chemistry chapter 21 buffers
definition of buffer solution?
minimises the change in pH when small amounts of acid or bases are added
What do acidic buffer solutions contain?
a weak acid and its salt
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
definition of buffer solution?
minimises the change in pH when small amounts of acid or bases are added
What do acidic buffer solutions contain?
a weak acid and its salt
example of what is in an acidic buffer?
CH3COOH and CH3COO-Na+
what are the two reactions happening in an acid buffer?
CH3COOH ←> CH3COO- + H+
Weak acid dissociates weakly so POE lies well to the left.
CH3COO-Na+ ←> CH3COO- + Na+
Salt dissociates strongly so POE lies well to the right.
what happens when you add H+ to an acid buffer?
H+ ions conc increases and they react with the negative ions. There is a high conc of these from the salt.
More acid is formed, so POE moves to the left to remove H+. Favours backwards reaction
What happens when you add OH- to acid buffer?
OH- conc increases and small conc of H+ reacts with OH-
Acid dissociates, and POE moves to the right favouring forward reaction and restoring H+.
what is the other method of preparing a weak acid buffer?
adding aqueous solution of alkali like NaOH to an axcess of the weak acid.
weak acid is partially neutralised by the alkali forming the conjugate base
When [HA] = [A-]…
pH of buffer is same as pKa value of acid
operating pH is typically over about two pH units centered at pH of the pKa value

how to find pH of buffer solution?
don’t assume [H+] = [A-] in Ka formula because A- has been added as one of the components
![<ul><li><p>don’t assume [H+] = [A-] in Ka formula because A- has been added as one of the components</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/71bf41b6-9373-411d-b298-823b429ebdcc.png)

do this calculation
3.45


do this calculation


do this calculation
4.68

What happens when the blood pH level goes below 7.35 and 7.45?
below is acidosis
above is alkalosis
what is the name of the buffer system set up in your blood?
carbonic acid - hydrogencarbonate buffer system
what are the formulas for this buffer system in blood?
H2CO3 ←> H+ + HCO3 -
H2CO3 ←> H2O + CO2
What happens when acid is added to blood?
H+ increases and reacts with HCO3- so POE moves to the left, fabouring backwards reaction and removing H+.
What happens when alkali is added to blood?
OH- increases and small conc of H+ reacts and forms water. HCO3- dissociates, POE moves to right favouring forwards reaction, restoring H+.
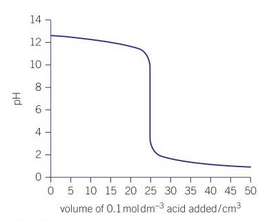
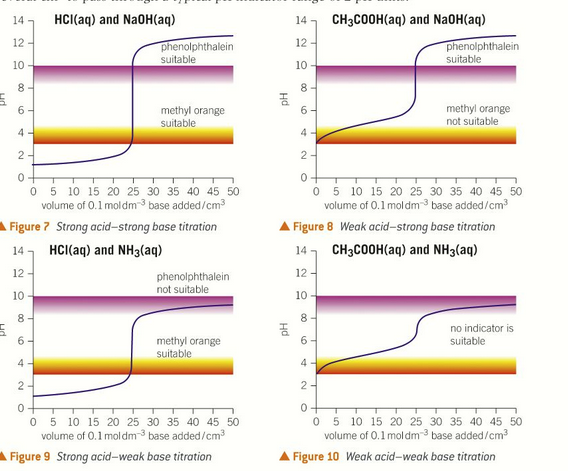
label parts of the titration curve
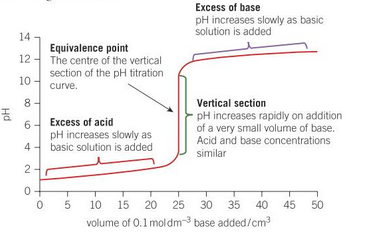
what is the equivalent point?
at this point the acid has been fully neutralised by the base. [H+] = [A-]
what features must a suitable indictator have?
must change colour entirely within the vertical part of the graph to determine the end point.
end point colour will be a mix of the colours of the indicator in acidic and alkaline conditions.
it is a weak acid
pH of the end point is the same as the pKa value of the indicator