Chapter 10: Sample Preparation and Handling
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Circadian
Cyclical changes throughout the day
Circannual
Seasonal changes over the course of a year
Cyclical
Occuring in cycles
Diurnal
Daily variation in blood levels at a particular time of day
Etiologic Agent
Viable microorganism or its toxin that causes or may cause human disease
Preexamination
All processes that it takes to collect the sample and get to the point in which the testing of the sample can occur
46-56%
Preexamination errors that occur prior to testing comprise how many percent of ALL errors encountered for laboratory samples?
Improper patient identification
What is the most serious and potentially most dangerous preexamination error?
Tourniquets
What is one factor under the phlebotomist’s control that can create a change in test results?
1 minute
The tourniquet should be on the arm no longer than?
Intervascular blood pressure
What does the tourniquet increase which results in a push of small molecules and fluid from the capillaries into the surrounding tissue?
Hemoconcentration
The reduction of fluid volume results in?
Potassium
The inability to circulate lowers the the pH and causes which analyte to be forced out of the blood cells?
Calcium and magnesium
The change in pH also causes an elevation in which two analytes?
Cell permeability
What will change in a patient if he or she has just completed vigorous exercise?
Creatinine kinase;
Aspartate aminotransferase;
Lactate dehydrogenase
Vigorous exercise causes an increase in concentration of:
1.) (?) (CK)
2.) (?) (AST)
3.) (?) (LDH)
4.) Bilirubin
5.) Creatinine
6.) Uric acid
Skeletal muscle
Lactate and pyruvate increase in even moderate exercise due to the increased metabolic activity of which muscle?
Runner's anemia
Long-term exercise by highly trained runners can cause which type of anemia?
2,000
Total WBC can increase by as much as much as (?) as a result of exercise or other stresses
Lactate
Which analyte is increased by 100% more when the patient makes an extremely tight fist or pumps the hand?
Hemoglobin
With the exception of this analyte, most analytes increase with exercise and stress
Creatinine kinase; Aspartate aminotransferase; Lactate dehydrogenase; Bilirubin; Creatinine; Uric acid; Lactate; Pyruvate; White blood cells; Neutrophils
Changes due to Exercise and Stress
List the 10 analytes increased
Glucose
Changes due to Exercise and Stress
List the analyte increased with stress but decreased with exercise
stress; exercise
Changes due to Exercise and Stress
Glucose is increased with (?) but decreased with (?)
Blood volume
Changes due to Posture
List the analyte decreased when changing from lying down to standing up
Blood pressure; Calcium; Cholesterol; Lipids; Drugs; Steroids; Thyroid hormones
Changes due to Posture
List the 7 analytes increased when changing from lying down to standing up
1 minute
After lying down, have the patient sit up for how long before you release him or her?
8-12 hours
Fasting usually means no food for how long?
morning
Fasting samples are generally collected in the (?) after an overnight fast
Water
The patient should not have had chewing gum, orange juice, or anything other than?
Glucose and triglycerides
Which 2 tests are affected when you collect a sample and label it as fasting when the patient was nonfasting?
No
Do fasting samples have a specific time for collection?
diurnal
Others tests may require that the sample be collected at a specific time because of medication or (?) rhythm
critical
For patients with diurnal rhythm or under medication, the precise timing of the collection for these samples is (?)
50%
Cortisol can vary as much as how many percent between samples collecting in the morning or evening?
morning
True or False? If false, replace the underlined word to make the statement correct.
“Serum iron levels are lower in the evening.”
Calcium
Which analyte demonstrates a circannual change, increases in the summer due to more sunlight exposure which results to increased Vitamin D?
75%
Most tubes should be filled at least how many percent of the stated volume to be accurate?
dilutional; decrease
If there is less blood in a tube, it causes a (?) effect, leading the RBCs to (?) in size
clot
If there is too much blood in an anticoagulant tube, it causes the blood to (?) because there is not enough anticoagulant for the volume of blood
Citrate tubes
Which tubes are the most critical for correct fill size?
10%
The variation in fill for citrate tubes can only plus or minus how many percent from the stated volume?
Draw another tube
When the blood tubes fill only partially, what must be done to obtain the proper amount?
poured
Partial tubes cannot be (?) together
doubled; altered
By pouring together partially filled tubes, the amount of anticoagulant in the tube is (?), resulting in (?) test results
mixed
Serum and plasma samples generally cannot be (?)
5-8
Inversion of (?) times must be done immediately after the tube is pulled from the holder
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and Sodium citrate
Which are the 2 most sensitive tubes?
Sodium heparin
Chromosome studies need which type of heparin tube since lithium is toxic to cells?
syringes
The Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines discourage the use of (?)
Butterfly system
Difficult draws are best performed with a (?)
Evacuated tube system
What is the preferred method of collection?
Potassium; Phosphorous; Uric acid
Which 3 analytes are increased with the use of iodine?
alcohol pad
The iodine must be removed with an (?) if any testing other than a blood culture is collected
Nonalcohol cleaner
What must be used when cleaning a venipuncture site for blood alcohol testing?
Order of draw
Which is the most common factor that varies tests results that the phlebotomist has control over?
Prothrombin (PT) and Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
Which 2 test results can be increased if EDTA or Heparin tubes are drawn before the Citrate tube?
High
If the tube drawn after the EDTA is tested for potassium, will the potassium give a high or low result?
Dipotassium EDTA; Tripotassium EDTA
The EDTA used in the tube is either (?) or (?)
Ammonia;
Acid phosphatase;
Catecholamines;
Lactic acid;
pH/blood glases
List the 5 common tests requiring the chilling of specimens
Potassium; Serum potassium
What analyte is released when you chill an uncentrifuged serum tube? Which value does it elevate?
instructions
Only chill a sample when the draw (?) specifiy

Cold agglutinins; Cryoglobulin
What are the two tests that must be maintained at 37 degrees Celsius?
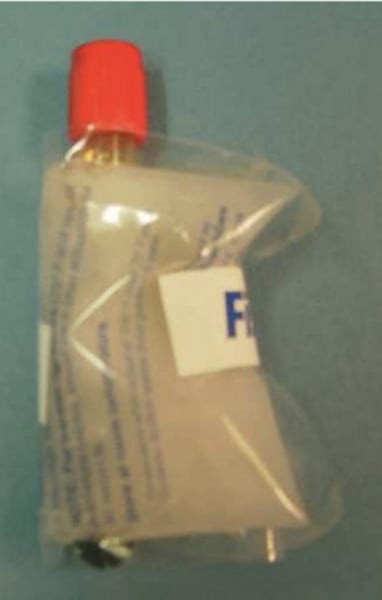
heel warmer
The best method of maintaining a sample 37 degrees Celsius is to wrap the sample in a (?)
warming block
Another method of maintaining a sample 37 degrees Celsius is to use a plastic block or (?)
amber tubes
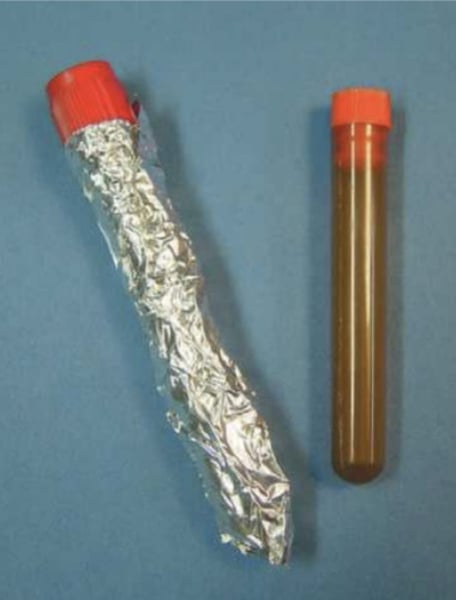
Bilirubin samples must be collected in (?) to protect them from light
Vitamins C, E, K
Aside from bilirubin, what 3 other tests must be protected from light?
Wrap in aluminum foil
What is the most efficient method to protect the sample from light?

hand
If a heel warmer or warming block is not available, the sample can be bagged and held in your (?) as you transport it to the laboratory
label
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
Each sample must have its own (?) attached to the sample's primary container.
test to be performed
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
Each sample must have on the label the name of the (?) (e.g., complete blood cell count [CBC], cholesterol).
complete name; hospital number
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
Labels must have the patient's (?) and (?) or unique identifier.
time limits
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
The sample must be collected within the (?) requested.
removed; capped
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
Samples in syringes must have needles (?) and the syringe (?) before transport.
container; lid
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
Urine samples must have the label on the (?) and not on the (?).
appropriate
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
The (?) anticoagulant must be used for samples requiring an anticoagulant.
expiration date
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
Tubes may not be used beyond the (?).
light
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
Certain samples may not be exposed to (?).
clots
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
Anticoagulated blood samples must be free of (?).
unacceptable
Criteria for Recollection/Rejection of a Sample
Blood samples drawn above an intravenous (IV) injection site are (?).
Primary container
What do you call the container in which the sample was collected?
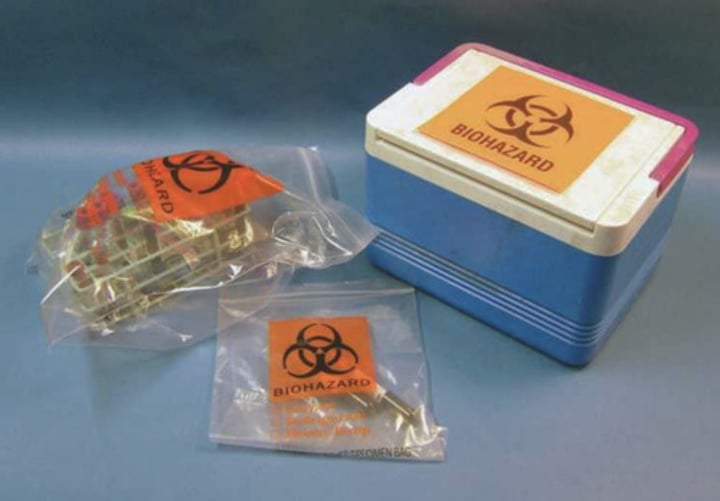
secondary container
When a sample is transported, the primary container must be placed in a (?)
Plastic self-sealing bag
Which type of secondary container is sufficient for most samples?
True
True or False? If false, replace the underlined word to make the statement correct.
“A single sample or multiple samples from one patient can be placed in the bag and then the bag sealed shut. However, samples from different patients should not be placed in the same bag.”
before
True or False? If false, replace the underlined word to make the statement correct.
“All labels must be attached to the sample tubes after they are placed in the bag.”
Biohazard emblem
Whatever secondary container is used, which emblem must be attached?

faster delivery
Pneumatic tube systems that transport samples are more traumatic than hand carrying the samples but have the advantage of (?)

padded container
What can be done to prevent trauma to the sample?
—the bagged sample is placed into a (?) to maintain the integrity of the sample
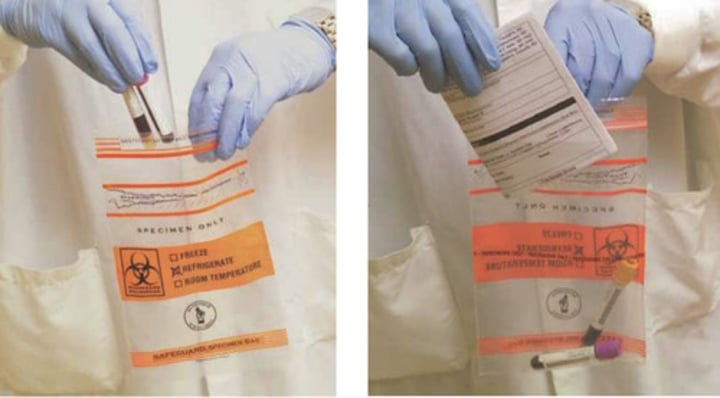
requisition
The self-sealing bags for these specimens have two compartments.
One compartment is for the sample and the other compartment is for the (?).
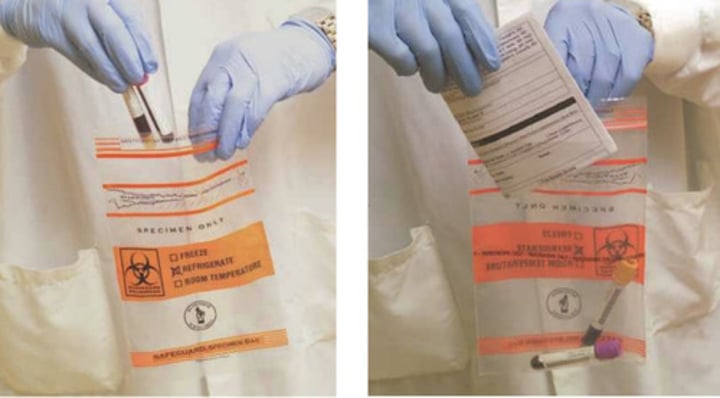
leak
Separate compartments prevent the requisition from being contaminated if the sample tube should (?)
absorbent

etiologic agent
The outside of the shipping container must have the biohazard emblem and wording that the container holds an (?) (infectious substance).

Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)
(?) and other government agencies regulate the shipment of etiological agents.
Category A; Category B
What are the 2 categories of infectious substances?
Category A
An infectious substance which in a form that, when exposure to it occurs, is capable of causing permanent disability, life-threatening or fatal disease in otherwise healthy humans or animals.
UN2814
What is the proper shipping name for Category A (infectious substances, affecting humans)?
UN2900
What is the proper shipping name for Category A (infectious substances, affecting animals)?
Category B
An infectious substance which does not meet the criteria for inclusion in Category A.
UN3373
What is the proper shipping name for Category B
Category B
What is the classification of clinical specimens requested in support of a VS acute gastroenteritis outbreak investigation?