Visual and Pupillary Pathway
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
LGN location
dorsolateral (up and out) aspect of the thalamus on the left and right side of the thalamus
main purpose of LGN
processing visual info from the retina and filtering the most relevant info to V1
what terminates in the LGN
RGC axons
what are the axons that leave the LGN called
optic radiations
what helps filter LGN output
input from the superior colliculus and feedback from the visual cortex regarding visual signal
what are the 6 layers of the LGN for
bottom up:
layers 1&2: magnocellular
layers 3-6: parvocellular
where are the koniocellular layers
in between the 6 layers of the LGN
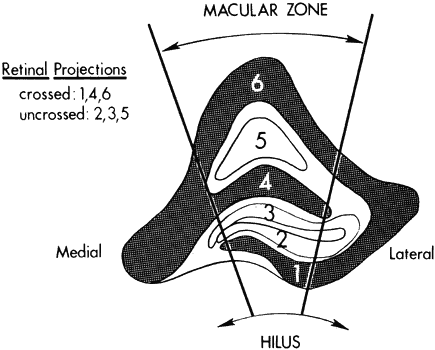
what is retinotopic mapping
each layer of the LGN only gets input from one eye
type of input depends on where the object is in the VF
fibers from each eye that carry info from the same part of the VF lie next to each other in the LGN
an object located in the right hemifield of each eye will project to the layers of the LGN in the (right/left) side
left
what layers do crossed and uncrossed fibers go to
uncrossed: 2, 3, 5
crossed: 1, 4, 6
ex: if something is located in the right visual field, it will project to the left LGN; contralateral nasal retinal fibers (temporal field of right eye) will go to layers 1, 4, and 6, while ipsilateral temporal retinal fibers (nasal field of left eye) will go to layers 2, 3, and 5
if something moves from the superior peripheral to inferior peripheral visual field, where does it travel in the LGN
medial to lateral
where do macular fibers project in the LGN
large central wedge
where do optic radiations leave the LGN
posteriorly
BV processing (does/does not) occur at the LGN
does not
receptive fields of magno and parvo cells
center surround
are parvo or magno cells most sensitive to red-green
parvo
parvo cells are sensitive to (high/low) SF and (high/low) temporal frequency
high SF (fine details)
low TF (slow movements)
magno cells are sensitive to (high/low) SF and (high/low) temporal frequency
low SF (large details)
high TF (fast movements)
what cells have a higher speed of visual signal transmission and why
magno
have larger axons
what cells are monochromatic
magno cells
konio cells respond to:
blue yellow contrast
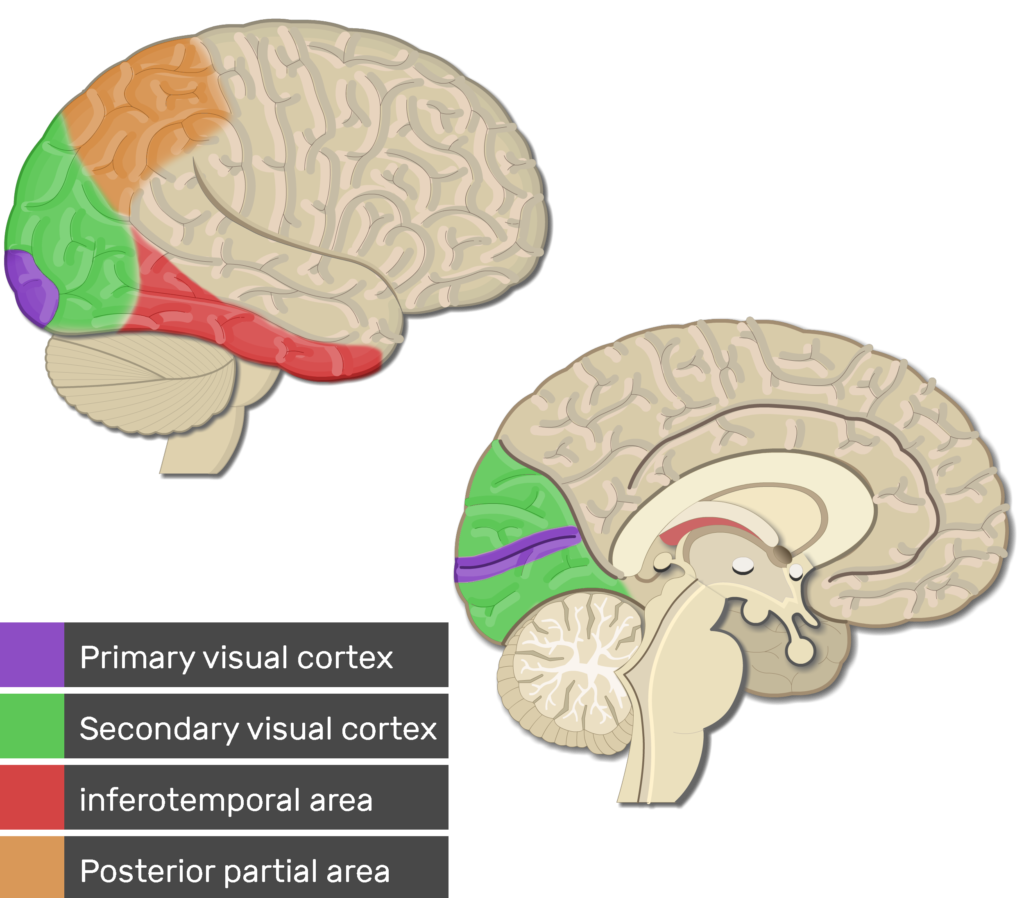
3 other names for the visual cortex
striate cortex
brodmann area 17
V1
borders/location of the visual cortex
outer surface of occipital lobe anteriorly towards the medial occipital lobe
ends anteriorly at the parieto-occipital sulcus
how is the visual cortex structured
6 layers
each layer has 2 maps (1 for each eye) of the opposite visual hemifield
what input drives V1
input from the LGN via optic radiations
V1 is the 1st location in the visual pathway to do what 2 things
binocular processing
evaluates visual input based on size, orientation, direction, shape, and texture
what layer of V1 receives primary visual input
layer 4
how are V1 cells organized
into ocular dominance columns that respond to visual input from only 1 eye
how are ocular dominance columns organized
hypercolumns that combine ocular dominance column with orientation column
4 types of cells in layer 4 of V1
non-oriented, simple, complex, end-stopped
non-oriented cells
cells with center-surround receptive fields that get input from the LGN
do not respond to stimulus orientation
simple cells
cells with elongated center-surround receptive fields that respond to stimulus orientation
stimulus has to be correct width, orientation, and position within the receptive field
also respond to edges, color, and depth
receptive fields likely product of multiple center surround LGN receptive fields
what type of cells are considered simple cells
P-cells
respond to color and edges
how are p-cells organized within V1
organized into blobs
blobs vs. interblobs
blobs: respond to color
interblobs: resppond to size and orientation
complex cells
respond to objects moving in a certain direction within a certain orientation
object needs to be located within the complex cell receptive field to get response, do not respond to object position in space
receptive fields do not have center-surround orientation, combined input from many simple cortical cells
what type of cells are complex cells
M-cells
respond to movement
end-stopped cells
respond to lines with a specific length and orientation
process combined input from multiple complex cells
role of V1 layers 2&3
processing layers that send axons to other layers
role of V1 layers 5&6
send axons to subcortical areas (superior colliculus, thalamus, midbrain, pons)
what layer provides feedback to the LGN and what is the purpose of that
layer 6
allows V1 to regulate its own input
extrastriate cortex
V2-V5
responsible for complex processing of visual info
2 main locations within extrastriate cortex
inferotemporal cortex: what
middle temporal cortex: where
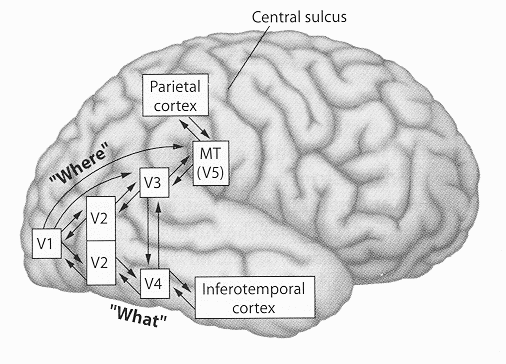
what is the inferotemporal cortex responsible for
ventral pathway (what)
identification, object recognition, object constancy
what is the middle temporal cortex responsible for
dorsal pathway (where)
spatial relationship of object to surroundings, direction, velocity, motion
where does the superior colliculus get info from
V1
posterior optic tract fibers before they reach LGN
what does the superior colliculus control
saccades, visual orientation, foveation
SC does not analyze visual input for perception
where do frontal eye fields get info from
V1
2 main functions of frontal eye fields
pupil response to near objects
initiation of voluntary and reflex eye movement
what area of brain initiates voluntary saccades
superior colliculus and frontal eye fields
what is cortical magnification of the fovea
foveal visual input makes up large percentage of visual cortex
allows us to identify central fine details more easily
what does EOG stand for and what does it measure
electrooculogram
measures the difference in electrical charge between the front and back of the eye to assess RPE health
how is EOG performed
electrodes attached to inner and outer canthus of eye
patient is told to make a series of left and right eye movements under light and dark adapted conditions
electrical potential is recorded over 30 minute period
when is electrical potential the lowest during EOG and what is this called
8 minutes of dark adaptation
dark trough
when is electrical potential the highest during EOG and what is this called
10 minutes of light adaptation
light rise
what is the arden ratio
light rise/dark trough
indicates health of RPE
what are arden ratio norms
greater than 1.8: normal
less than 1.65: very abnormal
1.65-1.8: subnormal
what can the EOG be clinically used for
diagnoses of diseases that impact RPE: Best’s, Stargardt’s, advanced drusen, RPE anomalies
not useful for disease differentiation, useful for confirmation
what does ERG stand for and what does it measure
electroretinogram
records retinal graded potentials in response to light to measure outer retinal activity
what layer of the retina is the ERG not assessing and why
ganglion cell layer
ERG assesses graded potential and GCL uses action potential
process of performing ERG
patient is maximally dilated and dark adapted for 45 minutes
retina is flooded with various light stimuli
patient is tested under dark and light adapted conditions to isolate rod and cone function
how is rod function isolated in ERG
using blue flash with slow flicker in dim background
how is cone function isolated in ERG
using red flash with fast flicker in bright background
what are the 3 waves of the ERG response
A wave: negative wave
B wave: positive wave
C wave: positive wave
what does each ERG wave represent
A wave: negative wave represents photoreceptor activity
B wave: positive wave represents bipolar and muller cells
C wave: positive wave represents RPE cells
which wave is rarely used clinically and why
C wave: tests for RPE cell function but if RPE function needs to be tested EOG is test of choice
how is an electronegative ERG classified
loss of B-wave
what is contribution of rods vs. cones to b-wave under dark adapted conditions
rods:cones ratio in retina: 13:1
rods contribute 75% and cones contribute 25% to dark-adapted b-wave amplitude
what are pattern ERGs used for
target RGCs by using a complex stimulus
what are multifocal ERGs used for
record responses of multiple retinal locations allowing for retinal disease to be localized
what are serial ERGs used for
track foreign bodies in the retina
what clinical signs classify retinitis pigmentosa
bone-spicule pigmentation, vessel attenuation, waxy optic disc pallor
what does an ERG look like in early vs. late RP cases
early: scotopic (rod) ERG response is abnormal
late: ERG is completely extinguished due to poor function of rods and cones
what does VEP stand for and what does it measure
visually evoked potential
electrical response of brain activity to visual stimulus
how is VEP performed
wires placed on scalp overlying V1 in back of head
patient looks at alternating checkerboard display
how long does response in visual cortex to visual stimuli take
100 milliseconds
normal vs. abnormal VEP
normal: large positive wave that peaks at 90-110 msec after stimulus presented
abnormal: waves that peak after 110 msecs
limitations of VEP
VEP tells you that there is something wrong between the fovea and V1, but it cannot tell you where
what diseases can be diagnosed with VEP
ON tumors, optic neuritis, retinal disorders, demyelinating disease
path of afferent pupillary fibers in light response
travel with RGC fibers to posterior 1/3 of optic tract, where they exit and synapse in the pretectal nucleus of the midbrain
fibers project from the pretectal nucleus contra and ipsilateral and go to the EW nucleus (tectotegmental tract)
what does damage to the tectotegmental tract (path to EW nucleus from midbrain/pretectal nucleus) lead to
argyll-robertson pupil
what characterizes argyll-robertson pupil
light-near dissociation
since the issue is at the path from the pretectal nucleus to the EW nucleus (light response), the near response is unaffected (path from FEF to EW)
pupils will not constrict for light, but will constrict for near
ARP = Accommodative Response Present
what disease is argyll-robertson pupil associated with
tertiary syphillis
path of pre-ganglion PS fibers from EW nucleus
leave each EW nucleus and go to ciliary ganglion in the orbit
path of post-ganglionic PS fibers in light response
go from ciliary ganglion to iris sphincter and ciliary muscles
where do efferent PS fibers for miosis and accommodation begin
EW nucleus
anisocoria is always a response of:
efferent pathology
when does near reflex triad occur
fixation is shifted from far to near object
what mediates pupillary constriction in the near reflex triad
frontal eye field
how does the pupil response innervation change in near reflex triad vs regular pupillary constriction
since it is mediated by the FEFs instead of the pretectal nucleus, the FEF activates the EW nucleus instead
from there, the fibers do the same projection to the ciliary ganglion, and then the sphincter and CM
efferent pathway stays the same but afferent pathway changes
how does the sympathetic NS impact pupil size
controls supranuclear activity, causing decreased EW activity
EW activity is what prompts pupillary constriction, so sympathetic innervation causes an increase in pupil size
when uninhibited, how do EW neurons function
continuously fire action potentials to sphincter for miosis
what happens to pupil size during sleep or anesthesia, and why
supranuclear control is inhibited so the SNS cannot control the EW nucleus
increase in EW activity causes miotic pupils
prectectal nucleus is associated with ______ while FEF is associated with _______
light response
near response
what is the main disease tested for with EOG and ERG
EOG: Best’s
ERG: RP
what CN is the EW nucleus part of
CN III
disease that causes damage at the ciliary ganglion
adie’s tonic pupil
how will Adie’s tonic pupil present
ADie’s: Acute Dilated pupil
since the issue is at the ciliary ganglion, both light and near response will be affected
light response is worse: segmental constriction and wormlike movement of pupil
also blur at near due to loss of accommodation from ciliary ganglion
what systemic side effect is common in Adie’s
loss of deep tendon reflexes
how is Adie’s tonic pupil diagnosed and why
.125% of pilocarpine in the eye will constrict the pupil
sphincter muscle is not getting any innervation/acetylcholine (super-sensitized muscle) so any little amount of cholinergic innervation will make it constrict