EQ: Free Cash Flow Valuation
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
The free cash flow to the firm (FCFF) valuation approach estimates the firm’s value as the present value of future FCFF discounted at the
weighted average cost of capital
FCFF firm value =
picture
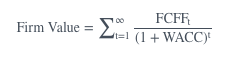
Equity Value =
Firm Value − Market Value of Debt
WACC =
picture

The value of equity can be arrived at by discounting the free cash flow to equity (FCFE) at the
required rate of return of equity, r.
FCFE equity value =
picture
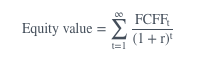
Given the firm's value, which of the following is the most appropriate way of computing the value of equity?
Adding the value of assets to the value of the firm.
Deducting the value of assets from the value of the firm.
Deducting the market value of debt from the value of the firm.
3
Under the free cash flow to equity (FCFE) approach, the ownership perspective is that of
an acquirer who can change the firm’s dividend policy
the discounted dividend approach takes the ownership perspective of
a minority shareholder who does not have control over a firm’s dividend policy
The free cash flow valuation approach may be preferred over the dividend discount model when:
The company does not pay dividends.
The company pays dividends, but it differs significantly from its ability to pay dividends.
Free cash flows align with profitability within a satisfactory forecast period.
An investor that takes control has discretion over the use of free cash flow.
Which of the following is least likely a reason why analysts use free cash flow valuation approach over the dividend discount approach?
The company does not pay dividends.
The company is being valued from a majority interest ownership perspective.
The free cash flow does not align with profitability within a satisfactory forecast period.
3
FCFF is the cash flow available to a firm’s capital providers after
deducting operating expenses, working capital expenses, and fixed capital investments
FCFF can be calculated from net income as FCFF =
Net Income + Net Non Cash Charges + Interest Expense(1−Tax Rate) − Fixed Capital Investments − Working Capital Investments
FCFF can be estimated from CFO as FCFF =
Cash Flow from Operations + Interest(1−Tax Rate) − Fixed Capital Investments
FCFF can be estimated from EBIT as FCFF =
EBIT ( 1 - t ) + Dep - FCinv - WCinv
FCFF can be estimated from EBITDA as FCFF =
EBITDA ( 1 - t) + Dep(t) - FCinv - WCinv
FCFE from FCFF, FCFE =
FCFF - Int ( 1 - t ) + Net borrowing
FCFE from NI, FCFE =
Net Income + Non Cash Charges − Fixed Capital Investments − Working Capital Investments + Net Borrowing
FCFE from CFO, FCFE =
Cash from Operations − Fixed Capital Investments + Net Borrowing
FCFF from EBIT, FCFF =
EBIT(1−Tax Rate) + Depreciation − Fixed Capital Investments − Working Capital Investments
FCFF from EBITDA, FCFF =
EBITDA(1−Tax) + Depreciation(Tax) − Fixed Capital Investments − Working Capital Investments
FCFE from FCFF, FCFE =
FCFF−Interest(1−Tax Rate)+Net Borrowing
FCFE from EBIT, FCFE =
EBIT(1−Tax Rate)−Interest(1−Tax Rate)+Depreciation−Fixed Capital Investment−Working Capital Investments+Net Borrowing
FCFE from EBITDA, FCFE =
EBITDA(1−Tax rate)−Interest(1−Tax Rate)+Depreciation(Tax Rate)−Fixed Capital Investments−Working Capital Investments+Net Borrowing
Which of the following is least likely reflected in the calculation of FCFF when beginning with cash flow from operations (CFO)?
Interest.
Depreciation.
Fixed capital investments.
2
Depreciation is not considered in the calculation of FCFF when beginning with CFO. It is already added back when computing CFO.
Blue Ltd.’s capital constitutes a debt of $200,000 and equity of $300,000. It recently announced a net income of $275,000. The company managers have invested $90,000 in fixed capital and $60,000 in working capital. The company’s only non-cash expense for the period was $40,000. If the company’s average after-tax interest on debt is 8%, the free cash flow to the firm (FCFF) is closest to:
$90,000.
$181,000.
$145,000.
2
FCFF=Net income+Net non-cash charges+Interest expense(1−Tax rate)−Fixed capital investments−Working capital investments=$275,000+$40,000+(8%×$200,000)−$90,000−$60,000=$181,000
Incremental fixed capital investments as a proportion of sales increases are computed as:
(Cap expenditures - Deprc Expense) / Incr in Sales
Incremental fixed working capital investments as a proportion of sales increases are computed as:
Incr in Working Capital Investments / Incr in Sales
FCFE using the debt ratio (DR) =
Net income−(1−DR)(Fixed Capital Investments−Depreciation)−(1−DR)Working Capital Investments
Which of the following is least likely a required input when forecasting FCFF?
Tax rate.
Forecasted sales growth rate.
Forecasted after-tax operating margin or profit margin
1
The tax rate is not an input required when forecasting the FCFF, especially when an analyst already has the after-tax operating margin or profit margin.
Which of the following valuation models is most appropriate when valuing a company from a minority shareholder perspective?
FCFE model.
FCFF model.
Dividend discount model.
3
Which of the following would most likely affect FCFE?
Dividends.
Debt increase.
Share repurchases.
2
Debt increases will have an impact on FCFE. In the period that the debt is issued, FCFE will increase by the debt amount, and in subsequent periods it will reduce by the after-tax interest expense.
Which of the following reasons most likely makes net income a poor measure of earnings in the discounted cash flow model?
It does not reflect the cash taxes paid by the firm.
It does not account for the depreciation tax shield.
It includes the effects of non-cash charges like depreciation.
3
If FCFF grows at a constant rate, the value of the firm is calculated as:
picture
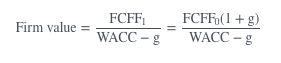
If FCFE grows at a constant rate, the equity value of the firm is calculated as:
picture
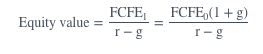
The general two-stage FCFF valuation model is:
picture
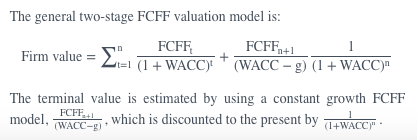
The general two-stage FCFE valuation model is:
picture

Which of the following discount rates is applied to FCFF when computing the firm’s value?
WACC.
r−g.
r.
1
A company’s current FCFF is $600,000. It is currently experiencing a growth rate of 8% that is expected to last for three years, after which its growth rate will decline to 4% and remain at that rate indefinitely. If its WACC is 9%, the value of the firm is closest to:
$13,907,095.
$950,230.
$18,750,300.
1

Which of the following is the least likely source of error in valuation results?
The duration of growth rate.
Estimating the future growth rate of FCFF and FCFE.
Choosing the correct base year for the FCFF and FCFE growth forecasts.
1
The duration of growth rate is not a source of error in valuation. However it is difficult to forecast.
The terminal value can be calculated using a:
Single-stage (constant-growth) model
Valuation multiples approach
Under the valuation multiples approach, there are two ways the terminal value can be calculated:
Terminal value in year n = Justified trailing P/E x Forecasted earnings in year n
Terminal value in year n = Justified leading P/E x Forecasted earnings in year n + 1
The EPS of a particular company is estimated to be $5.00 in five years. The EPS in six years is estimated to be $5.90. If the median trailing industry P/E is estimated as 28, the terminal value in year 5 is closest to:
Terminal value in Year 5=28×$5.00=$140
Given the following information,
EPS2019=2.30
EPS2020=3.00
EPS2021=3.50
If the median trailing industry P/E in 2020 is estimated to be 32, the terminal value in 2020 is closest to:
73.6.
96.0.
112.0.
2
Terminal value in year n=Justified trailing P⁄E×Forecasted earnings in year n =3×32=96
Which of the following situations most likely results in a stock being overvalued?
When the market price is higher than the intrinsic value.
When the market price is less than the intrinsic value.
When the market price is equivalent to the intrinsic value.
1