RAF general Service knowledge
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Who was the father of the RAF?
Lord Trenchard
When was the RAF formed?
1st April 1918
What services were the RAF FORMED FROM?
Royal Flying corps and the Royal Naval air service
Who invented the jet engine?
Sir Frank Whittle and Hans Von Ohain
What was the first Jet fighter used by the RAF?
Gloster meteor
What is the RAF motto in english?
Through adversity to the stars
What is the RAF motto in latin?
Per adura ad astra
Where is RAF college?
RAF Cranwell
Where is HQ air cadets?
RAF Cranwell
Where is the RAF HQ?
RAF High Wycombe
Who is the Marshall of the royal air force?
Prince Charles
Where are the Red Arrows based?
RAF Scampton
What is the aircraft currently used by the Red Arrows?
BAE systems hawk T1
Who is commandant of the air cadets?
Allen Lewis
What is the purpose of group 1 in the RAF?
To understand, control and exploit the battle space in order to deliver battle winning Combat Air power
What is the purpose of Group 2 in the RAF?
Generate, sustain and develop the forces needed to succeed on current and future operations
What is the purpose of Group 22 in the RAF?
Training
Where is operation shader?
Syria
Where was Operation Azotize?
Estonia and Lithuania
What is the RAF communications network called?
RAF Telecommunications network
What does RADAR stand for?
Radio Detection and Ranging
What factors affect Lift?
Airspeed, Angle of Attack, Air density and wing shape
What is the priority of right of way from Glider, Balloons, Airships and powered aircraft?
Balloons, Gliders, Airships, powered aircraft
What is the Aerodrome Controller?
They work in the airfield where they have a clear view of the whole airfield and they are in charge of all aircraft on the ground and in the air
What does the runway controller do to allow take off
Shows a steady green lamp
What does the runway controller do to prevent a landing?
Shows a steady red lamp
What does the runway controller do to prevent take off?
Fires a red cartridge
When were the air cadets formed?
5th February 1941
Where is the main RAF show held every year?
RAF Fairford
How do you convert between magnetic North and grid North?
Grid to Mag add, Mag to grid get rid +-3 degrees
If two aircraft are flying along side each other at the same height which aircraft would give way?
The one on the right
What does ILS stand for?
Instrument Landing System
What are airways?
They are imaginary tunnels in the sky between 10 and 20 nautical miles wide
If an Aircraft is flying under an airway do they need permission?
no
Where is RAF Mount Pleasant?
Falkland Islands
What is teletalk used for on an airfield?
Communicating with Air Traffic Control, station commander, fire services and medical
What was the name of the first jet bomber to enter service with the RAF?
The Canberra
When was the RAF's nuclear strike force formed?
1955
What was the name given to the volunteer American pilots who flew with the RAF?
Eagle Squadrons
Who was the first female jet fighter in the RAF?
Flight Lieutenant Jo Salter
What is the average stalling angle?
about 15 degrees
What are the free types of telephone systems used on an airfield?
BT system, The Defence Fixed Telecoms System and landlines
Which north do you use in navigation
Grid North
Which star do you use to find North?
the Pole star
How can you find the Pole star?
follow the pointers in the group of stars known as the Great Bear or Plough.
How to find North with a watch
hold your watch horizontally with the hour hand pointing at the sun. Now bisect (halve) the angle between the hour hand and the 12 o'clock position. This line points due south. In British Summer Time (Apr - Oct) bisect the angle between the hour hand and the 1 o'clock position.
Difference between Grid and Mag North in degrees
In the British Isles the magnetic north pole is presently between 3° and 5° west of true north
The difference between true north and grid north arises because:
Grid lines get closer together near the poles of the Earth.
A one sided arrow represents
magnetic north
An arrow with a star represents
true north
The angular difference between magnetic north and true north is called.
Variation
Positioning your map to relate to features on the ground is called:
Setting the map.
Which north changes its position slightly over the years?
magnetic North
The capsule of a Silva compass is often filled with a liquid to:
"damps" the compass needle so that it settles down quickly.
What do the needle colours in a compass mean
half red (points north) and half white (points south)
What is resection in navigation?
determining your position more accurately
ways of estimating distance:
a. Timing.
b. Pacing.
Speed of a fit walker 13-16
4 km per hour as measured on the map, plus 1 / 2 hour for every 200m of climbing.
What is handrailing?
following a wall, river, a ridge, electricity pylons or any other linear feature that leads the right way
What is contouring?
Going around a feature such as a hill or valley, rather than over it, as it will take less time overall
An attack point would be:
Any prominent feature that can easily be identified
Where does the runway controller work
in a caravan, painted in red and white squares, positioned to the left of the touch-down end of the runway in use
How would a runway controller warn aircraft to vacate the landing area
showing red flashes on the signalling lamp.
ground to air communications
by radio telephony (RT)
What does a helicopter operating area look like
A white letter "H", 4 metres high with a 2 metre crosspiece
Stationary object hazards are marked by
a three sided solid, mounted on a pole set in a round base.
Indicator of bad ground
A white canvas "V" marker with a red band.
A 1m-long striped solid, alternating yellow and black
Yellow flags or squares on light stakes (sides of squares are approximately 0.61 m)
The two main radio aids likely to be seen at Royal Air Force airfields are;
a) Digital resolution direction finding (DRDF)
b) Instrument landing system (ILS)
You can use an airway if:
a. The pilot has a valid instrument rating.
b. The aircraft is fitted with appropriate radio and navigational equipment.
c. The flight is made in accordance with the rules.
Is clearance needed to use an airway?
Yes, and the flight plan must be submitted to the ATCC
Does a pilot need permission to fly through an airway?
provided clearance and radar control is obtained from the appropriate ATCRU.
What does the abbreviation DRDF stand for?
Digital resolution direction finding
When two aircraft are approaching head on...
They both move to their respective right
When two aircraft are on converging courses...
The one on the left gives way
An aircraft being overtaken...
has right of way and the overtaking aircraft must move to the right
When two or more aircraft are approaching to land at the same time...
the lower one has right of way, unless the captain of the lower aircraft becomes aware that one of the others has an emergency.
First jet bomber in the RAF
Canberra
In what year did the Falklands conflict take place?
1982
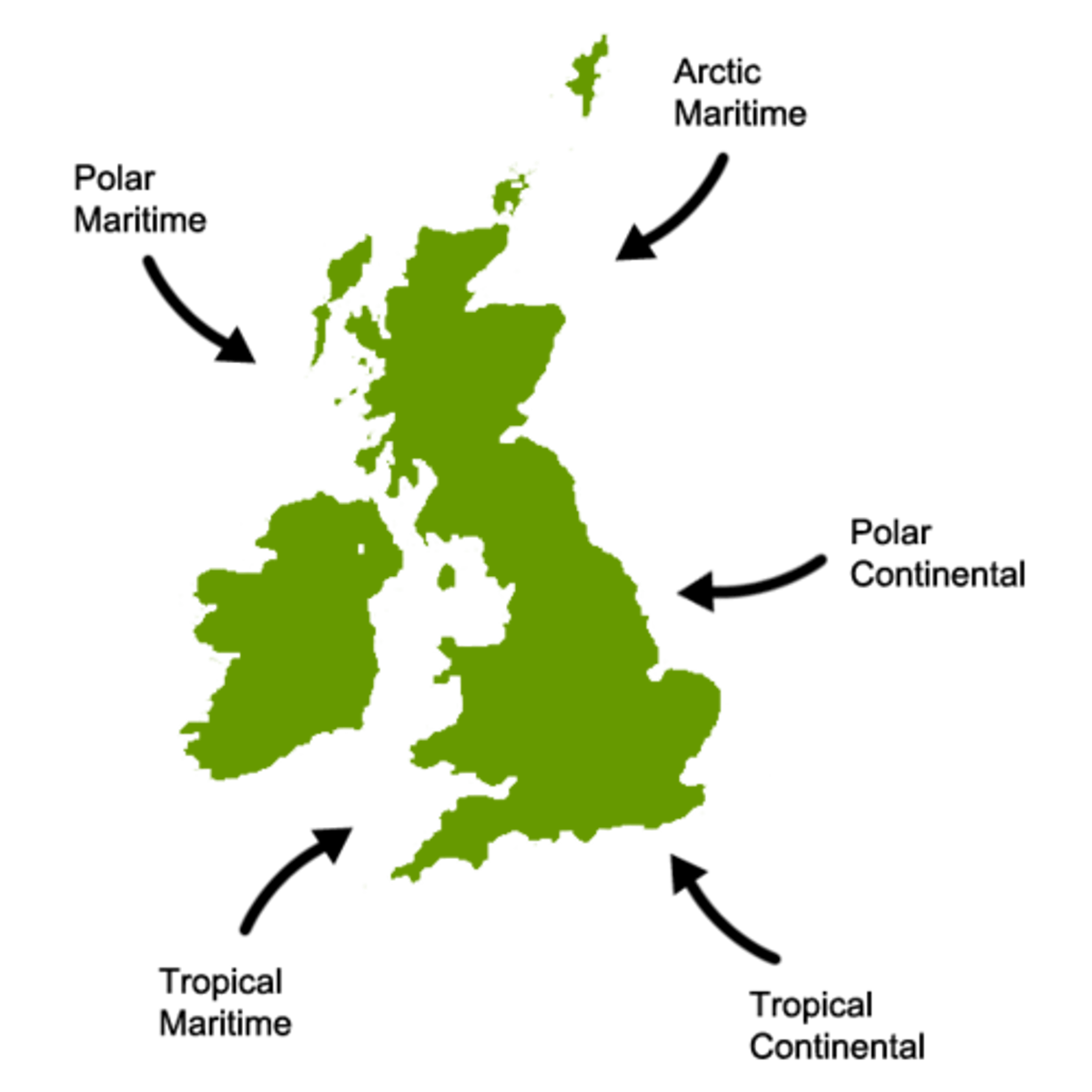
Which air mass affects the UK from the southwest?
Tropical maritime
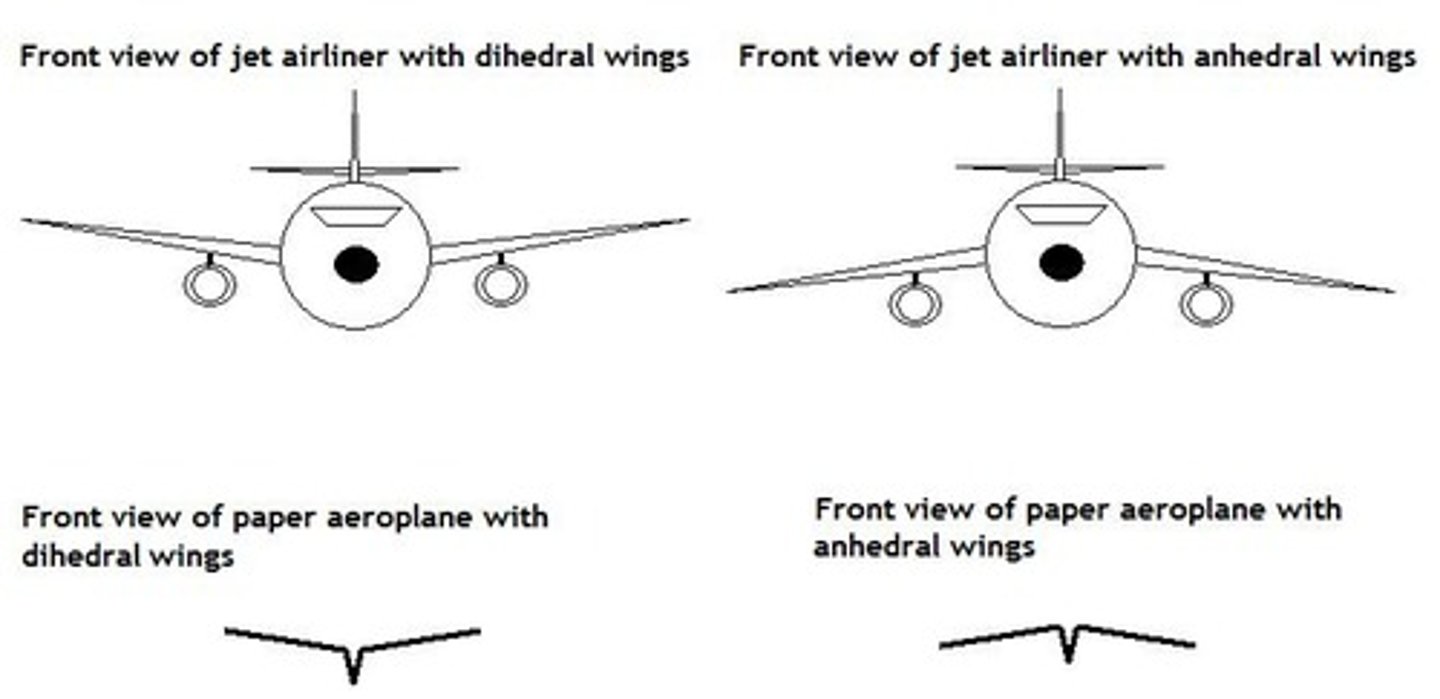
When the wings of a plane point downwards (front view), what is the name of the angle?
Anhedral
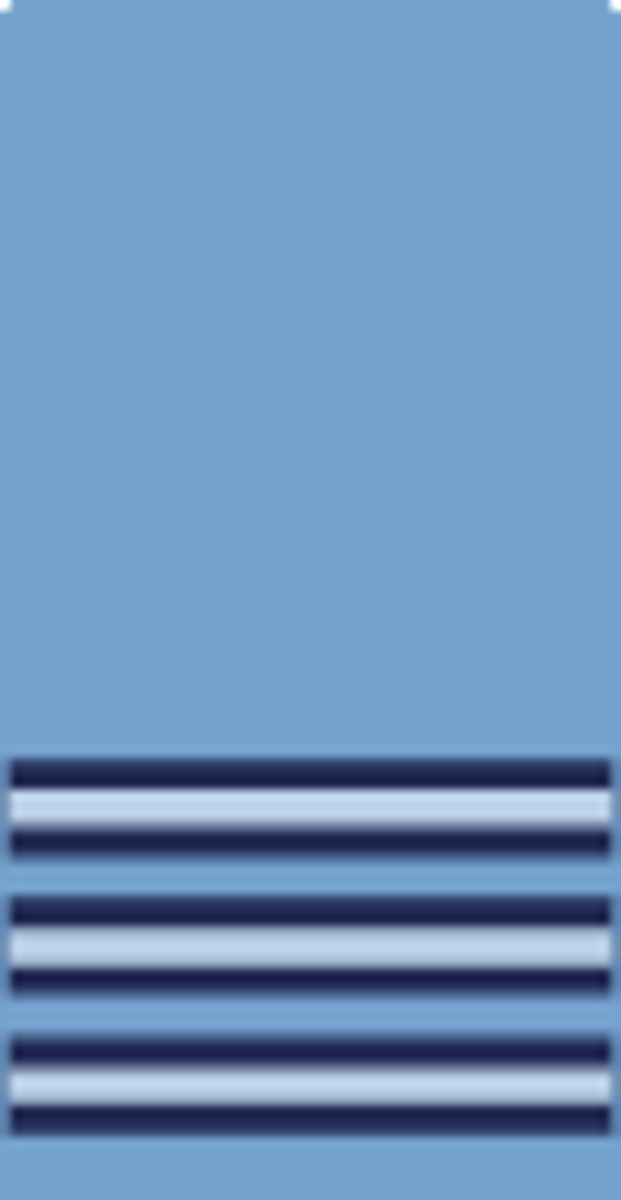
Which rank is shown?
Air commodore

Which rank is shown?
Squadron leader

Which rank is this?
Group captain

Which rank is shown?
Pilot officer

Which rank is shown?
Flying officer

Which rank is shown?
Flight lieutenant

Which rank is shown?
Wing commander

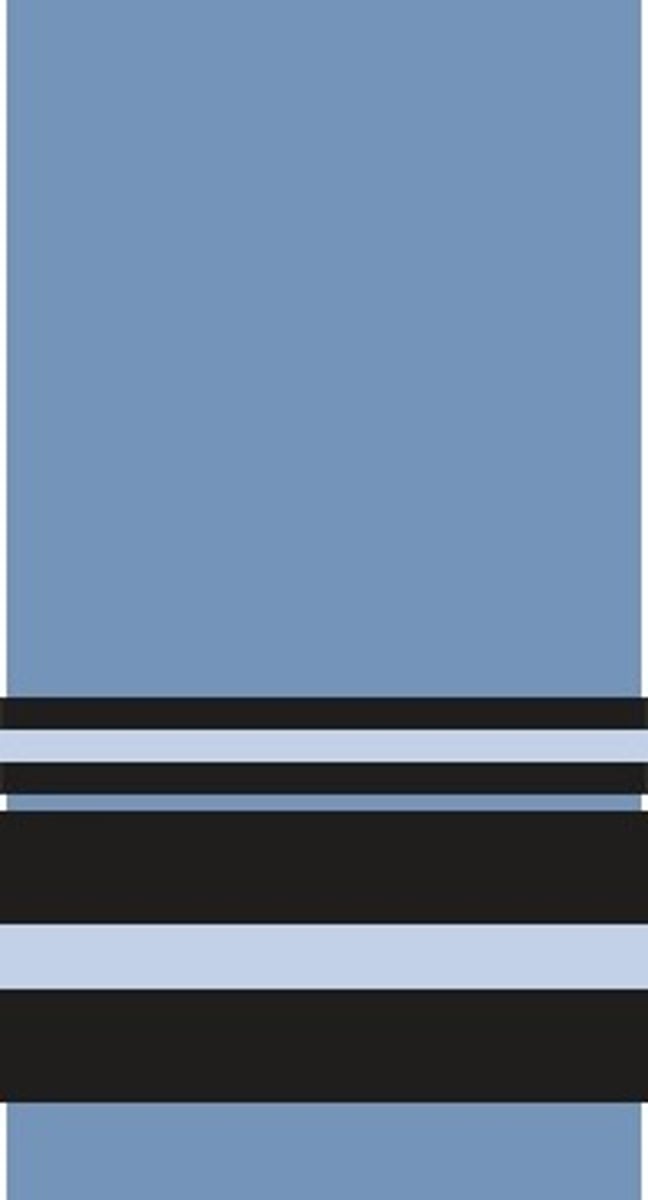
Which rank is shown?
Air vice marshal

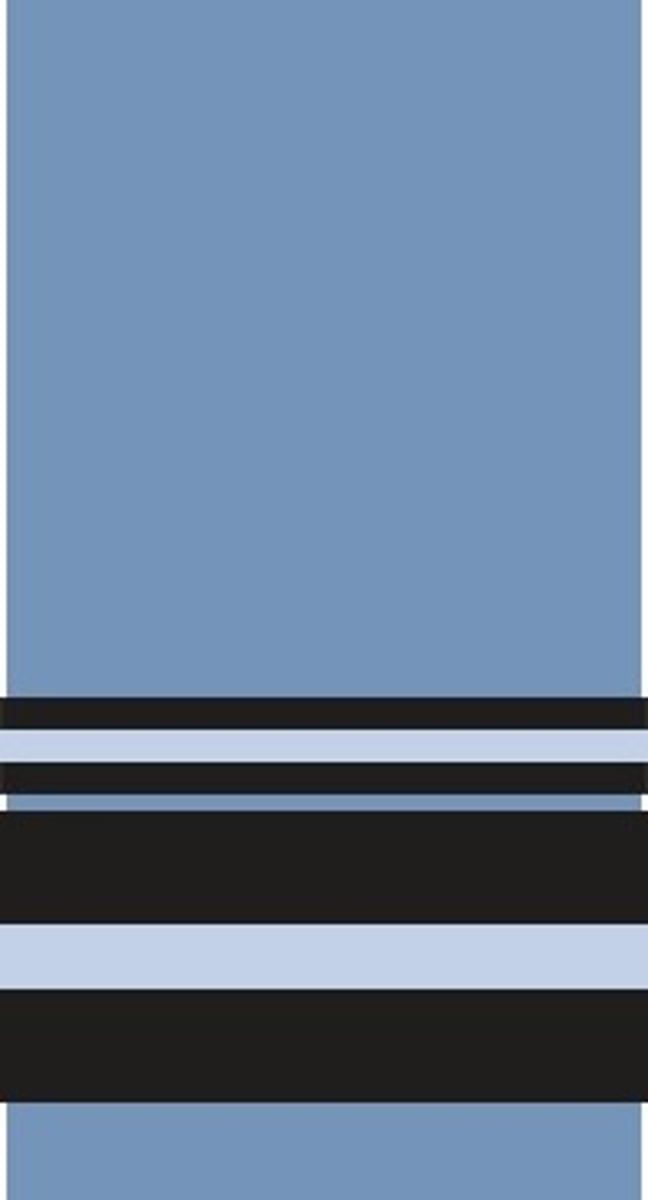
Which rank is shown?
Air marshal

Which rank is shown?
Air chief marshal

Which rank is shown?
Marshal of the Royal Air Force

Which equation relates drag to airspeed?
Drag = airspeed^2
Which aircraft was used by Amy Johnson in her pioneering solo flight to Australia?
Tiger moth
In what year did the Hindenburg disaster occur and which gas was involved?
1937 - hydrogen gas
Which of the 3 V-fighters was the only one to drop live nuclear weapons?
Valiant