Cel Biology - Section 4: Stages of the Cell Cycle
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
!A!: stages of the cell cycle
G1, S, G2, M (s3)
2
New cards
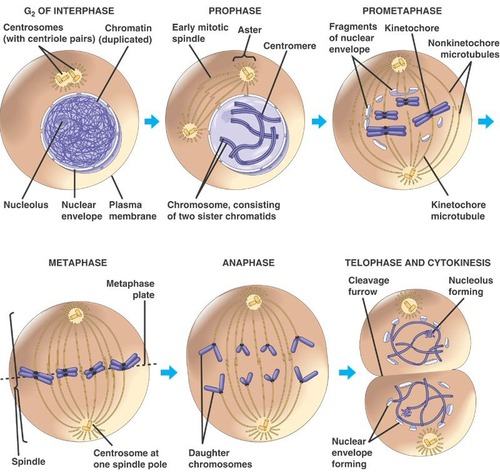
stages of m phase
1. prophase
2. prometaphase
3. metaphase
4. anaphase
5. telophase
6. cytokinesis
2. prometaphase
3. metaphase
4. anaphase
5. telophase
6. cytokinesis
3
New cards
G1 phase
preparation of cell for DNA replication
4
New cards
S phase
DNA replication
5
New cards
G2 phase
cell growth (size, biomass, materials)
6
New cards
M phase
- sorting of materials (chromosomes, organelles) in prep. for separation
- separation of cell into two daughter cells
- separation of cell into two daughter cells
7
New cards
M phase: prophase
- chromosomes begin to condense
- mitotic spindle begins to assemble
- mitotic spindle begins to assemble
8
New cards
M phase: prometaphase
- breakdown of nuclear envelope to allow chromosomes to position accordingly
- attachment of the chromosomes to the spindles (microtubules)
- attachment of the chromosomes to the spindles (microtubules)
9
New cards
M phase: metaphase
alignment of chromosomes at equator (site at which cells will eventually separate)
10
New cards
M phase: anaphase
- sister chromatids (copies of same chromosomes) separate
- chromatids are pulled apart towards spindle poles
- chromatids are pulled apart towards spindle poles
11
New cards
M phase: telophase
- full sets of daughter chromosomes arrive @ spindle poles
- a contractile ring begins to form that starts to "pinch" the cytosol @ site that cells will eventually separate
- nuclear membrane begins to re-form on either pole of cell
- a contractile ring begins to form that starts to "pinch" the cytosol @ site that cells will eventually separate
- nuclear membrane begins to re-form on either pole of cell
12
New cards
M phase: cytokinesis
- a contractile ring "squeezes" the cell to form two daughters
- once fully contracted, this generates cleavage furrow, which reps final stages of separation of two daughter cells
- once fully contracted, this generates cleavage furrow, which reps final stages of separation of two daughter cells
13
New cards
!B!: 3 distinct checkpoints/regulation points of cell cycle
- G1/G0 cell cycle start
- G2/M checkpoint
- metaphase to anaphase transition
- G2/M checkpoint
- metaphase to anaphase transition
14
New cards
G1/G0 cell cycle start (G1-->S)
to enter cell cycle and proceed to S phase:
- is the environment favourable?
- replicating chromosomes costs a lot of E so are there enough nutrients (glucose, AAs, etc.)?
- has it received growth factors and hormones?
- is the environment favourable?
- replicating chromosomes costs a lot of E so are there enough nutrients (glucose, AAs, etc.)?
- has it received growth factors and hormones?
15
New cards
G2/M checkpoint
to enter mitosis:
- is all DNA replicated?
- is environment favourable?
- condensing DNA is extremely dangerous for cells
- is every chromosome anchored and ready to be pulled apart?
- is all DNA replicated?
- is environment favourable?
- condensing DNA is extremely dangerous for cells
- is every chromosome anchored and ready to be pulled apart?
16
New cards
metaphase to anaphase transition
to trigger anaphase and proceed to cytokinesis:
- are all chromosomes attached to the spindle?
- are all chromosomes attached to the spindle?
17
New cards
cell cycle is controlled by..
cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs)
- can phosphorylate several diff. substrate proteins that are critical to cell cycle
- phosphorylation of proteins by CDKs acts as "switch" to progress through specific stages of cell cycle
- can phosphorylate several diff. substrate proteins that are critical to cell cycle
- phosphorylation of proteins by CDKs acts as "switch" to progress through specific stages of cell cycle

18
New cards
what is the switch mechanism to turn the CDK on?
binding to one of several specific cyclin proteins
19
New cards
there are several diff cyclin proteins and their levels..
.. rise and fall at different stages of the cell cycle
20
New cards
cyclins not only "activate" CDK but also...
.. target activate CDKs (active when cyclin-bound) to specific substrates
21
New cards
levels of specific cyclins rise and fall at
different stages of the cell cycle
CDK: levels do not change during stages of cell cycle
cyclin: levels rise and fall with specific stages of the cell cycle (e.g. G1/S-, S-, M-, G2M-cyclins), appear and disappear when needed
CDK: levels do not change during stages of cell cycle
cyclin: levels rise and fall with specific stages of the cell cycle (e.g. G1/S-, S-, M-, G2M-cyclins), appear and disappear when needed
22
New cards
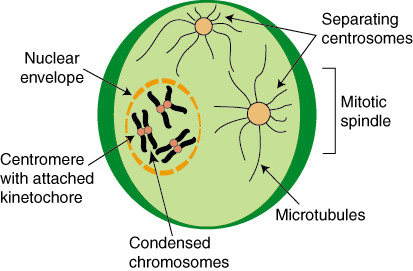
how does M-CDK control G2/M transition? (s7)
- M-CDK activation triggers condensin (protein complex), which causes concensation of chromosomes (orange loops in diagram)
- M-CDK activation causes formation of the mitotic spindle
- M-CDK activation causes formation of the mitotic spindle
23
New cards
M-CDK activation starts mitosis but ... (s8)
... removal of M-CDK needed to finish mitosis
APC/C is a protein complex
- required to allow metaphase to anaphase transition
- leads to degradation (removal of M-CDK)
APC/C is a protein complex
- required to allow metaphase to anaphase transition
- leads to degradation (removal of M-CDK)
24
New cards
cyclin-CDK complexes act like a "timer"
- in some cases, causes degradation or removal of cyclin of previous stage of cell cycle
- in some cases, will eventually cause up-regulation of cyclin of next stage of cell cycle
OVERALL, allows cyclin-CDK complexes to make sure that stages of cell cycle don't all happen at the same time
- in some cases, will eventually cause up-regulation of cyclin of next stage of cell cycle
OVERALL, allows cyclin-CDK complexes to make sure that stages of cell cycle don't all happen at the same time
25
New cards
cyclin-CDK complexes allow for cell cycle checkpoints
- cyclin-CDK complexes can be controlled (i.e. turned off) if cell cycle conditions are not met: damage, insufficient nutrients, insufficient growth factor simulation, failure to complete prev. stage)
OVERALL, allow cyclin-CDK complexes to monitor to make sure moving to next stage of cell cycle is SAFE, if DNA didn't replicate, cycle stops, repair occurs, cycle resumes
OVERALL, allow cyclin-CDK complexes to monitor to make sure moving to next stage of cell cycle is SAFE, if DNA didn't replicate, cycle stops, repair occurs, cycle resumes
26
New cards
triggers for checkpoints that arrest cell cycle s10
3 checkpoints:
1. favourable extracellular environment (arrest in G phase if not)
2. unreplicated/damaged DNA (arrest at G2/M phase if so)
3. chromosome unattached to spindle (arrest in M phase)
- BUT cancer cells can pass these checkpoints and continue the cell cycle over and over again
1. favourable extracellular environment (arrest in G phase if not)
2. unreplicated/damaged DNA (arrest at G2/M phase if so)
3. chromosome unattached to spindle (arrest in M phase)
- BUT cancer cells can pass these checkpoints and continue the cell cycle over and over again
27
New cards
some CDKs are very effective
cancer drug targets
- palbociclip, ribocuclib, abemaciclib
- used for treatment of metastatic breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, other cancers
- palbociclip, ribocuclib, abemaciclib
- used for treatment of metastatic breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, other cancers
28
New cards
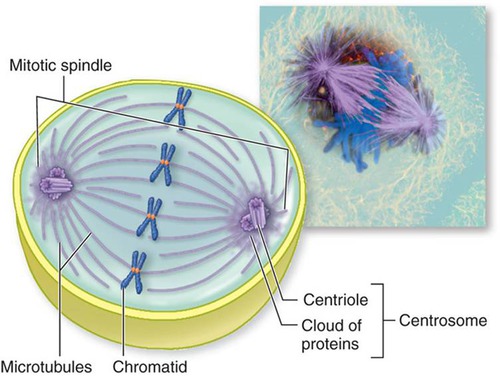
!C!: mitotic spindle begins to assemble in...
.. early mitosis
- begins in prophase
- involves microtubules, centrosomes to anchor microtubules, and many other proteins
- way for cells to ensure that chromosomes are counted for ad divided equally
- begins in prophase
- involves microtubules, centrosomes to anchor microtubules, and many other proteins
- way for cells to ensure that chromosomes are counted for ad divided equally
29
New cards
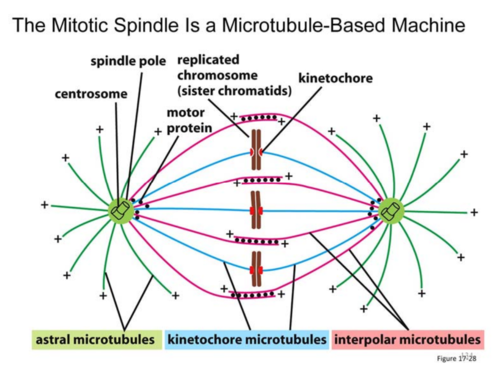
mitotic spindle s4
- bipolar array of microtubules involved in proper separation of chromosomes and other materials during mitosis
30
New cards
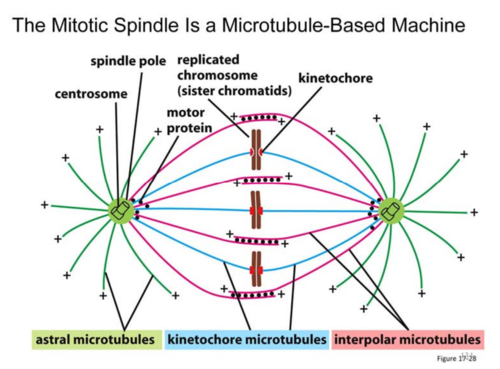
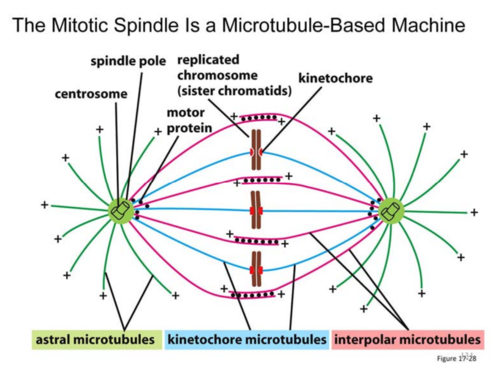
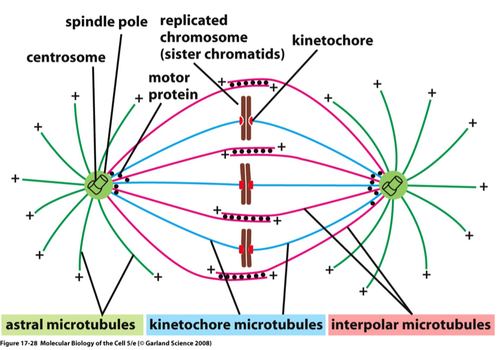
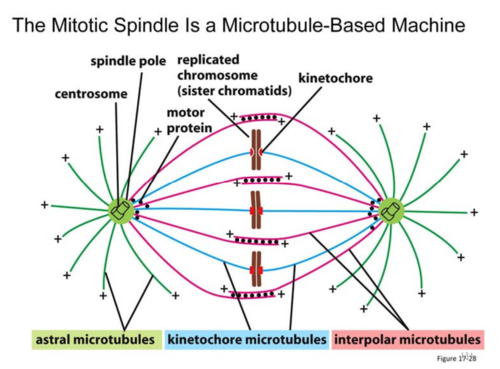
spindle pole
made up of centrosome and other components, all 3 types of microtubules emanate from here
31
New cards
astral microtubules
from spindle pole to cell cortex, helps to "anchor" spindle poles
32
New cards
kinetochore microtubules
from spindle pole to chromosome (attaches @ kinetochore region of chromosome)
33
New cards
interpolar microtubules
from spindle pole to interpolar microtubule coming from other spindle pole to ensure spindle poles stay at opposite poles of cell
34
New cards
kinetochore s5
region of chromosome made up of proteins that allow for anchoring of spindle (kinetochore) microtubules
35
New cards
sister chromatids
identical copies of chromosomes that are held together during early stages of mitosis (i.e. through metaphase)
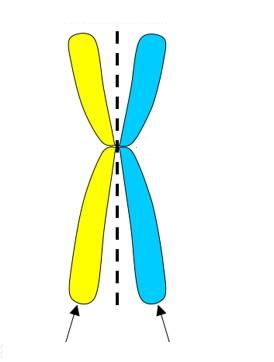
36
New cards
positioning chromatids for correct separation into daughter cells
at transition from metaphase to anaphase, the "glue" that holds sister chromatids together is removed and each sister chromatid is "pulled" towards one spindle pole
37
New cards
how does a cell know when it is time to proceed from metaphase to anaphase
- in metaphase, all chromosomes need to be attached to kinetochore microtubules to prevent improper sorting of chromosomes during cell division
- this can be sensed by making sure all kinetochores are attached to microtubule (that no "free" kinetochores remain)
- this is the metaphase to anaphase transition checkpoint (sensing that there are no "free" kinetochores remaining)
- this can be sensed by making sure all kinetochores are attached to microtubule (that no "free" kinetochores remain)
- this is the metaphase to anaphase transition checkpoint (sensing that there are no "free" kinetochores remaining)
38
New cards
mitotic assembly is a major checkpoint, sensed by..
.. APC/C and controlling metaphase to anaphase transition
- when APC/C blocked, cell stops @ anaphase
- when APC/C blocked, cell stops @ anaphase
39
New cards
drugs targeting the mitotic spindle assembly are..
.. effective cancer therapies
40
New cards
paclitaxel, docetaxel
- chemotherapies used in many types of cancer treatment
- these work by binding and stabilizing microtubules, prevents assembly of mitotic spindle
- trigger metaphase-anaphase checkpoint arrest
- these work by binding and stabilizing microtubules, prevents assembly of mitotic spindle
- trigger metaphase-anaphase checkpoint arrest