Animal Physiology Exam 2
1/247
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
248 Terms
Classic non-neural endocrine
Hormones are released into the blood and exert actions at distant site
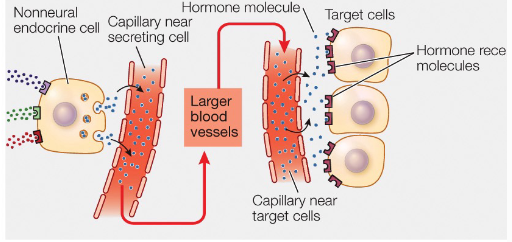
Neuroendocrine
Hormones are released by neural cells into the blood and exert actions at distant sites
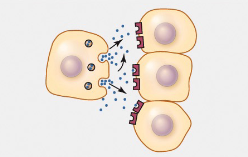
Paracrine
Hormones diffuse to a target cell located in proximity (neighboring cells)
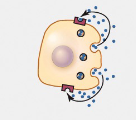
Autocrine
Hormones affect secreting cell itself
Hormone secretion
What is the primary role of the “classic” endocrine glands?
Pancreas
Exocrine digestive enzymes + endocrine islets
Gonads
Gamete production + sex steroids (testosterone + estrogen)
Stomach / intestine
Digestion + gastrointestinal hormones (gastrin, CCK)
Liver
Metabolism + insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I)
Adipose tissue
Energy storage + leptin (regulates appetite, energy balance)
Peptide Hormones
Most hormones. Short chains of amino acids. Ex: insulin and hypothalamic hormones
Steroids
Hormones derived from cholesterol. Ex: Adrenal and gonadal hormones
Amino acid derivatives
Hormones derived from amino acids. Ex: thyroid hormones and catecholamines
DNA transcribed to mRNA
Translation of mRNA into pre-hormone (an inactive precursor)
Pre-hormone processed in ER and Golgi —→ Prohormone ——> Hormone
Hormone is packaged in vesicles and stored in the cytoplasm
Secretion occurs (specific stimulus required)
Hormone transported and dissolved in blood
Describe the steps of synthesis, storage, and release of a peptide hormone.
Requires series of enzymatic reactions
Different types of steroidogenic cells have different sets of enzymes, therefore they have different end products
Hormones are not stored; diffuse out of cell and are transported bound to plasma protein
Describe the synthesis and secretion of steroid hormones
Surface receptors (extracellular / membrane R) as they cannot pass through the hydrophobic lipid bilayer
Peptide hormones and amines bind to?
Ligand binds receptor
G protein is activated
Second messenger produced (cAMP, cGMP, IP3/DAG, Ca2+)
Cellular response
Explain G protein-linked receptors
(For majority of hormones)
Ligand
Intrinsic tyrosine kinase auto phosphorylates
Recruits intracellular signaling proteins
Triggers metabolic or gene expression responses
Explain Enzyme-linked receptors (catalytic R)(For Insulin + Growth Factor)
Steroid hormones are lipophilic and diffuse across the cell membrane
Hormone binds to intracellular receptors (cytoplasm or nucleus)
Hormone bindings causes receptor conformational changes and activation
Activated receptors bind to hormone response element (HRE)
Hormone receptor complex acts as a transcription factor which regulates gene expression
Synthesized protein results in physiological response
Explain how steroid hormones bind to intracellular hormone receptors (how steroid hormones act)
Negative Feedback
Most hormone secretion results in what kind of feedback?
High blood glucose —→ increases insulin —→ lowers glucose
Give an example of negative feedback
hormone concentrations; hypothalamus-pituitary
Hormone Mediated feedback is controlled by _______ and involves the ________ axis.
Hypothalamus
Secretes releasing hormones
Pituitary
Secreted tropic hormones
Rhythmic basis
Many hormones are secreted on a?
light-sensitive retinal
Neural input is generated from specialized _________ cells.
The superchiasmatic nucleus (SCN) and further to the hypothalamic releasing hormone-secreting neurons
Signals from neural input are sent to?
The circadian rhythm
SCN neurons impose a daily rhythm called?
melatonin; pineal gland
In addition to the circadian rhythm, the SCN regulates ______ secretion for the _______.
Upregulation
More receptors result in increased sensitivity. Ex: prolactin increases the number of receptors in the mammary gland
Downregulation
Fewer receptors result in decreased sensitivity. Ex: when this process occurs, insulin receptors become less sensitive and high insulin levels prolong.
Additive effect
Combined effect equals the sum of individual effects
Synergism
Combined effect greater than sum of individual effects
Permissiveness
One hormone is required for another to exert the full effect
Antagonism
One hormone opposes the effect of another
Hypothalamus
The base of the brain that contains several nuclei (groups of cell bodies of neurons)
Pituitary stalk
The pituitary (hypophysis) is connected to the hypothalamus by the?
Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) + Anterior lobe (adenohypophysis)
Name the lobes of the pituitary
Intermediate lobe; MSH
In some animals a third pituitary lobe called ________ is present and secretes _____.
Vasopressin + Oxytocin (peptide hormones)
What hormones are released from the posterior pituitary?
Vasopressin (VP)
Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH) that increases reabsorption of H2O by kidneys and increases vasoconstriction. Released by the posterior pituitary.
Oxytocin (OC)
Released during uterine contraction during childbirth and results in milk ejection during breast feeding. Released by the posterior pituitary.
ADH
Increases water reabsorption in kidneys
Thyrotropin (TSH), Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), Growth hormone, Gonadotropins (LH + FSH), MSH (in some animals), and Prolactin
Which hormones are released from the anterior pituitary?
Posterior pituitary is a neural extension of the hypothalamus composed of axons of hypothalamic neurons. Hormones are produced by Paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and Supraoptic nucleus (SON). Hormones travel down the axon where they are stored in axon terminals in the posterior pituitary
Describe the hypothalamic control of the Posterior pituitary.
No direct nervous connection between anterior pituitary and hypothalamus. Hypothalamic hormones are released in hypothalamic capillaries where they enter the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system. The portal system controls the release of pituitary hormones in blood. Releases hormones and inhibiting hormones.
Describe the hypothalamic control of the Anterior pituitary.
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)
Stimulates thyroid hormone secretion (T3/T4); Thyrotroph —→ TSH
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH)
Stimulates cortisol secretion from the adrenal cortex
Corticotroph ——> ACTH
Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH)
Stimulates growth hormone release
Somatotroph —→ GH
Somatostatin (GHIH)
Inhibits GH and TSH release
Somatotroph —→ GH
Thyrotroph ——→ TSH
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
Stimulates sex hormone production and gametogenesis
Gonadotroph —→ LH, FSH
Prolactin-Releasing Hormone (PRH) (ex: TRH)
Stimulates prolactin secretion
Lactotroph ——> PRL
Prolactin-Inhibiting Hormone (PIH / Dopamine)
Inhibits prolactin secretion
Lactotroph ——→ PRL
IGF-1
GH does not directly cause growth. Instead, growth-promoting effects are largely mediated by _____ which stimulates the growth of soft tissues and bones.
Spherical follicles
What is the thyroid composed of?
Follicular cells; colloid-filled space
Each follicle of the thyroid is lined by a single layer of secretory epithelial cells called ________ around a _________.
Thyroxine (T4) + Triiodothyronine (T3)
Follicular cells synthesize?
Thyroglobulin
A large protein with tyrosine residues, secreted by follicular cells in the colloid. Used to produce thyroid hormones
Iodination
Tyrosine residues on Thyroglobulin are iodinated which forms monoiodotyrosine (MIT) or diiodotyrosine (DIT)
Coupling
MIT and DIT are combined, forming T3 or T4 which remains attached to TG
T4 (inactivated form)
90% of thyroid hormones are secreted as?
Increase basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Increase oxygen consumption and energy expenditure in most tissues
Increase heat production
Increase glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
Increase lipolysis
Maintains normal excitability, reflexes, and alertness
Essential for normal growth in children; critical for brain development during fetal and postnatal life
What are the actions of thyroid hormones?
Metamorphosis (in fish and amphibians) and migratory behavior and adaptive osmoregulatory changes in salmonids
What is the action of thyroid hormone in lower vertebrates?
Hypothyroidism
A TH deficiency which causes developmental cretinism (stunted growth and impaired CNS development) and slows growth, lowers metabolism, causes fatigue, cold intolerance, and weight gain in adults and children
Goiter
A thyroid enlargement caused by either hypothyroid or hyperthyroid disorder
Hypothyroid goiter
A goiter resulting from TH deficiency. Ex: Iodine deficiency or Hashimoto’s thyroidits
Hyperthyroid goiter
A goiter resulting from TH excess. Ex: Grave’s disease
From sun exposure or from diet via absorption by the small intestin
Where do you get vitamin D from?
Cholecalciferol
D3 (animals)
Ergocalciferol
D2 (plants)
Ultraviolet (UV) light
D3 is synthesized from dehydrocholesterol in the skin and requires?
Liver: Vitamin D converted to 25(OH)-D
Kidney: 25(OH)-D converted to 1,25 (OH)2-D
What two reactions activate vitamin D (which is inactive on its own)?
Vitamin D and Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
What two things regulate calcium?
Regulates Ca metabolism. Stimulus is decreased calcium levels, action is to increase calcium levels.
What does the Parathyroid hormone do?
Kidney: Increases calcium reabsorption and increases the production of active vitamin D
Bone: Bone resorption increases calcium in the blood
How does the parathyroid hormone (PTH) increase Ca levels?
Calcitonin
Decreases bone resorption by decreases osteoclast activity, and further decreasing calcium levels. Also results in small decrease in renal calcium reabsorption
Adrenal Gland Medulla
Secreted catecholamines (Epinephrine + norepinephrine) stimulated by the sympathetic system (stress).
Catecholamines (epinephrine +norepinephrine)
Released by the adrenal gland medulla; reinforces the “fight-or-flight” response; increases heart rate and blood glucose levels
Adrenal Gland Cortex
Secretes mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids (cortisol), and androgens (with some estrogens)
Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone)
Secreted by the adrenal gland cortex; regulates Na+ balance (in kidney ——> osmoregulation)
Glucocorticoids (cortisol)
Secreted by the adrenal gland cortex; regulates fuel metabolism; increases blood glucose levels and has anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects
Androgens
Secreted by the adrenal gland cortex; mostly dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and some estrogens
Glucose enters the B-cell (via facilitated diffusion via GLUT-2)
Glucose phosphorylated to G6P (glucose-6-phosphate)
Oxidation of G6P generates ATP
ATP closes ATP-sensitive K+ channels
Depolarization opens voltage-gated Ca channels
Ca enters the cell
Exocytosis of insulin vesicles
Explain how insulin is released in the body.
Incretins
Hormones released by the digestive tract in response to food which increases insulin secretion
The gastrointestinal (digestive) tract (GIT)
Digestion occurs in?
Sphincters
The gastrointestinal tract is separated by muscular valves called?
Injestion
Getting food into the gastrointestinal tract (eating)
Mechanical digestion
The breakdown of food into small molecules by teeth (chewing) or stomach (churning)
Chemical digestion
The breakdown of food into small molecules by specific enzymes
Mouth and esophagus
The main parts of the body used in mechanical digestion (and some chemical)
Stomach
The organ that functions in digestion
Small intestine
The organ that functions in digestion and absorption
Large intestine
The organ that functions in the reabsorption of water during digestion
Carnivores: canines have pointed teeth for tearing
Herbivores: have incisors for cutting and molars for grinding
Filter feeders: Gill rakers and baleen plates
What are some adaptations of teeth?
Saliva
Produced by salivary glands in the mouth; lubricates food, digests polysaccharides, and has roles in taste and maintaining pH
Water (99%)
Electrolytes (Na+ and K+)
Mucin
Antibodies
Salivary amylase
What are the main components of saliva?
Mucin
A protein that forms thick, slimy mucus
Salivary amylase
Breaks down carbohydrates in the mouth
Esophagus
Secretes mucus and alternates contraction and relaxation of muscle along the side (peristalsis); moves food toward the stomach
Crop
A sac-like enlargement of the esophagus in birds that stores undigested food, have bacteria that aid in pre-digestion, and secretes “crop milk”