9 Motivation in substance abuse
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Motivation in substance abuse
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
10 broad principles of druguse
Drug use is a chosen behavior
Drug problems emerge gradually & occur along a continuum of severity
Once well-established, drug problems tend to become self-perpetuating
Motivation is central to prevention andintervention
Drug use responds to reinforcement
Drug problems do not occur in isolation, butas part of behavior clusters
There are identifiable and modifiable risk & protective factors for problem druguse
Drug problems occur within a family context
Drug problems are affected by a larger socialcontext
Relationship matters
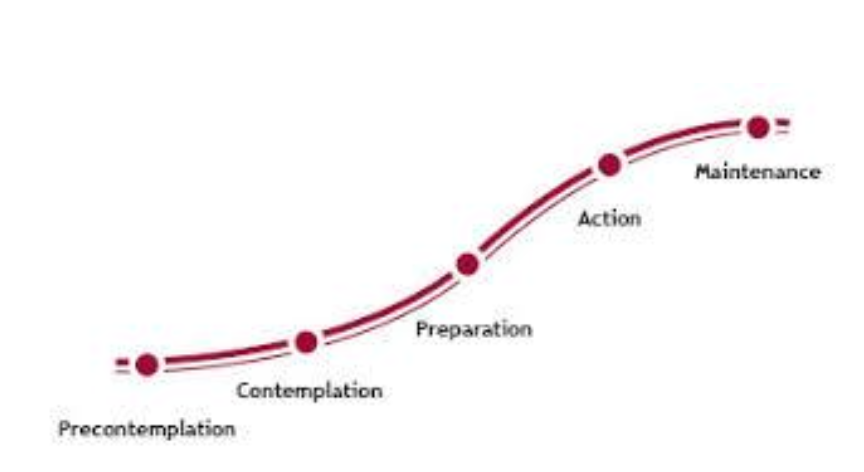
preconetemplation
not seeing advantages in quiting
contemplation
seeing advantages in quitting
preparation
taking first steps, but still drinking
action
quitted & modified the behaviour
maintenance
maintenance of behaviour
Transtheoretical model
Model of behavioural change
Describes how people modify a problem behavior or acquire a positive behavior.
Stages of Change
Self-efficacy construct represents
the situation specific confidence that people have that they can cope with high-risk situations without relapsing to their unhealthy or high-risk habit.
The Situational Temptation Measure
reflects the intensity of urges to engage in a specific behavior when in the midst of difficult situations.
Motivational interviewing
evidence-based intervention designed to enhance client motivation for change
Tested in a variety of clinical intervention modalities (substance abuse treatment, chronic disease managment, behavioral health interventions)
Motivational interviewing types
Traditional approach
Motivational Interviewing approach
Traditional approach
Increased patient knowledge will translate into behaviour change
Increases clinician & patient frustration due to poor outcomes
‘You should quit smoking because it will preventdisease’
Motivational Interviewing approach
Based on the assumption that individuals are motivated to change when change is connected to something they value
Source is then internal
MI begins with
exploration of the patients’view of the potential benefits of changing
“Tell me about any benefitsyou see in quitting smoking”
A client-centered directive method for
Enhancing intrinsic motivation to change by exploring an resolving ambivalence
work from the client’s perspective
Elicit from the patient whatever reasons he or she has for engaging in that health behaviour
Intrinsic (internal) reasons for change tend to be associated with
greater adherence to medical recommendation, persistence, & long-term behaviour change
Three major elements of spirit
Collaboration
Evocation
Autonomy
Collaboration
Style of working with the patient
Fostering a partnership with the patient rather than assuming an expert role
Working together toward a common goal
Autonomy
Patients have the freedom to make their own choices
The role of the clinician is to facilitate the change, not to impose it
Final decision rests with the patient
Express empathy
patient’s perspective
Need to avoid judgment although there may be
conflicts with our own beliefs
MI - MajorPrinciples
Express empathy
Develop discrepancy
Roll with resistance
Support self-efficacy & optimism
Being non-judgmental helps to
reduce self-defend
Develop discrepancy
Between the patient’s current behaviour & his or her important goals or values
Roll with resistance
Essential to avoid arguing
Support self-efficacy & optimism
If the clinician expresses doubt regarding the ability or likelihood or a patient to succeed with making a change, that will undermine the patient’s self-efficacy
Fields of application emotion
Emotional intelligence
Association with Psychological well-being
Authors in emotional intelligence
Mayer & Salovey
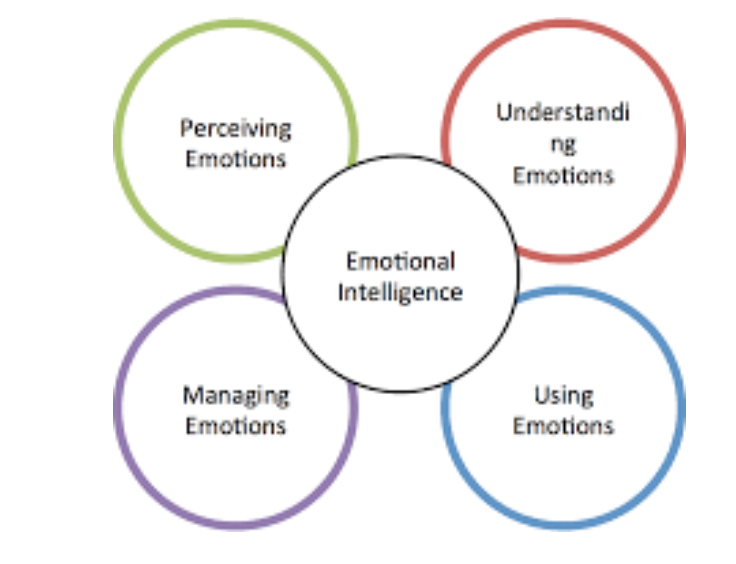
According to Mayer and Salovey, emotional intelligence refers to the
involved in:
recognizing
using
understanding
manage
other & owns emotional states to solve problems & regulate behaviour.
ABILITY MODEL
components such as sociability, self-control, & emotionality
illustration of emotional intelligence components
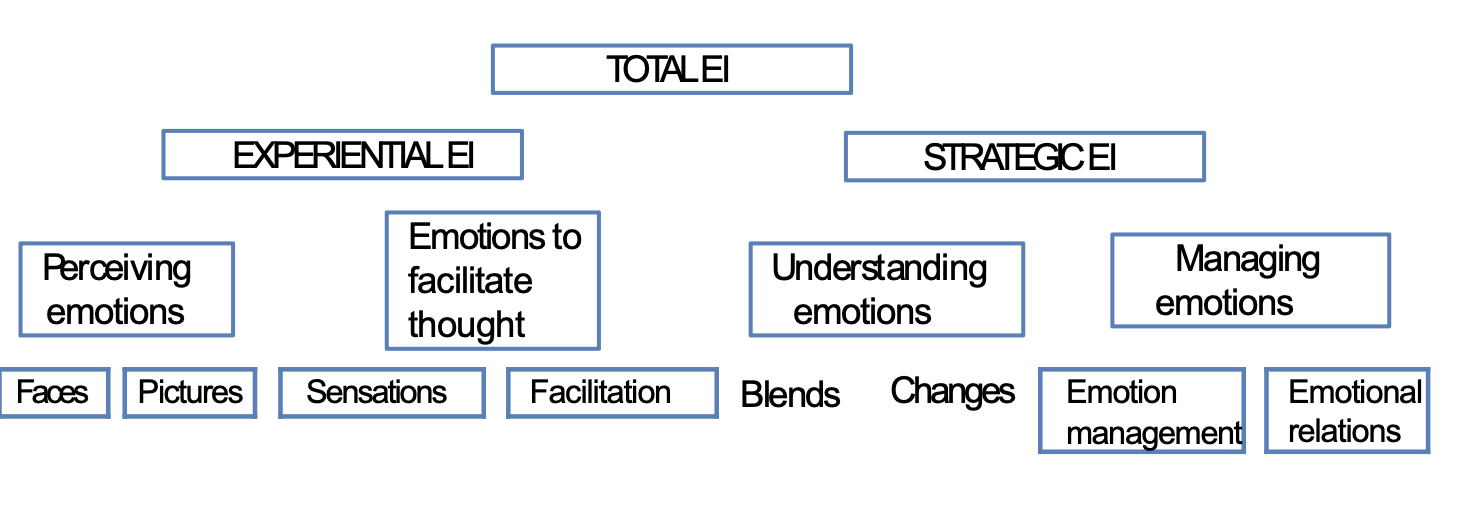
two ways of measuring emotional intelligence
EXPERIENTIAL emotional intelligence
STRATEGIC emotional intelligence
two components of experiential emotional intelligence
Perceiving emotions
Emotions to facilitate thought
two components of Strategy emotional intelligence
Understanding emotions
Managing emotions
Perceiving emotions
Faces
Pictures
Emotions to facilitate thought
Sensations
Facilitation
Understanding emotions
Blends
Changes
Managing emotions
Emotion management
Emotional relations
Measurement of emotional intelligence: MSCEIT
What does emotional intelligence predict?
Physical & psychological well-being.
Link between emotional intelligence & education.
Emotional intelligence & organizations.
Physical & psychological well-being
MSCEIT scores correlate positively
MSCEIT scores correlate negatively
The MSCEIT scores correlate positively with
Ryff Scale of Psychological Well-Being
In areas related to growth & social relationships.
MSCEIT scores correlate negatively with
depression & anxiety scales, such as the BDI & STAI.
less vulnerable to negative affect & depression
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE & EDUCATION
Relationship between academic achievement & emotional intelligence
Emotional regulation have impact on academic performance
emotional intelligence associated with social skills in the classroom
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE & ORGANIZATIONS
Emotional intelligence & goal achievement & organizational behaviour assessed by a supervisor.
important skill for supervisors
influencing organizational commitment & emotional regulation