First Aid USMLE Step 1: Hematology & Oncology
1/425
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
426 Terms
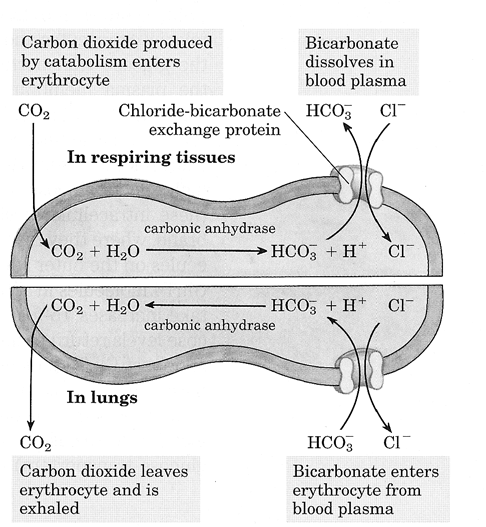
What does the Cl−/HCO3− anti porter allow RBCs to do?
Allows export of HCO3− and transport of CO2 from the periphery to the lungs for elimination
microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
disorders associated
RBC appearance
hemolytic anemia caused by mechanical destruction of red blood cells (RBCs) as they pass through small, damaged blood vessels. It is characterized by schistocytes (fragmented RBCs) on a peripheral blood smear.
TTP
HUS
DIC
HELLP
What is Erythrocytosis, anisocytosis and poikilocytosis?
Erythrocytosis = polycythemia = hematocrit.
Anisocytosis = varying sizes.
Poikilocytosis = varying shapes.
The small cytoplasmic fragment of a thrombocyte (platelet) is derived from what? What is its lifespan?
Megakaryocytic, 8-10 days
What protein do platelets interact with to form the platelet agreggates ?
Fibrinogen
What causes petechiae?
Thrombocytopenia or ↓platelet function
What do dense granules and alpha granules in platelets contain?
Dense granules: Ca2+, ADP, Serotonin, Histamine; CASH
Alfa granules contain vWF, fibrinogen, fibronectin, platelet factor four.
Approx. 1/3rd of platelets are stored where?
In the spleen
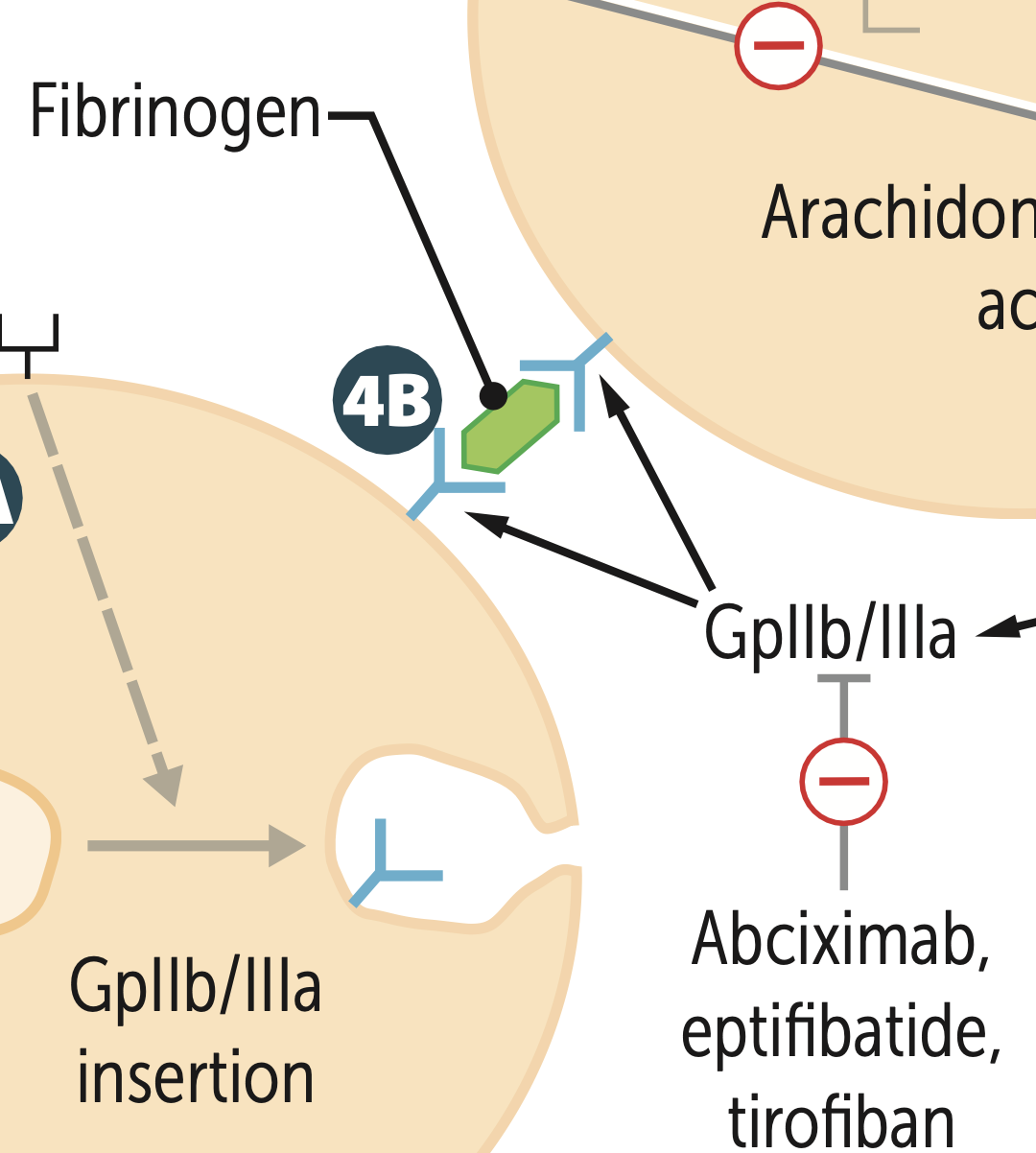
What is the fibrinogen receptor?
GpIIb/IIIa
What is the vWF receptor?
GpIb
What are my three granulocytes?
Neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil
List the WBC differential for ranges
Neutrophils (54-62%)
Lymphocytes (25-33%)
Monocytes (3-7%)
Eosinophils (1-3%)
Basophils (0-0.75%)
What do the specific granules in neutrophils contain?
Specific granules contain ALP, collagenase, lysozyme, and lactoferrin
What do the azurophilic granules in neutrophils contain?
Azurophilic granules (lysosomes) contain proteinases, acid phosphatase, myeloperoxidase, and β-glucuronidase.
Involved in killing and digesting pathogens through enzymatic degradation and reactive oxygen species production
In what deficiency do we see hypersegmented neutrophils?
Vitamin B12/ folate deficiency.
What are band cells?
Immature neutrophils- reflect states of myeloid proliferation (bacterial infections, CML).
What are some neutrophil chemotactic agents?
C5a, IL-8,
LTB4, 5-HETE (leukotriene precursor),
kallikrein, platelet-activating factor,
N-formylmethionine (bacterial proteins).
Left shift neutrophils
def
when is this seen
increase in immature neutrophil precursors (band cells, metamyelocytes) in the peripheral blood.
This occurs when the bone marrow is responding to an increased demand for neutrophils, such as in infection, inflammation, or myeloid proliferation (e.g., CML).
Leukoerythroblastic reaction
Left shift + immature RBCs (nucleated RBCs)
Suggests bone marrow infiltration (e.g., myelofibrosis, metastasis)
What is a plasma cell cancer?
Multiple myeloma
For T cells what does CD28 do?
CD28 (costimulatory signal) necessary for T-cell activation.
What are dendritic cells called in the skin? What type of MHC do they bear?
Langerhans cell in the skin; MHC II, and Fc receptors
macrophages in
liver
bone
brain
Kupffer cells in liver, histiocytes
in connective tissue, osteoclasts in bone,
microglial cells in brain
link between innate and adaptive immune systems (eg, via T-cell stimulation).
dendritic cells
.
✅ Activate CD4+ T cells via MHC class II
✅ Enhance antigen uptake via Fc receptors
✅ Activate CD8+ T cells through cross-presentation (MHC class I)
can present EXOgenous antigens
usually MHC 1 can only present endogenous antigens
Lipid A binds to what on macrophages to initate septic shock?
Lipid A from bacterial LPS binds CD14 on
macrophages to initiate septic shock.
What cytokine can activate Macrophages?
γ-interferon
What are the causes of eosinophilia?
(PACMAN Eats):
Parasites
Asthma
Chronic adrenal insufficiency
Myeloproliferative disorders
Allergic processes
Neoplasia (eg, Hodgkin lymphoma)
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
What are the two main products of the antihelminthic eosinophil?
Produce histaminase, major basic protein (MBP, a helminthotoxin),
eosinophil peroxidase,
eosinophil cationic protein, and eosinophil-
derived neurotoxin.
Basophilia is a sign of what?
Myeloproliferative disease, particularly CML
What are the 3 main products of basophils?
Heparin (anticoagulant) and
Histamine (vasodilator).
Leukotrienes synthesized on demand
basophils function
mediate allergic reactions
Basophilia is uncommon, but can be a sign of
myeloproliferative disorders, particularly CML.
Mast cell release
release of histamine, heparin, tryptase, and
eosinophil chemotactic factors.
What prevents mast cell degranulation?
Cromolyn sodium prevents mast cell degranulation (used for asthma prophylaxis).
What type of hypersensitivity reaction is implicated with Mast cells?
Involved in type I hypersensitivity reactions
c- kit gene mutation + increase in serum trypase and histamine
mastocytosis
proliferation of mast cells in skin or organs
flushing , pruritis, hypotension, abdominal pain and diarrhea, peptic ulcer disease
apoptosis of cells which do not express MHC class 1 is induced by what cell
NKC
NKC release
perforins and granzymes
_____ is a plasma cell dyscrasia
Multiple Myeloma
What type of antibodies are found in blood type
A
B
O
AB
A= IgM anti A
B= IgM anti B
O= IgG anti A+ B
AB = NONE
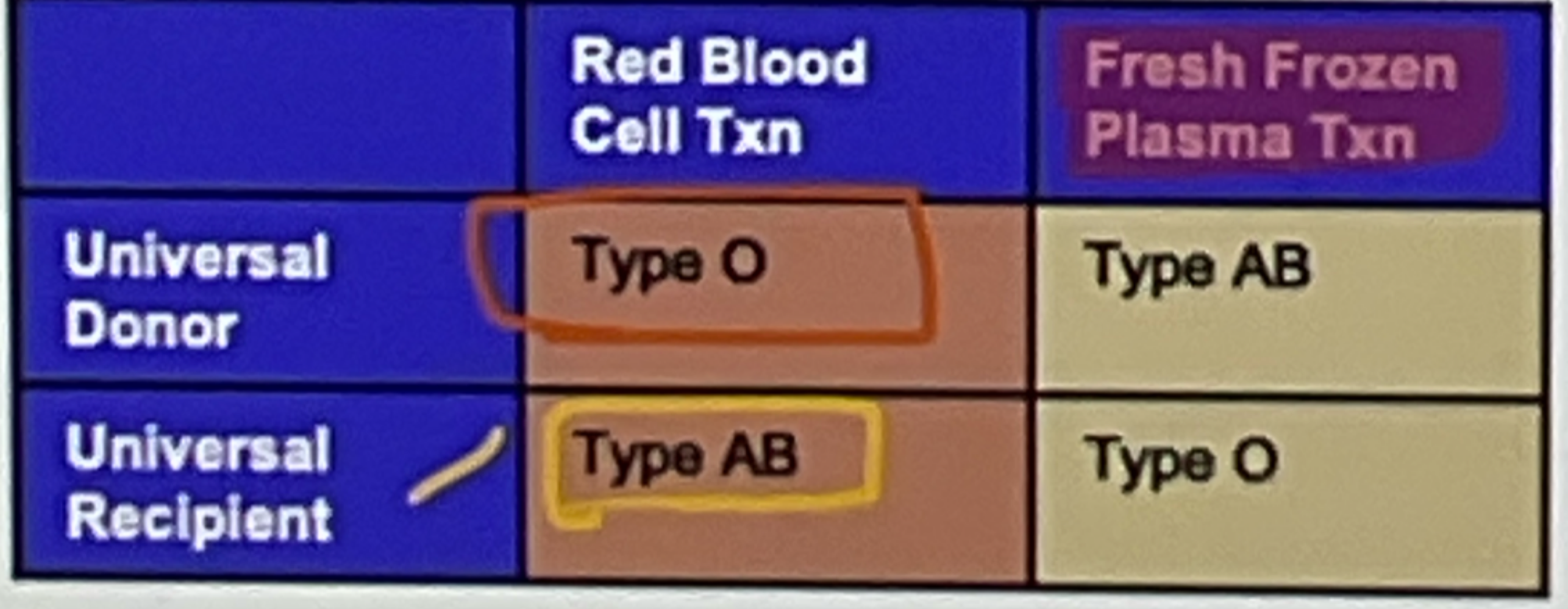
universal recipient and donor PLASMA vs RBC
AB
universal recipient RBC
bc has all the antigens
universal donor of PLASMA
NO antibodies
RBC= antigen
plasma = antibodies
recipient = has the component above
What type of antibodies are found in Rh⁺ blood type plasma?
No anti-D
individuals with Rh⁺ (Rhesus positive) blood, their plasma does not contain anti-Rh (anti-D) antibodies. This is because their red blood cells express the Rh (D) antigen, and the immune system does not recognize it as foreign.
universal recipient of RBC
What type of antibodies are found in Rh - blood type plasma?
IgG anti D
True or False, IgM and IgG both cross the placenta.
IgM does not cross placenta; IgG does cross placenta.
What is hemolytic disease of newborn?
Rh− mothers exposed to fetal Rh+ blood (often during delivery) may make anti-D IgG. In
subsequent pregnancies, anti-D IgG crosses the placenta hemolytic disease of the newborn (erythroblastosis fetalis) in the next fetus that is Rh+.
ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn
most commonly seen in what blood group mother?
Usually occur in type O mother with a type A or B fetus.
bc contains IgG Anti- B + A antibodies
Can occur in the first pregnancy. neonate present with jaundice within 24hrs of birth
Tx phototherapy or transfusion exchange
Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (HDFN)
can be cause by what antibodies
anti-Kell antibodies
ABO antibodies
anti D antibodies ( RH )
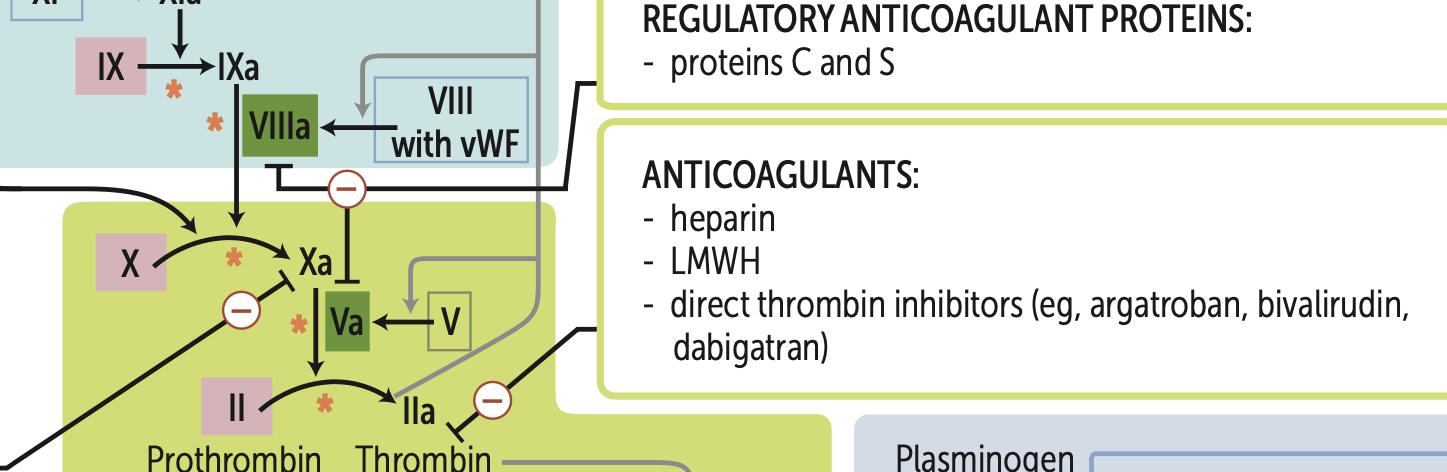
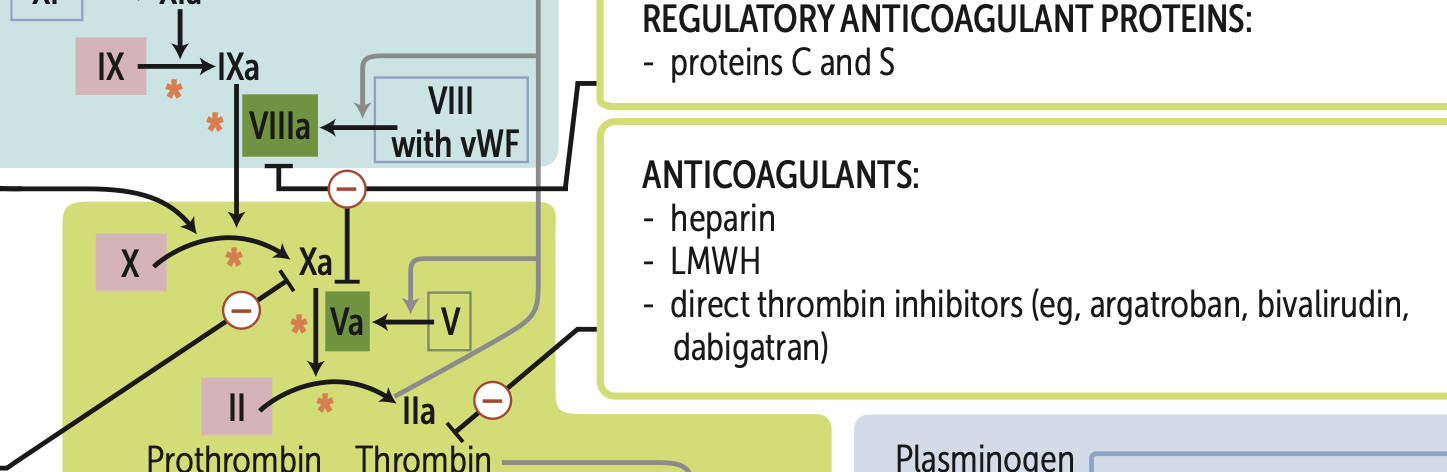
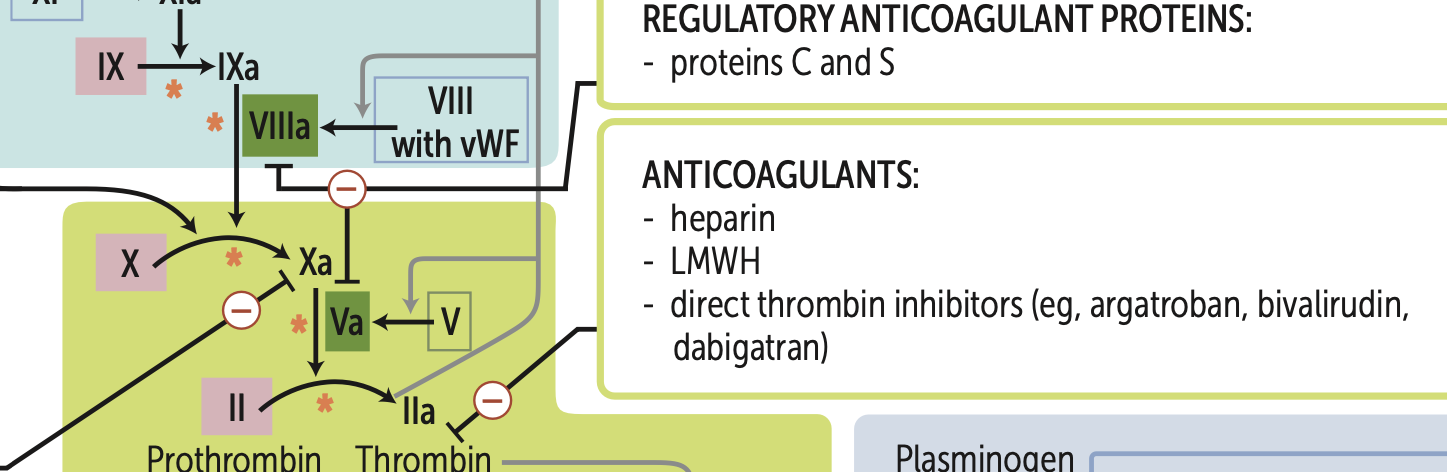
What are my four main types of anticoagulants that target factor X?
1. LMWH (greatest efficacy)
2. heparin
3. direct Xa inhibitors (apixaban, rivaroxaban)
fondaparinux
What are the 3 effects of bradykinin in the kinin cascade?
1. ↑ Vasodilation
2. ↑ Permeability
3. ↑ Pain
Kallikrein
purpose
what inhibits it
HMWK—> Bradykinin
ACE I inhibit it
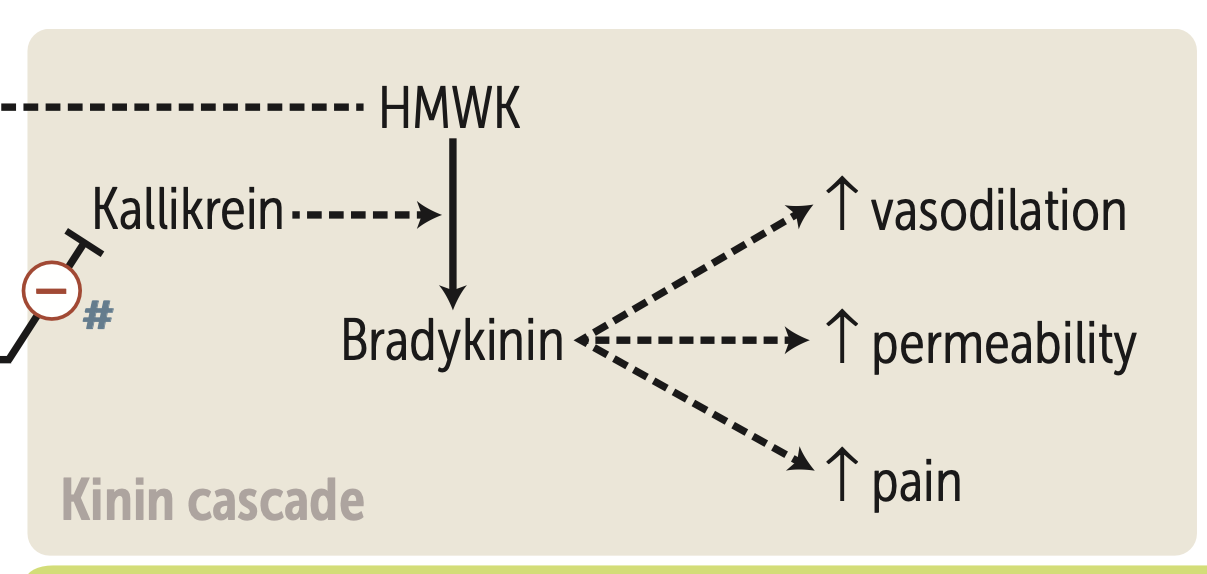
What is HMWK?
High molecular weight kininogen (HMWK or HK) is a circulating plasma protein initiates in blood coagulation, and in the generation of the vasodilator bradykinin via the Kallikrein-kinin system.
What are my three main types of anticoagulants that target thrombin (IIa)?
1. heparin (greatest efficacy)
2. LMWH (dalteparin, enoxaparin)
3. direct thrombin inhibitors (argatroban, bivalirudin, dabigatran)
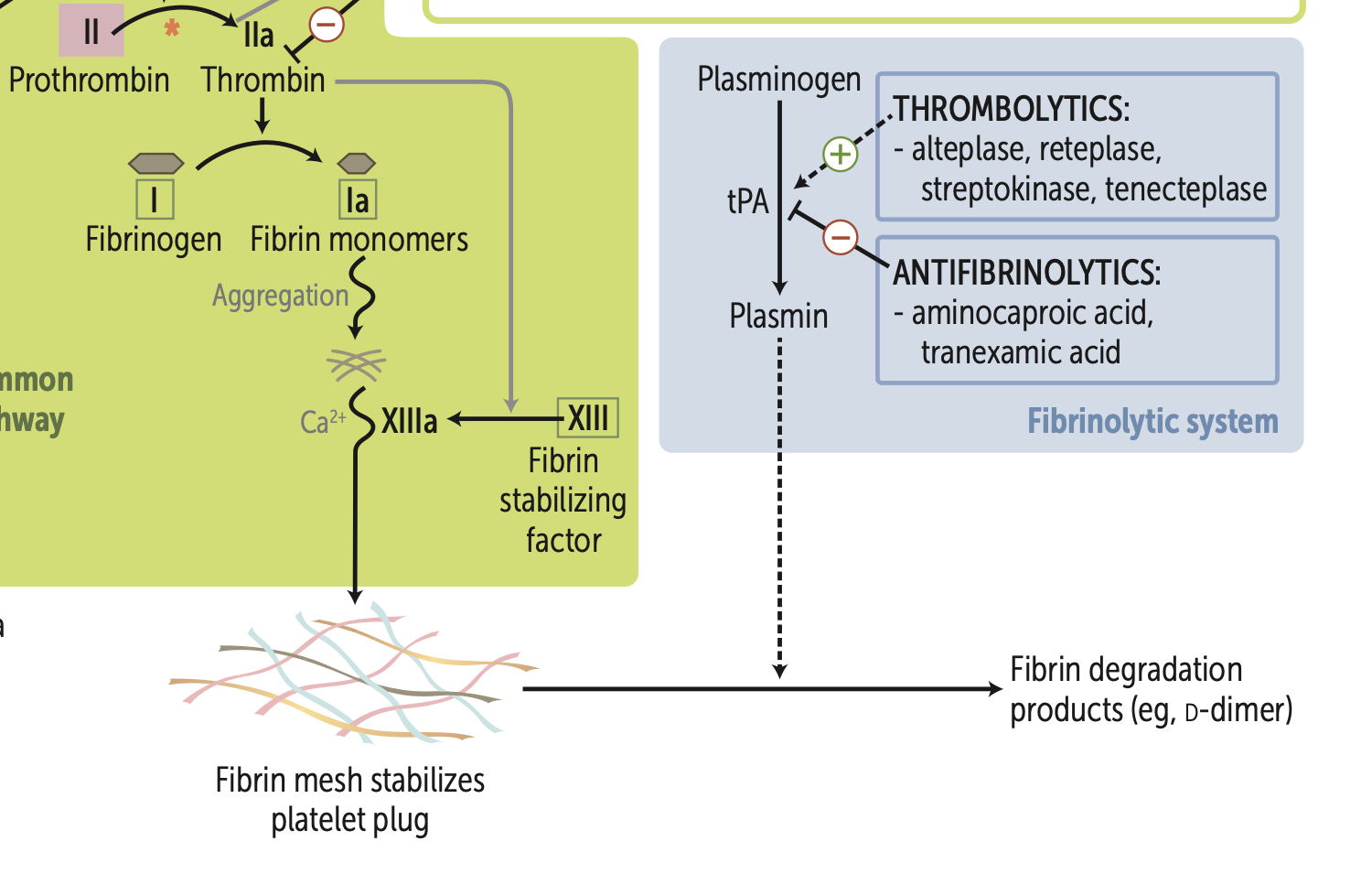
What are my 4 thrombolytics which activate tPA but are not part of the coagulation cascade?
THROMBOLYTICS:
1. alteplase,
2. reteplase,
3. streptokinase,
4. tenecteplase
Plasminogen is converted to plasmin via what?
What does this also inhibit?
tPA
Inhibits Aminocaproic acid

Prothrombin and thrombin are also known as?
Factor II and IIa
Hemophilia A is a deficiency of?
Deficiency of factor VIII (XR)
Hemophilia B is a deficiency of?
Deficiency of factor IX (XR)
Hemophilia C is a deficiency of?
Deficiency of factor XI (AR)
Describe the extrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade.
VII leads to VIIa via TF
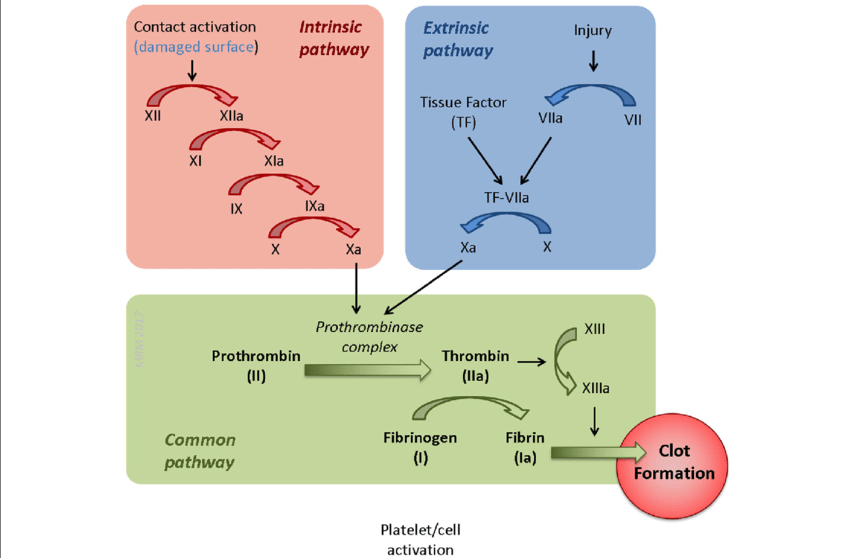
Describe the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade.
12—> 11—→ 9—+8a→ 10
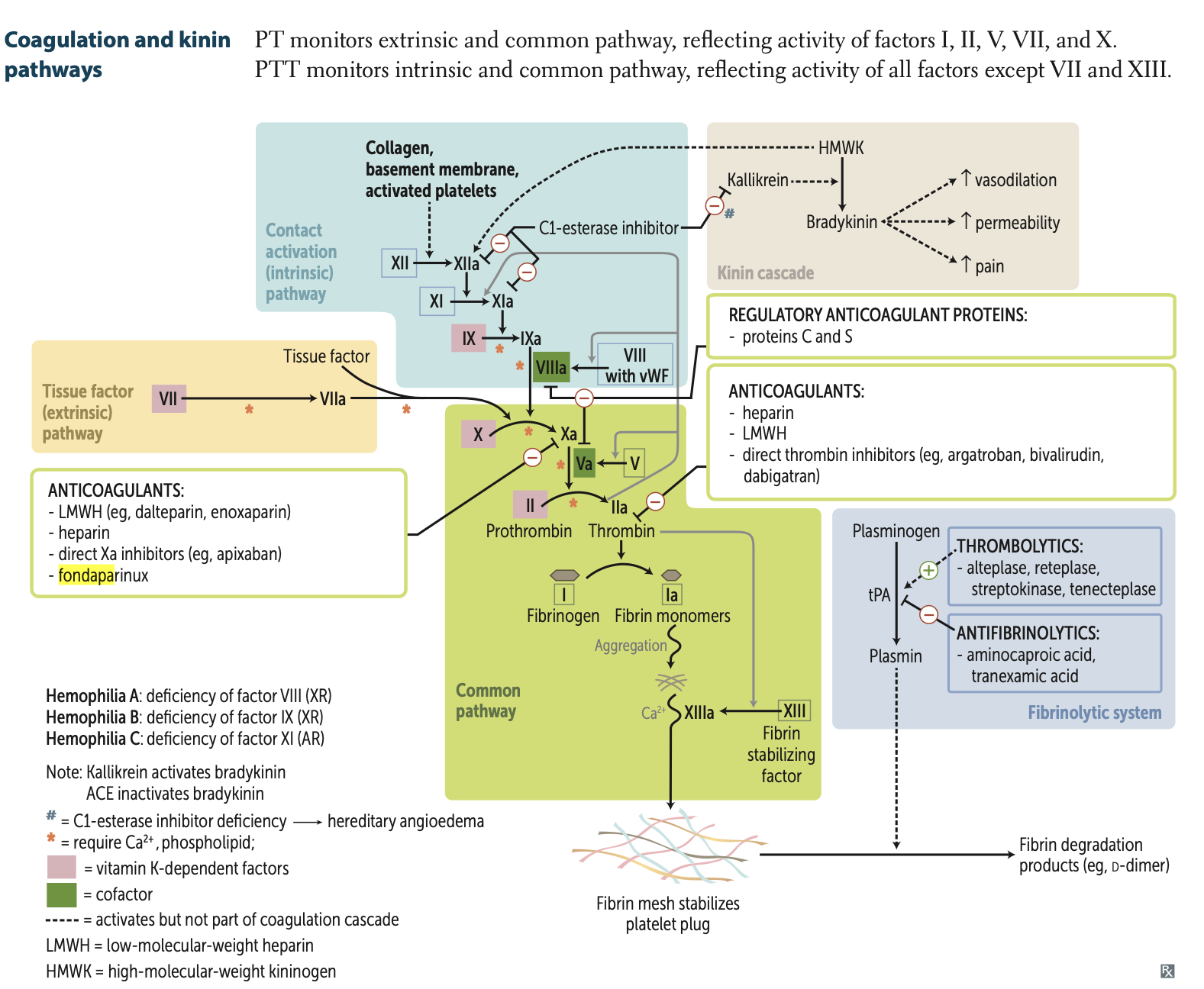
Describe the 4 pathways mediated by Ca and phospholipid.
1. VII to VIIa,
2. VIIa to activate X to Xa
3. IXa coupled VIIIa mechanism to activate X to Xa and,
3. Xa coupled with Va mechanism to activate II to IIa
Describe the combined pathway. (6 steps)
Xa (via VIIa and VIIIa)
Va (via IIa)
IIa (via Xa and Va)
Ia (via Thrombin)
XIIIa (via IIa)
XIIIa combines with Ca2⁺ and Ia to form fibrin mesh
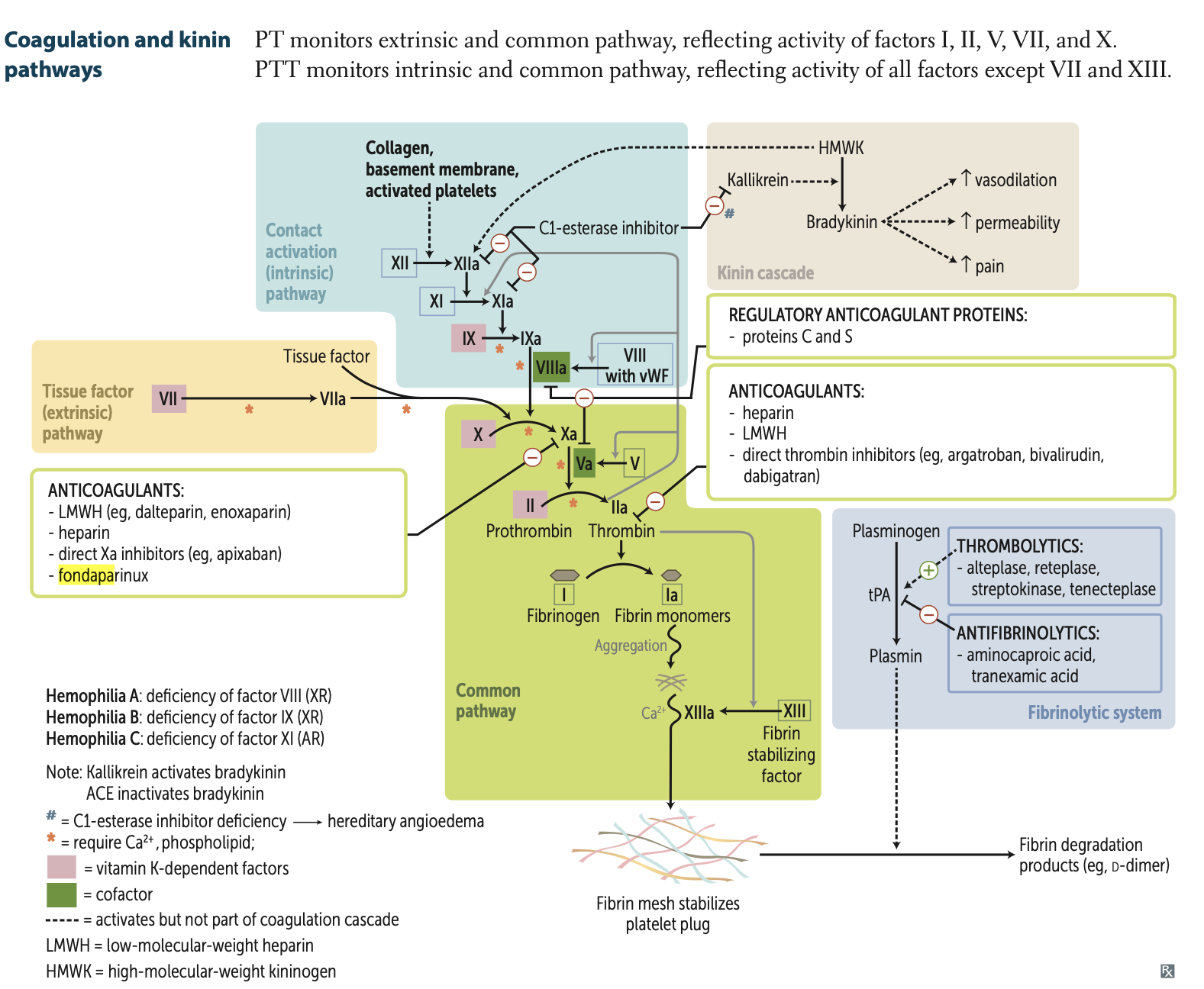
Tue or false, Mg2 ⁺ is required for fibrin mesh to form.
False, Ca2 ⁺ is required for fibrin mesh formation
Factor I and Ia are also known as?
Fibrinogen and Fibrin monomers
Plasmin acts on Fibrin mesh to result in?
Fibrin degradation products.
d- dimers
Vit. K deficiency leads to ↓ synthesis of what 6 proteins?
Factors, X, IX, VII, II, protein C, protein S.
vWF carries what factor?
VIII
Warfarin inhibits which enzyme?
Vitamin K epoxide reductase.
Neonates lack enteric bacteria, which produce which vitamin?
Vit. K
Epoxide reductase does what to Oxidized reductase
vitamin K?
Turns it into reduced vitamin K
Principal targets of antithrombin are?
Thrombin and factor Xa.
Factor V Leiden mutation produces a factor V resistant to inhibition by?
Normally, activated protein C, with the help of protein S, inactivates Factor Va and Factor VIIIa, preventing excessive clot formation. → anticoagulant
,
Factor V Leiden mutation, Factor V is resistant to cleavage by activated protein C, leading to increased thrombin production and a hypercoagulable state
tPA is used clinically as a?
Thrombolytic
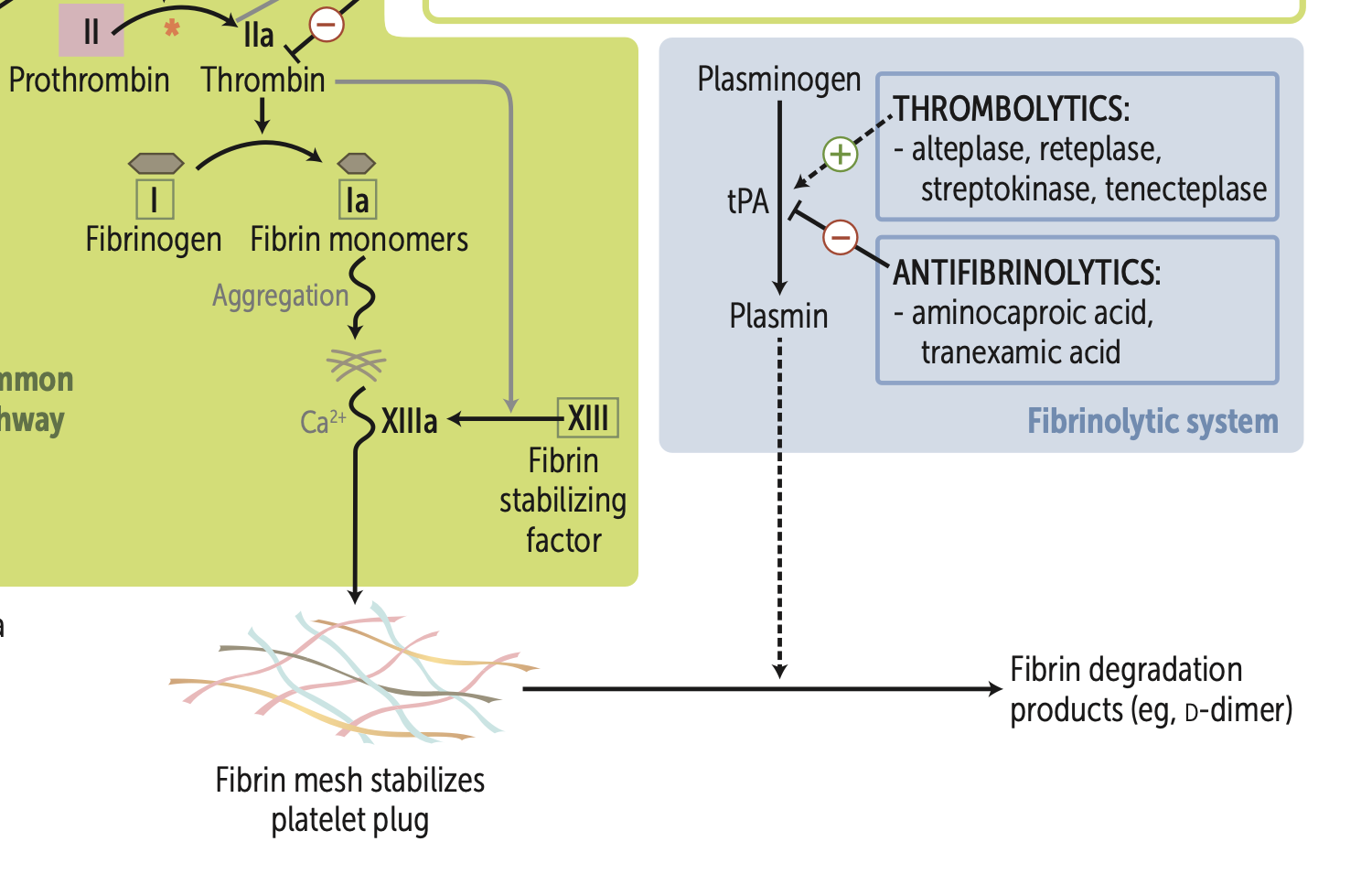
Fibrinolysis is defined as (2 things)
1. cleavage of fibrin mesh
2. destruction of coagulation factors
Activated protein C combines with protein S to cleave and inactivate?
cleaves and inactivates Va, VIIIa
they are thrombolytics
hereditary angioedema
C1 esterase deficiency
inhibits
Factor XII (Hageman Factor) → XIIa
XI → XIa
Kalkirenin
Factor ______ stabilizes fibrin mesh
Factor XIIIa stabilizes fibrin mesh (deficiency = delayed bleeding).
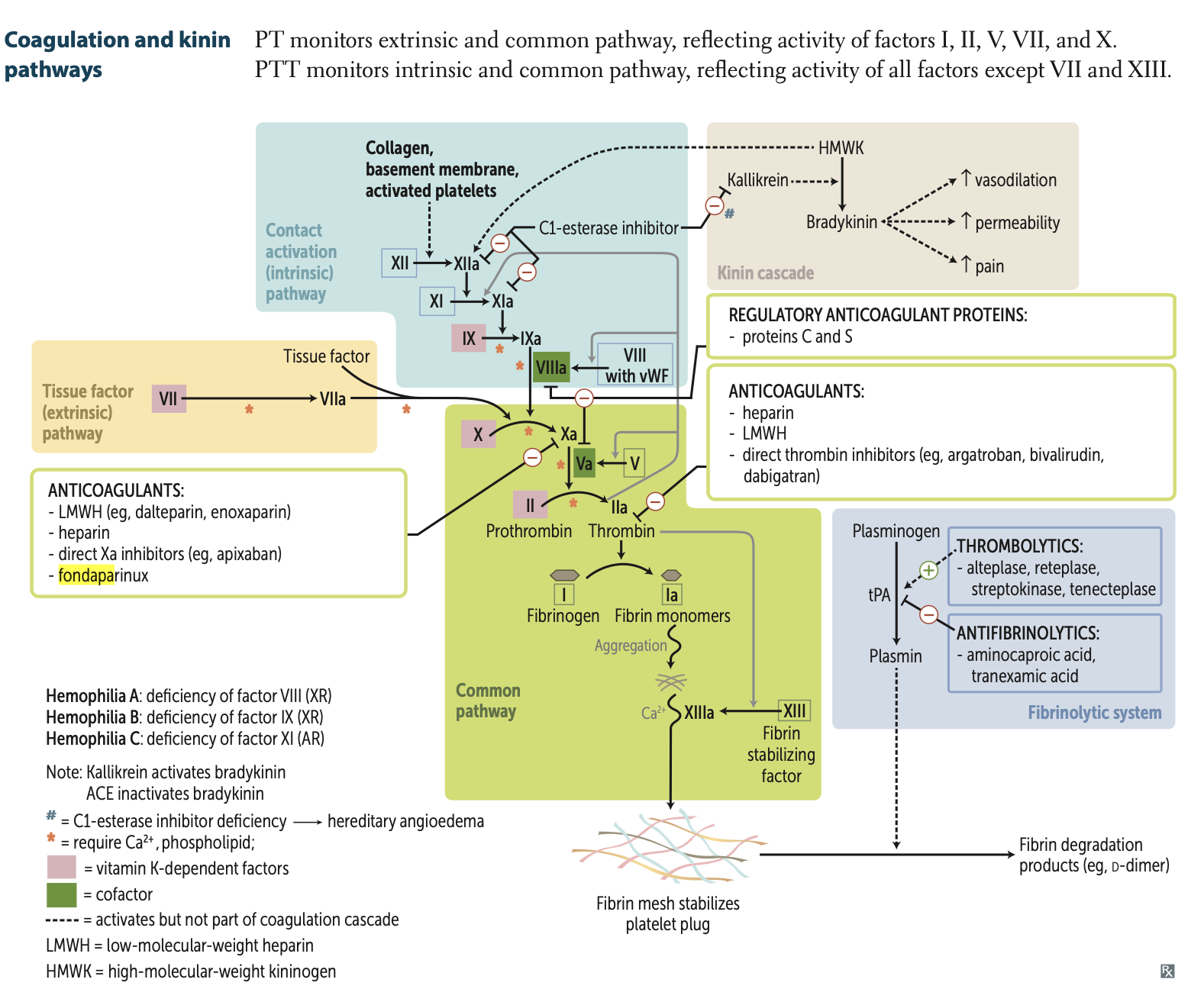
PT (Prothrombin Time)
PTT (Partial Thromboplastin Time):
where is it found in the cascade
which factors does it effect
PT (Prothrombin Time): Monitors extrinsic + common pathway (Factors I, II, V, VII, X).
(Play Tennis outside [extrinsic pathway]).
PTT (Partial Thromboplastin Time): Monitors intrinsic + common pathway (all factors except VII and XIII).
(Play Table Tennis inside).
![<ul><li><p><strong>PT (Prothrombin Time)</strong>: Monitors <strong>extrinsic + common pathway</strong> (Factors I, II, V, VII, X).</p><ul><li><p>(Play Tennis outside [extrinsic pathway]).</p></li></ul></li><li><p><strong>PTT (Partial Thromboplastin Time)</strong>: Monitors <strong>intrinsic + common pathway</strong> (all factors <strong>except VII and XIII</strong>).</p><ul><li><p> (Play Table Tennis inside).</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d7c773c2-ff70-482a-8188-723ab9a7f5f3.png)
Protein C is activated by what complex?
Thrombin-thrombomodulin complex in endothelial cells
Primary hemostasis is also known as?
Platelet plug formation
What are the 5 steps of platelet plug formation?
1. Injury
2. Exposure
3. Adhesion
4. Activation
5. Aggregation
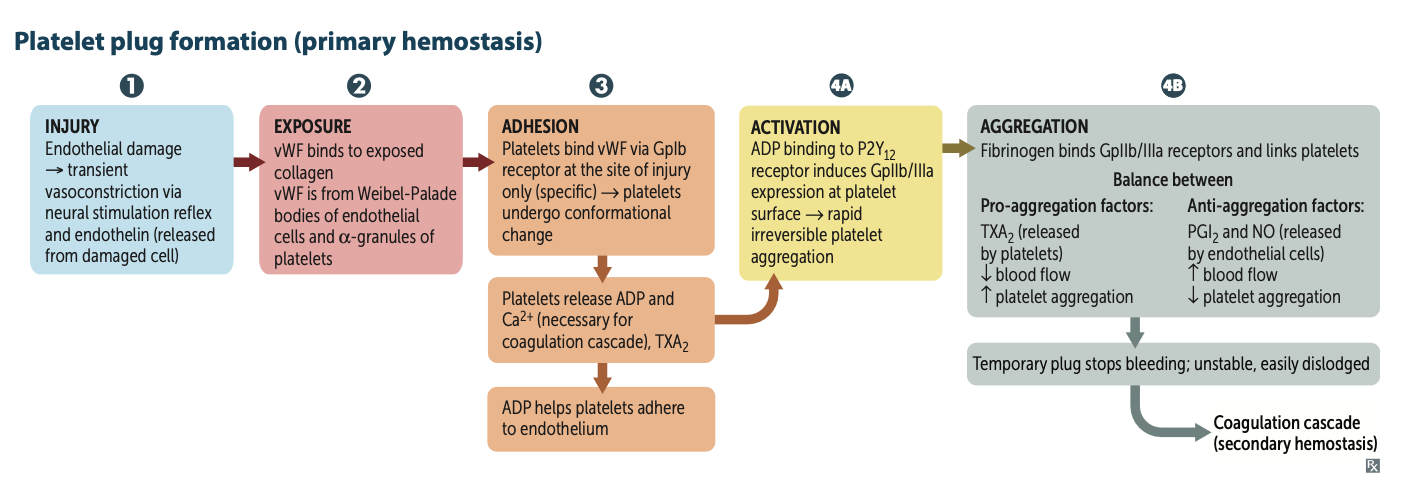
What product causes vasoconstriction due to endothelial cell damage?
Injury → transient vasoconstriction via neural stimulation reflex and endothelin (released from damaged cell)
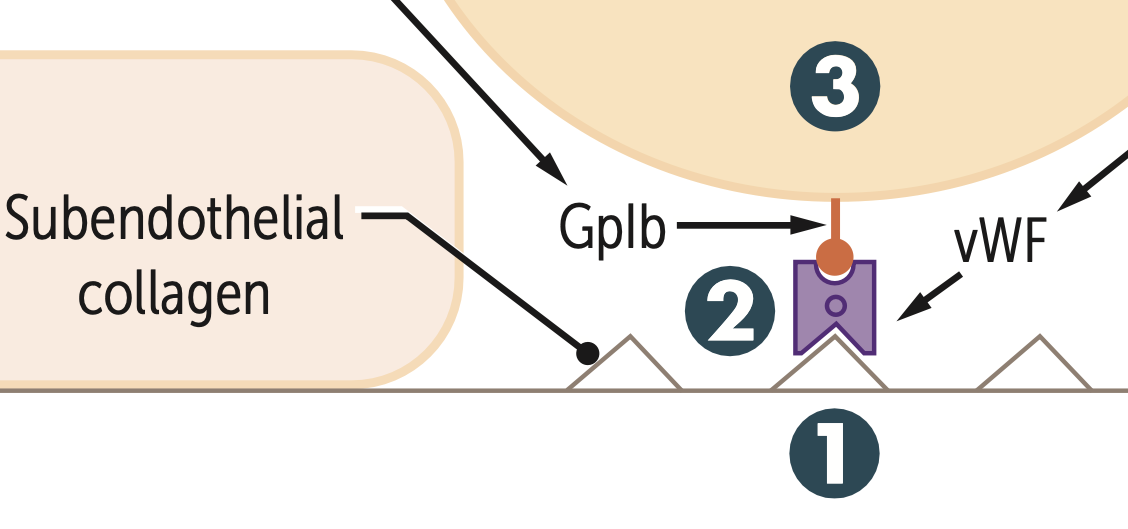
What binds to exposed collagen?
Exposure → vWF binds to exposed collagen
What 2 places are vWF found in?
vWF is from Weibel-Palade bodies of endothelial
cells and α-granules of platelets
What do platelets bind to during adhesion via the GpIb receptor?
They bind to vWF and the platelets undergo a conformational change
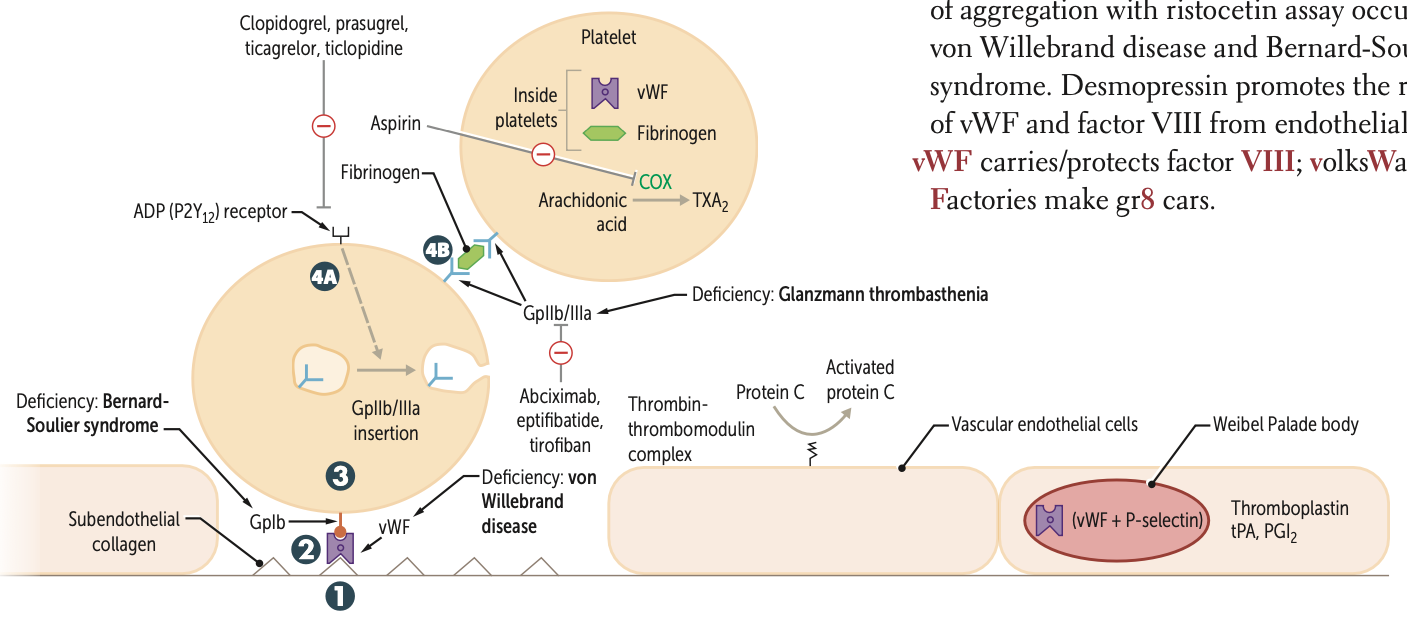
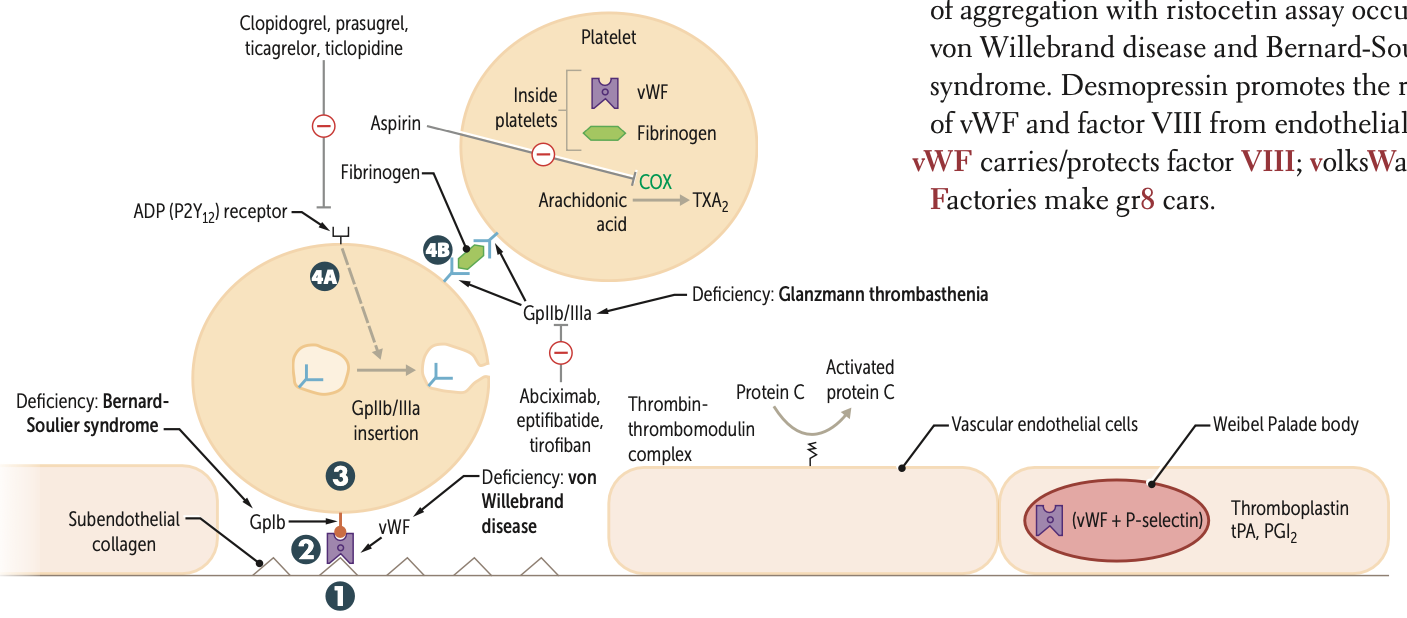
After undergoing conformational change during adhesion what three molecules do platelets release?
They release ADP, Ca2⁺, and TXA2.
ADP helps platelets adhere to endothelium.
CA necessary for coagulation cascade
released from platelet dense granules
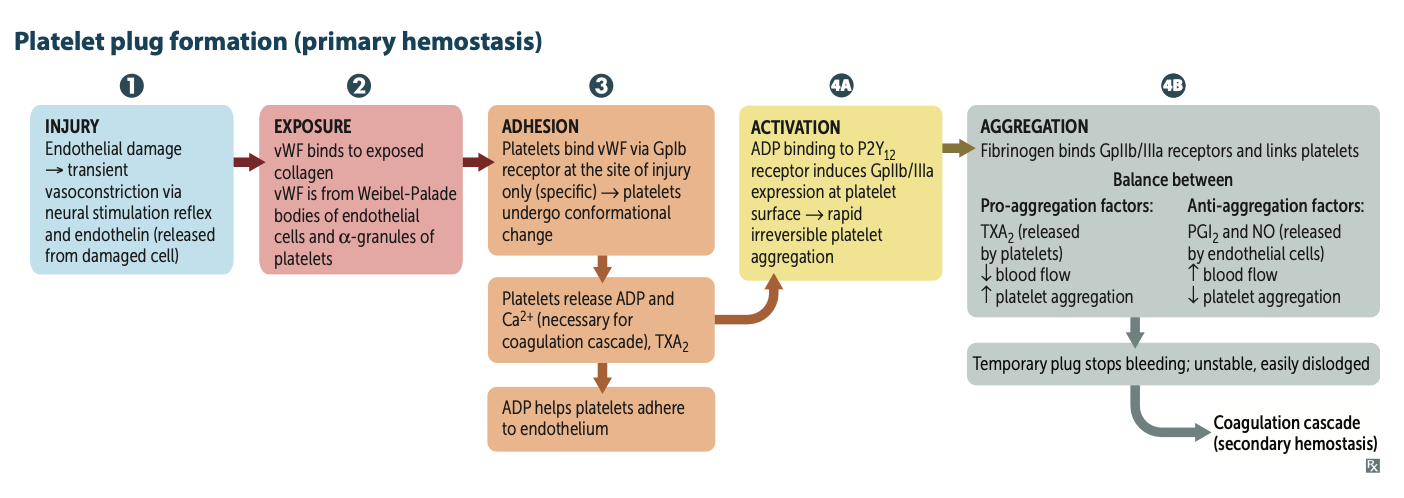
During Activation, after ADP binds to P2Y12 receptor, two receptors are expressed at the platelet surface?
GpIIb/IIIa
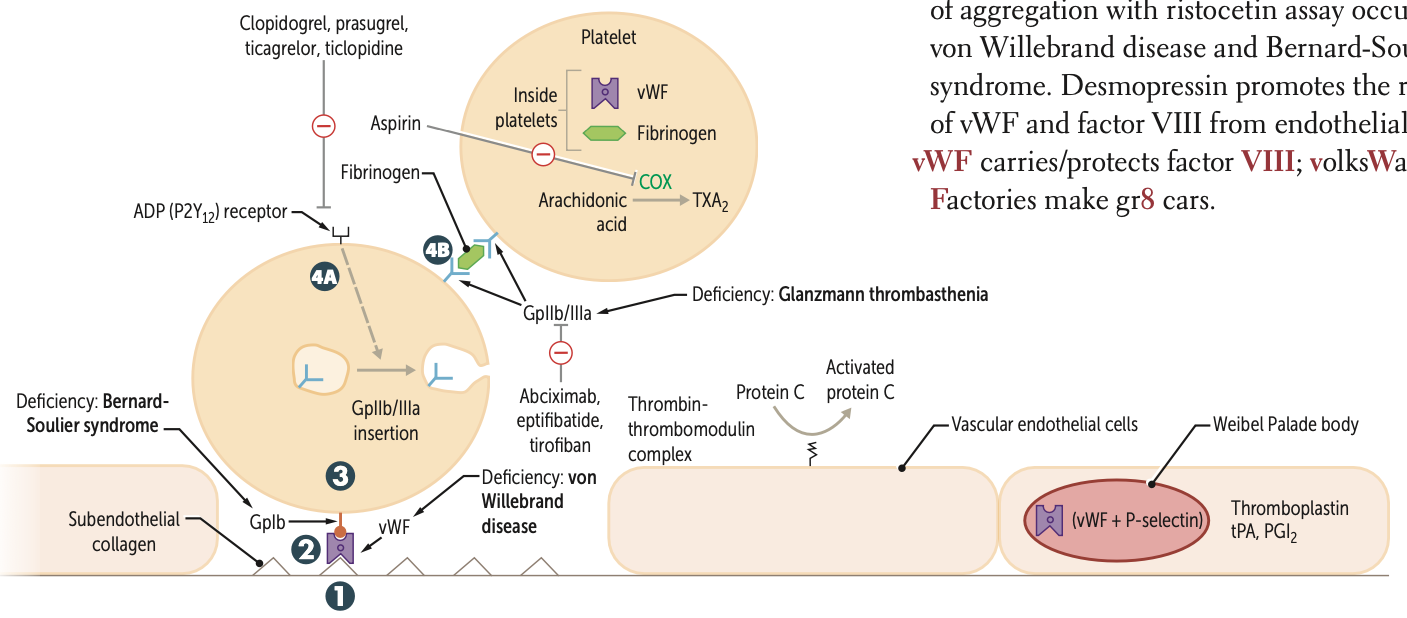
During Aggregation, what binds to GpIIb/IIIa receptors and links platelets?
Fibrinogen
What is a pro-aggregation factor released by platelets?
What is its effect on blood flow?
TXA2;
↓ blood flow; ↑ platelet aggregation
What are anti-aggregation factors?
PGI2 and NO ;
↑ blood flow; ↓ platelet aggregation
Platlet plug is weak what processes strenghtens it ?
2dary homeostasis via the coagulation cascade starts!
Clopidogrel, prasugrel, and ticlopidine inhibit ADP induced expression of ____
GpiIb/IIIa
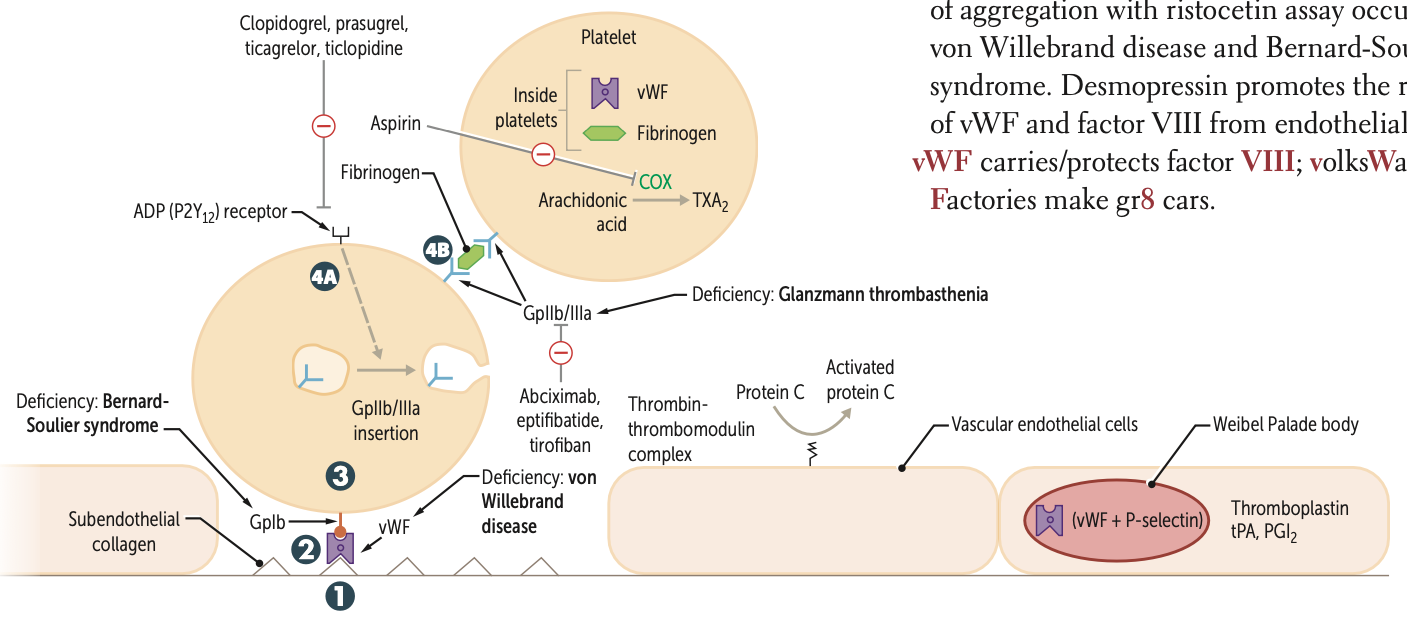
Abciximab, eptifibatide, and tirofiban inhibit ___ directly
GpIIb/IIIa
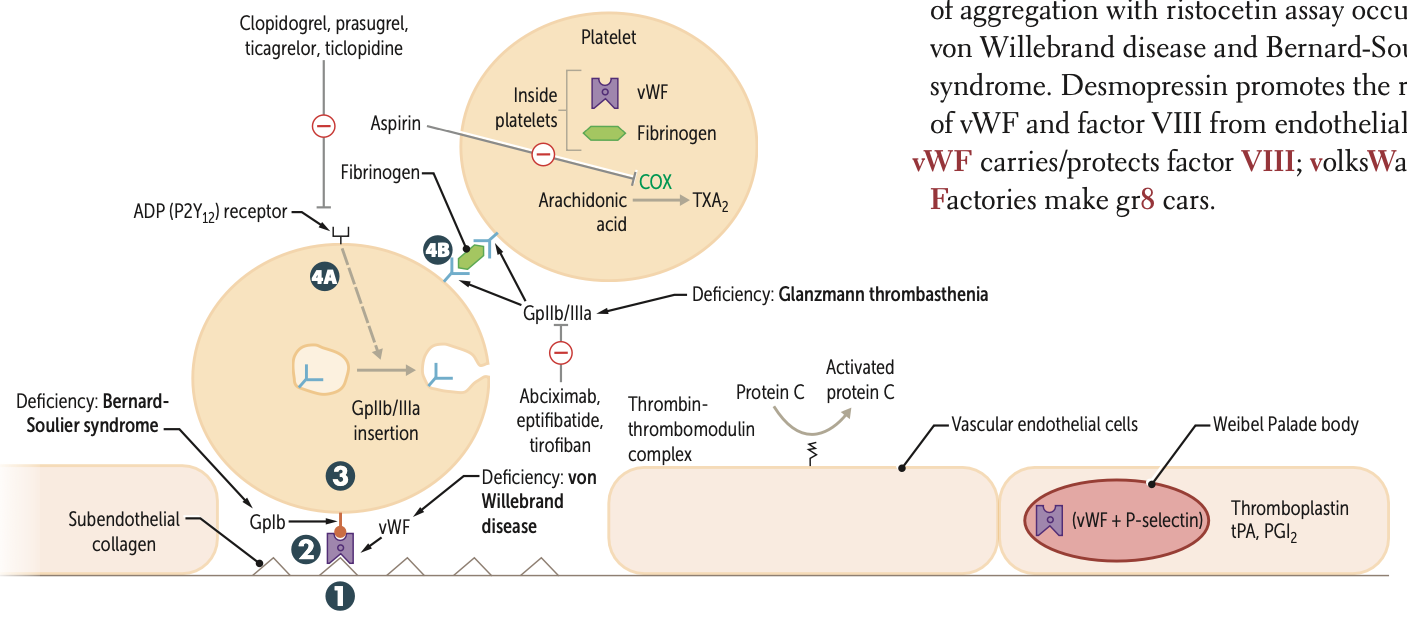
Risotecetin is a test for
tests for what disorder
failure to do so ….
vWF
von Willebrand disease and Bernard-Soulier syndrome
NO aggregation = B S
decreased = vWF disease
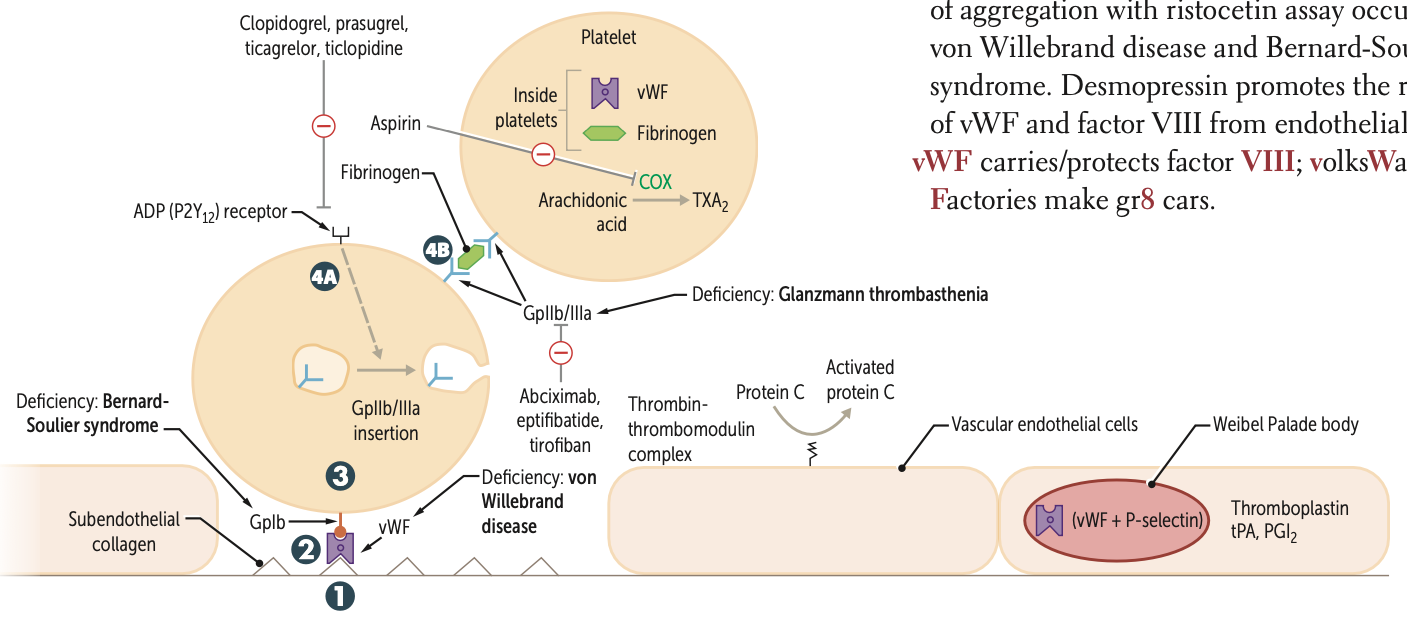
What is the ultimate goal of thrombogenesis?
Formation of insoluble fibrin mesh
A deficiency of GpIb is known as what syndrome?
Bernard-Soulier syndrome
A deficiency of GpIIb/IIIa is known as?
Glanzmann thrombasthenia
What is an acanthocyte?
another name
3 associated pathologies
Spur cell:
Liver disease, abetalipoproteinemia, vitamin E deficiency
(acanthocytes are asymmetric)..
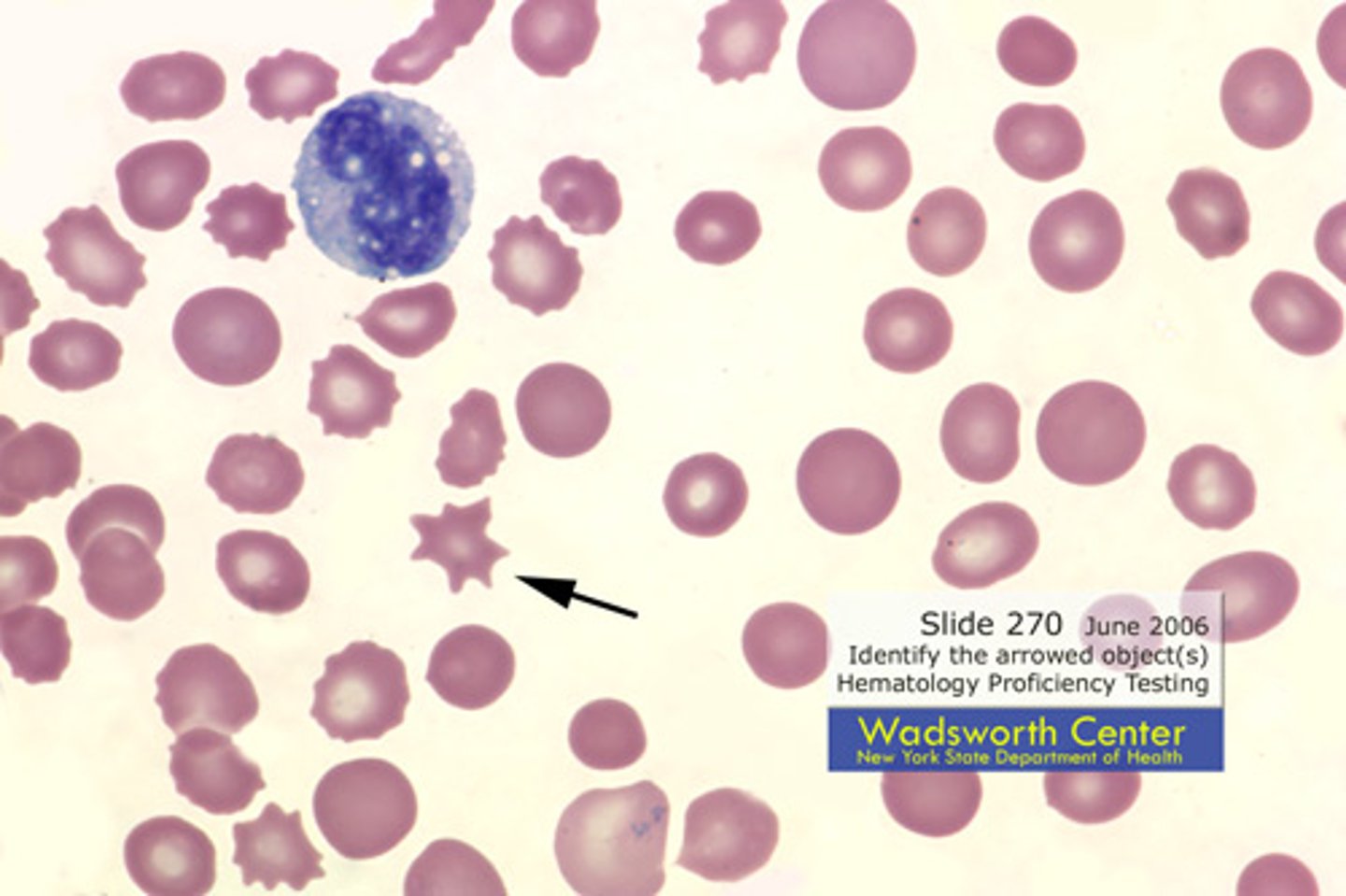
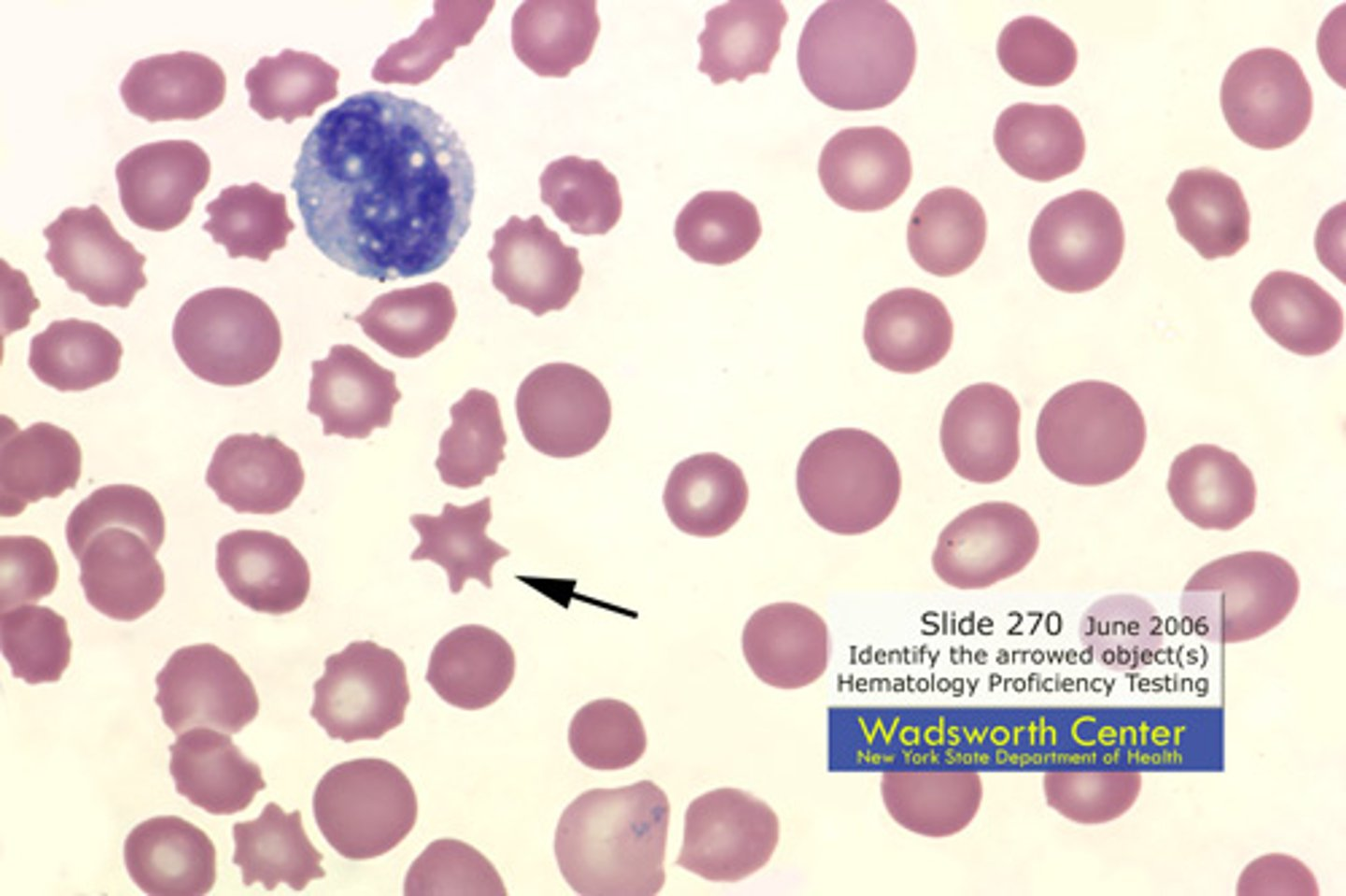
spur cells
(acanthocytes are asymmetric)..
What does basophilic stippling occur due to?
What is it?
blue granules in RBCs
ribosomal RNA remnants that persist bc impaired RNA degradation
🔹 Causes
Lead poisoning – inhibits rRNA degradation
Sideroblastic anemia – defective heme synthesis
Thalassemias – imbalance in globin chain production
Myelodysplastic syndromes – ineffective erythropoiesis
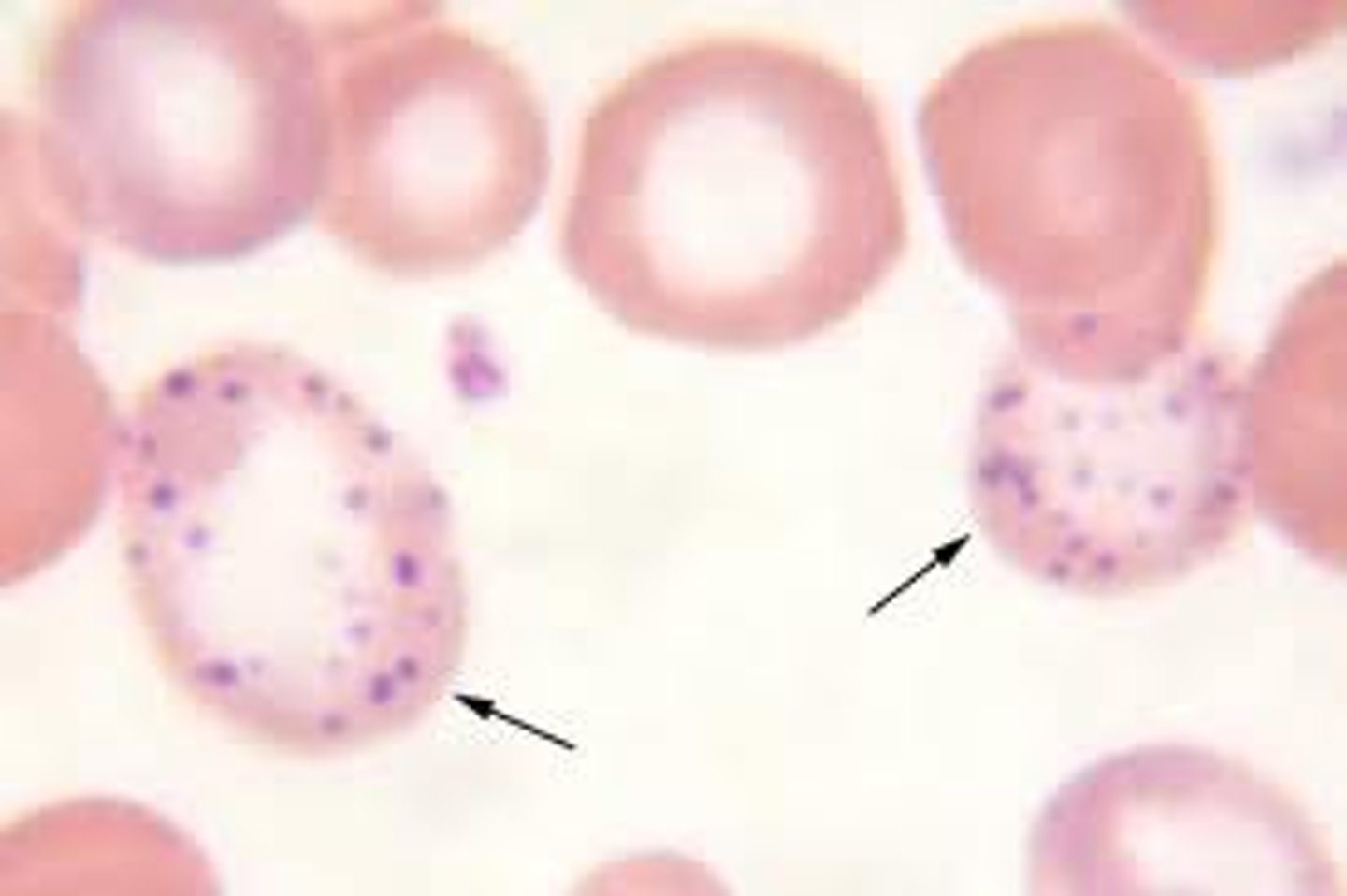
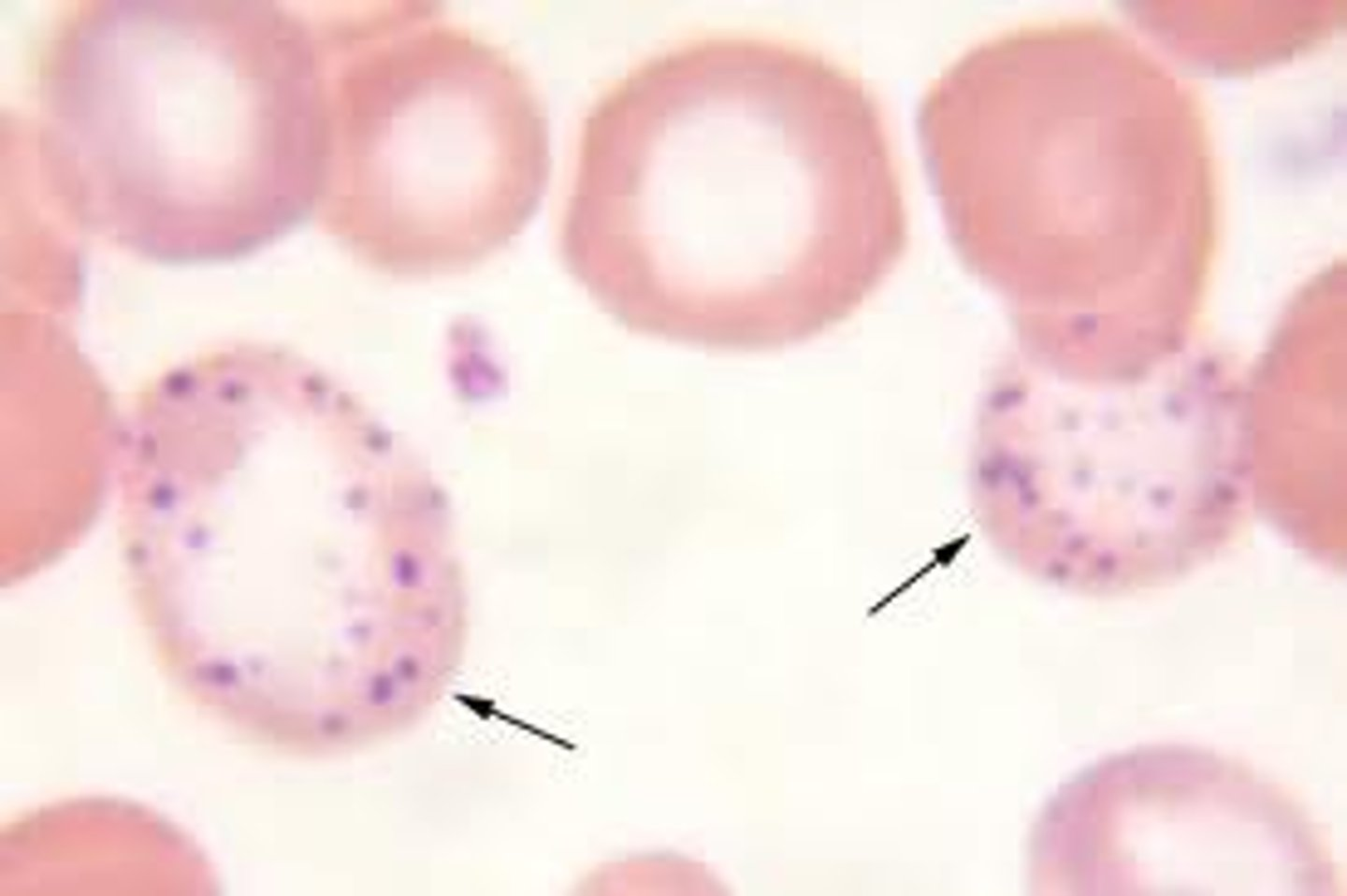
basophillic stippling