Chemistry calculations
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is Avogadros constant
Formula for number of moles
6.02 × 10^ 23
𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑛 = 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑙𝑒𝑠 (𝑁) /
𝐴𝑣𝑜𝑔𝑎𝑑𝑟𝑜′𝑠 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 (𝑁𝐴)
what is molar mass
what is the formula for molar mass (mr)
The molar mass is quite simply the mass of one mole of a substance.
• It has units of grams per mole (g/mol or gmol^-1)
𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑚 = 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑎𝑟 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝐴𝑟 𝑜𝑟 𝑀𝑟 × 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 (𝑛)
what is stoichiometry
The stoichiometry of a reaction is the molar ratio between the number of
moles of reactants and products in the reaction equation
when your calculating mass planning reactions what table is used
Mass
Mr
Moles
Molar ratio
when you get moles you divide by your own column then multiply by how many
what is the percentage yield formula
Actual yield or mass obtained / theoretical mass or theoretical yield x 100
what is the limiting reagent
how do you calculate the limiting reagent
the reactant that is completely used up
when you work out moles you divide both values by the smallest mole value
how to work out percentage yield of a reaction eg; C6H6 + I2 → C6H5I + HI Calculate the percentage yield for this reaction if 30.2 g of iodobenzene are obtained from 60 g of benzene and 60 g of iodine.
mass, mr, moles, ratio table
work out limiting reagent (smaller mole value out of benzene and iodine)
multiply mr of what you are trying to find with moles of limiting reagent
calculate percentage yield
what is molar volume (Vm)
𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑉 = 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑎𝑟 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑉𝑚 × 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 (𝑛)
The molar volume (Vm) is the volume of one mole of a gas)
Vm = 24.0 dm3 at
Room Temperature (20 °C)
Room Pressure (1 atm)
Vm = 22.4 dm3 at
Standard Temperature (0 °C)
Standard Pressure (1 atm)
what is avogadros law
the volume of reactants is = to the volume of the products
what is Boyles law
if you halve the volume of a gas you double the pressure, they have an inverse relationship
PV = Constant
P1V1 =,P2V2
What is Charles law
if you increase the temperature of a gas, the volume increases
they are directly proportional
V/T = Constant
V1/T1 = V2/T2
What is the ideal gas law
PV = nRT
Pressure in pascals
Volume in metres cubed ³ (1m³, 1000dm³, 1,000,000cm³)
n = number of moles
R = gas constant = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1
T = Temperature in kelvin = + 273
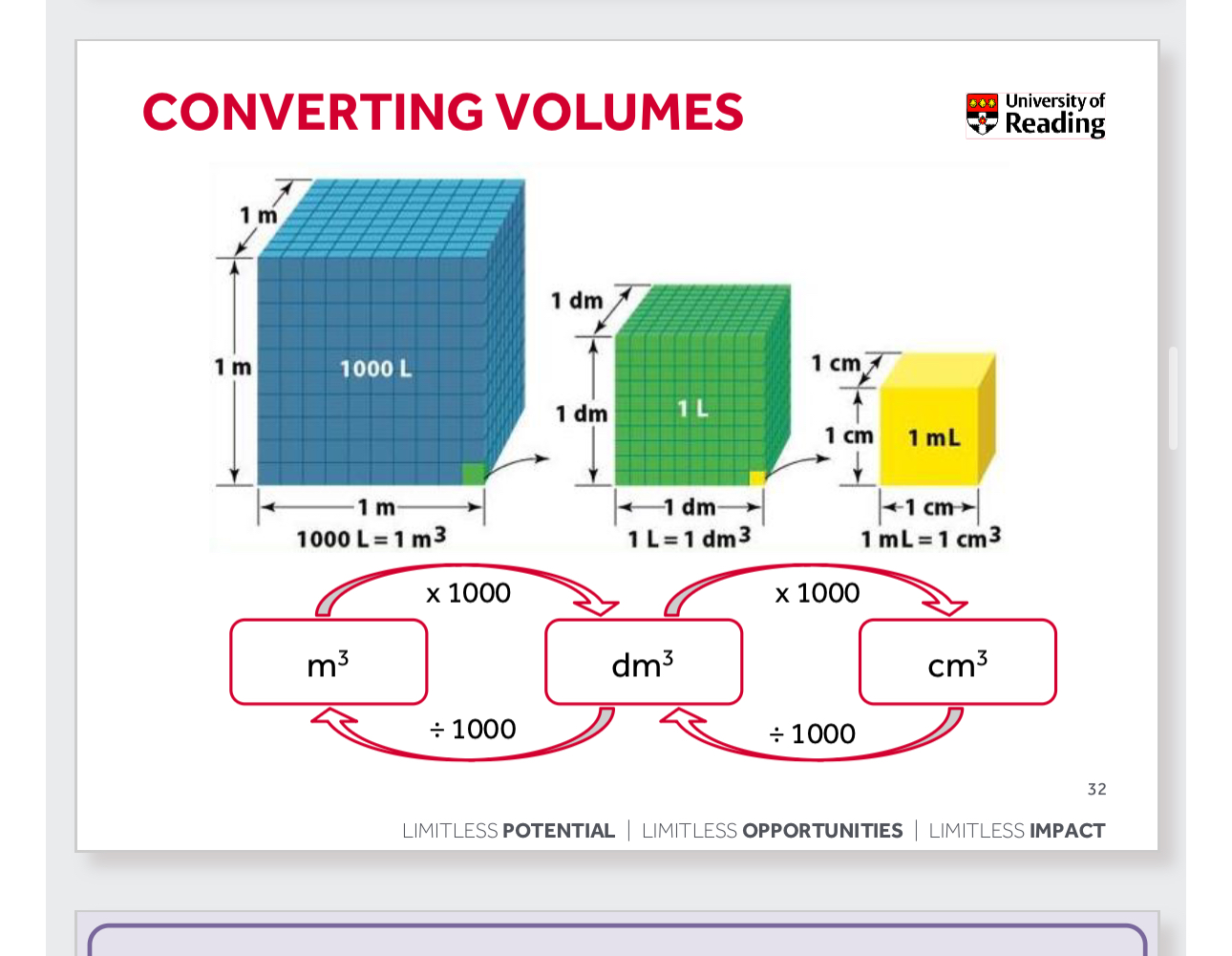
How to go from m³ to dm³
Go from dm³ to cm³
Go from cm³ to dm³
Go from dm³ to m³
Formula for concentration with moles and volume
Concentration (C) = moles (n) / volume (dm³)
What is a titration
A technique used to work to work out concentration of a known substance
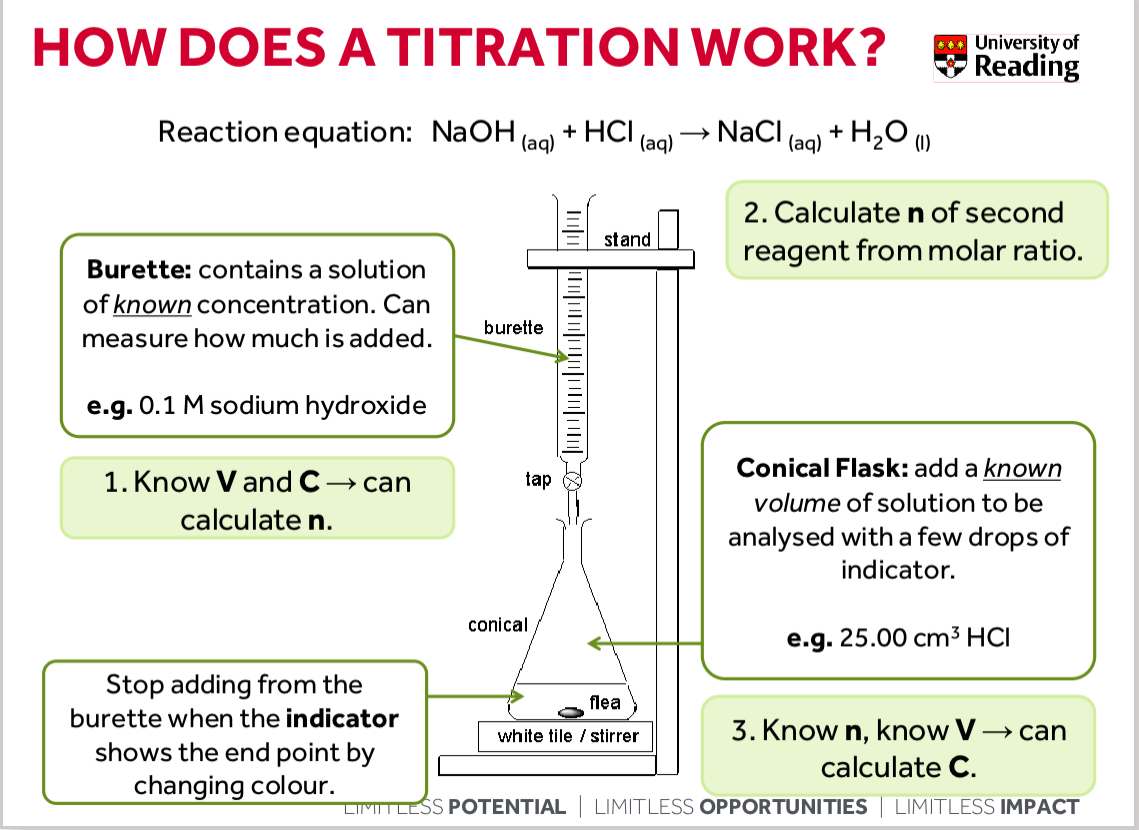
How does a titration work
You know volume and concentration do you can calculate moles
Calculate moles of second reagent from molar ratio
You know moles and volume so you can calculate C
What is Accuracy
What is precision
The closeness of agreement between final average result and value
Closeness of agreement between independent measurements
Percentage error formula
Accepted result - measured result / accepted result x100
3 types of error
Human, environmental, instrumental
Precision error calculation equation
%precision error = no. of readings x uncertainty/ measurement x 100%