Roman Archeology Exam 3
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
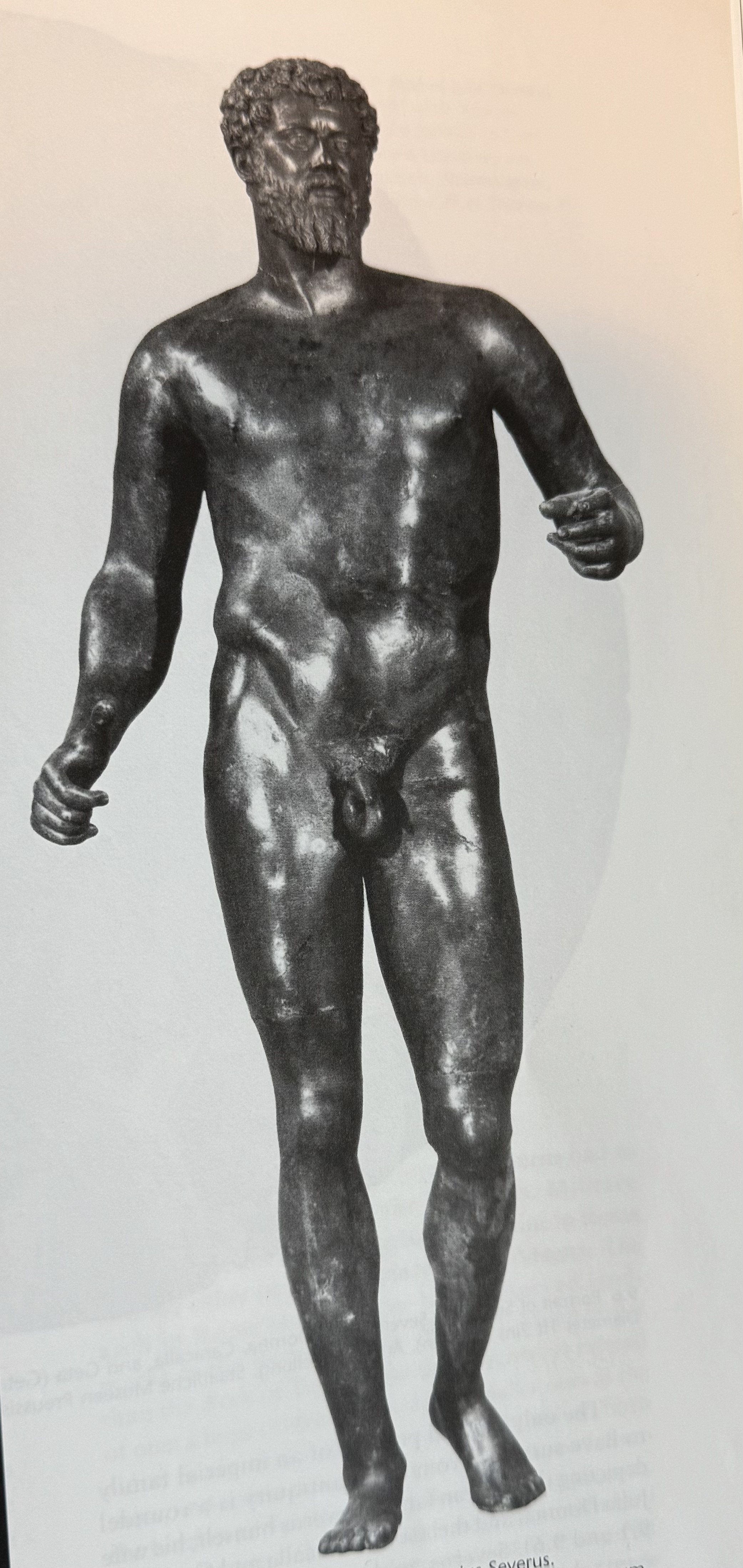

Full-length naked portrait of Septimius Severus. Bronze. Tells us about the workshop traditions of bronze workers.
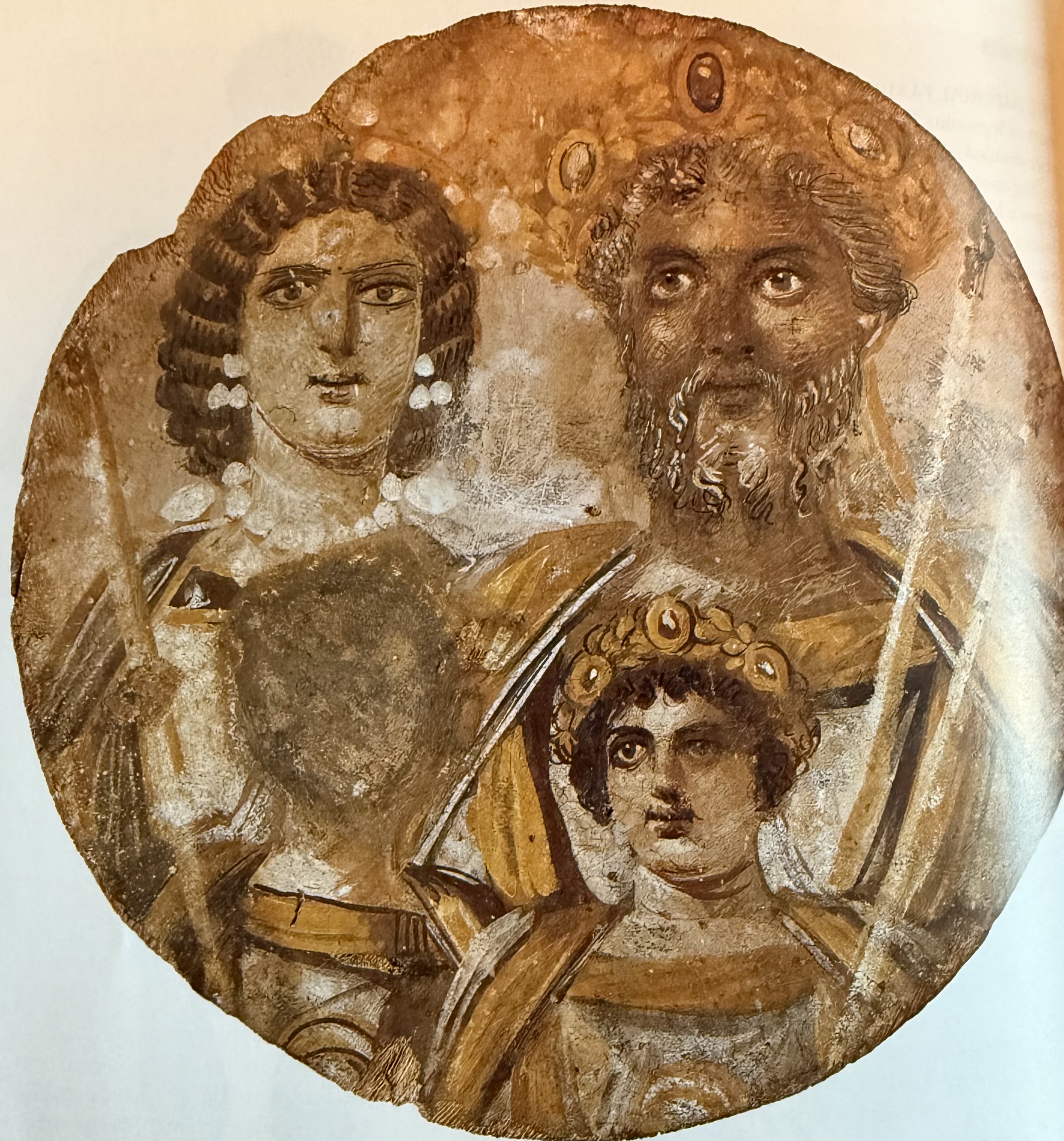

Portrait of Septimius Severus, Julia Domna, Caracalla and Geta. The only painted portrait of an imperial family to survive. Same technique as Fayum portraits. Dynastic. Example of damnatio.
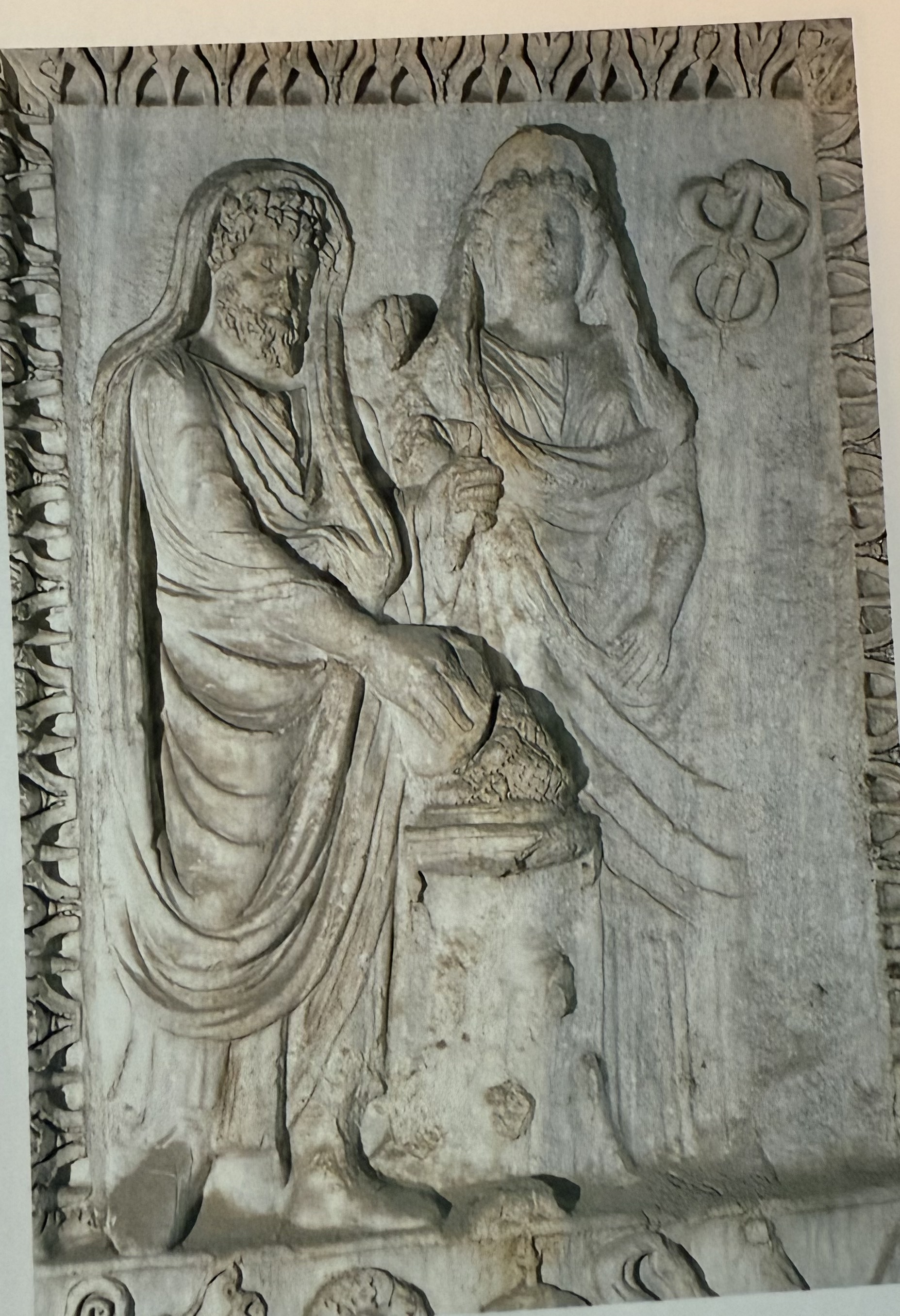

Detail on Arch of Argentarii. Celebrates wedding of Caracalla and Plautilla. Geta missing in bottom right corner, example of damnatio. Built by local silver smiths.
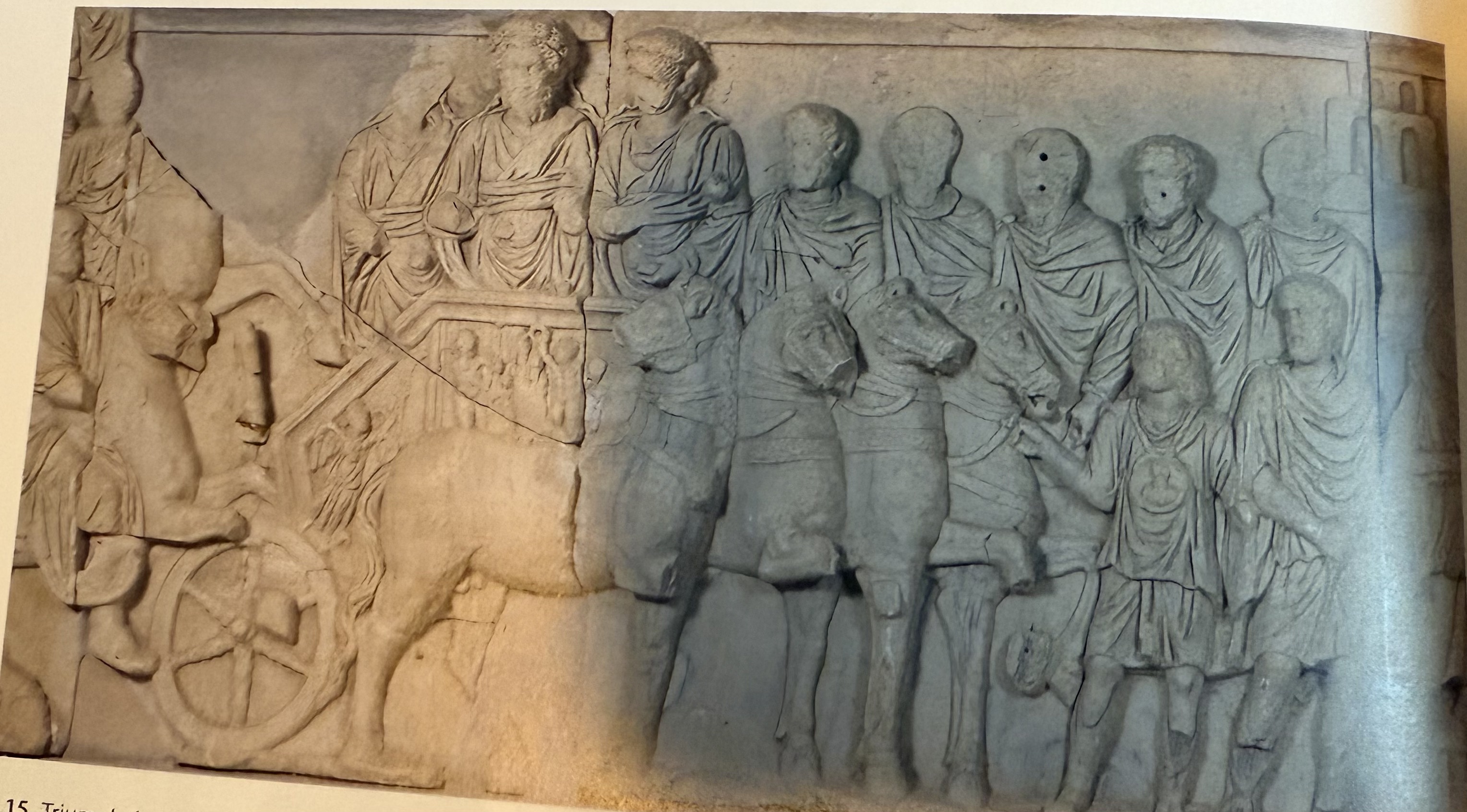

Triumphal procession of Septimius Severus and his two sons. Arch of Septimius Severus in Leptus Magna. Cannot tell which of the boys is who, one more deliberately destroyed. Local iconography on chariot. Potential example of triumphal parade outside of Rome.
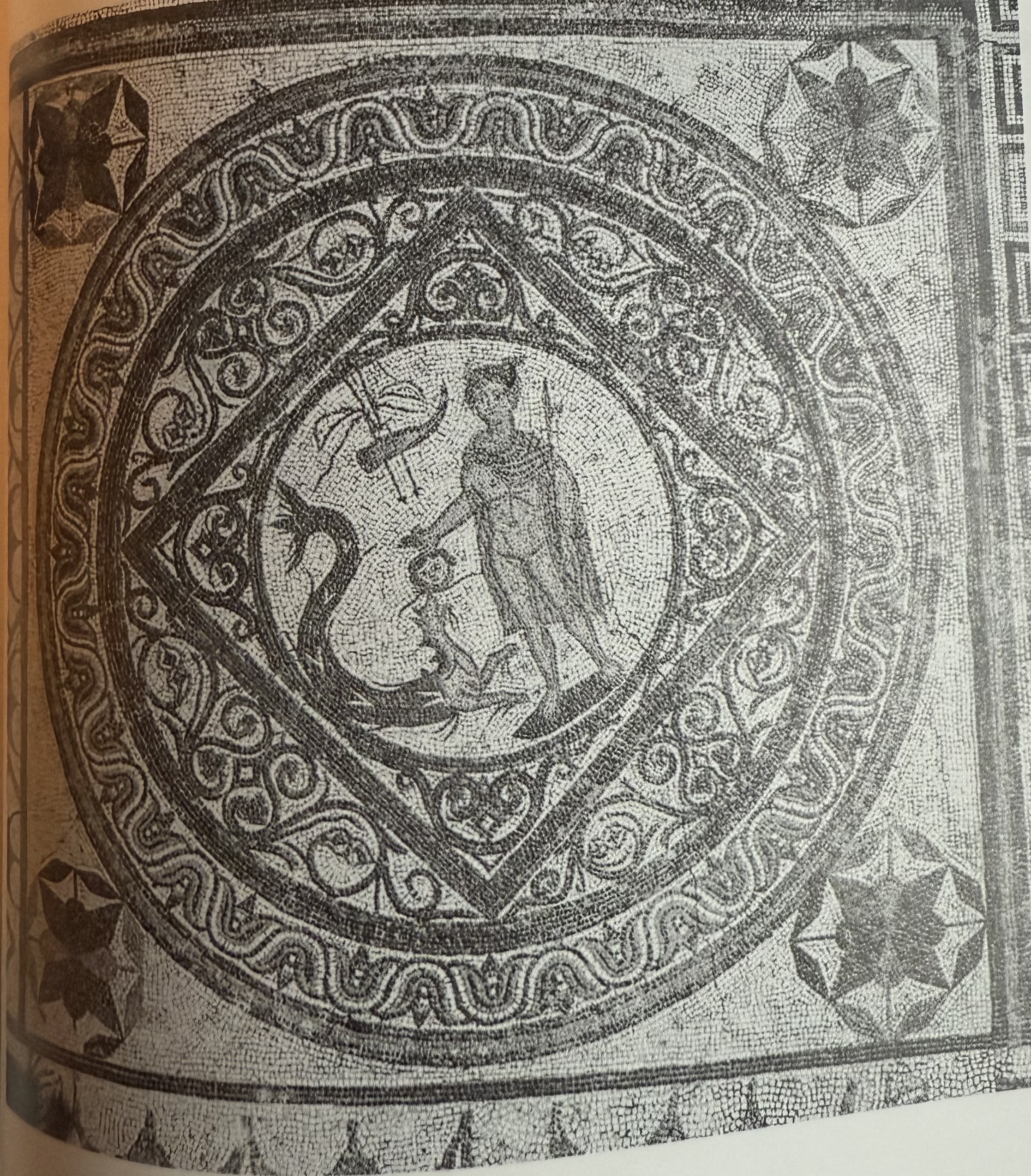

Perseus with head of Medusa. 500 year old greek myth that still holds meaning. Universality of Romanness.
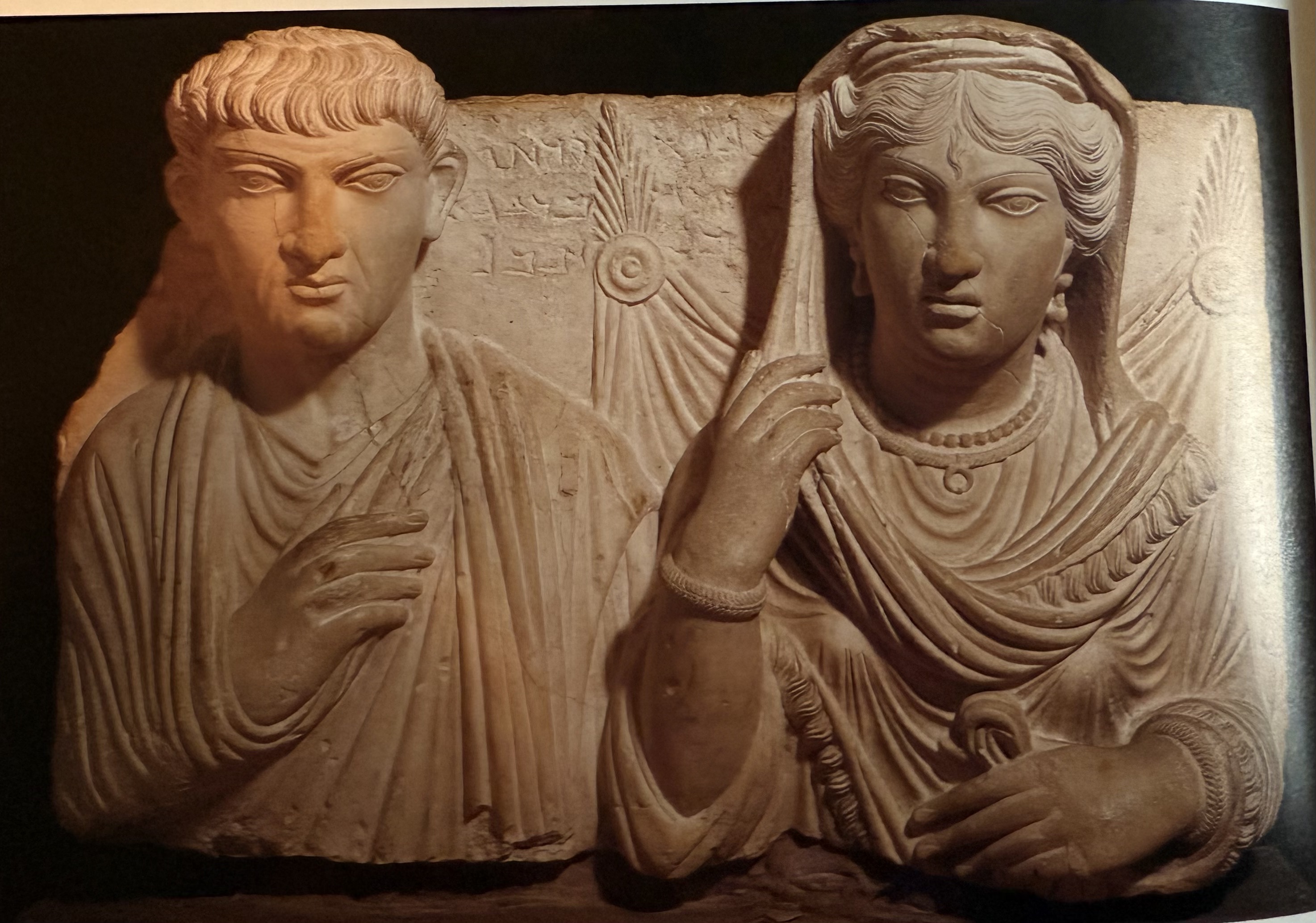

Funerary relief. Local palmyrans. Palmyran version of Fayum portraits.
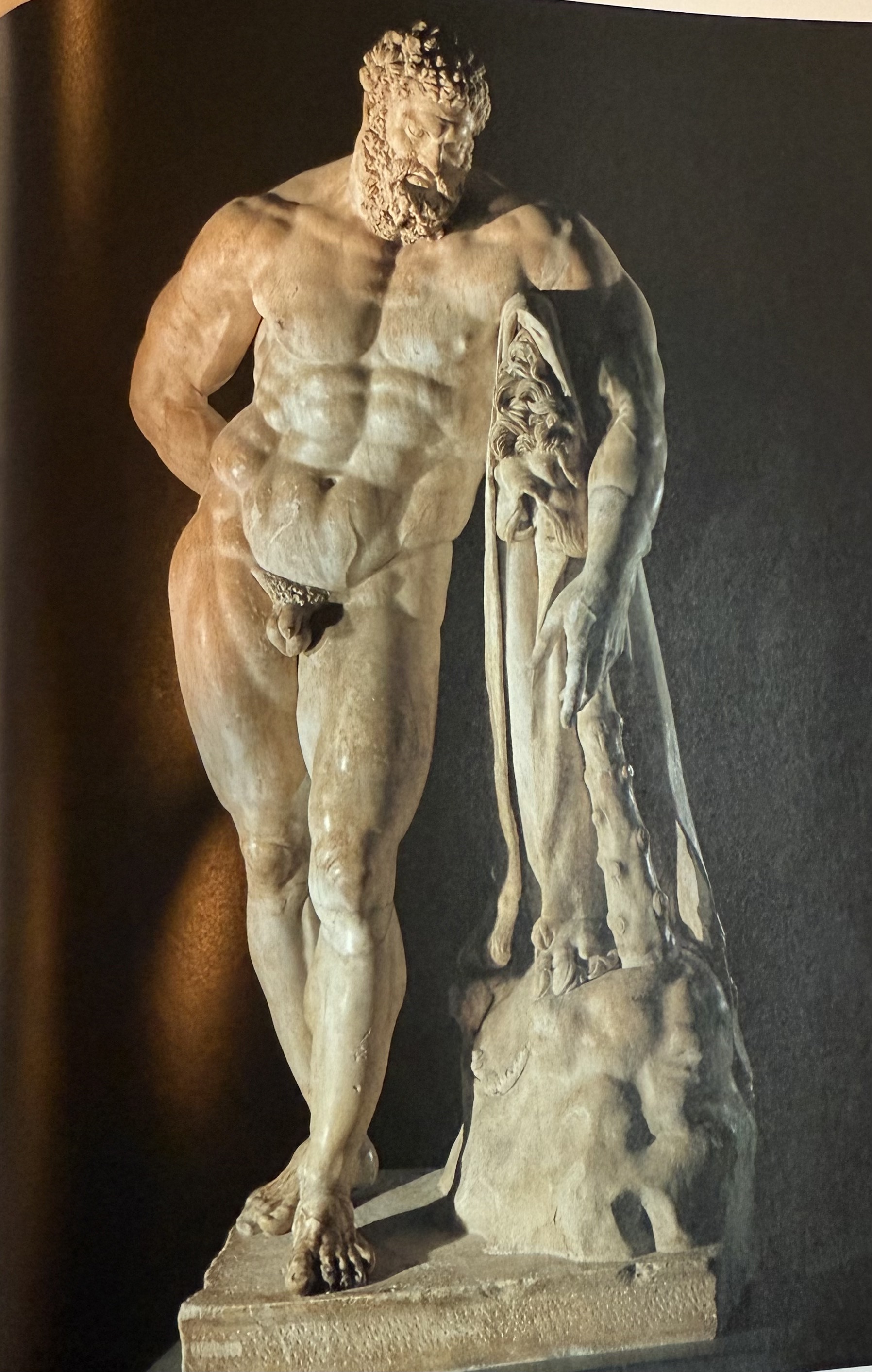

Colossal hercules from Baths of Caracalla. Connection to the age of heroes.
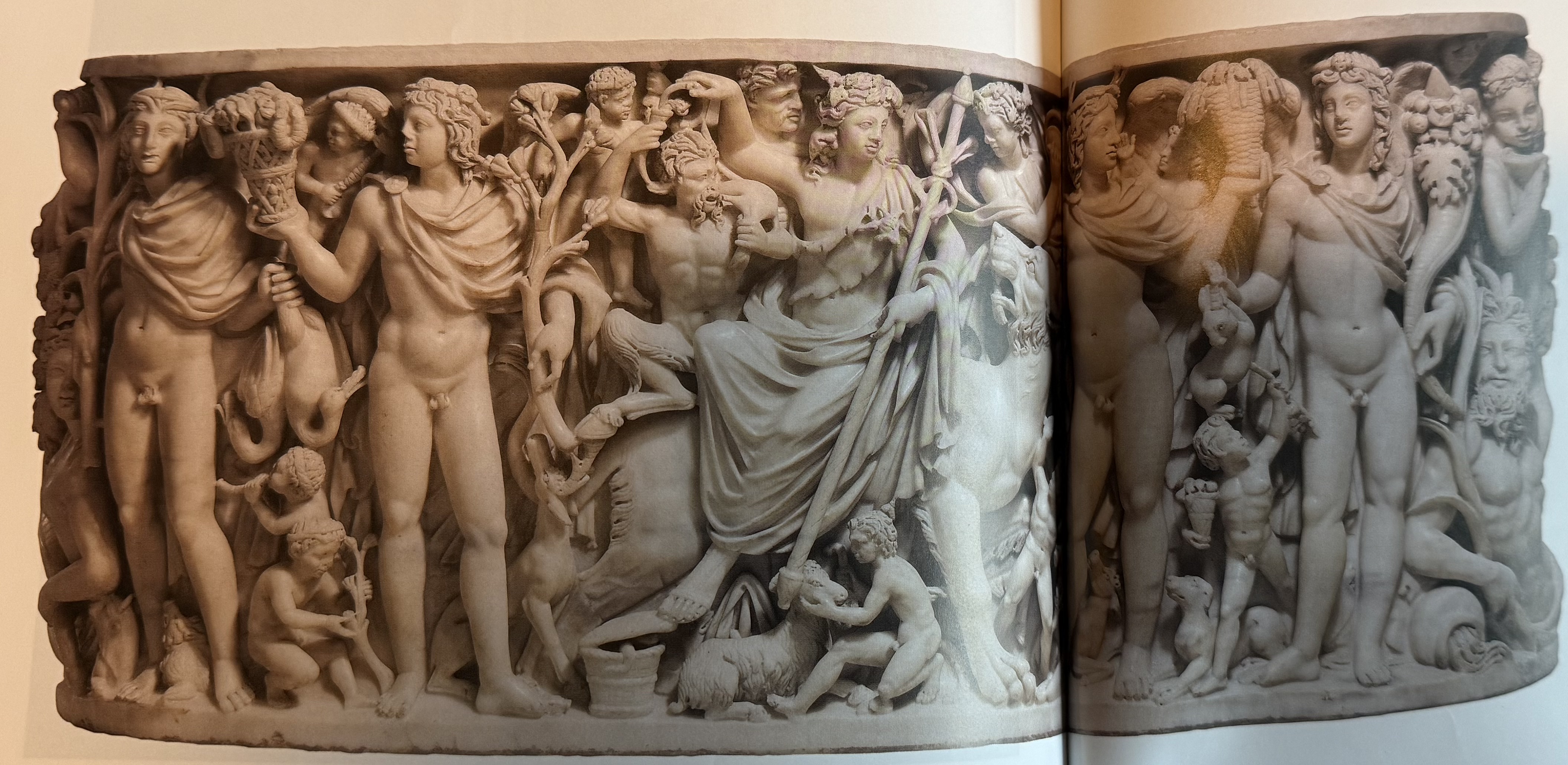

Bachhus and 4 seasons of Badminton Sarcophagus. Bath tub shaped. Promise of youthful return, escapism, and renewal. Example of Spolia.
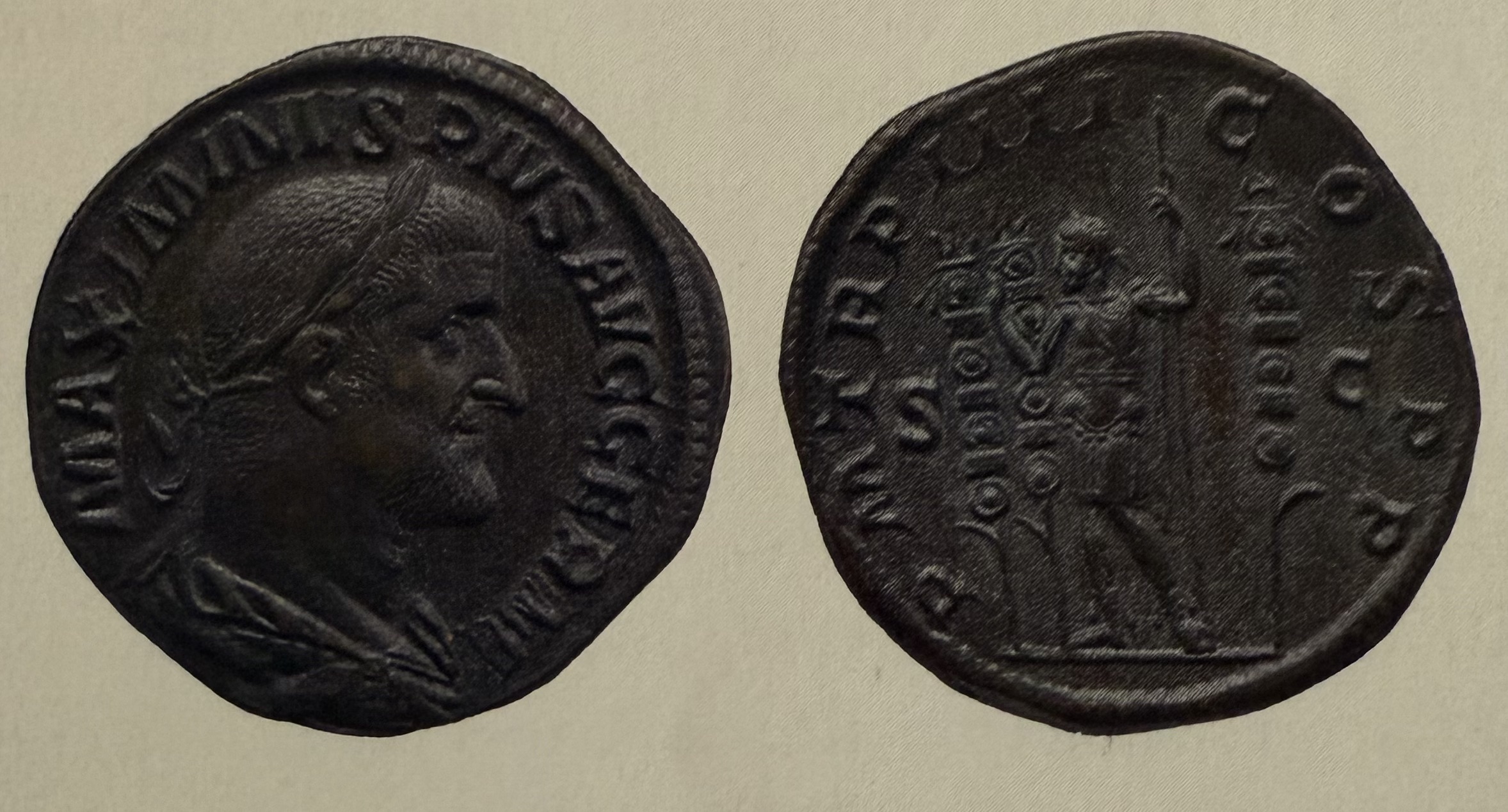

Coin of Maximius Thrax, 1st soldier emperor. Showcases Mars & Military standards. Eventually overthrown.
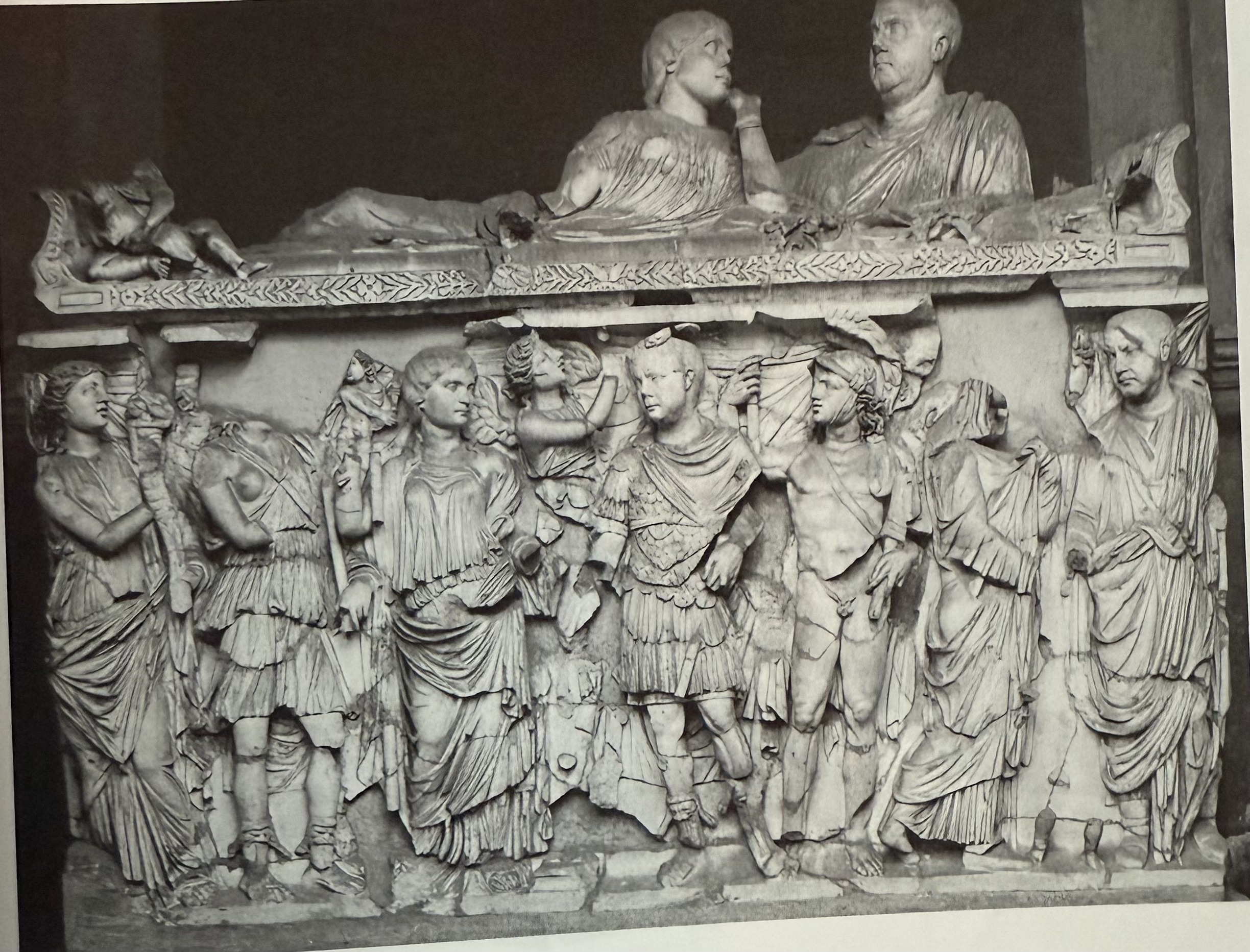

Sarcophagus of Balbinus. Showcases their portraits, a custom that goes back to Etruscan times.
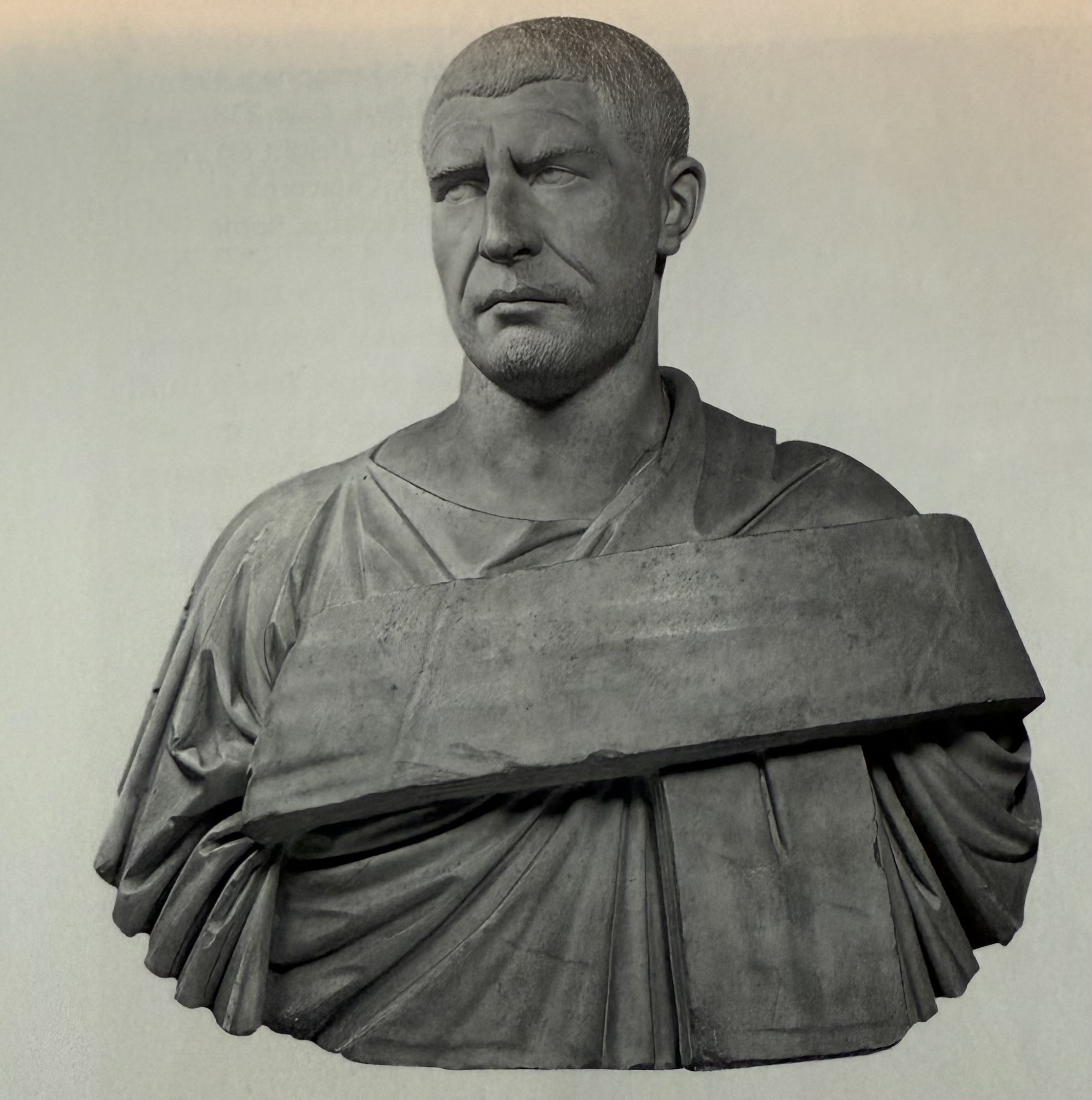

Bust of Phillip the Arab. Showcases the trabeated toga, the new standard.
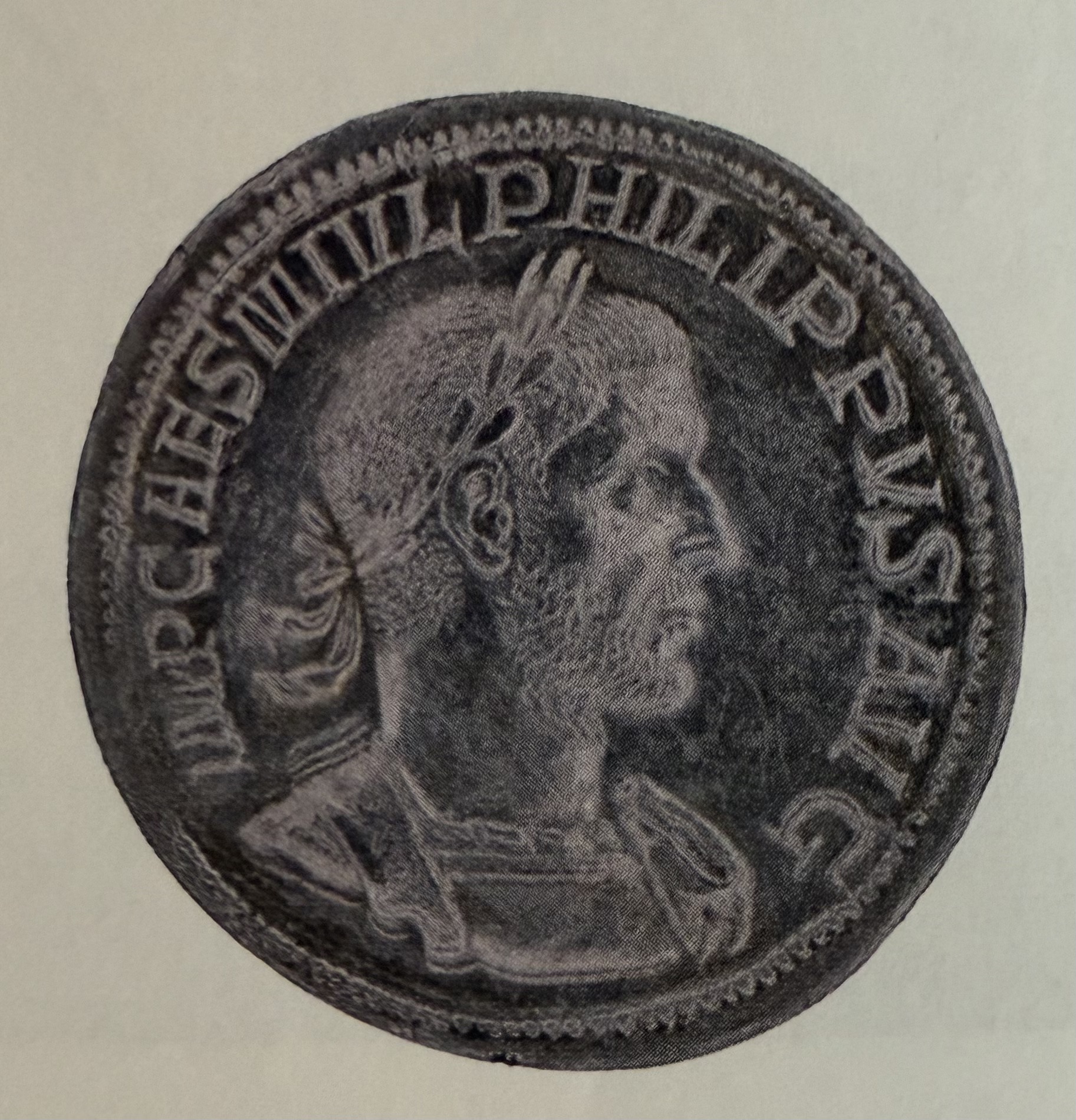

Medallion of Phillip the Arab. Communicates that everything is the same. Security and Continuity.

Bronze portrait of Trebonianus Gallus. Not part of a dynasty, but still using stock images to communicate power. Not the perfect body typically seen in heroic nudity.
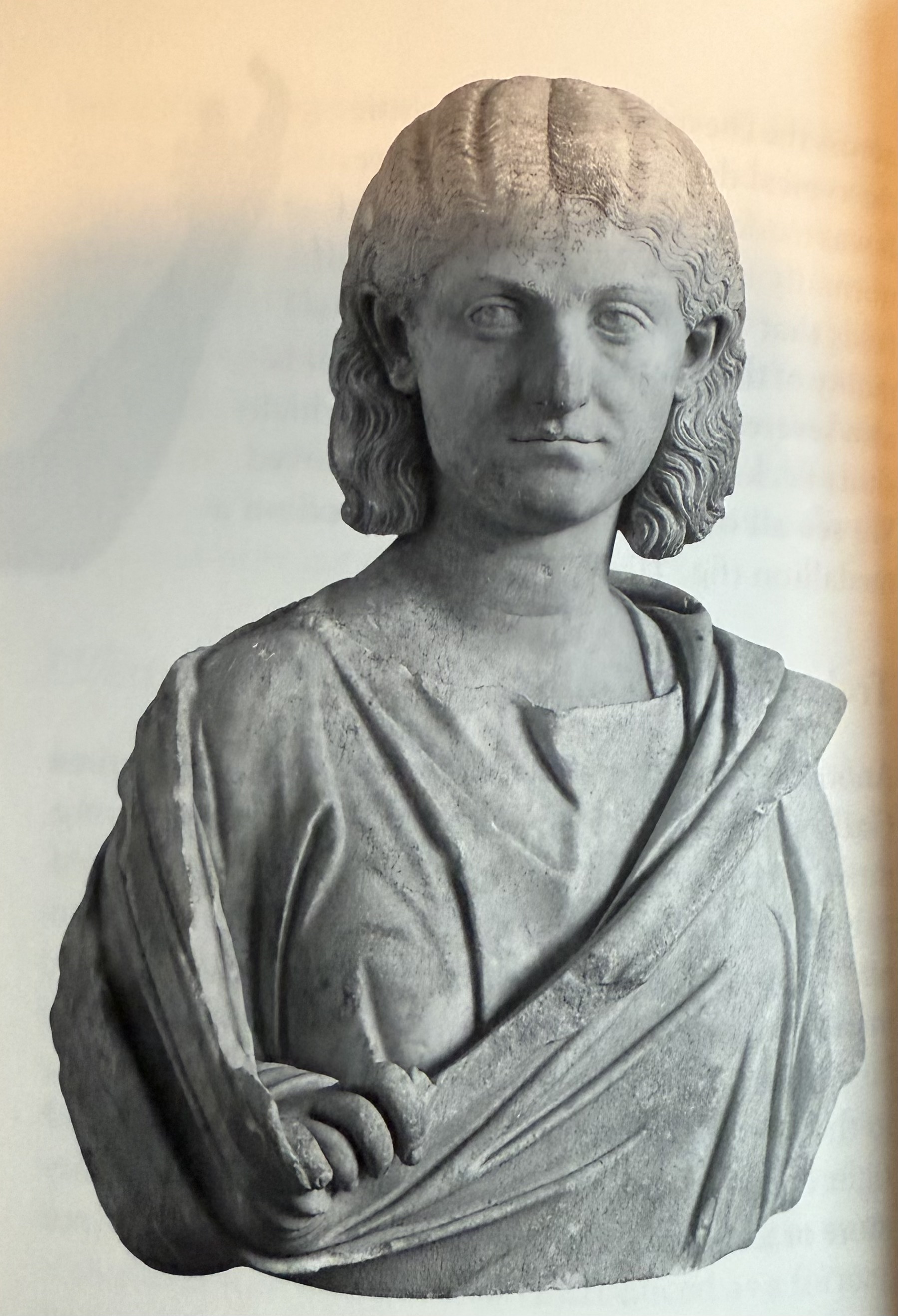

Female portrait. Hairstyle similar to Julia Domna.
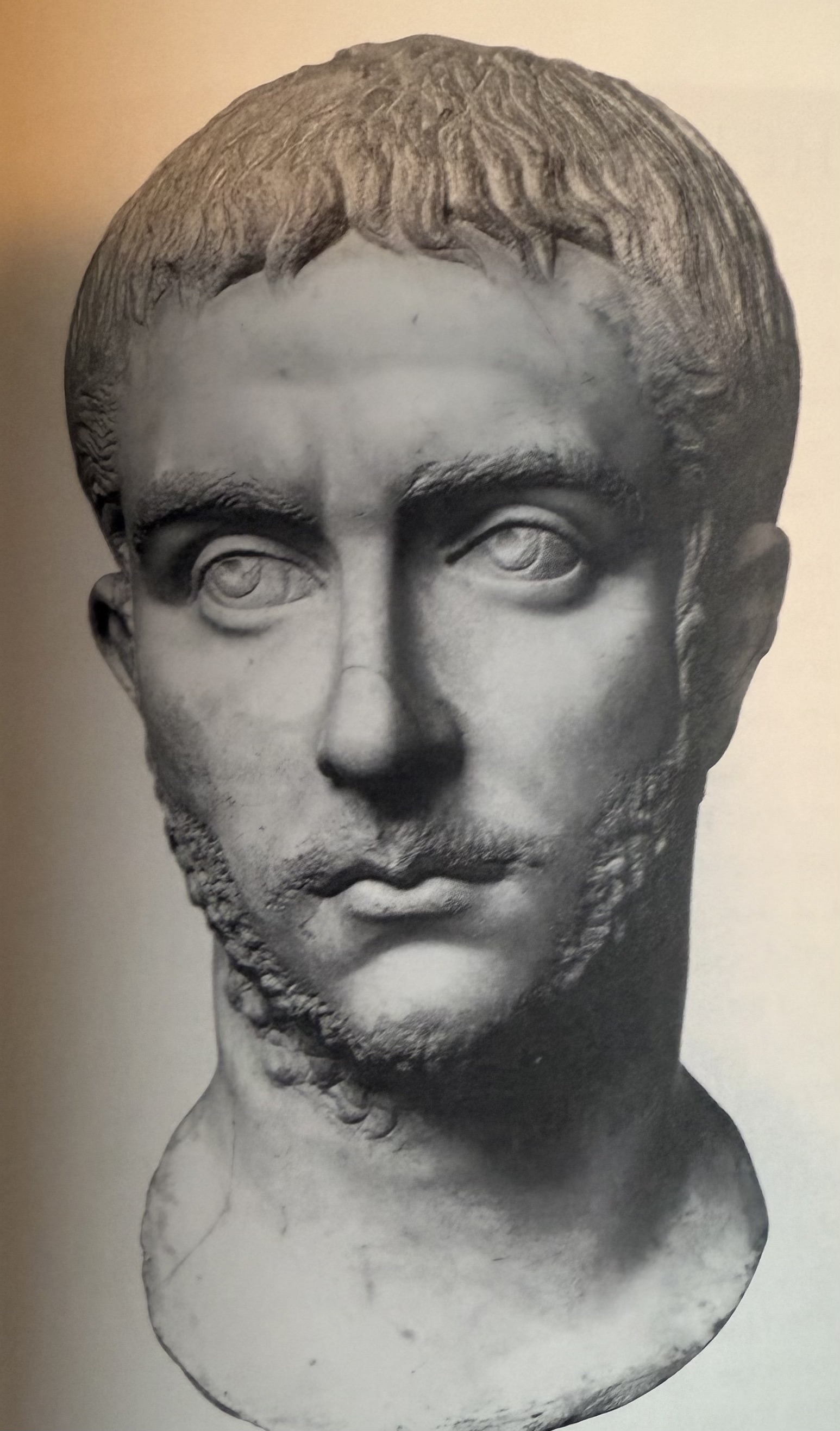

Portrait of Gallienus. Renaissance of old roman values. Augustan revival (haircut).
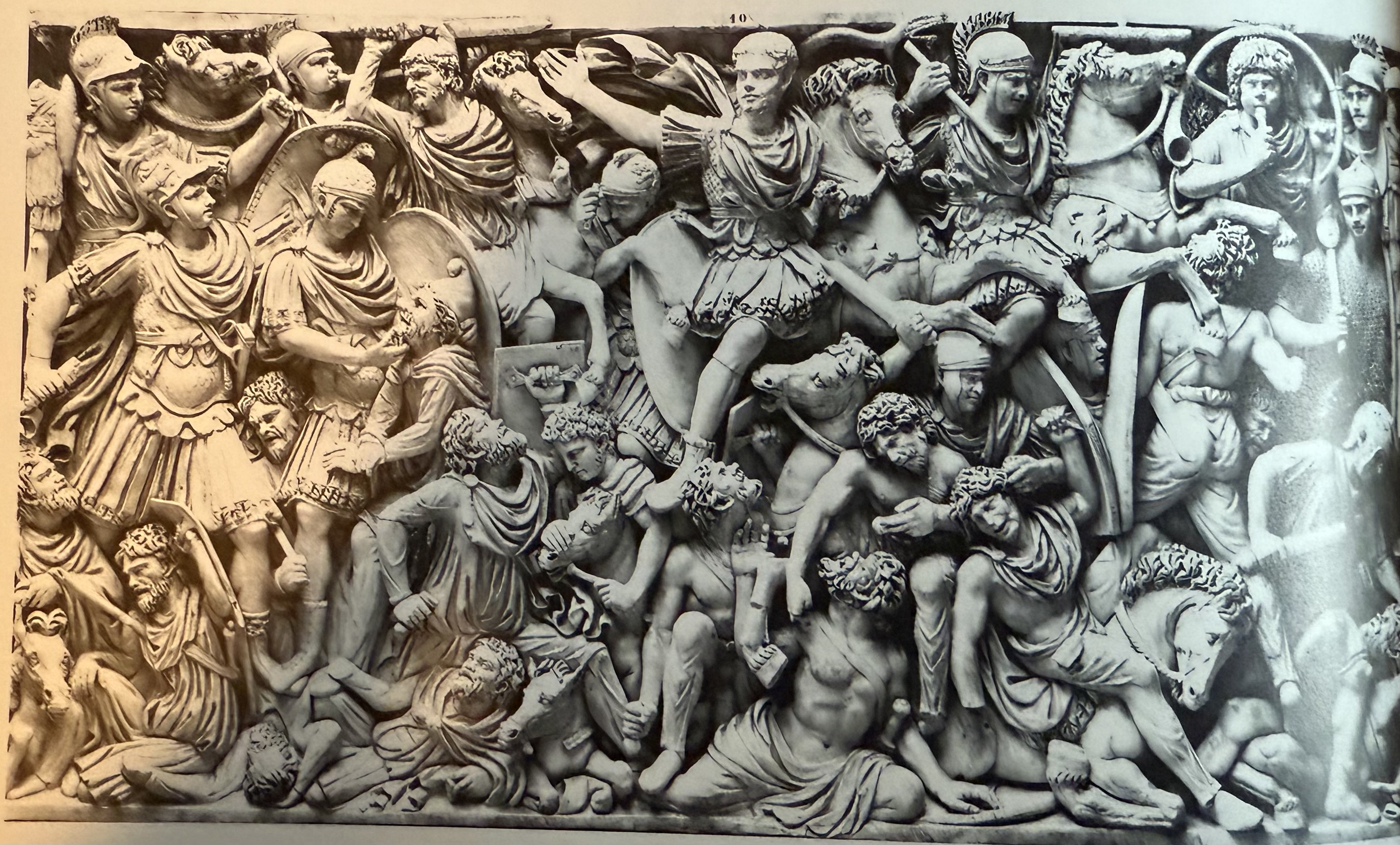

Battle between Romans and barbarians. Battle sarcophagi were popular under Antonines and then again under Soldier emperors. Biographical or aspirations? Likely not a soldier, but someone who participated in governance.
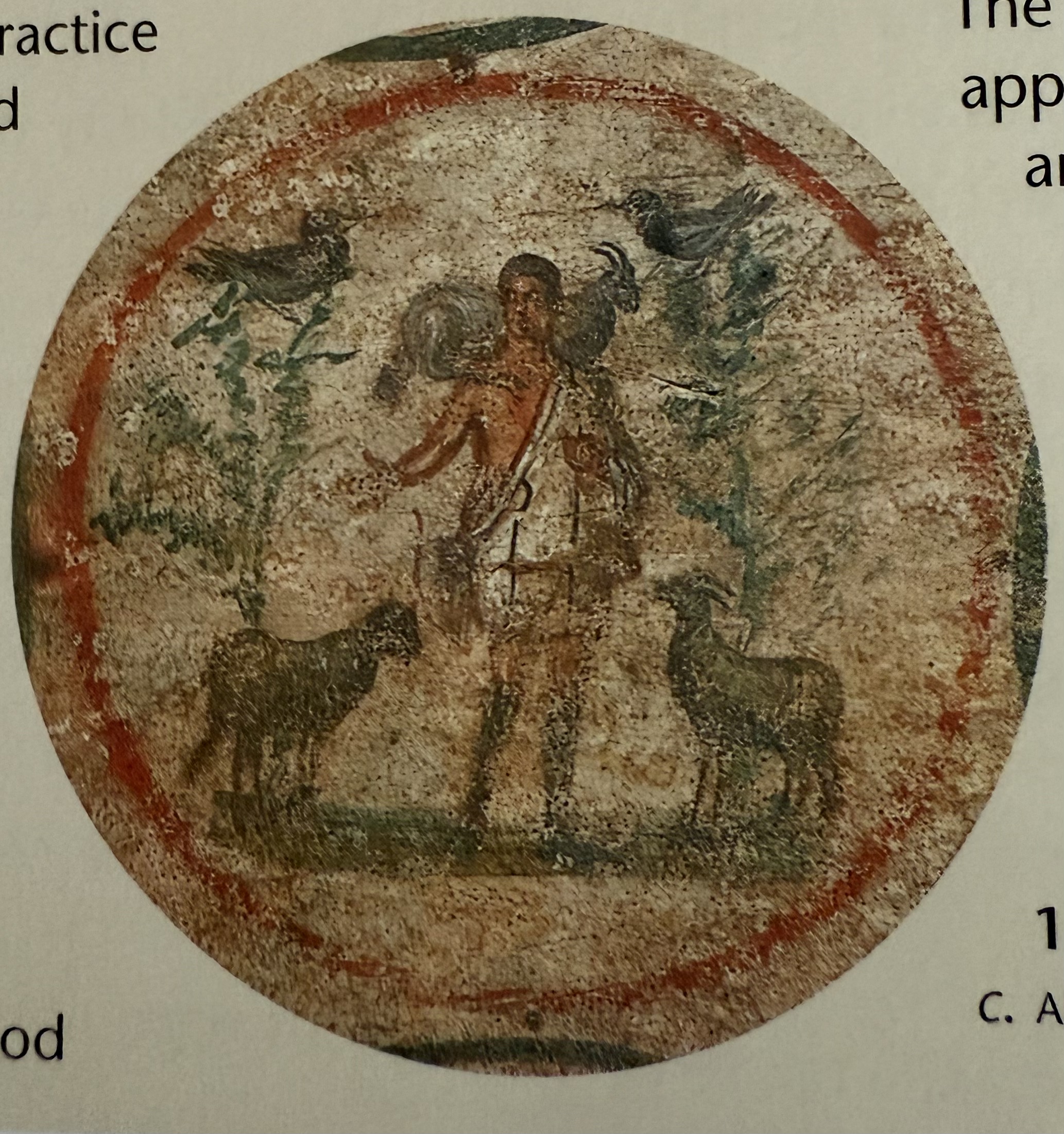

The good shepherd painting. Story goes back to early greek, but is reworked for Christianity.
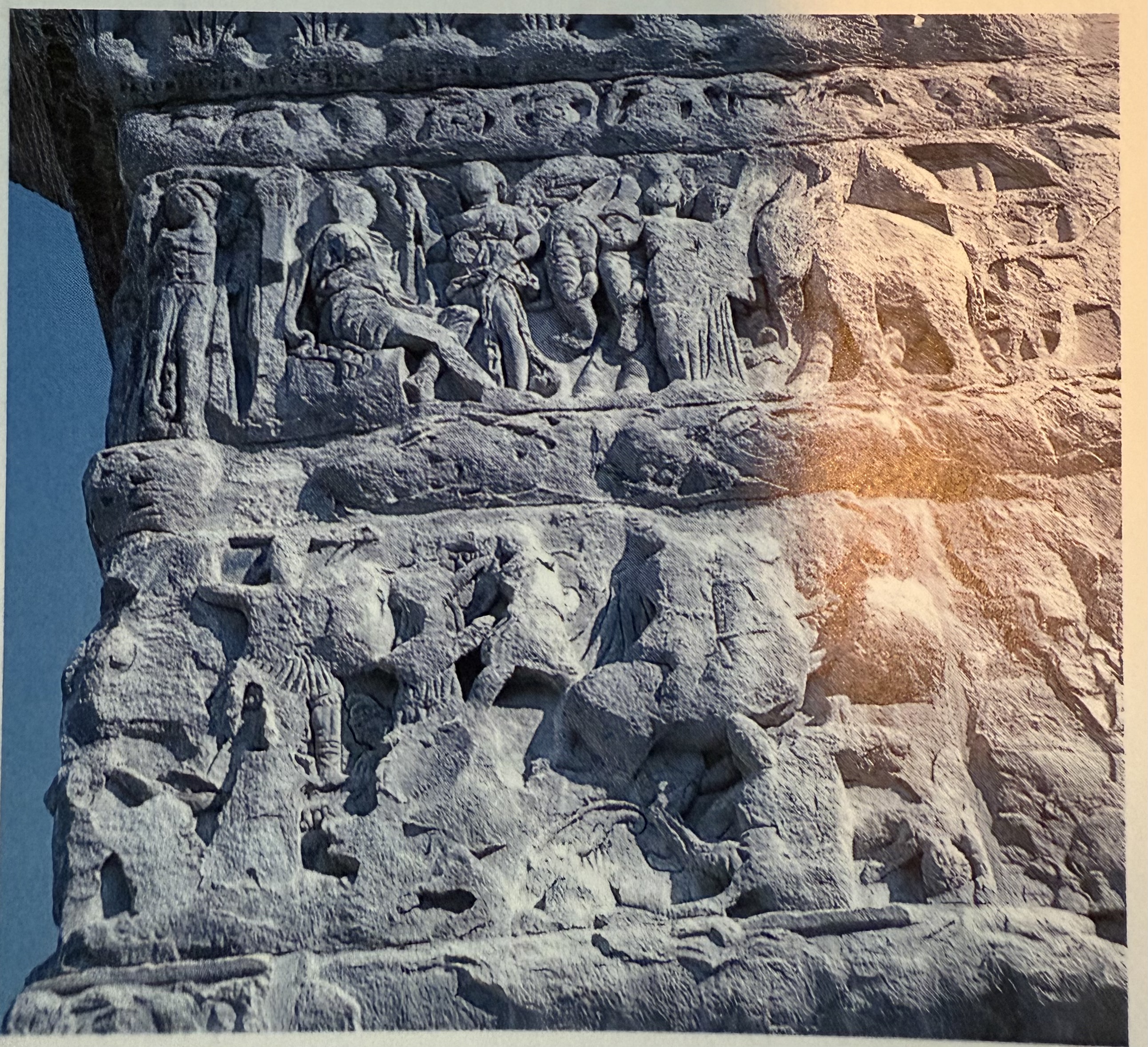

Battle scene with elephant on arch of Galerius. Extremely formulaic, stock type images.
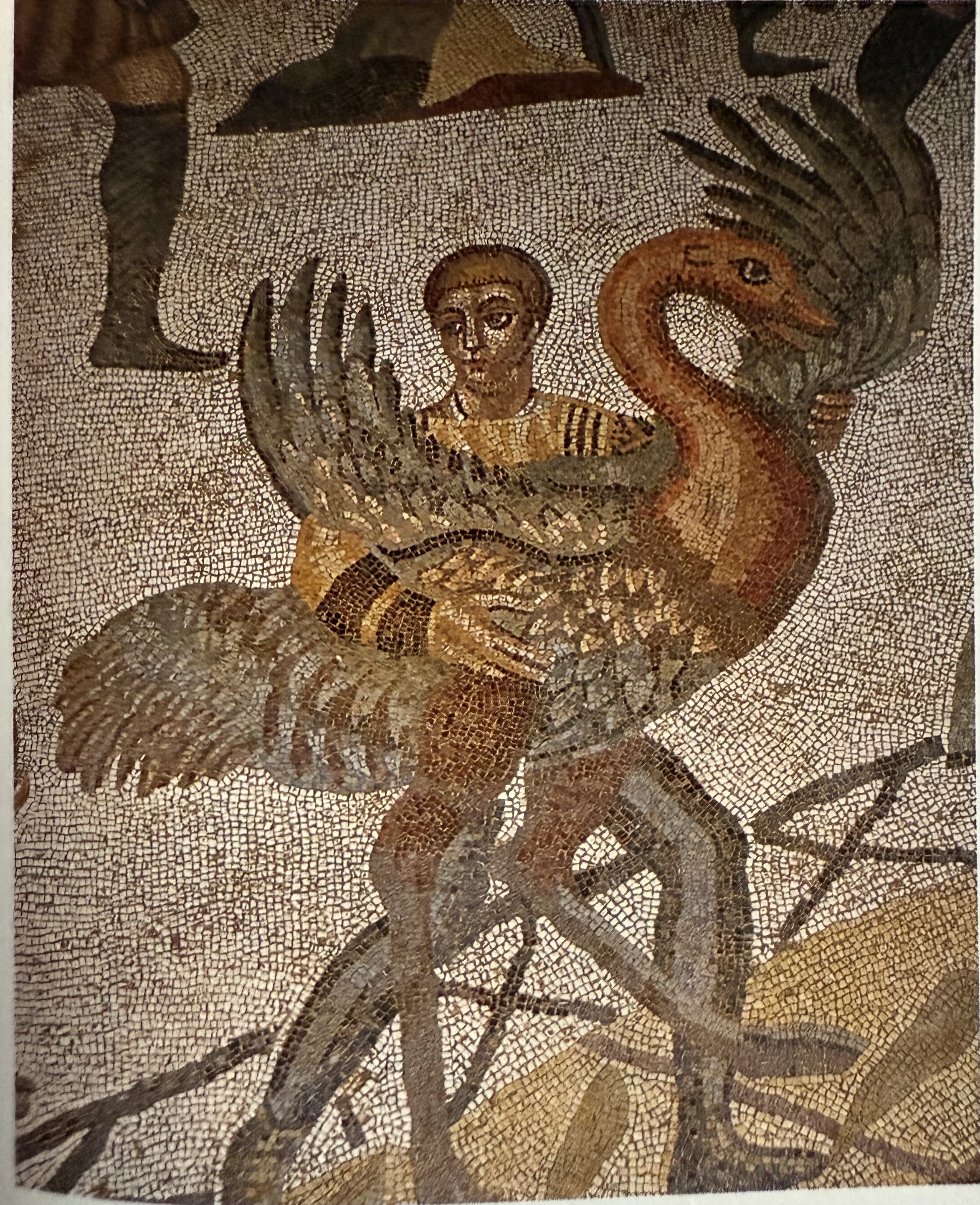

Detail of great hunt at villa at Piazza Armerina. Biographic and historical narrative. Details dress, ships, and local economy.
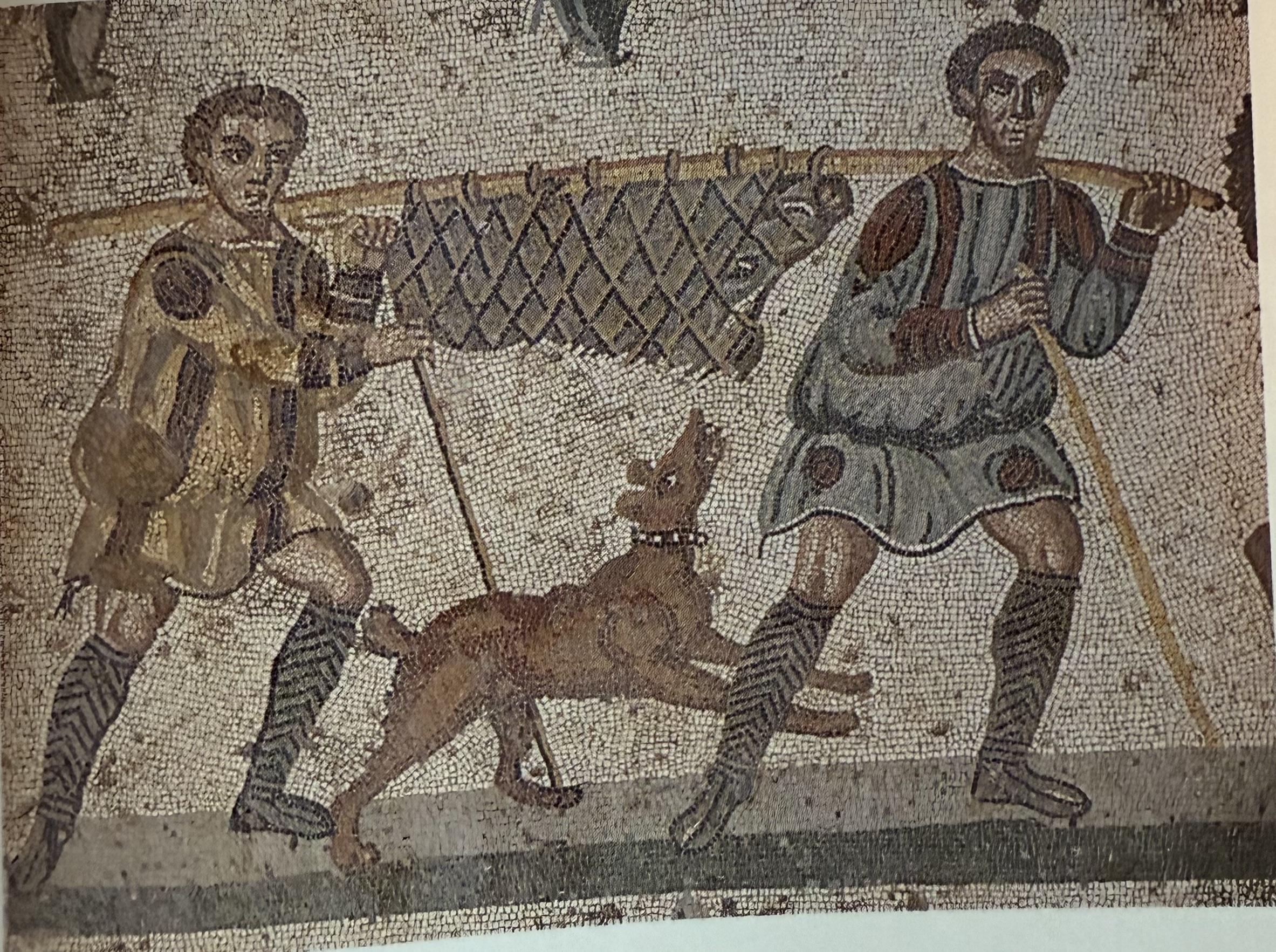

A captured boar mosaic at villa at Piazza Armerina.
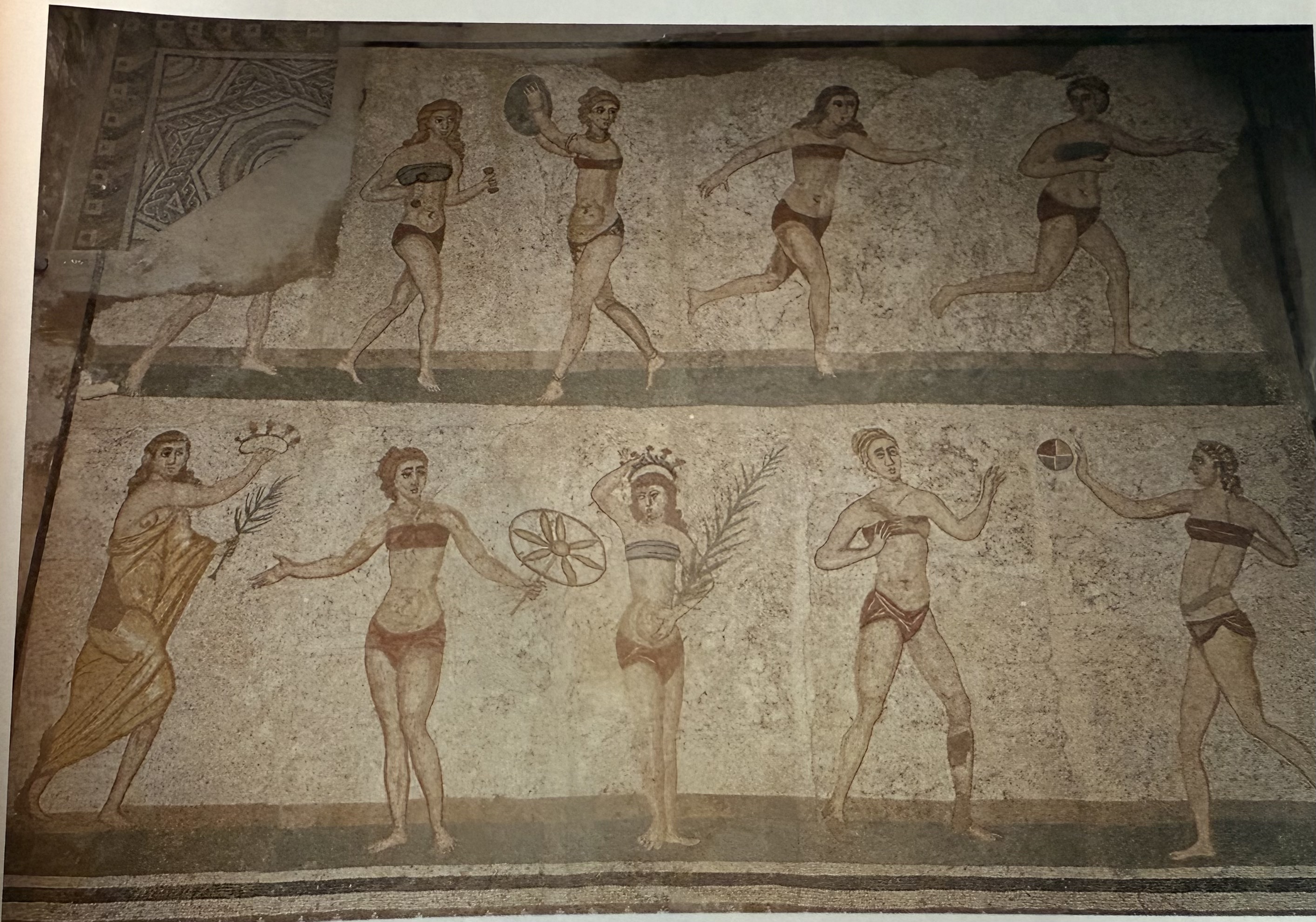

Bikini Girls mosaic at villa Piazza Armerina. Do not have representations of women doing this in public art.
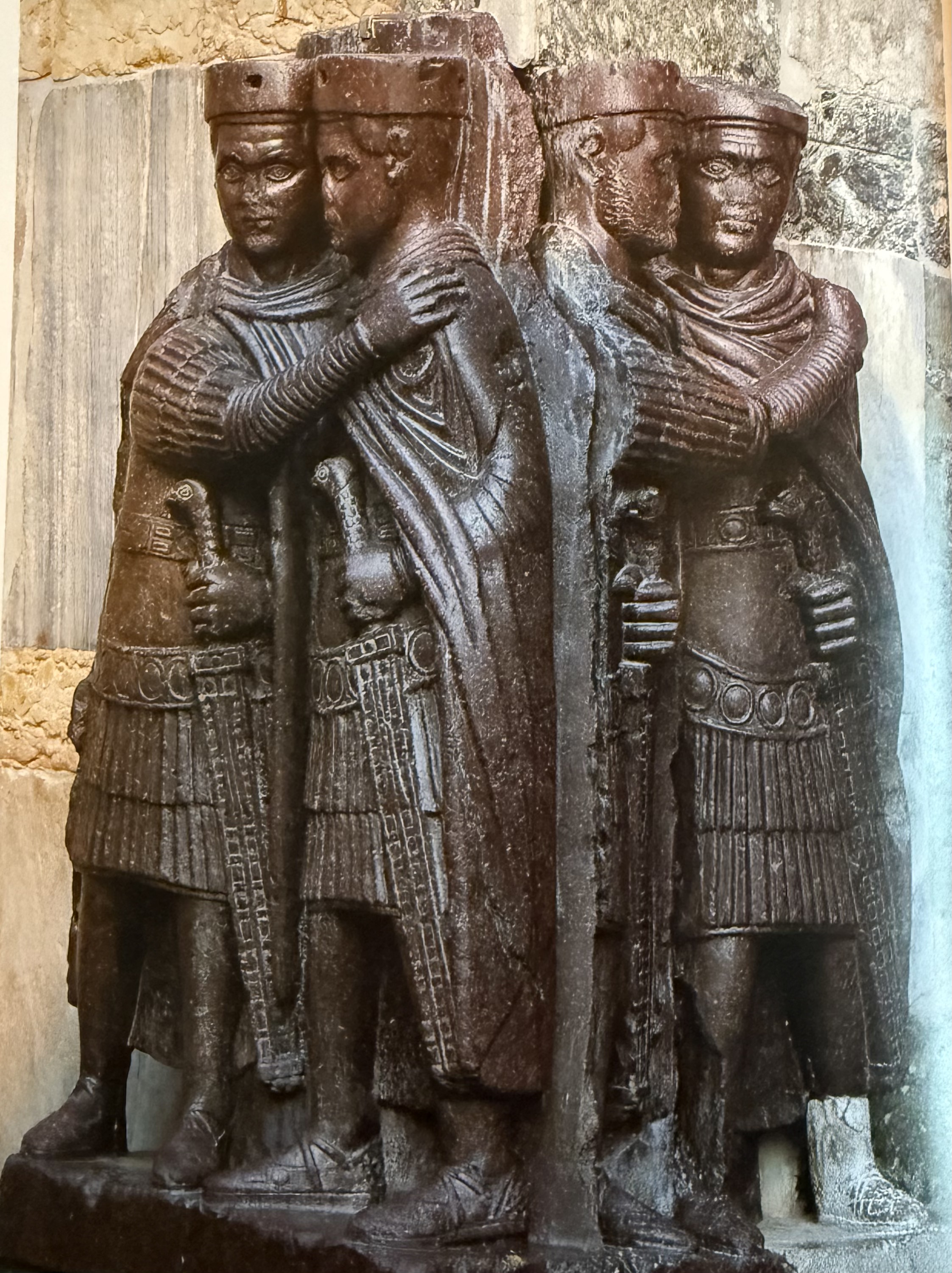

The tetrarchs. Carved from single block of porphyry. Taken from Constantinople and set up in Venice. Augusti embracing the junior. Venitians recycling and reusing symbols of Roman power and turning into symbols of Christian power.
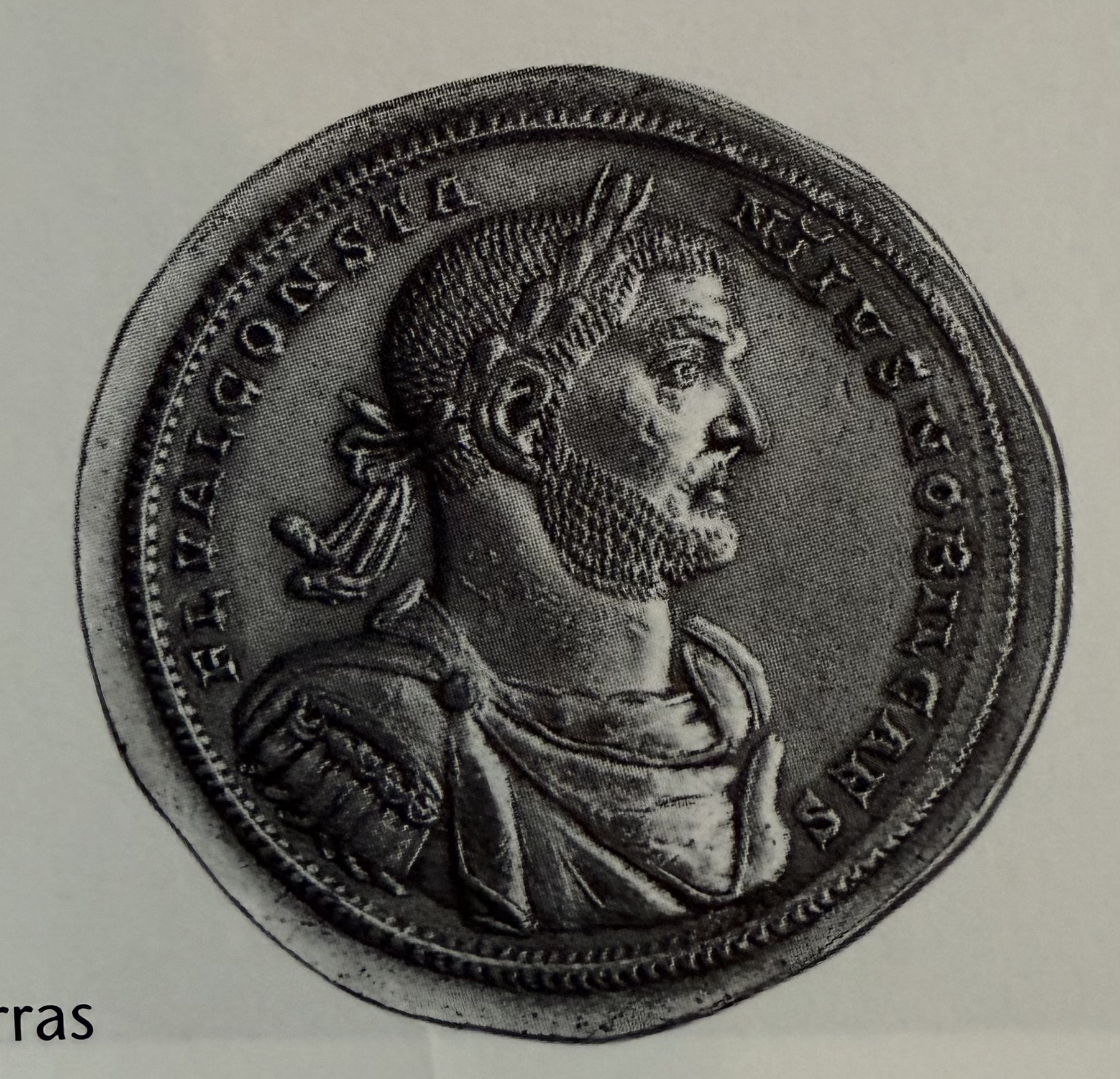

Portrait of Constantius Chlorus on coin. Father of Constantine.
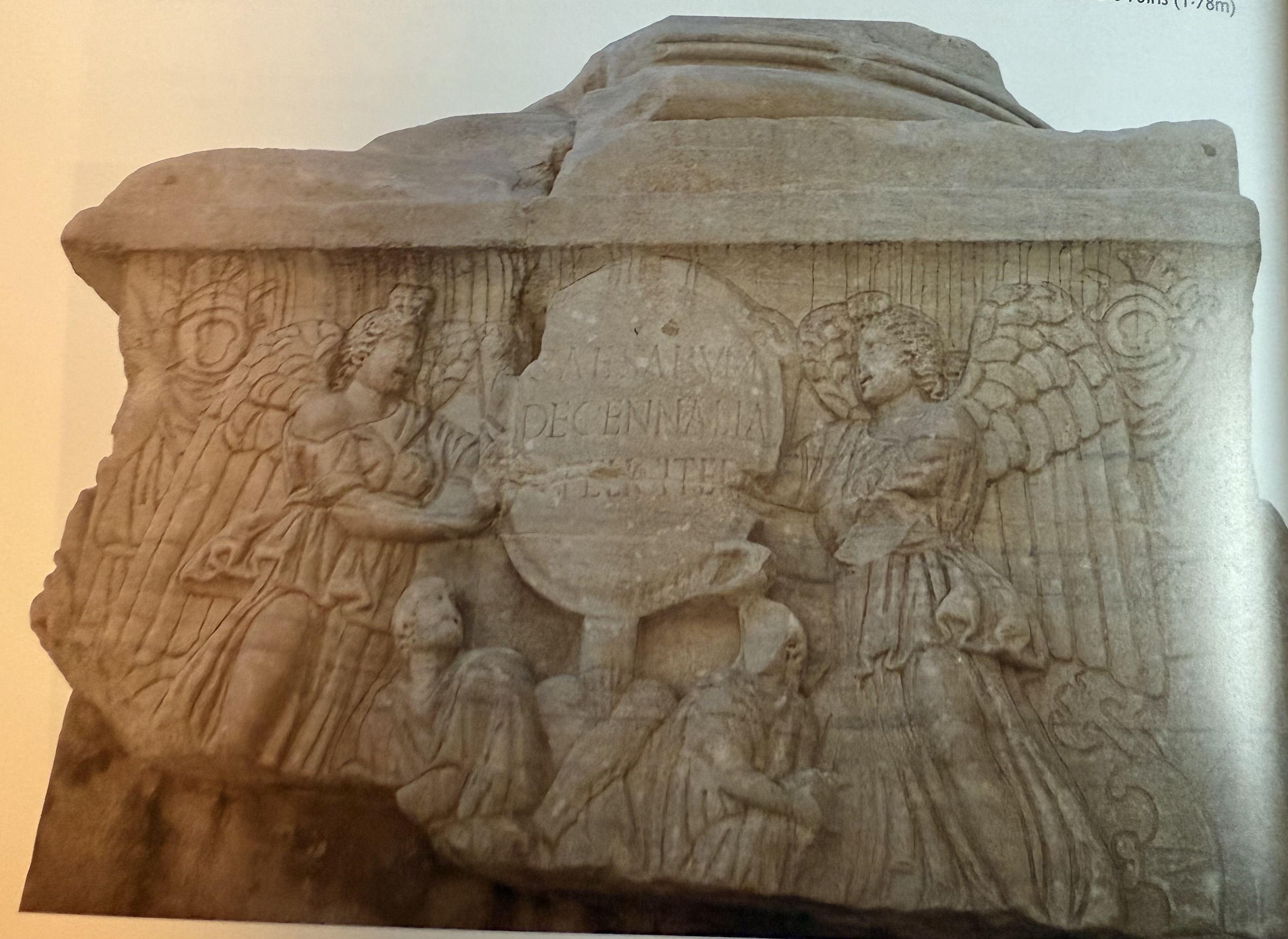

Sacrifice scene from Decennalia Base in roman forum. 5 columnated monument. No longer a concern to show living emperor with the gods.
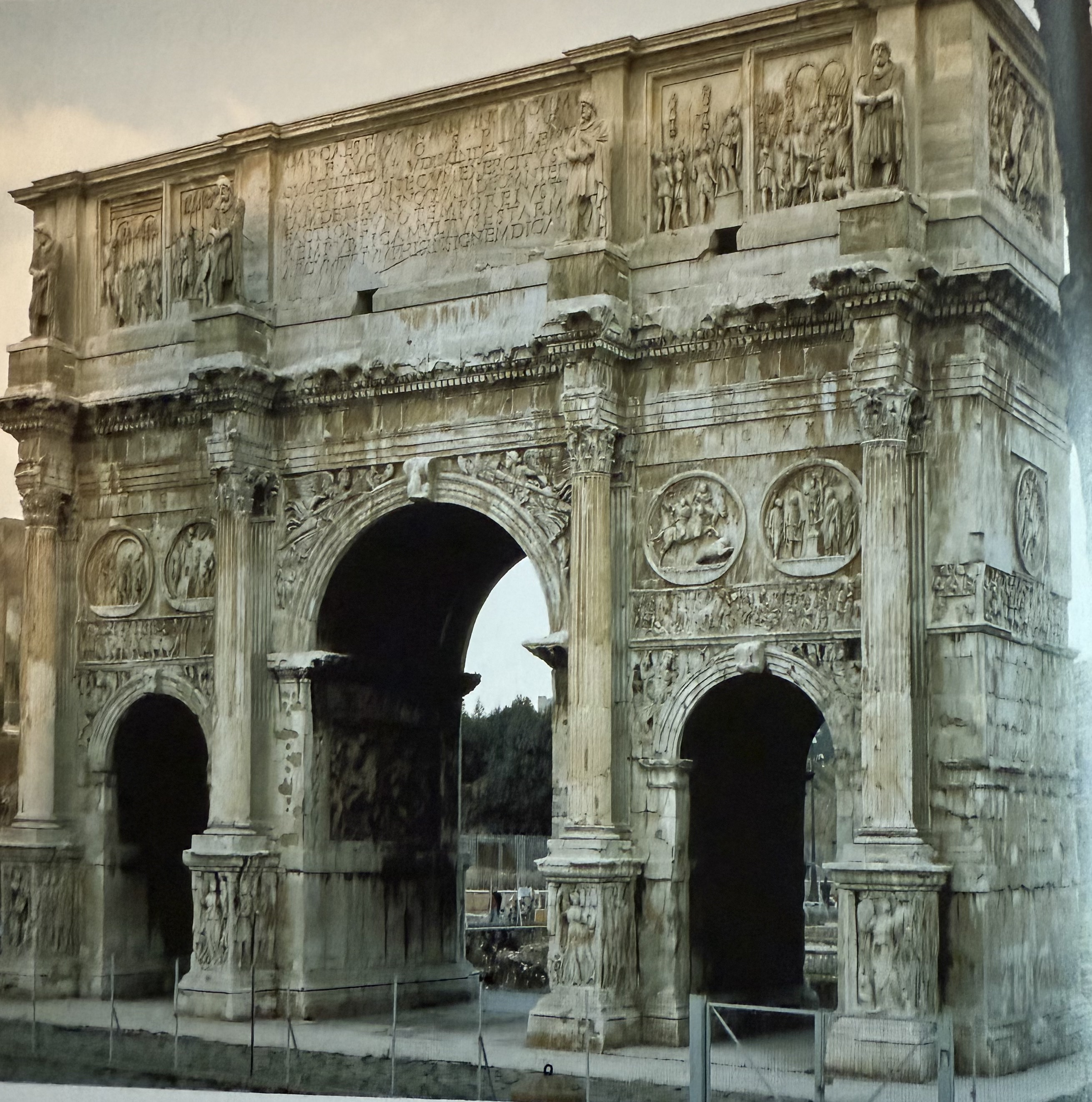

Arch of Constantine. Celebrates a civil war, something a triumphal arch had never done before. Made up of Spolia from previous emperors monuments.
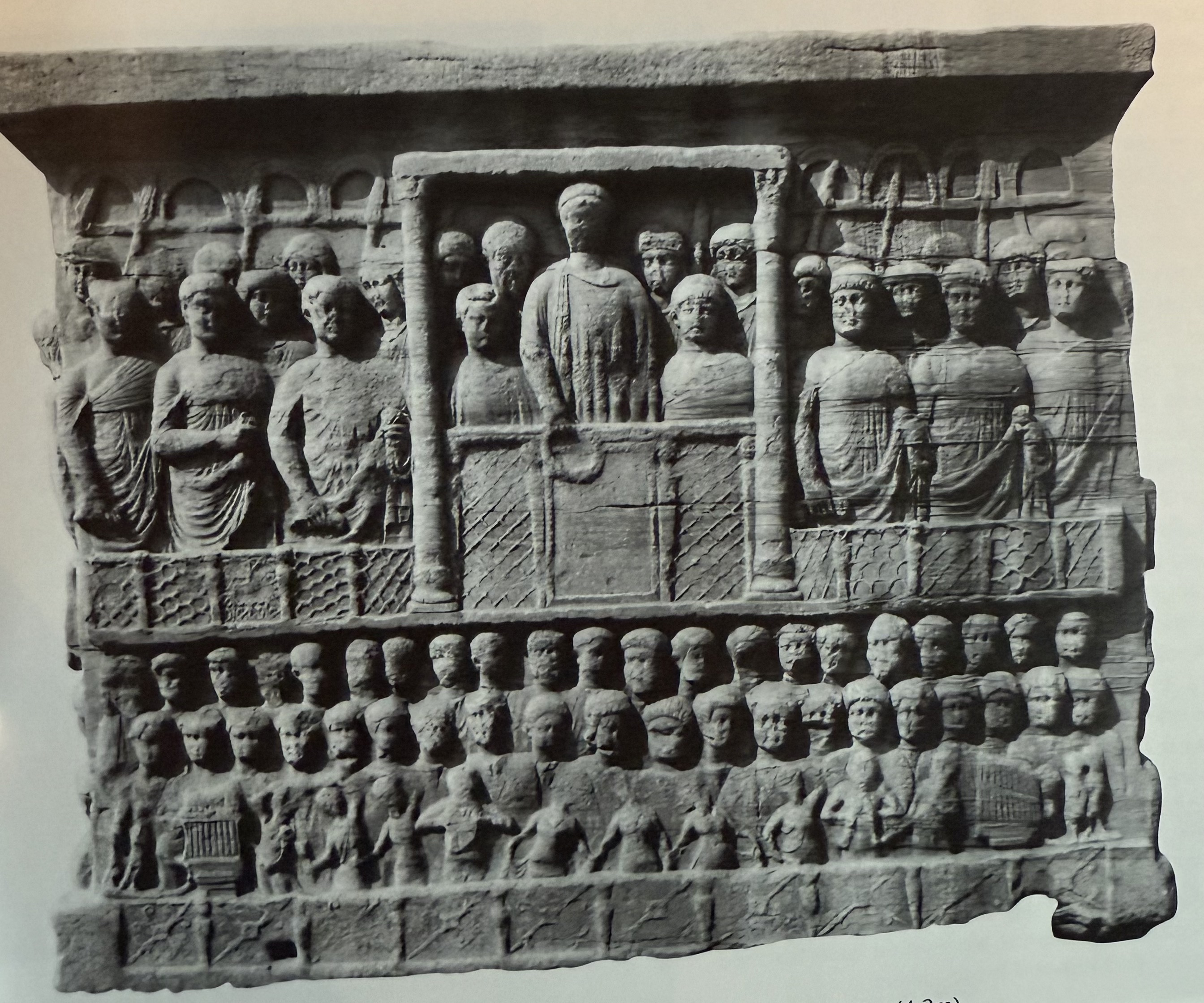

Base of the obelisk of Theodosius. Historical narrative errecting the obelisk. Shows the administrative and military entorage (court of Theodosius).
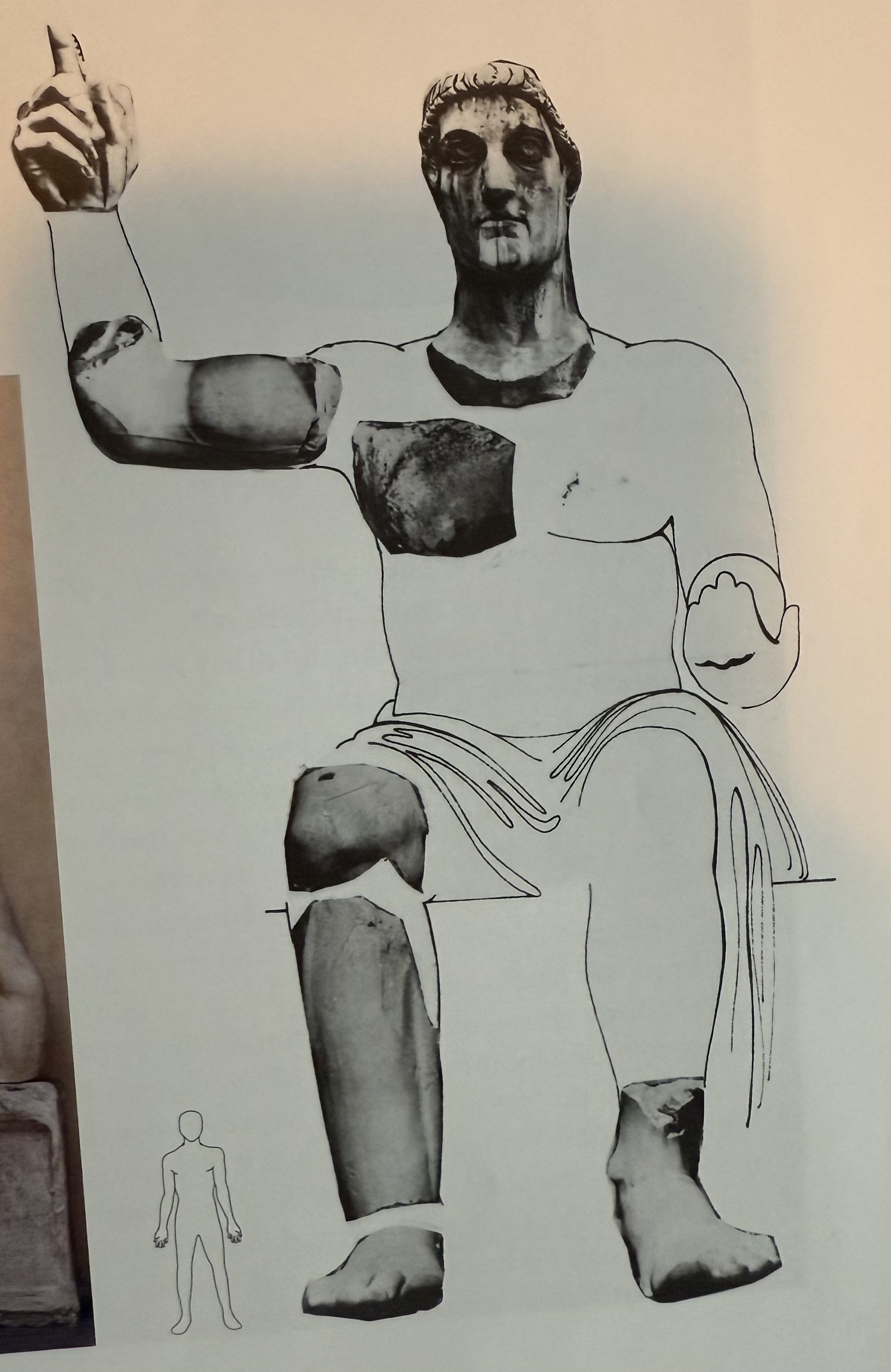
Reconstruction of the Colossal statue of Constantine. Would have been in Maximius basilica. New hand gesture not seen before.
Peacock Mosaic
Example fo roman/pagan symbolism being used for Christianity. Peacocks, which are sacred to Juno now a symbol for paradise. Now about “gods creations”.
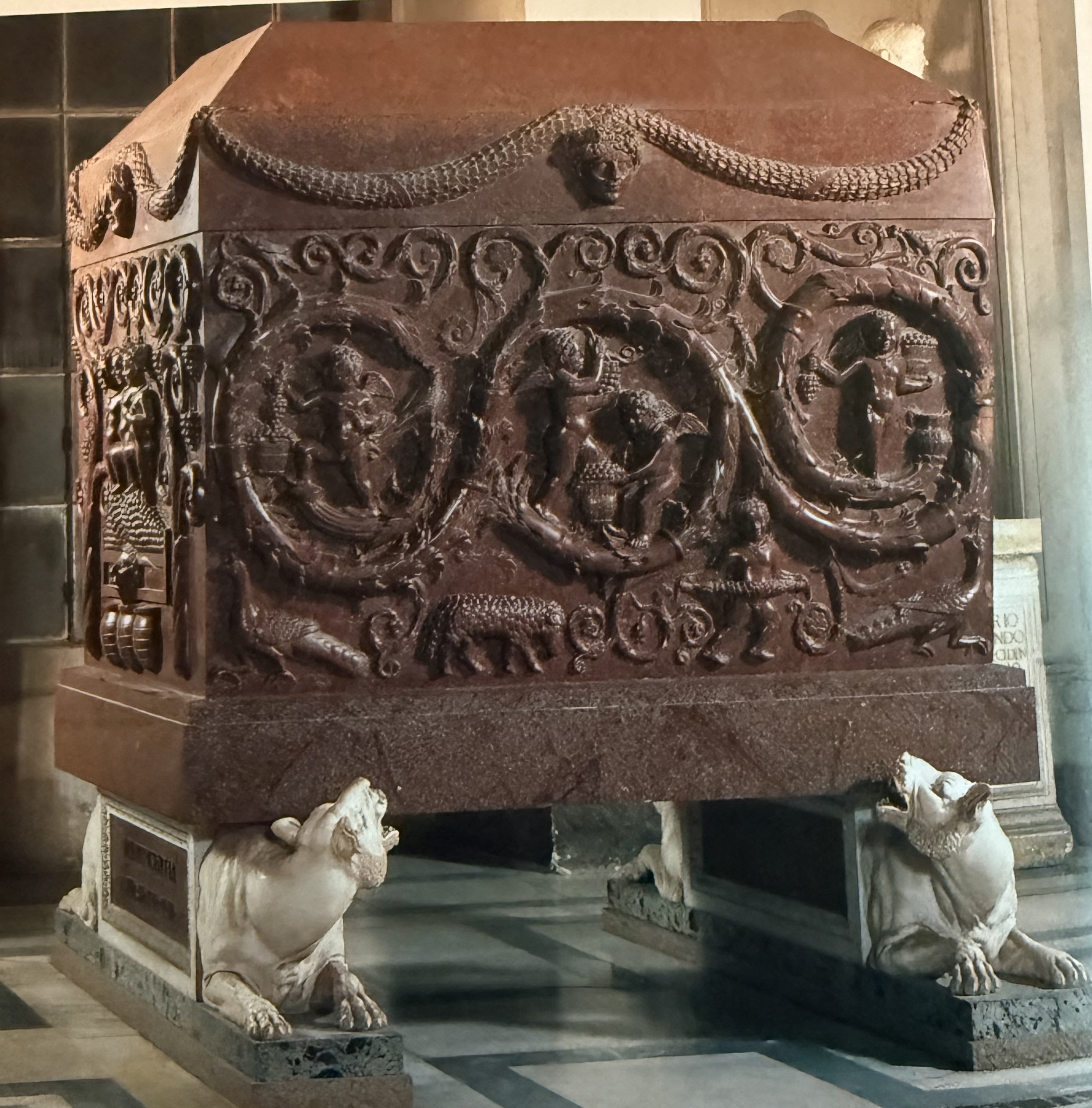

Sarcophagus of Constantia. Pagan Iconography in a Christian Context.
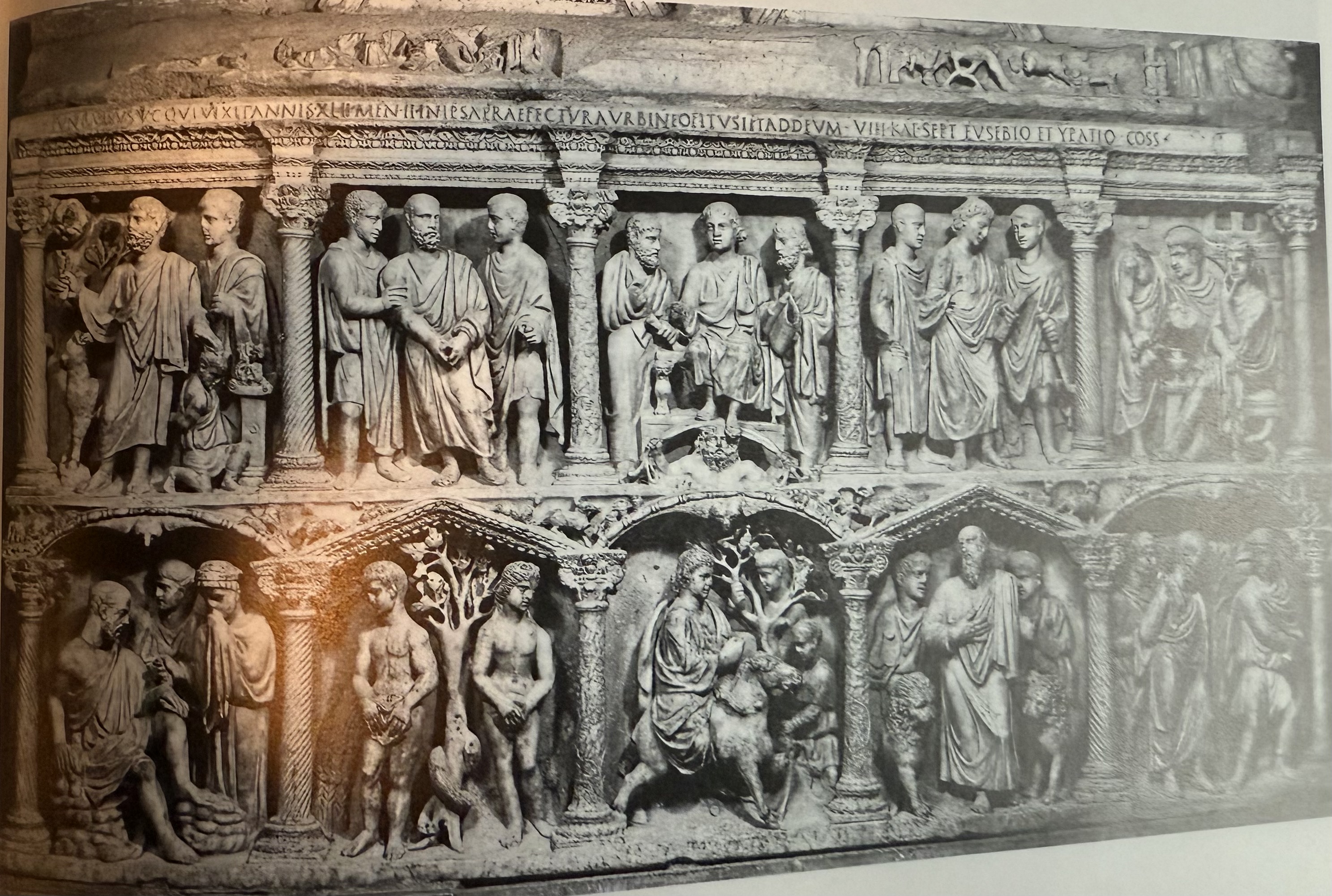

Sarcophagus of Junius Bassus. Roman elements with biblical stories. Same iconography in different context. Biblical heroes vs pagan.
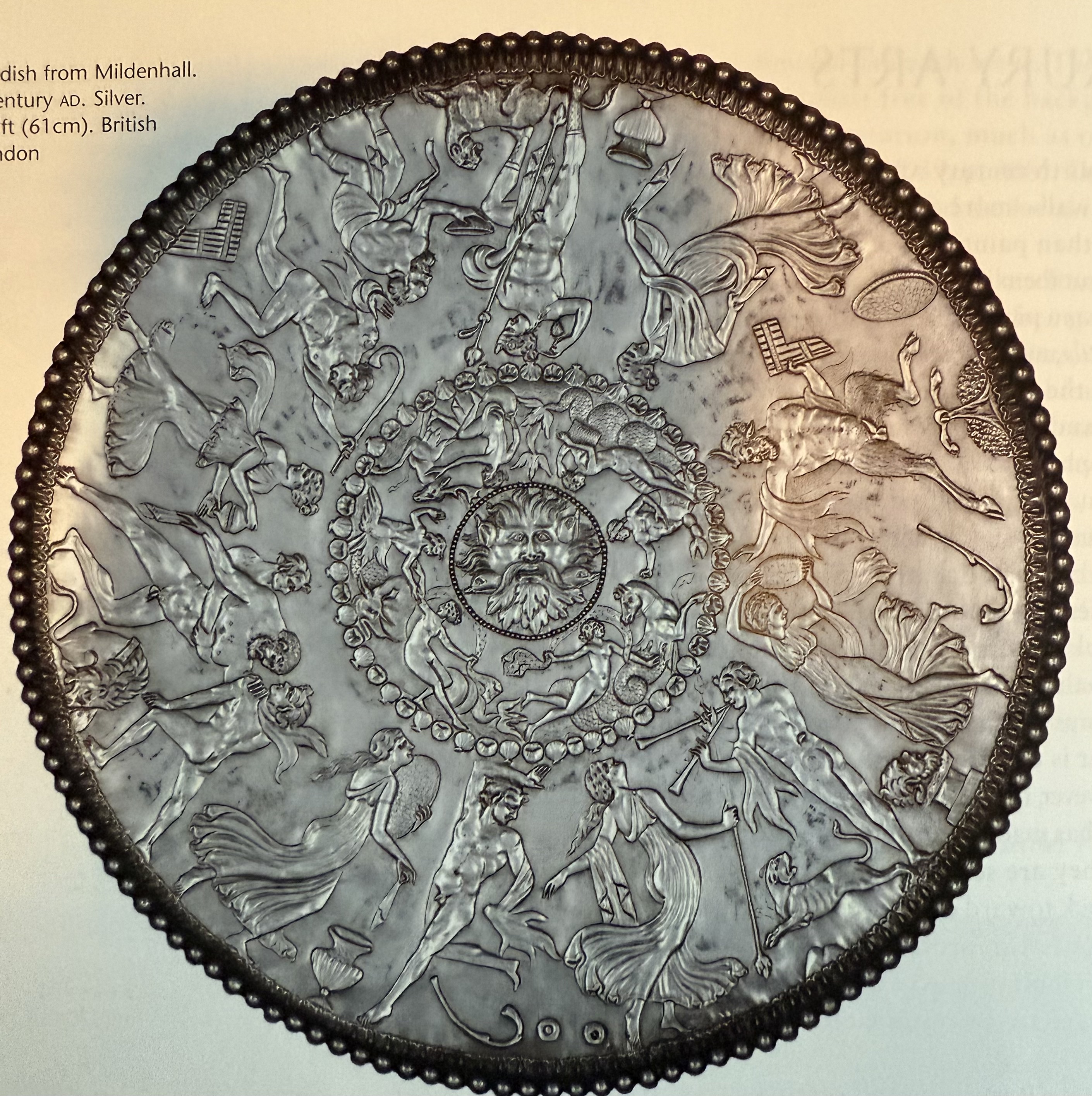

Great Dish. Bacchic revelry. Subject is still pagan. Drunken Heracles.
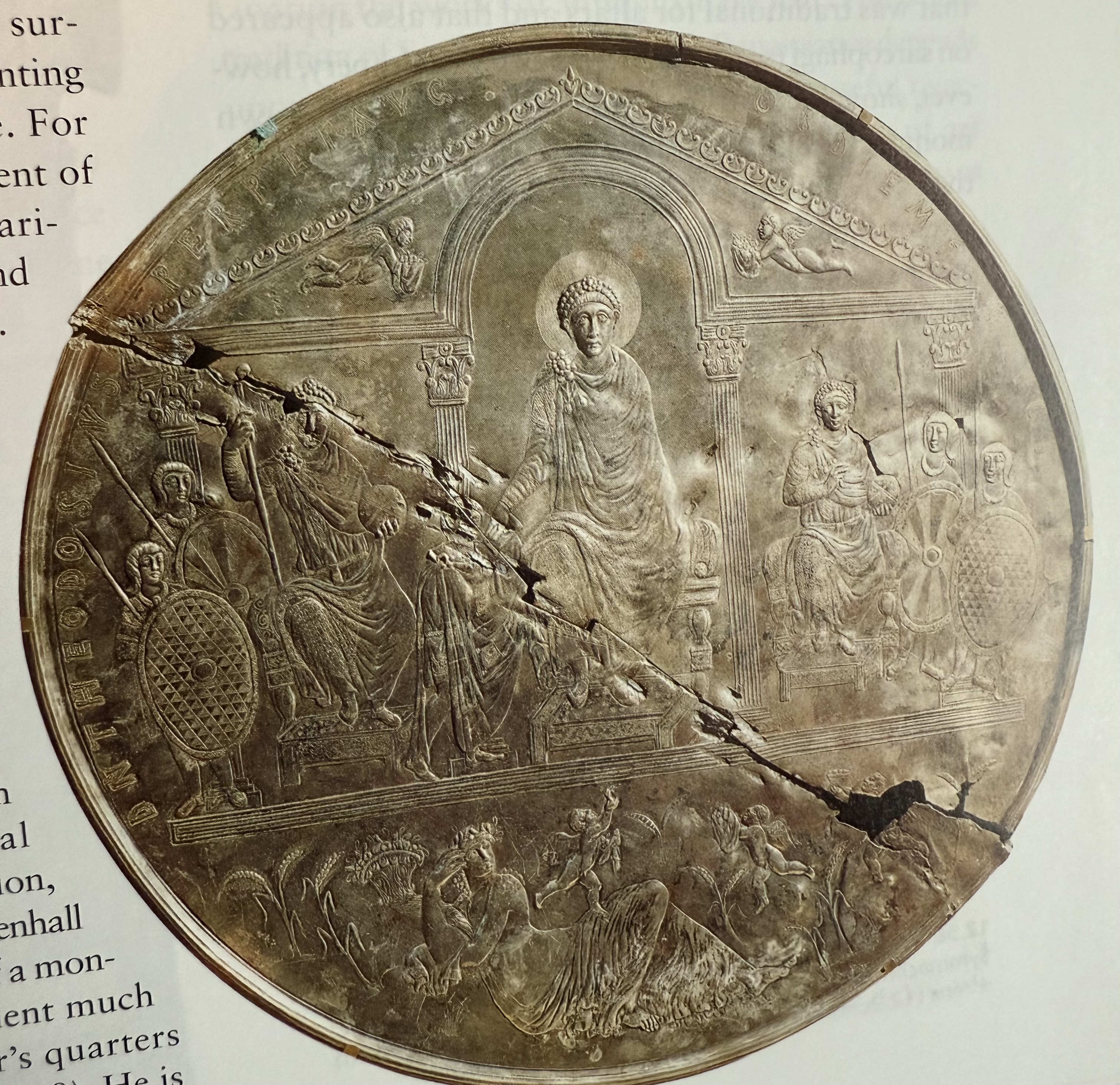

Ceremonial dish from Constantinople. Christina emperor with pagan icongraphy. Purposely broken in half.
Julia Domna
The wife of Septimius Severus. She wielded great power during Severan dynasty.
Caracalla
Son of Septimius Severus. A cruel leader, who was often pictured with a harsh scowl. Accused of murdering his brother Geta to avoid sharing power.
Fayum
A town in egypt which was known for their wooden funerary portraits.
frigidarium
The cold room of a roman bath. The frigidarium of the baths of Caracalla was inspired by the markets of Trajan.
tepidarium
The warm room of a roman bath.
caldarium
The hot room of a roman bath. The caldarium of the baths of caracalla was inspired by the pantheon.
antoninianus
The new coin developed by Caracalla. This coin worsened inflation, as it was debased.
tetrapylon
A four way arch, usually triumphal or commemorative, found at a crossroads. The arch of Galerius provides an example.
bachhus
The roman wine god. His revelry was typical on scenes of sarcophagi and represented escapsim.
Maximinus Thrax
The 1st of the soldier emperors. He continued the tradition of using portariture on coins, He only held power for 3 years.
Balbinus
One of the soldier emperors. His sarcophagus depicts him and his wife, in a rather unflattering manner.
Gallienus
He brought a new portrait style and instituted a renaissance of old roman values. His portraits make him look a bit like Augustus. Emphasis on sensitivity and intellect instead of brute strength.
Aurelian Wall
Built to fortify Rome. It greatly increased the boundaries of rome. The wall is an example of Spolia as it was made of anything they could find.
Ephesus
Tetrarchs
4 joint rulers of Rome. They had two senior partners, the Augusti and two junior partners, the caesares. The tretararchy does not continue after the original 4.
Spalato
The city that Diocletian built his retirement villa. The villa included a mausoleum and an audience hall for the emperor emeritus.
similitudo
The idea that the office of the emperor is important, and the man holding it secondary. This was a particulalry important idea for the tetrarchs.
Diocletian
The last of the soldier emperor and the creator of the tetrarchy. He was the first emperor to ever retire, instead of dying while in office.
groin vault
The intersection of two barrel vaults of the same height. It becomes a popular design technique in christian architecture.
Piazza Armerina
Holds a great assembly of surviving mosaics. The mosaics are both biogaprhic and historical. They showcase the local economy of animal hunting. There is a particularly unqique mosaic, the bikini girls.
Decennalia reliefs
A relief set up in the roman forum to celebrate the 10 year anniversary of joint rule with the caesares. The monument consisted of 5 columns, 4 tetrarchs and jupiter in the middle.
porphyry
A dense red volcanic stone quarried in egypt. The tetrarch statue found in Venice was carved of this stone.
oratio
The public speech given by the emperor. An example of this can be seen on the arch of Constantine, to celebrate one of his first acts as emperor.
donatio
A gift of money to the people of rome at the emperors expense. An example of this can be seen on the arch of Constantine, to celebrate one of his first acts as emperor.
basilica
The conventional name for the civic and administrative building in Rome. They were public places.
Santa Costanza
The mausoleum of Constantia, which was eventually converted into the church. While it was built for the Christian daughter of a Christian emperor, it is decorated with pagan iconography.
opus sectile
Thin pieces of colored stones/marble cut and set for decorative effect in floors and walls. There is an example of Junius Bassus in his chariot race.
Junius Bassus
Prefect of the city of rome. His sarcophagus is decorated in Christian iconography, with scenes from the bible, however in the roman style.
Cities of the Roman provinces. Where were they and what types of monuments, decorations and artifacts found there help us understand their role in the empire?
The culture of early Christianity in arts and monuments. What did it look like and why?
Psychological portraiture. What does it mean and what are some examples?
Topography of Rome and the Forum. How does it change during the period of the Tetrarchs and Constantine. Why and what does it look like?
Spolia. Describe the process and some examples of monuments that include spolia.
Coins used to communicate messages about the imperial family during Severans and later. Why do they do this, what are some features and motivations of images on coins from these periods.