politics of the late republic key words
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
cursus honorum
a system of political offices in the senate in Rome, elected annually
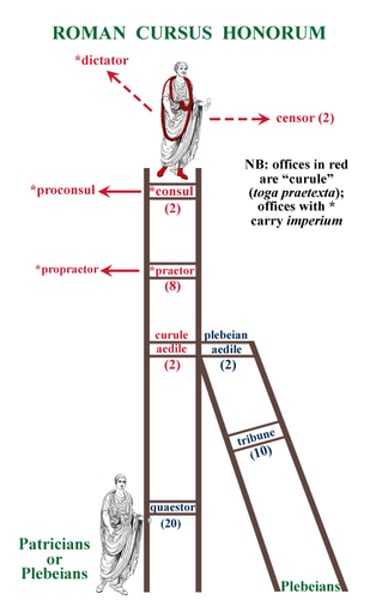
dictator
a position of state established in periods of military crisis and awarded to one man by the consuls for 6 months ONLY
aedile
magistrate in charge of games, markets or buildings in Rome(optional)
amicitia, amicitiae, f.
friendship, bond between friends; alliance, association; friendly relations that furthers the success of influential Romans
augur
a state religious official at Rome who could "read" the flights of birds(known as talking to the auspices)
boni
Men considered to be ideal statesmen: well-educated, traditional, patriotic and experienced enough in politics to accept responsibility for making good decisions for the moral and political health of the state. (a term used by Cicero)
censor
two officials elected by the centuriate assembly for 18 months who were responsible for the census and supervising public morality
centuriate assembly
a voting body of citizens organised into 193 voting "centuries"(determined by wealth), responsible for electing consuls and praetors
clients
citizens who were bound by loyalty to a wealthy patron to support him in all his public interests(e.g. in elections)in return for support and resources
concordia ordinum
"The agreement of the orders": a political ideal held by Cicero in which the original structures of the Republican constitution were encouraged to flourish and continue, with the aristocracy and equites united in the common good of governing the Roman state
consul
one of the two leading senators who presided over the senate
cum digntate otium
"Leisure with prestige": Used in a wider sense by Cicero to refer to an absolute social, religious, legal and political status quo
dignitas
rank, dignity, importance, honour associated with social, religious and political standing
dominatio
a form of autocracy or despotism, which Romans loyal to the res publica loathed
Equites
a rank in the Roman class system which grew in wealth and status through occupation in commerce and finance
First Triumvirate
a private alliance formed in 60 between Julius Caesar, Pompey the Great and Marcus Licinius Crassus enabling each of the 3 men to achieve their personal political short-term goals. It lasted until Crassus's death in 53.
governor
men selected from an elite group of senators who had previously served as praetors or consuls, responsible for the smooth running, safety and taxation of a province of the state.
imperium
the power invested in a consul giving him the military command of the state army
inimicitia
enmity, hostility between families
libertas
freedom
nobiles
a select group of senatorial families distinguished by the inclusion of a consul in their ancestry
novus homō
"new man"; a man who is the first in his family to achieve the senatorial rank
optimates
a group of aristocratic senatorial families whose energies were channelled into the preservation of the political and social status quo
patricians
families whose ancestry could be traced back to the early days of Rome when they formed a ruling aristocratic group from whom the mythical founder of Rome- Romulus- chose the first 100 senators
patron
a man of significant social standing able to offer resources(financial, legal or simply food) to his clientela in return for loyalty
plebeians(plebs)
Roman citizens who weren't patricians. Originally a "lower" order, the plebeians gained significant wealth and nobility as a result of an ongoing "Conflict of the orders" from the 5th-3rd centuries BC
Pontifex Maximus, Pontificis Maximi (m)
Pontifex Maximus, high priest of the Roman state religion, most influential office in Ancient Roman religion
populares(-is singular)
noble senatorial families that aimed to secure power through the support of the people by appealing to them directly with proposals for improving their standards of living.
praetor
2nd in authority to the consuls and presiding over the law courts in Rome
quaestor
the first rung of the ladder of offices; responsible for the state treasury
res publica
"public affairs", Government, State that replaced the monarchy
senate
a deliberative assembly central to the government of the Roman Republic
senatus consultum ultimum (SCU)
abbreviated form of senatus consultum de re publica defendenda, a decree of the senate passed in times of crisis allowing the suspension of normal restrictions placed on consuls to do whatever was necessary to protect the state.
Senates Populusque Romanus (S.P.Q.R.)
The Senate and People of Rome
stoicism
this was a philosophical school founded by Zeno in Greece in the 4th Century BC; stoicism maintained that reason and soul were far more important than the body and it believed Virtus was the ultimate good
the philippics
a term used to refer to Cicero's final series of vitriolic speeches attacking Mark Antony from 44-43, named after the Athenian Demosthenes's Philippic delivered against Philip II of Macedon in the 4th century. Cicero wrote 14 Philippic speeches in all
tribal assembly
a voting body of citizens organised into the traditional 35 "tribes" of Rome(determined by family or by place of habitation), responsible for electing the lower offices in the senates, such as the aediles and quaestors
tribune of the plebs
10 officials elected from the plebeian order to act as a check on the senate and the cursus honorum in Rome
virtus, virtutis, f.
courage, virtue- a defining concept in the life of a Roman man
anaphora
word or phrase that is repeated at the start of neighbouring clauses for emphatic effect
apostrophe
a direct address to a 3rd party to break up the narrative voice
asyndeton
lack of conjunctions in a list to give the description intensity
hyperbole
exaggeration used for literary effect
polysyndeton
the use of unnecessarily large number of conjunctions in a list to emphasise the number of things being listed
praeterito
saying you will not mention something and in doing so deliberately mentioning it and bringing it to mind
rhetorical question
a question to make a point- a question that expects no answer.
tricolon
a series of 3 clearly defined words, phrases or clauses in a sentence. An ascending tricolon is one in which each word, phrase or clause is successively more powerful