BIO65 || CH2: Cytology - The Study of Cells
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Apical surface
The surface of a cell that opens up to the world, typically superficial and at the top.
Basal surface
The deep surface of a cell, located at the very bottom.
Lateral Surface
The sides of the cell surface.
Plasma Membrane
A protective barrier that separates the cell from the external environment, consists of phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol, glycolipids, proteins
Cytoplasm
The contents of the cell, including the cytosol, organelles, and the cytoskeleton.
Nucleus
An organelle that contains nucleoplasm (chromatin/DNA) and serves as the control center of the cell.
Phospholipids
Lipids that make up 75% of the plasma membrane, with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails arranged in a lipid bilayer.
Cholesterol
Constitutes 20% of the plasma membrane, increasing its fluidity.
Glycolipids
Make up 5% of the plasma membrane, consisting of glucose (sugar) and phospholipids for cell signaling and recognition.
Integral (transmembrane) proteins
Proteins that pass through the membrane.
Glycoproteins
Proteins that adhere to either face of the membrane.
Peripheral proteins
Proteins that do not penetrate the entire plasma membrane.
Villi & Microvilli
Plasma membrane extensions that increase surface area, known as brush border.
Cilia
Motile cellular structures that help move substances along another structure.
Flagella
Cellular structures that propel sperm cells.
Tight Junctions
Cellular junctions that act as a sealant to prevent cells from detaching.
Desmosomes
Cellular junctions that help resist stress, similar to tight junctions, often found in muscle cells.
Gap Junction
Cellular junctions that allow communication between cells and enable them to send signals for a common function.
Cytoskeleton
Structural components of the cell that maintain its shape and organization, composed of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules.
Microfilaments
Thin filaments made mostly of actin, supporting the plasma membrane and contributing to cell movement.
Intermediate filaments
Thicker filaments that provide strength to cells and tissues.
Microtubules
Largest filaments that hold organelles in place, guide organelles to their destinations within the cell, and are involved in cell division.
Organelles
Specialized structures within the cell that perform various functions, such as the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi complex, proteasomes, lysosomes, mitochondria, and centrioles.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
An organelle with rough and smooth types involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and detoxification.
Lysosomes
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell (taking out the trash)
Ribosomes
Made in the nucleolus a portion of the nucleus in the cell
Assembles amino acids into proteins for use within or outside the cell; found in Rough ER & Cytoplasm
Golgi complex (aparratus)
Composed of cisterns
Vesicles (carrying something to be transported) are transported from the RER to Golgi complex
Golgi vesicles - packaged protein
→ Insertion into plasma membrane
→ Lysosomes
→ Secretory vesicles (releases components out of the cell)
Autophagy
A process in which lysosomes decompose damaged organelles to reuse their organic monomers
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
Proteasomes
breakdown and recycling of damaged or abnormal intracellular proteins
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
Centrioles/Centrosomes
Centrioles
→ Made of microtubules arranged in nine groups of three
Centrosome
→ Cytoplasm that contains the perpendicular pairs
**active during cellular division (mitosis)
The Cell Cycle
series of events in which a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells
Includers Interphase & Mitotic (M) Phase
Phases of Interphase
First gap phase (G1)
→ Growth & normal metabolic roles
Synthesis phase (S)
→ DNA replication
Second gap phase (G2)
→ Growth & preparation for mitosis
→ DNA proofreading
Mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
Phases of Mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms

Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
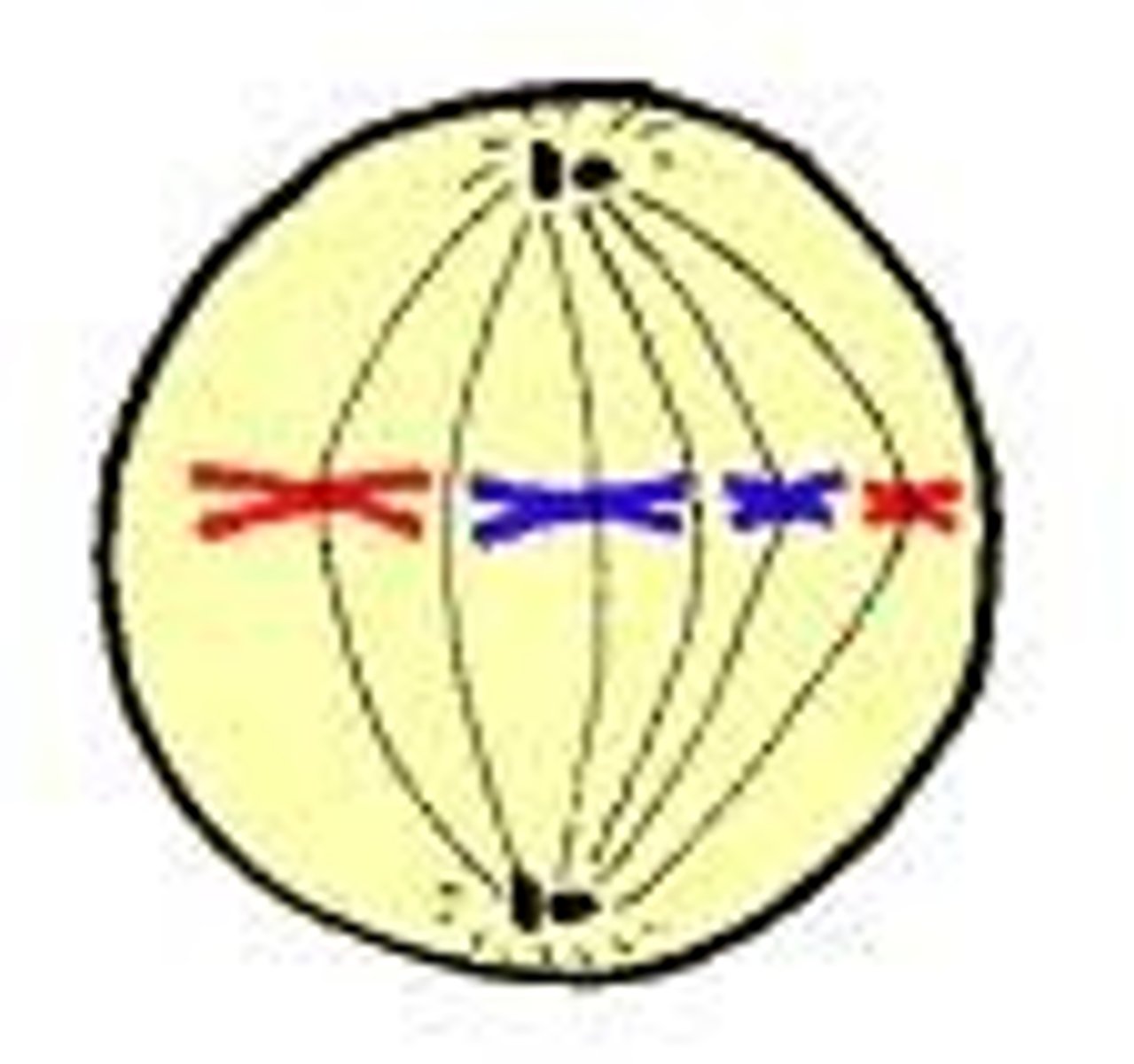
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
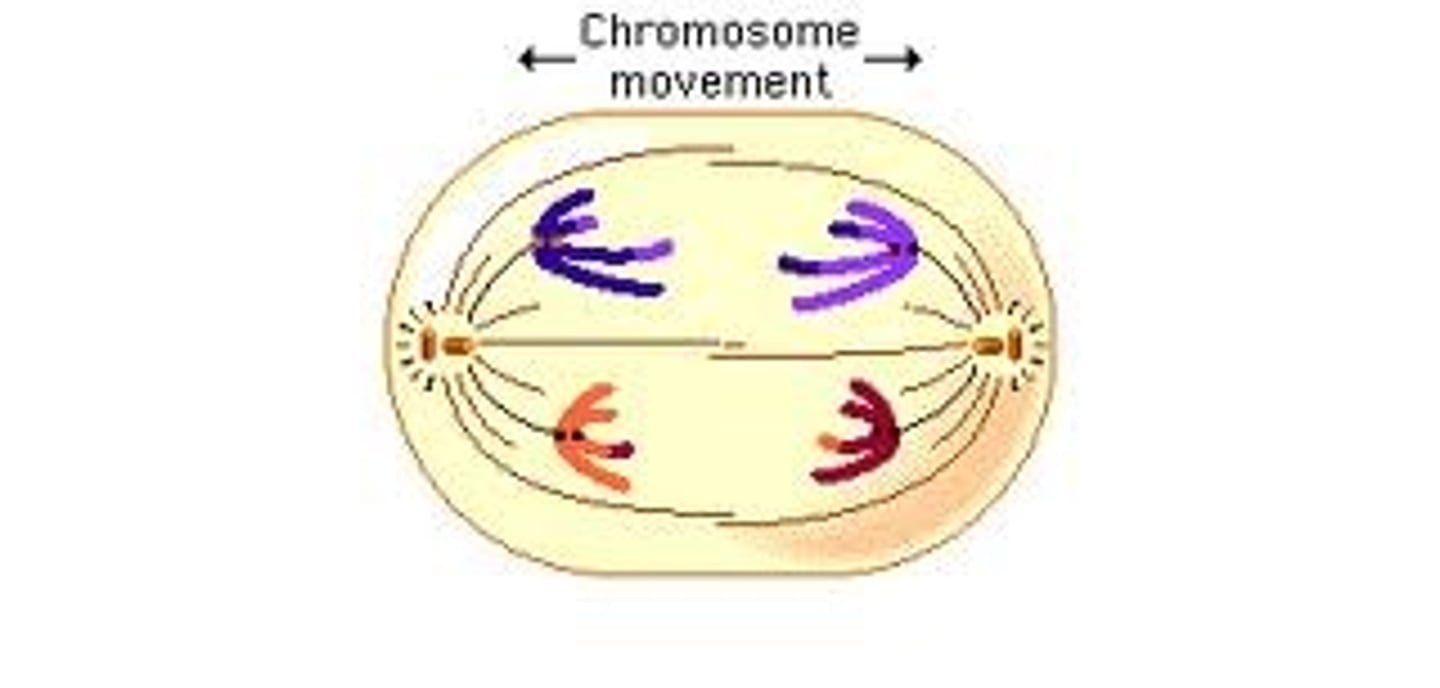
Telophase
After the chromosome seperates, the cell seals off, Final Phase of Mitosis.
Cytokenesis
Division of cytoplasm, cleavage furrow develops end of anaphase/beginning of telophase, ultimately cell pinches into two identical daughter
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
Glycolipids (in Plasma Membrane)
Lipids that have carbohydrates attached to them, glucose (sugar) + phospholipid for cell signaling and recognition
Intracellular
within the cell
Extracellular
outside the cell