NMSK - forelimb anatomy
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
what is the name of the joint found in the shoulder
glenohumeral joint
what 3 joints are found in the elbow
humeroulnar
humeroraidal
proximal radioulnar
What is the role of extrinsic muscles?
attachment of the limb to the axial skeleton
Name the 6 extrinsic muscles of the forelimb
trapezius muscle (cervical and thoracic part)
rhomboideus muscle (cervical and thoracic part)
brachiocephalicus muscle (cleidocervicalis, cleidobrachialis and further division into cleidooccipitalis and cleidomastoideus)
omostransversarius muscle
latissimus dorsi
superficial pectoral muscle (transverse and ascending parts)
Outline the trapezius muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: funicular part of nuchal ligament on cervical and thoracic region
Insertion: spine of scapula by a flat aponeurosis
Action: contraction elevates the scapula
Extrinsic
has a cervical and thoracic part
Outline the rhomboideus muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin:
rhomboideus cervicis: funicular part of nuchal ligament b/w C2 and T2
rhomboideus thoracis: thoracic spines
Insertion: Dorsal and medial borders of scapular cartilage
Action: draws scapula dorsally
Extrinsic
In the dog, also has a part called rhomoideus capitis
in some breeds of cattle, a hump is present (an enlargement of the rhomboideus muscle) - not european breeds
Outline the brachiocephalicus muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
origin = clavicular intersection cranial to shoulder joint
insertion:
cleidobrachialis: brachium or crest of humerus
cleidoccipitalis: nuchal crest and funicular nuchae
cleidomastoideus: Mastoid process of petrous division of temporal bone
Action: dependent on if the limb is weight bearing or free to swing.
during motionL extends shoulder joint and advances whole limb forward
contraction on one side of the neck (ipsilateral muscle), pulls head and neck laterally
head is pulled ventrally when both contact (on either side of neck)
Extrinsic
cleidoccipitalis is absent in horse
cleidomastoideus forms ventral part of cleidocephalicus and forms dorsal boundary of external jugular groove.
Outline the Omotransversarius muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: Acromion of scapula
Insertion: Part of axis and wing of atlas (C1)
Action: bends neck laterally
Extrinsic
located deep to this muscle are the superficial cervical lymph nodes
Outline the Latissimus Dorsi muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: Thoracolumbar fascia on dorsal midline of thorax and lumbar regions
Insertion: Teres major tuberosity on medial-proximal side of humerus
Action: depends on limb position
draws limb caudally when limb is free
Draws trunk cranially when limb is fixed
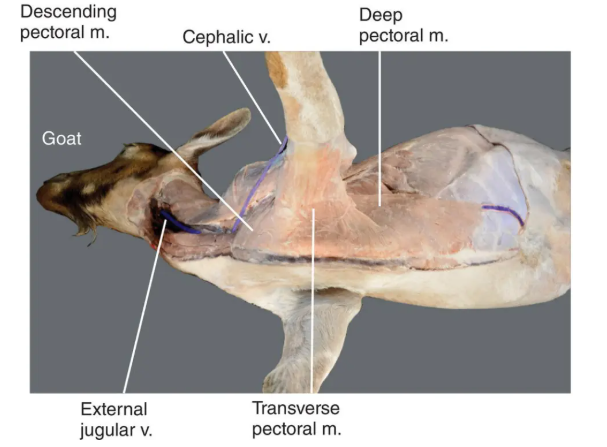
Outline the superficial pectoral muscle (descending and transverse parts); origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin:
descending = manubrium
transverse = 2-6 sternebrae
Insertion:
descending = crest of humerus
transverse = proximal one-third of the medial forearm
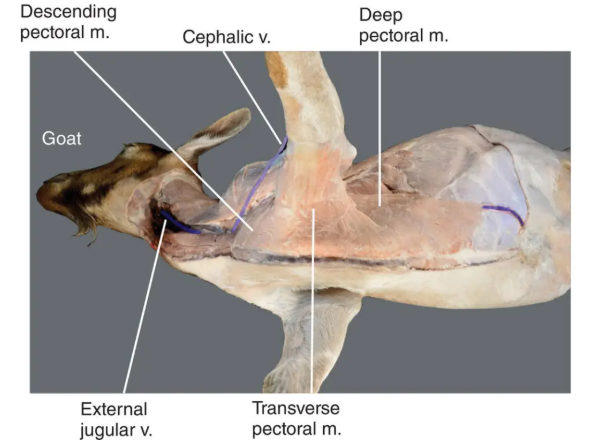
Outline the Deep (ascending) pectoral muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: Median raphe along entire ventral surface of sternum
Insertion: Lesser and greater tubercle on proximal humerus
Action: Adducts and draws limb caudally when limb is free to swing
when limb is advances and fixed = advances trunk
extrinsic
thicker than superficial pectoral muscle
Outline the Serratus Ventralis muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: Last 4-5 cervical vertebrae, first 7-8 ribs
Insertion: serrated surface of scapula
Action:
Cervical part = draws scapula cranially when limb swings caudally
Thoracic part = moves scapula caudally when limb is advanced cranially
act as a ‘sling system’ to support trunk
Extrinsic
has a thoracic and cervical part
Different attachment than normal - bone-muscle-bone = synsarcosis, part of thoracic sling
Outline the Subclavis muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: First rib cartilage
Insertion: Clavicular intersection of brachiocephalicus muscle
Action: none that deserves attention
what is the role of intrinsic muscles
movement of the limb
what are the 2 groups of muscles on the antebrachium
Caudolateral
Caudomedial
Name the 12 intrinsic muscles
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
deltoideus
teres minor
teres major
subscapularis
triceps brachii muscle
anconeus
tensor fasciae antebrachii
biceps brachii
brachialis
Name the acronym used and the first 4 extensor muscles, what side of the distal limb are these found?
ECLU
Extensor carpi radialis
Common digital extensor
Lateral digital extensor
Ulnaris lateralis
Extensor carpi obliquus
Craniolaterally
Name the 5 muscles found caudomedially on the distal limb
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Flexor carpi radialis
SDF muscle - flexor manica
DDF muscle
Interosseus muscle (suspancial ligament) with axial and abaxial extensor branches
what are the 2 retinacula muscles?
Extensor retinaculum (deep fascia-dorsal carpus)
Flexor retinaculum (deep fascia-palmar carpus)
what are the ligaments of the digits
annular ligaments
interdigital
Outline the supraspinatus muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
origin: supraspinous fossa
Insertion: split insertion on greater and lesser tubercles
Action: stabilised and extends shoulder joint
Outline the Infraspinous muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: supraspinous fossa
Insertion:
deep tendon = proximal caudal border of greater tubercle
superficial tendon = distal to greater tubercle
Action = stabilises shoulder joint
Intrinsic
- infraspinatus subtendinous bursa is deep to superficial tendon in ruminants and most other domestic animals (dog and horse), may be absent in small ruminants.
Outline the teres minor muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: distal third of caudal border of scapula
Insertion: teres minor tuberosity proximal to lateral deltoid tuberosity
Action: flexes shoulder joint
Intrinsic
Outline the Teres major muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
origin: proximal caudal border of scapula
insertion: teres major tuberosity on proximal medial surface of humerus - with insertion tendon of latissimus dorsi
Action: flexes shoulder joint
Intrinsic
what does the acronym DTT stand for?
D= deltoideus
T = teres major
T = teres minor
all flex the shoulder joint
Outline the subscapularis muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: subscapular fossa
Insertion: lesser tubercle
Action: stabilises shoulder joint and adduction of brachium
Outline the triceps brachii muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: caudal border of scapula (long head), proximal to lateral humerus and tricipital line (medial, accessory and lateral heads)
Insertion: Olecranon tuber
Action:
extend elbow
Long head flexes shoulder joint
Intrinsic
Horse only has 3 heads (no accessory)
other species have long, lateral, accessory and medial heads
accessory head is only small in ruminants and may be absent
Outline the Anonceus muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: Caudodorsal part of humerus (olecranon tuber)
Insertion: lateral surface of olecranon
Action:
extends elbow joint.
Tenses elbow joint capsule during extension
Outline the tensor fasciae antebrachii muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: Caudal border of scapula
Insertion: olecranon tuber and deep antebrachial fascia
Action: extends elbow
Outline the Coracobrachialis muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
origin: coracoid process of scapula
Insertion:
Horse = teres major tuberosity
Ruminants = distal medial surface of humerus, distal to teres major tuberosity
Action: flexes, adducts and stabilises shoulder joint
Intrinsic
Outline the Biceps Brachii muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: supraglenoid tubercle
Insertion: radial tuberosity and medial elbow region
Action: flexes elbow and extends shoulder joint
Intrinsic
Features:
transverse humeral retinaculum (a flat tissue structure). Wraps around tendon of origin - prevents eversion of tendon from intertubercular groove
intertubercular bursa - under tendon of origin.
In bovine and equine = independent synovial sac
Dogs - extension of shoulder joint capsule
Outline the brachialis muscle; origin, insertion, action, intrinsic/extrinsic and any additional notes
Origin: proximal part of caudal surface of humerus and brachialis groove
Insertion: Medial elbow and proximal part of medial surface of radius (cattle) and medial coronoid process of ulna (goats)
Action: flexes elbow joint
what are 4 common characteristics of the craniolateral muscle group in the distal limb?
common origin from lateral epicondyle of humerus, exception of extensor carpi radialis and obliquus
all are innervated by the radial nerve
collectively extend the carpus with some extending digital joints too
located on the craniolateral aspect of antebrachium
Outline the extensor carpi radialis muscle; origin, insertion, action and any additional notes
Origin: lateral supracondylar crest and radial fossa
Insertion: metacarpal tuberosity at base of Mc III and IV
Action: extends carpus
Outline the Common digital extensor muscle; origin, insertion, action and any additional notes
Origin: lateral epicondyle of humerus
Insertion:
medial tendon - P2 and extends to P3 (ox) of medial digit.
splits into two thin tendons that insert on extensor processes of P3 of digits III and IV
Action: Extends carpus and digital joints
Outline the Lateral digital extensor muscle; origin, insertion, action and any additional notes
origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus and lateral collateral ligament of elbow
Insertion: on P2 and P3 (ox) of lateral digit IV
Action: extends carpus on phalangeal joint of digit IV
Outline the Ulnaris lateralis muscle; origin, insertion, action and any additional notes
Origin: lateral epicondyle of the humerus
Insertion: accessory carpal bone and Mc IV/V
Action: flexes or extends carpus depending on position and action of other muscles
Outline the Extensor carpi obliquus muscle; origin, insertion, action and any additional notes
Origin: lateral distal half of the body of the radius, deep to the common and lateral digital extensor muscles
Insertion: medial-proximal surface of large metacarpal bone
Action: extends carpus
Outline the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle; origin, insertion, action and any additional notes
Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus and olecranon
Insertion: Accessory carpal bone
Action: Flexes carpus and extends elbow
Outline the flexor carpi radialis muscle; origin, insertion, action and any additional notes
Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: proximomedial surface of large metacarpal bone
Action: flexes carpus
Outline the superficial digital flexor (flexor manica) muscle; origin, insertion, action and any additional notes
Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: palmar surface of middle phalanx of digits III and IV
Action: extends elbow and flexes carpal, fetlock and pastern joints
Additional information:
split into the SDF and DDF
join in the mid-metacarpal region to form a single tendon
SDF acts as a sleeve for the passage of the DDF tendon to the palmar surface of P3
Outline the DDF muscle; origin, insertion, action and any additional notes
Origin:
ulnar head = olecranon
radial head = proximal medial radius
humeral head = medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: flexor tubercle of distal phalanx of digits III and IV
Action: extends elbow and flexes carpal, fetlock, pastern and coffin joints
Outline the Interosseus muscle; origin, insertion, action and any additional notes
Also known as suspensory ligament
Origin: Distal row of carpal bones and palmar carpal ligament
Insertion: proximal sesamoid bones
Action: prevents overextension fo fetlock joints by pressure produced from the animal’s weight. Opposes flexor tension.
Additional notes:
horse has a single suspensory ligament
more fleshy in ruminants
which nerves are protractors for extrinsic muscles
accessory spinal and/or segmental cervical nerves
which nerves are involved in the thoracic sling for extrinsic muscles
brachial plexus
segmental spinal nerves
what nerve is a retractor for extrinsic muscles
brachial plexus
name the 9 nerves that serve the extrinsic nerves
accessory spinal
spinal segmental C1-C7
spinal segmental C5-C8
pectoral
spinal segmental C6-T7
spinal segmental C8-C10
long thoracic
thoracodorsal
lateral thoracic
name the roots of the 9 extrinsic serving nerves
accessory spinal - c1-C7 (ascends within spinal canal to exit from skull)
spinal segmental - C1-C7
spinal segmental - C5-C8
pectoral - C6, 7, 8, T1
spinal segmental - C6-T7
spinal segmental - C8-C10
long thoracic - C7, 8
thoracodorsal - C8
lateral thoracic - C8
name the function of each of the 9 nerves that serve the extrinsic muscles
accessory spinal - protraction
spinal segmental - C1-C7 - assists accessory spinal
spinal segmental - C5-C8 - thoracic sling
pectoral - thoracic sling
spinal segmental C6-T7 - thoracic sling
spinal segmental C8-C10 - thoracic sling
long thoracic - thoracic sling
thoracodorsal - retraction
lateral thoracic - skin twitch
name which muscles are supplied by each of the nerves that serve the extrinsic muscles
accessory spinal - long strap neck muscles, trapezius cervicis
spinal segmental C1-C7 - long strap neck muscles
spinal segmental C5-C8 - serratus ventralis cervicis
pectoral - pectoralis grp
spinal segmental C6-T7 - rhomboidei
spinal segmental C8-C10 - trapezius thoracis
long thoracic - serratus ventralis thoracis
thoracodorsal - latissimus dorsi
lateral thoracic - cutaneous trunci
How is the skin innervated
Segmentally:
C1 = purely motor
cervical region = C2-C5
Dorsal shoulder region = C6-T2 (not C7,8 or T1)
Dorsal thorax and abdomen = T3-L4
Lateral thorax and abdomen = lateral cutaneous branches T3-L2
ventral thorax and abdomen starting at base of neck = T2 - L1
what does the brachial plexus serve?
intrinsic muscles
what nerves form the plexus?
ventral rami of spinal nerves
what is the location of the plexus
in axilla i.e. medial to shoulder joint
name the 7 nerves that leave the plexus
suprascapular
subscapular
axillary
musculocutaneous
radial
median
ulnar
Name the roots of the 7 nerves that serve the intrinsic muscles
suprascapular - C6 (7)
subscapular - C6, 7
axillary C7, 8
musculocutaneous, C (6), 7, (8)
radial - C7,8, T1
median C8, T1, 2
ulnar - C8, T1, 2
name the function of the 7 nerves that serve the intrinsic muscles
suprascapular - shoulder stability
subscapular - shoulder stability
axillary - shoulder flexion
musculocutaneous - elbow flexion
radial - extension of all shoulder joints exc. shoulder
median - flexion of carpus and digits
ulnar - flexion of carpus and digits.
name the muscles supplied by the 7 nerves that serve the intrinsic muscles
suprascapular - supraspinatus, infraspinatus
subscapular - subscapularis, teres major
axillary - teres major and minor, deltoideus, cleidobrachialis
musculocutaneous - biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis
radial - extensors of elbow, carpus and digits
median - flexors of carpus and digits
ulnar - flexors of carpus and digits
what is the cutaneous supply provided by the 7 nerves that serve intrinsic muscles?
suprascapular
subscapular
axillary - cranial lateral brachium, lateral antebrachium
musculocutaneous - medial antebrachium
radial - lateral antebrachium, dorsal carpus
median - palmar carpus
ulnar - caudal lateral antebrachium digit 5
what are 2 important things to note about the nerves?
cutaneous innervation for a nerve is distal to the muscles supplied by the same nerve
coracobrachialis is innervated by musculocutaneous nerve but is actually a shoulder flexor.
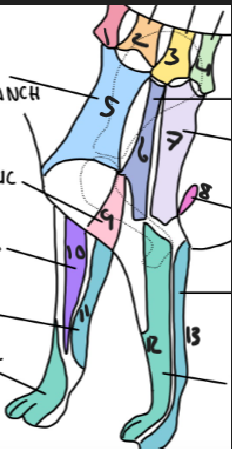
name 1.
C5
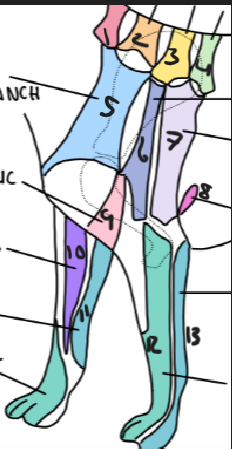
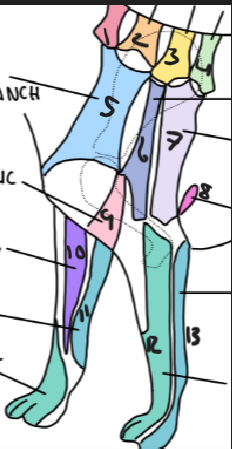
name 2
C6
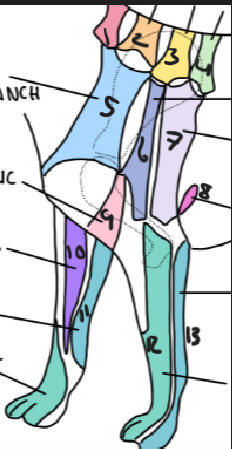
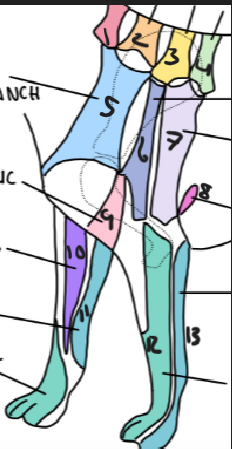
name 3
T2
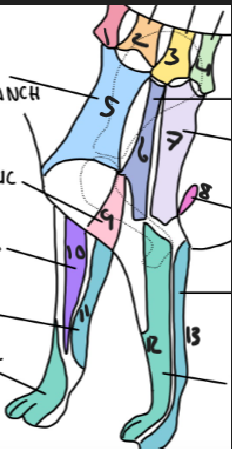
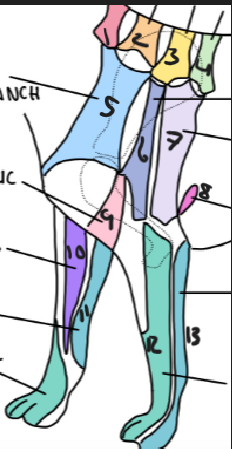
name 4
T3
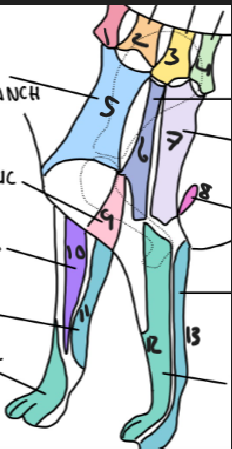
name 5
C5 ventral cutaneous branch
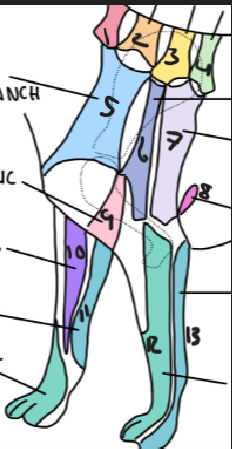
name 6
Axillary nerve
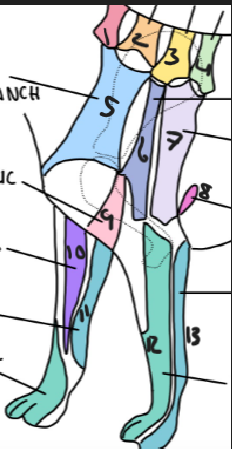
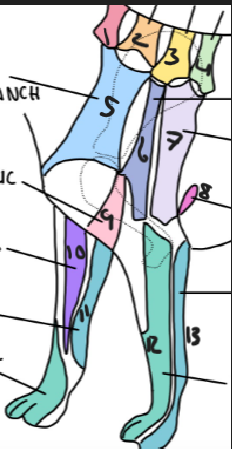
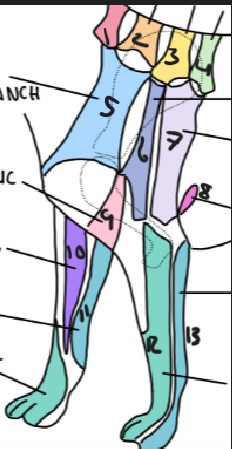
name 7
T2 lateral cutaneous branch
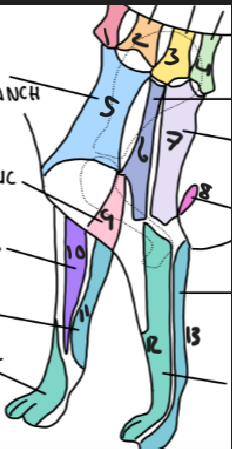
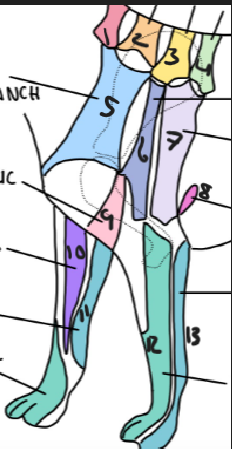
name 8
T3 lateral cutaneous branch
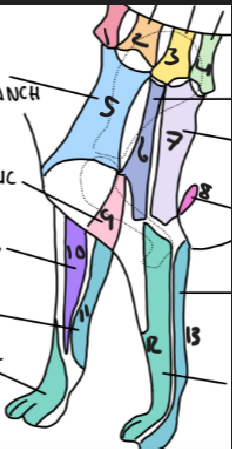
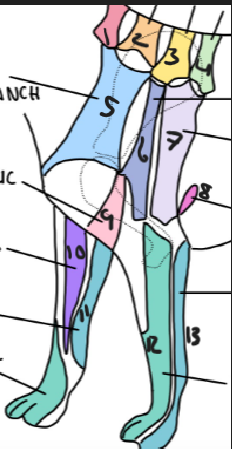
name 9
brachiocephalic nerve
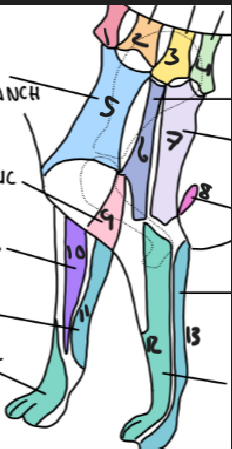
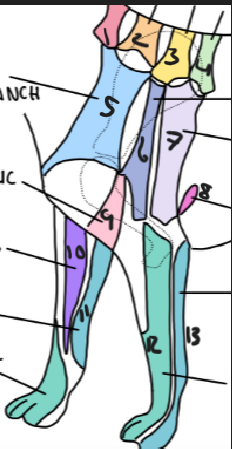
name 10
musculocutaneous nerve
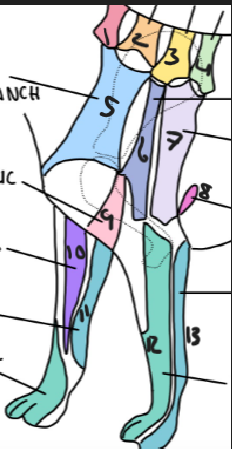
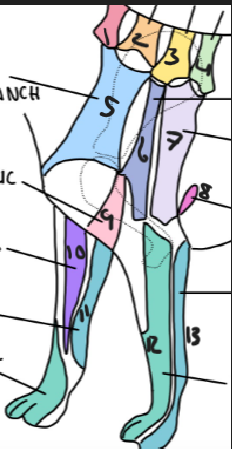
name 11
ulnar nerve
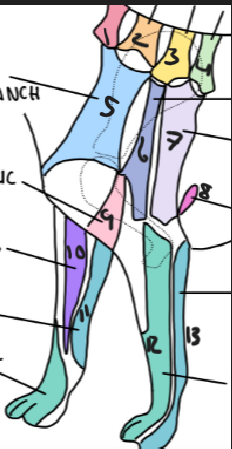
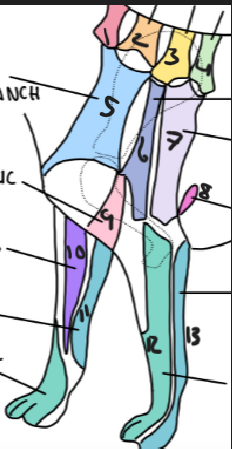
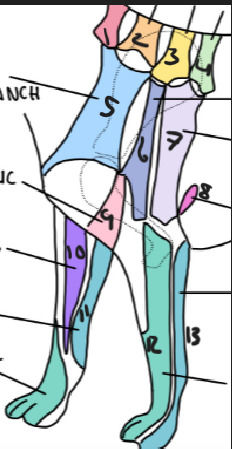
name 12
radial nerve
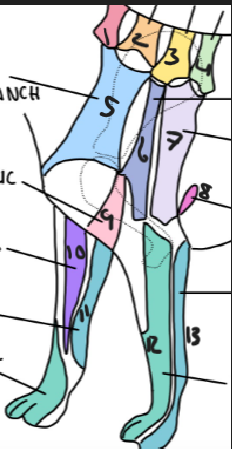
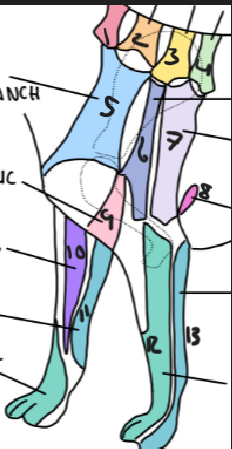
name 13
ulnar nerve
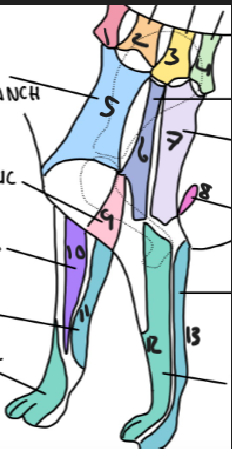
name the bones involved and the movement(s) that can occur normally in the shoulder
Bones: scapula and humerus
Movement: extension and flexion
name the bones involved and the movement(s) that can occur normally in the elbow
Bones: broad distal condyles of humerus, concave articular surfaces of ulna and radius
Movement: cranially-caudally
name the bones involved and the movement(s) that can occur normally in the carpus
bones: 2 rows, 3 joints (antebrachiocarpal, middle carpal and carpometacarpal)
Movements: Antebrachiocarpal and middle = hinge joints
Carpometacarpal = sliding joint
Extension/over-extension in dogs and cats, some adduction and abduction in primates.
Pigs, ruminants and horses - only flexion and extension
name the bones involved and the movement(s) that can occur normally in the metacarpo-phalangeal joint
Bones: metacarpals and phalanges
Movements: flexion through to hyperextension, abduction and adduction in primates.
name the bones involved and the movement(s) that can occur normally in the proximal interphalangeal joint
Bones: proximal phalanx and middle phalanx
Movement: extension and flexion only
name the bones involved and the movement(s) that can occur normally in the distal interphalangeal joint
Bones: middle and distal phalanges
movement: extension and flexion
name the extensor muscles of the shoulder
brachiocephalicus (if limb isn’t weight bearing)
biceps brachii
supraspinatus
name the muscles that stabilise the shoulder
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
subscapularis
coracobrachialis
name the muscles that flex the shoulder
trapezius (elevates)
rhomboideus (draws dorsally)
deltoideus
teres minor
teres major
long head of triceps brachii
Name the muscles that extend the elbow
triceps brachii
anonceus (tenses joint capsule during extension)
tensor fasciae antebrachii
SDF
DDF manica
name the muscles that flex the elbow
brachialis
biceps brachii
coracobrachialis
brachialis
Name the muscles that enable extension of the carpus
extensor carpi radialis
common digital extensor
lateral digital extensor
ulnaris lateralis
extensor carpi obliquus
Name the muscles that flex the carpus
ulnaris lateralis
flexor carpi ulnaris
superficial flexor manica
deep digital flexor manica
name the muscles involved in extension of the digits
extensor carpi radialis
common digital extensor
lateral digital extensor
name the muscles involved in the flexion of the digits
superficial digital flexor manica
deep digital flexor manica
Name some species differences in the scapula
Dogs: acromion process is absent, supraglenoid tubercle is part of the glenoid cavity, no glenoid notch
Horses: narrow supraspinus fossa, absent acromion, prominent tuber spine, SGT separate from glenoid cavity. Has a glenoid notch
Ruminants: Broad dorsal and larger infraspinous fossa, blunt acromion, doesn’t reach glenoid cavity, tuber spine is less present/absent. Indistinct glenoid notch
Birds: not flattened, only one supraspinous fossa?
Pig: rounded cranial margin, poorly defined acromion, prominent tuber.
Name some species differences in the humerus:
Dogs: single greater tubercle and supratrochlear foramen
Horses: greater tubercles are level with eachother, lesser tubercle is similar in size. Supratrochlear foramen is absent, very prominent deltoid tuberosity. Doubler intertubercular groove
Ruminants: cranial and caudal greater tubercles are higher than head. Greater tubercle overhangs intertubercular groove medially. Single intertubercular groove. Circular infraspinus insertion area. Small deltoid tuberosity. No supratrochlear foramen
Birds: ovoid head for articulation with scapula, coracoid and clavivle. Pneumatic bone.
Pig: greater tubercle has cranial and caudal parts higher than humerus head, rounded shape, almost encloses (single) intertubercular groove, no supratrochlear foramen
name some species differences in the radius and ulna
Dogs and cats: 2 separate bones, rotation is possible
Horse: proximal ulna present only, distally fused with radius. No rotation possible
Ruminants: 2 complete bones, fuse as animal ages, no rotation
Birds: ulna is thicker and longer, radius lying laterally to ulna
Pig: 2 separate bones, same diameter, no interosseus space, no rotation
Name some species difference in carpal bones
Carpal bones: radial and intermediate are fused, ulna is larger and has a different shape, all 4 in distal row
Horse: distal row: 1st is very small by second. 3rd and 4th span the rest of thwidth.
Bovine: distal row: no 1st carpus, 2nd and 3rd are fused, 4th present.
Pig: has 4, with increasing size (1-4)
Birds: carpus of the adult only has the ulnar and radial.
Name some species difference in metacarpal bones
Dog: 5 metacarpal bones
Horse: only the 3rd, with the 2nd and 4th present as vistigial.
Ruminants: third and fourth are fused with the 5th being a small button/visitigial bone
Birds: A single bone, a fused bone of metacarpal 1-3.
Pig: 4 metacarpals, 5th is absent.
which is the only animal to have 4 tricep heads?
dog
how does the horses deltoideus differ from other species?
no acromial division
Why do horse muscles tend to be larger and longer?
larger animal
more robust muscle development for weight bearing
powerful limb contraction needed
what is the synsarcosis
where parts of the skeleton e.g. shoulder form a union to the rest of the skeleton via muscles alone.
what muscles do you expect to atrophy most in a dog with elbow disease/a painful elbow and why?
triceps major
brachialis
muscles that are most vulnerable to atrophy are anti-gravity that cross a single joint.
How could we investigate forelimb lameness?
palpation (swelling, localised head, asymmetry)
walk/trot
obeserve gait and movement
radiography
ultrasound
Name 3 examples of conditions which are generally called ‘elbow dysplasia’
ununited anconeal process (UAP)
osteochondrosis dissecans (OCD) of humeral condyle
fragmented coronoid process (FCP)