Plant Anatomy, Growth, and Water Transport: Key Concepts for Biology
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the three types of plant tissues?
Dermal tissue, ground tissue, and vascular tissue.
What is the function of dermal tissue in plants?
Protection from animals, pathogens, and water loss.
What is the role of ground tissue in plants?
Photosynthesis in leaves and storage in stems and roots.
What are the functions of vascular tissue?
Transport of water, nutrients, and sugars.
What type of growth do apical meristems produce?
Primary growth, which lengthens roots and stems.
What is the role of the vascular cambium?
Produces xylem and phloem for water and sugar transport.
What are the two types of xylem cells?
Tracheids and vessel elements.
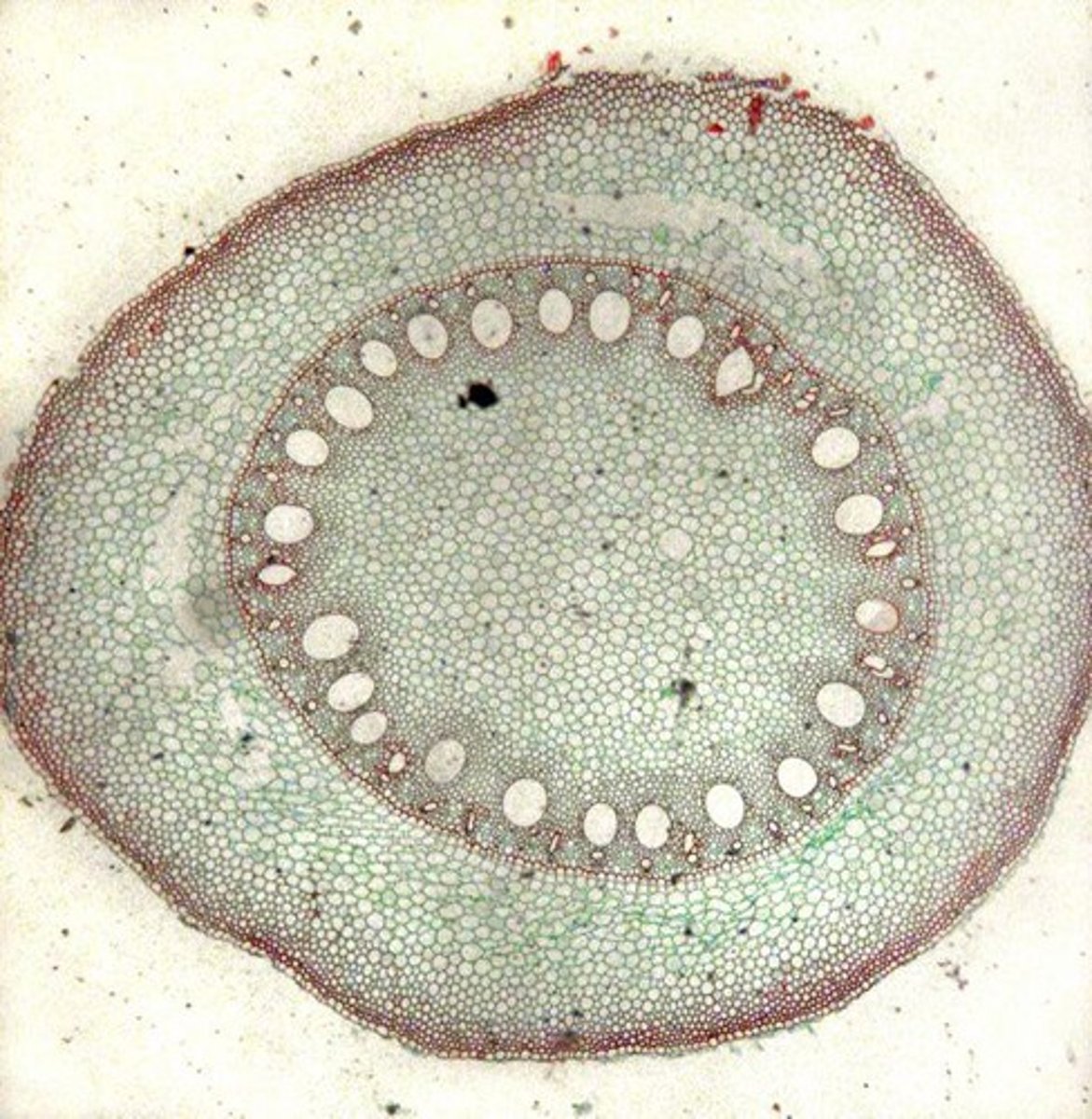
What is cavitation in the context of xylem?
Blockage of xylem by air bubbles due to hot, dry conditions.
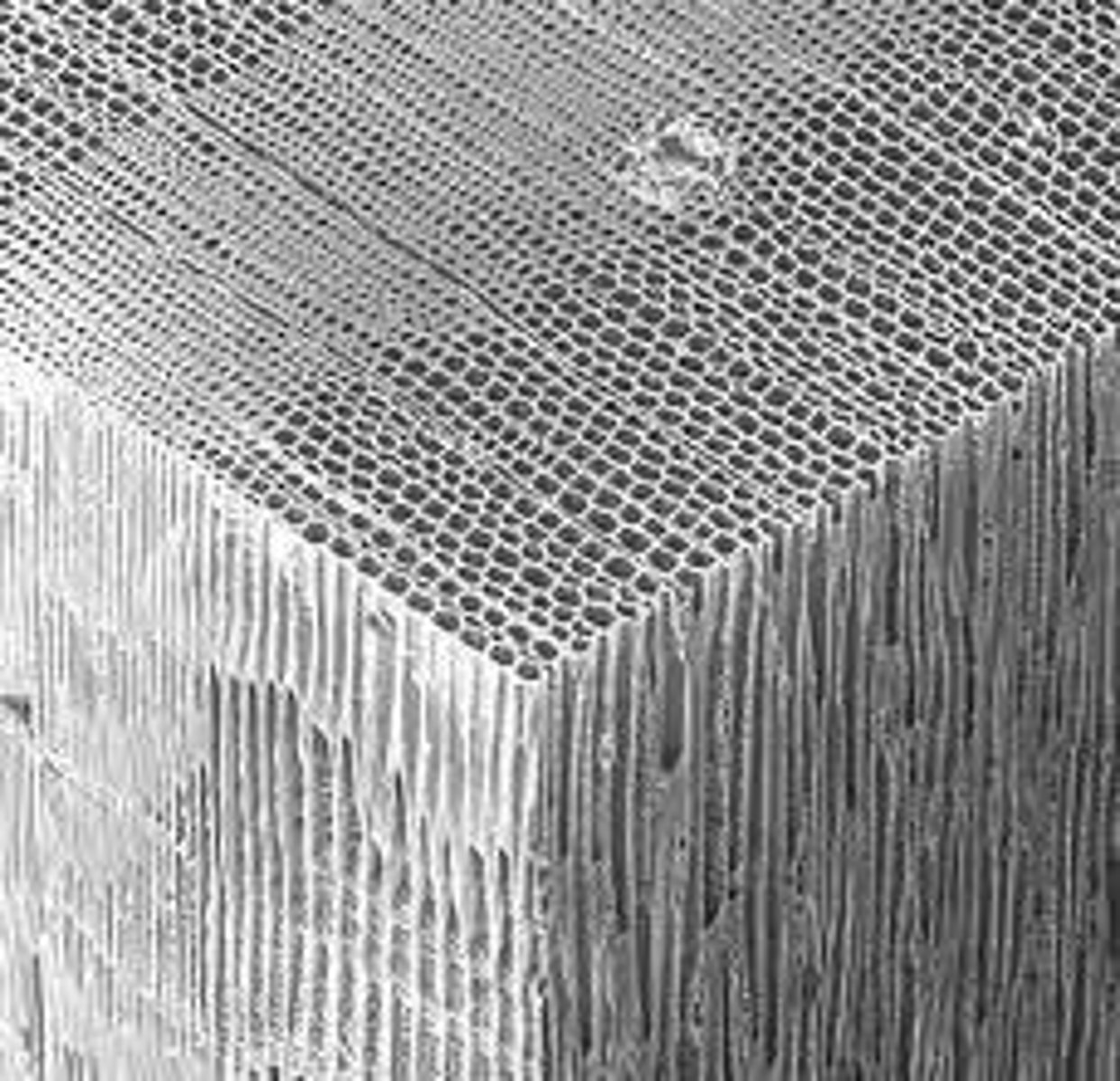

How do growth rings in trees vary with climate?
They decrease in size and produce more tracheids than vessels during drier months and in drier climates.
What are the three types of plant organs?
Stems, leaves, and roots.
What is the primary function of stems in plants?
Position leaves for photosynthesis, transport resources, and store nutrients.
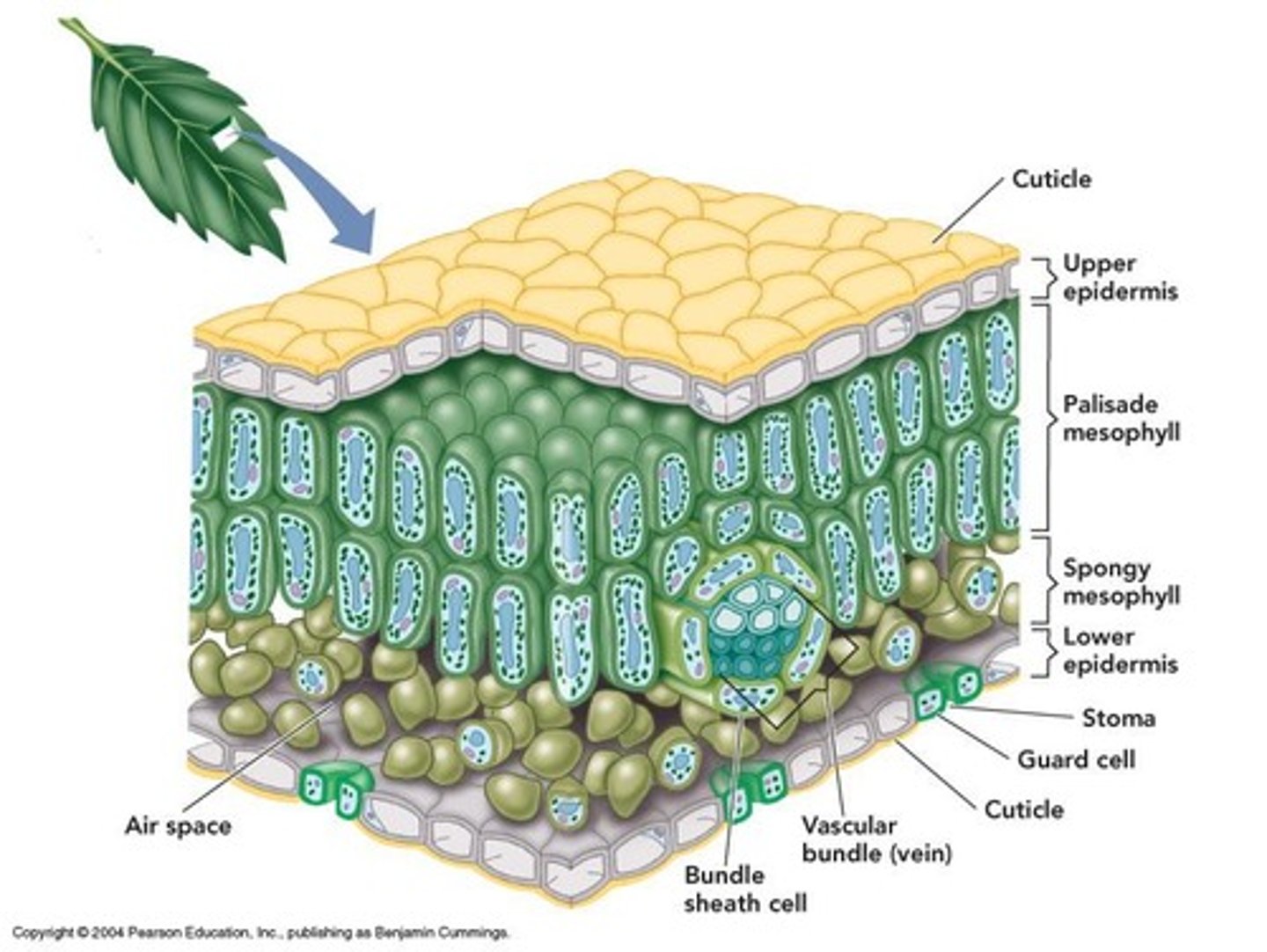
What is the function of leaves in plants?
Photosynthesis and transpiration, balancing light and CO2 capture with water loss.
What is the role of roots in plants?
Anchor the plant, absorb water and minerals, and store resources.
What is the function of mesophyll in leaves?
Internal cells packed with chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
What do stomata do in leaves?
Regulate water loss and CO2 uptake.

What are guard cells?
Cells that flank stomata and control their opening and closing.
What distinguishes apical meristems from lateral meristems?
Apical meristems are responsible for primary growth, while lateral meristems contribute to secondary growth.
What is the function of cork cambium?
Produces bark and contributes to the protective outer layer of stems and roots.
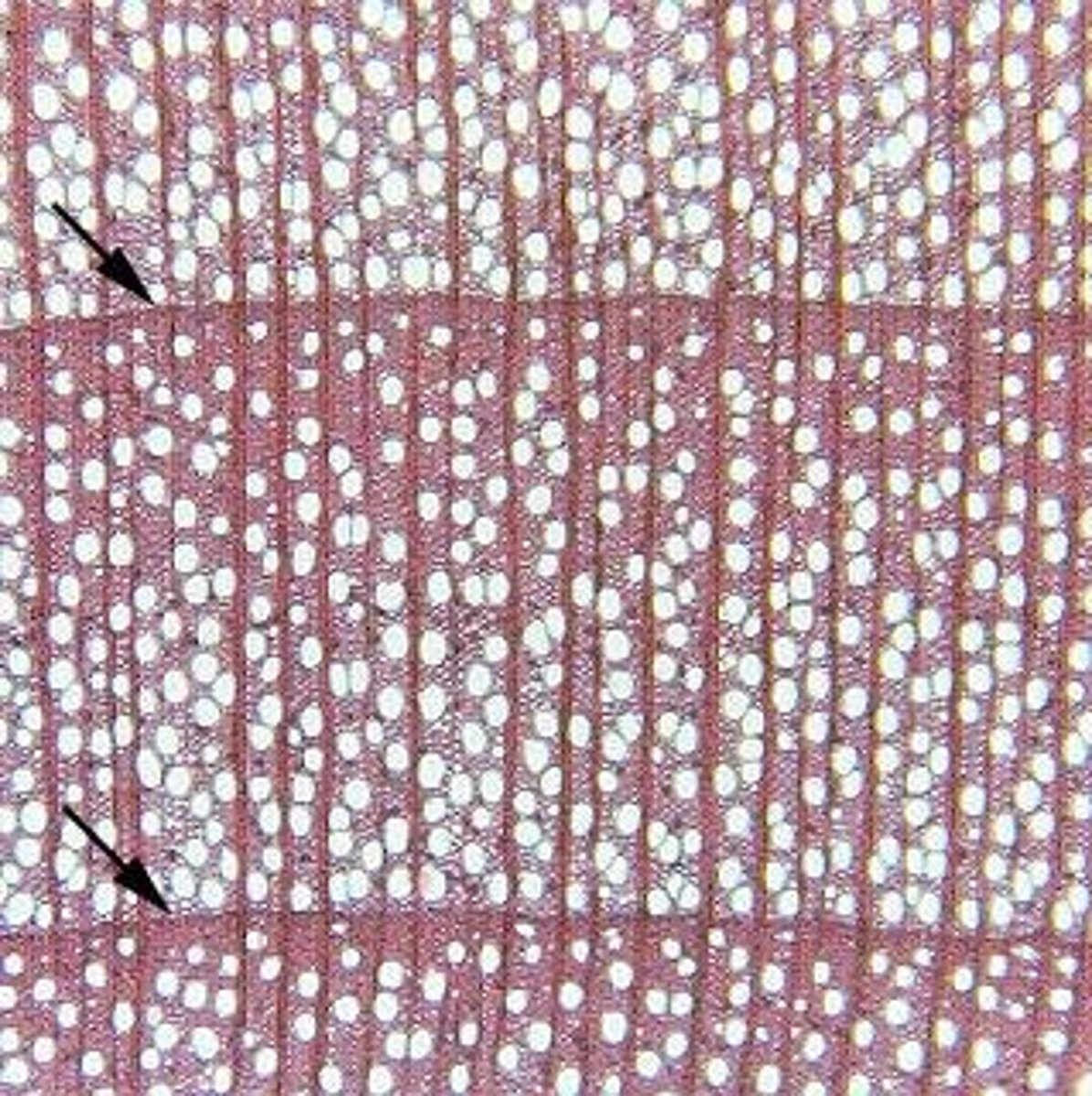
How do xylem cells contribute to water transport?
They are dead at maturity, forming a pathway with reduced resistance for water movement.
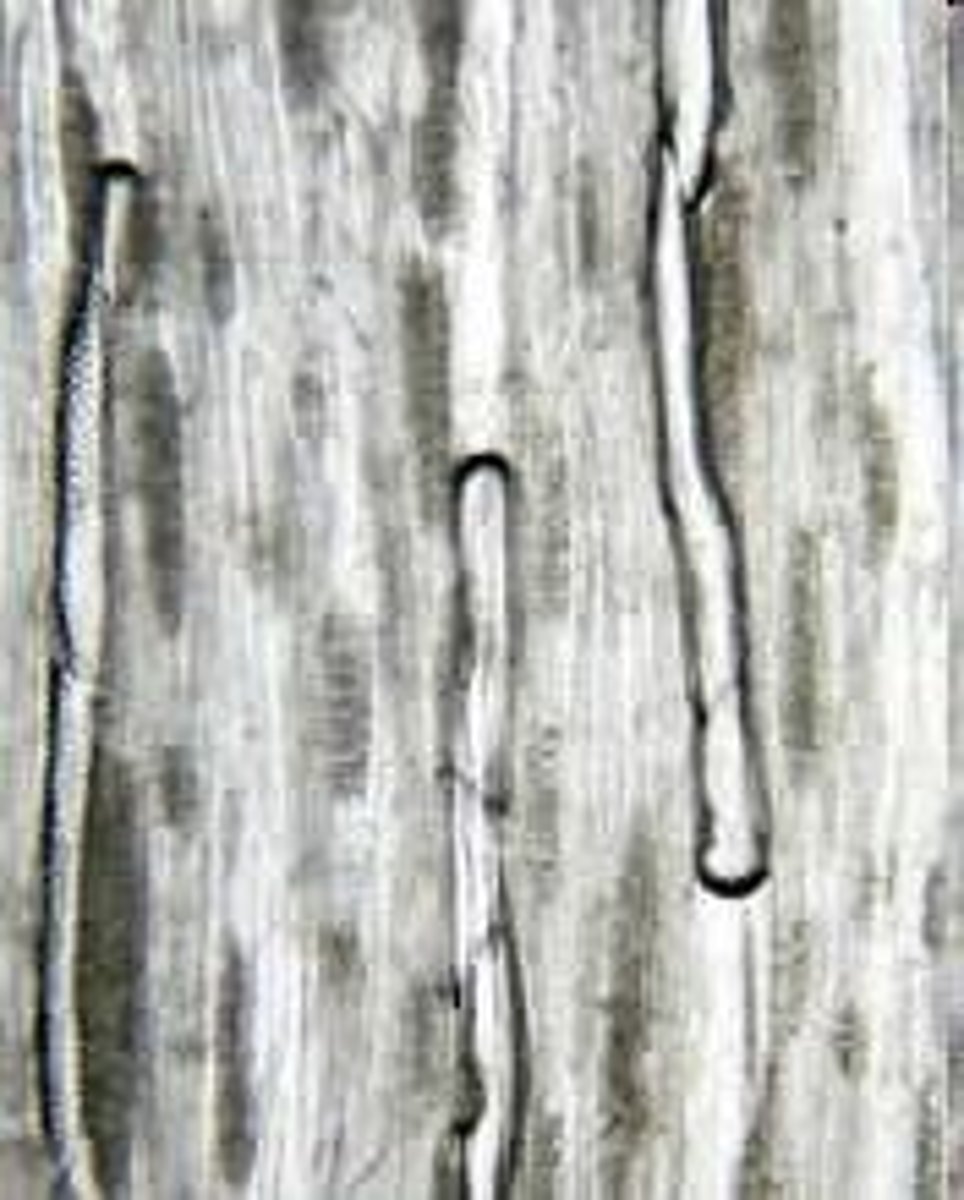

What are the characteristics of tracheids?
Long, slender cells found in all vascular plants, aiding in water transport.
What are vessel elements?
Short, wide cells found only in flowering plants, with a much greater water-carrying capacity than tracheids.
In what conditions does cavitation occur?
During freeze-thaw cycles and hot, dry weather, leading to air bubble formation in xylem.
How do plants adjust to their environment regarding xylem production?
They can alter the number of xylem cells produced and the vessel to tracheid ratio based on environmental conditions.