressure
White blood cells respond to site of damage
Substances in blood like cholesterol get caught by white blood cells and form atheroma
Calcium salts build up and form a hard plaque
Arteries harden
Blood flow restricted, increasing blood pressure
Explain how atherosclerosis can impact blood flow and respiring tissue.
Blood flow restricted by the build up of plaque.
Stops transport of oxygen to cells downstream.
Cells cannot respire due to lack of oxygen.
How is atherosclerosis a positive feedback loop?
Damage is caused by high blood pressure
Damage then increases blood pressure
Blood pressure then further damages arteries
Define atherosclerosis.
The build up of plaque that either fully or partially blocks an artery.