Ecological Succession: Primary, Secondary, and Climax Communities
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is succession in ecology?
A series of more-or-less predictable changes that occur in a community over time.
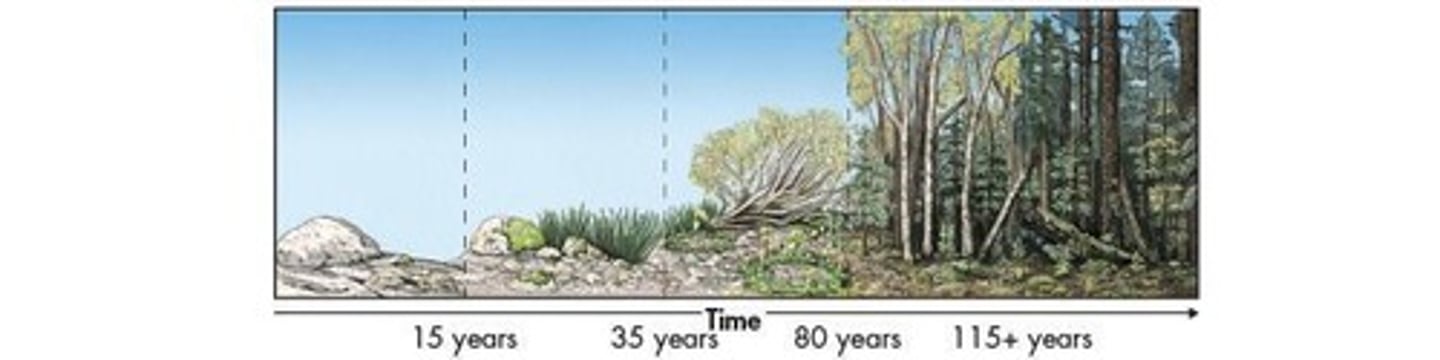
What happens to species during ecological succession?
Some species die out while new species move in, typically increasing the number of different species present.
What is primary succession?
Succession that begins in an area with no remnants of an older community, often following events like volcanic explosions or retreating glaciers.
What are pioneer organisms?
The first species to colonize barren areas, such as lichen, which is a mutualistic symbiosis between a fungus and an alga.
What is secondary succession?
A type of succession that occurs when existing communities are not completely destroyed by disturbances, allowing for faster regrowth.
Why does secondary succession proceed faster than primary succession?
Because soil exists after the disturbance, allowing new and surviving vegetation to regrow rapidly.
What types of disturbances can lead to secondary succession?
Natural disturbances like wildfires and hurricanes, as well as human activities such as logging and farming.
What is a climax community?
A stable and mature ecosystem that can return to its original state following a disturbance.
Do ecosystems always return to their original state after a disturbance?
Secondary succession in healthy ecosystems often reproduces the original climax community, but recovery may vary after extensive human-caused disturbances.
What role do forest fires play in secondary succession?
While they can kill some trees, other trees are spared, and fire can stimulate their seeds to germinate.
What is an example of secondary succession in the Carolinas?
Abandoned fields that have matured into oak forests over the last century through several stages of succession.
What can create new land or sterilize existing areas leading to primary succession?
Volcanic explosions and retreating glaciers.
What is the impact of disturbances on ecological communities?
Disturbances can lead to changes in species composition, allowing for new species to establish and thrive.
What is the significance of soil in secondary succession?
Soil provides a foundation for new vegetation to grow after a disturbance, facilitating faster recovery.
How do ecosystems respond to natural disturbances?
Many species are adapted to natural disturbances, allowing ecosystems to recover and maintain biodiversity.
What is the relationship between disturbance and biodiversity?
Disturbances can create opportunities for new species to enter and thrive, potentially increasing biodiversity.