Personality Psychology - Final Exam
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Cognitive Perspective:
Premise 1: Thinking influences emotion and behavior.
Premise 2: There are individual differences in how people think.
Premise 3: Patterns of thinking are relatively consistent over time.
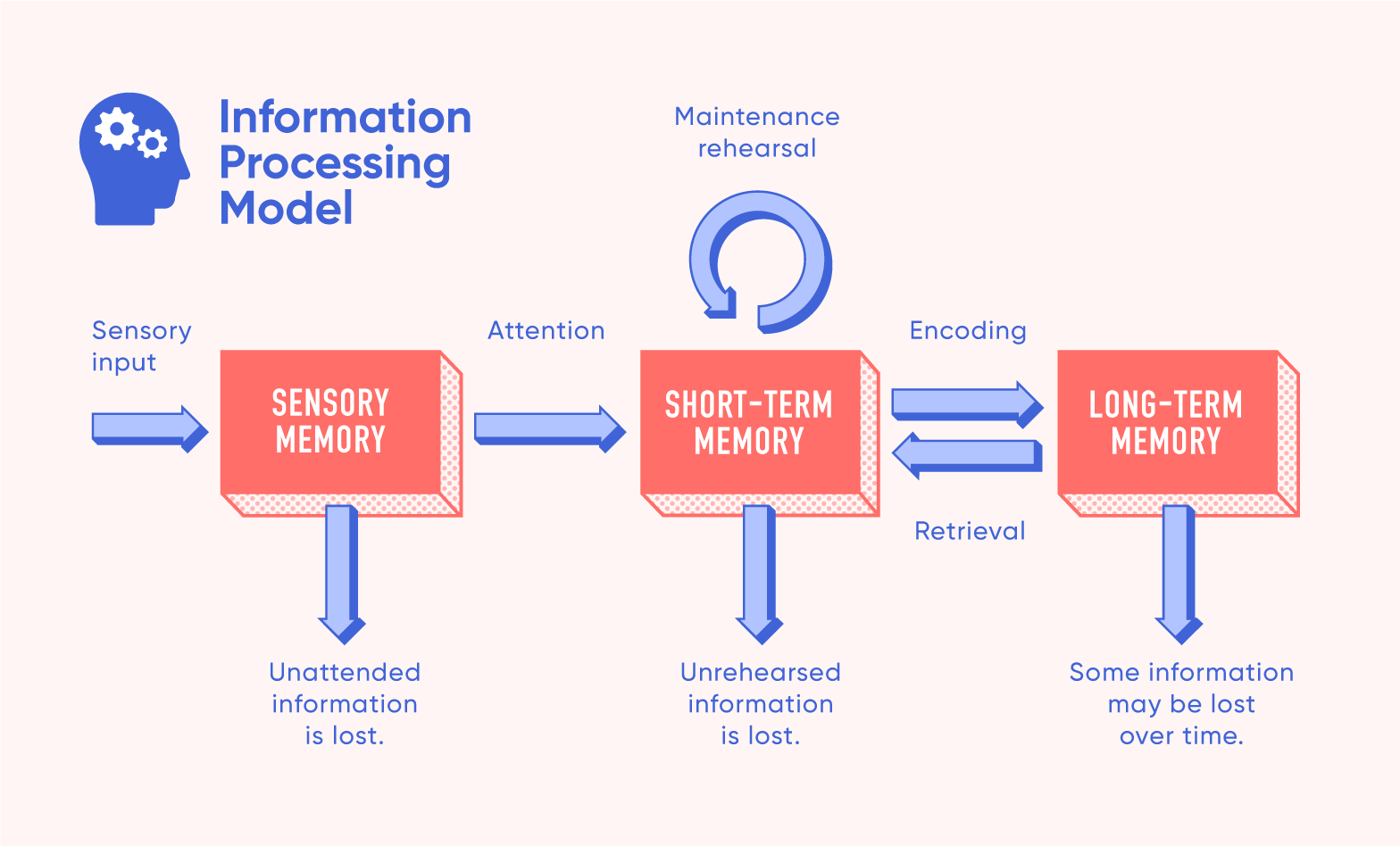
Information Processing Model
A cognitive framework comparing the human mind to a computer, explaining how we acquire, process, store, and retrieve information through stages like sensory, short-term (working), and long-term memory.
Field Dependence
Externally oriented
Need cues
People-oriented approach
See whole
Learn in social settings
Recall names and faces
Lack details
Field dependent seem to do better in open skill sports than in closed skill sports.
Field Independence
Internally oriented
Can separate figure
and groundField Independent are more likely to be physically active and play organized sports.
Analytical Approach
Seeing the parts
Impersonal relationship
Prefers data
Rely on perceptions
Perform better in academic settings
Field Independent people are better at sports that involve open skill, like baseketball, football, etc. and close skill like swimming
Rod and Frame Test - Witkins 1962
Can tell if you’re field dependent or independent
George Kelly - Personal Construct Theory
Proposes that individuals act like scientists who create their own "constructs" to interpret and predict events in their lives
We have a NEED to predict actions and events
With experience we revise our predictions
Predictions flow from bi-polar categories we construct.
George Kelly - Personal Construct Theory More info
What categories or theories does a person use to understand and predict the world?
“Range of convenience”
Construct = element of knowledge
Two poles
To understand what ”good” is you have to have a conception of bad
CAPS Theory:
Objective situations are viewed through personal C.A units/easily accessible schema, then that is processed and forms your behaviors/subjective interpretations/individual differences.
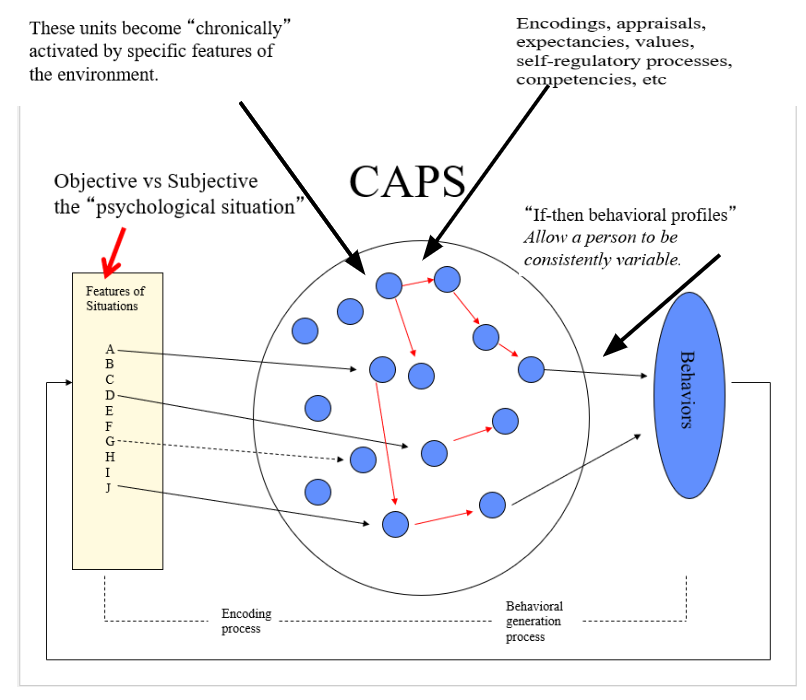
Cognitive-Affective Units (CAUs):
Which are stable mental representations (like encodings, beliefs, goals, affects, competencies)
If-then profiles:
CAPS (Cognitive-Affective Processing System) theory's "if-then" profiles are stable, situation-specific patterns of behavior that explain why individuals react differently to different situations, even though their underlying cognitive-affective system remains stable.
These profiles, also known as "behavioral signatures," illustrate that personality isn't about a person acting the same way everywhere, but rather about having a predictable, but situation-dependent, pattern of behavior
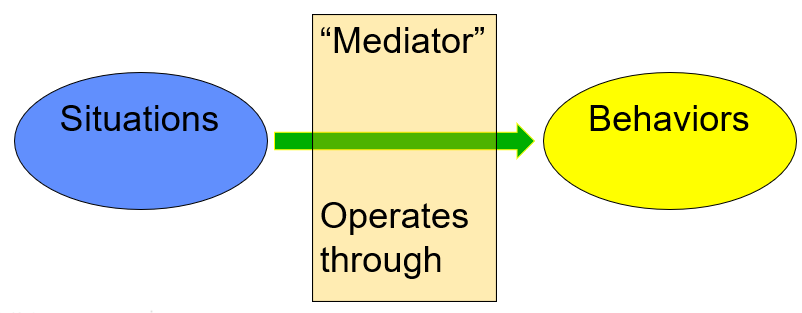
Trait theory tries to account for the average/predict hedonic tone, your average
CAPS theory (a mediational model) would try to account for the differences in the pattern
“Construals, Goals, Expectancies, Passions, Competencies”
Albert Bandura
Social-Cognitive Theory
Reciprocal Determinism
Behavior, personal factors (cognition), and environmental influences constantly interact and shape each other

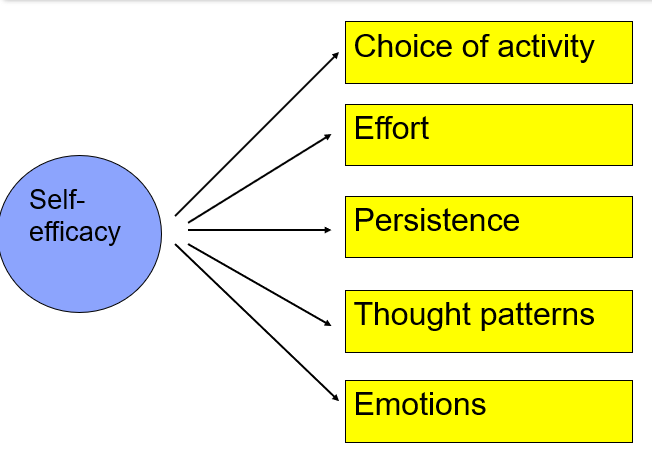
Self-Efficacy
not the same as global confidence, it is about specific task confidence
Situation/task specific confidence that you have the skills to achieve a certain level of performance/outcome.
Two parts:
To what level do I believe I can achieve?
How confident am I that I can reach that level?
(It can be too high if your skill level doesn’t match your self-efficacy)
How to Raise Self-Efficacy
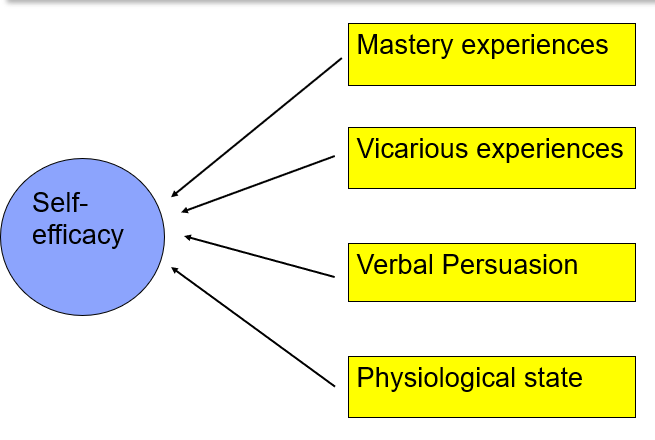
What does Self-Efficacy predict?
Self-Efficacy
Does it Predict Academically-specific Outcomes?
Who: Lent, Brown, & Larkin (1986)
What:
105 Freshman and Sophomores considering science and engineering majors
Self-efficacy assessed
Level of skills that could be successfully completed
Degree of confidence that they could complete each level
Several outcomes a year later
Relationships According to Jones
A relationship exists when:
“two people are aware of each other’s existence and, more important, both persons believe a relationship exists and both feel some sort of commitment or emotional bond toward each other” (pg 511).
Initiation
Awareness, interaction,
acquaintance, affiliation
Enhancement
Self-disclosure, feelings of a bond
Maintenance
Development after it is established
Termination
All relationships come to an end
Attachment
Bond that forms that has survival value
Characteristic of a relationship but has implications for the organism
Why do children form an attachment to a primary caregiver?
Bowlby’s Need for a Secure Base
Need for safety
Need to explore
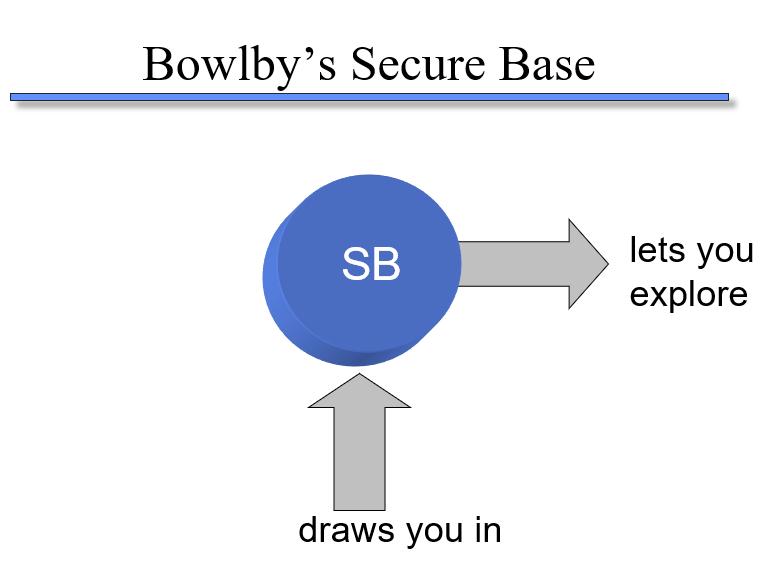
Internal Working Models
A cognitive framework comprising mental representations for understanding the world, self, and others.
Mary Ainsworth - Attachment
The course of development
6 - 12 months of age
Sensitivity is the key issue
How it’s Attachment assessed in young children
the Strange Situation (Ainsworth)
A = Avoidant,
B = Secure,
C = Anxious,
D = Disorganized
How it’s Attachment assessed in In Adolescents and Adults . . .
surveys
The Strange Situation (Ainsworth)
A =
Avoidant
The Strange Situation (Ainsworth)
B =
Secure
The Strange Situation (Ainsworth)
C =
Anxious
The Strange Situation (Ainsworth)
D =
Disorganized
How long does it take personality to form
Freud
Its from birth (Oral) til your 12 years old (Genital)
How long does it take personality to form
Erik Erikson
From Birth (Trust vs. Mistrust) til Death (Integrity vs. Despair)
Albert Bandura
Social-Cognitive Theory
Reciprocal Determinism
P =
Person’s awareness and thinking
Albert Bandura
Social-Cognitive Theory
Reciprocal Determinism
E =
Person’s environment
Albert Bandura
Social-Cognitive Theory
Reciprocal Determinism
B =
Person’s behavior
William James
“Set like plaster”
“In most of us, by the age of 30, the character has set like plaster, and will never soften again.”
William James
Promoting Change / Consistency
Environment
Same environments over time
Cumulative experiences in environments
Gets harder and harder to have “new” experiences
William James
Promoting Change / Consistency
These all play a roll in why you either change or stay the same
Environment
Genes
Psychological Makeup
Interactions
Identity structure
William James
Promoting Change / Consistency
Psychological Makeup
Resiliency
William James
Promoting Change / Consistency
Interactions
Goodness-of-fit or Niche Development
Types
Reactive = interpret experience consistently
Evocative = elicit consistent reactions in others
Proactive = select consistent environments
Manipulative = actively change environments to fit
William James
Promoting Change / Consistency
Identity structure
The better you “know” yourself, the more consistent you’ll be
William James
Promoting Change / Consistency
Interactions
Types - Reactive =
Interpret experience consistently
William James
Promoting Change / Consistency
Interactions
Types - Evocative =
Elicit consistent reactions in others
William James
Promoting Change / Consistency
Interactions
Types - Proactive =
Select consistent environments
William James
Promoting Change / Consistency
Interactions
Types - Manipulative =
Actively change environments to fit
Personality-Induced Hyper-reactivity Model
Different personalities react to stress differently, since there are more or less stressors in the environment.
Proposes that certain individuals, due to inherent personality traits, experience exaggerated physiological (like heart/blood pressure) and emotional responses to everyday stressors, viewing them as more threatening, which can increase risks for conditions like cardiovascular disease (CVD) and affect emotional regulation, seen often in Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) where intense emotions stem from heightened self-relevance and stress sensitivity.
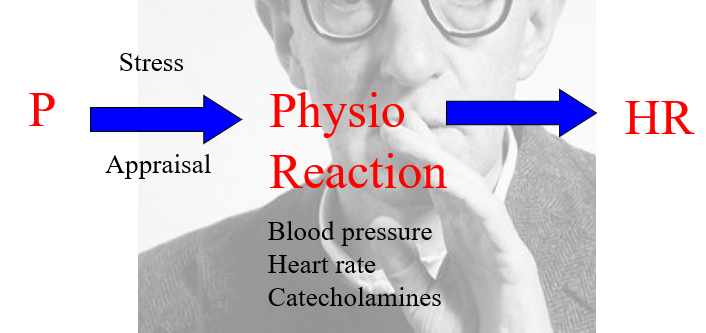
Primary Appraisal
When a person is in a situation with expectation of them, they ask what is there to gain and/or lose.
Do I have the resources needed
the initial, immediate evaluation of a situation to determine if it's irrelevant, benign-positive, or stressful (a harm/loss, threat, or challenge) and how it affects your well-being
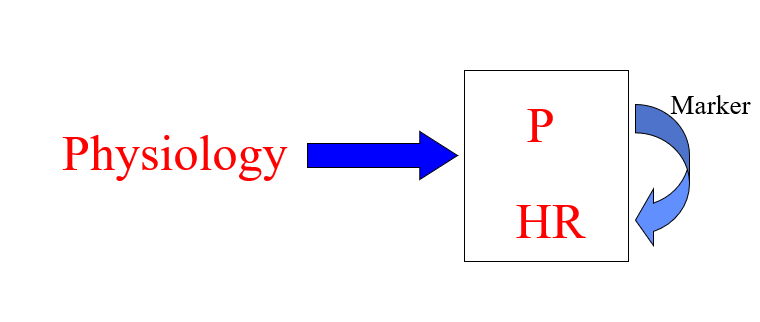
Constitutional Predisposition
Physiology causes the personality and the health risk
Marker- we can predict health risk from personality because we can see personality first
an individual's inherent, often genetic, susceptibility to developing certain diseases or traits, stemming from their fundamental makeup (constitution) rather than just external factors, encompassing inherited genetic variations (like BRCA mutations for cancer) or epigenetic changes, influencing health outcomes and even personality/behavioral tendencies
Risky Behaviors
Putting yourself in dangerous situations due to personality

Type A Behavior
Friedman & Rosenman
Observations in the waiting room
Personality differences
excessive competitive drive
intense striving for achievement
exaggerated sense of time urgency
easily provoked hostility
aggressiveness
Impatience
Termed the Coronary Prone Behavior Pattern
a personality pattern characterized by impatience, time-consciousness, and a drive for achievement, often accompanied by stress and aggressive communication
Personality types are
a continuum and NOT a type
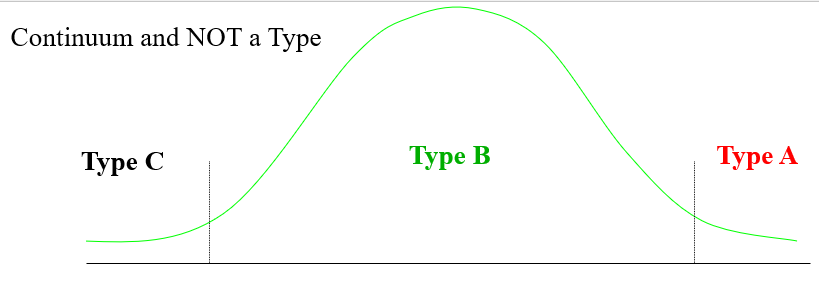
Western Collaborative Study
3524 employed men (1960-61)
Assessed
Predictors
Type A
Host of other behavioral and medical variables
Outcomes
Angina
MI
Originally followed 8 years
Additional follow-up for mortality in 1982-83
Western Collaborative Study
Findings
TABP was positively associated with incidence of CHD at 2 years, 4.5 years, and 8.5 years of follow-up
BUT
Not associated with 22-year risk of CHD death in three of 4 follow-up intervals.
AND
If you survived a heart attack for at least 24 hours you were MORE likely to die if you were Type B
Measurement of Type A Behavior
Structured Interview
25 questions
Deliberately challenging
Scoring
Jenkins Activity Survey
21 self-report items
Correlates .30 with the structured interview
Type C Behavior
The opposite of Type A
Non-emotional, non-assertive, passive, self-sacrificing
for a long period of time
Type C-like statements
I have difficulty showing anger.
I have trouble confronting people when I think they've hurt me.
I tend to have a few close relationships.
I feel as if I can do little to change my life.
When a disappointment occurs, I tend to dwell on it for a long period of time.
The three super traits with personality types
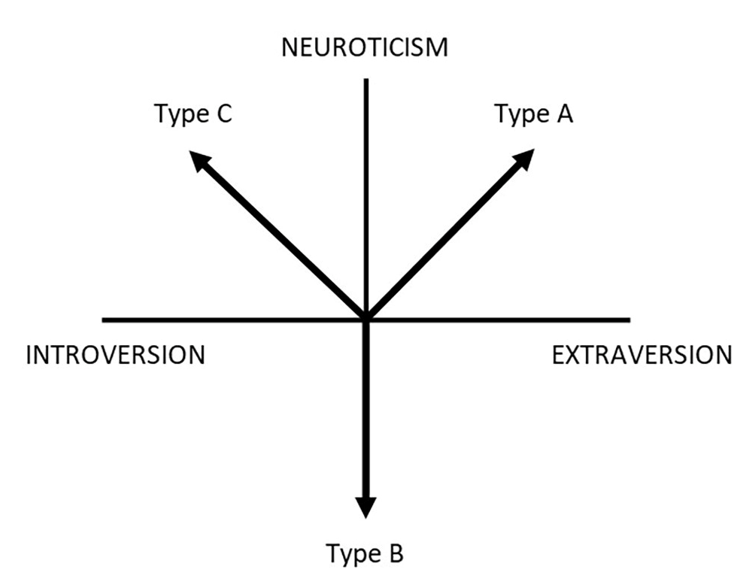
Does Type-C and Cancer Hold Up?
Perhaps Not . . .
Lemogne et al (2013)
16 year follow-up of 13,768 people (1993- 2009)
Suppressed emotion type decreased risk of breast cancer
Reciprocal determinism (Textbook Definition)
The mutual, back-and-forth effects of variables on one another; in social-cognitive theory, a fundamental causal principle in which personal, environmental, and behavioral factors are viewed as causally influencing one another.
Abnormal
Having a characteristic that is very different from the general public
Ex, abnormally short, abnormally smart - statistical
Maladaptive Abnormal
Does it inhibit you from performing your life?
Do you cut yourself
The DSM System
Purpose
Provide a listing of mental disorders and their associated systems, criteria for diagnosis
The DSM System
Use
Provide common language, 3rd party reimbursement
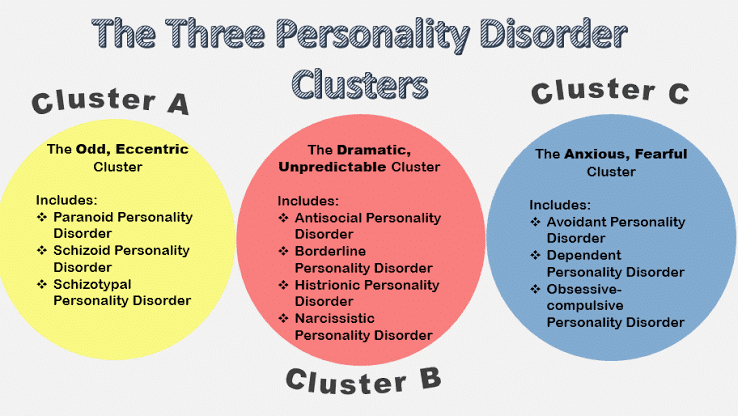
Personality Disorders
A set of behaviors that are:
Inflexible, Maladaptive
Pervasive Across Life Activities
Chronic - Early Origin (by Adolescence)
Functional Impairment or Subjective Distress
Issues With Personality Disorders
What precisely is being talked about? What is meant by certain terms?
Does a categorical approach to disorders make sense?
Reliability issues, internal consistency, inter-rater, test-rater
Too much overlap between the 10 PDs
Heterogeneous symptoms within clusters, two people can receive the same diagnoses and have different symptoms.
What’s Sort of the NEW DSM? Alternative Model
A reduced number or disorders
Antisocial
Avoidant
Borderline
Narcissistic
Schizotypal
Rating on five traits domains
Negative Affectivity
Detachment
Antagonism
Disinhibition
Psychoticism
Further broken down into 25 facets
What’s Sort of the NEW DSM? Alternative Model
To be diagnosed with a PD
Significant impairment is
Self Functioning
Interpersonal functioning
One or more pathological trait domains or facets
Stability in impairments across time and situations
Impairments can’t be accounted for by substance, medical condition, developmental stage, cultural facets
Eaton et al CAPS
I can or can’t view differences in situations/diagnosis
I respond the same to different situations even though I can see differences in the situations
I have many different ways to respond to different situations but I always pick the wrong response
I don’t see the situation correctly
Antisocial Disorder
More likely to be diagnosed in Men, 3.6 present in the U.S
“Psychiatric conditions characterized by chronic behavior that manipulates, exploits, or violates the rights of others. This behavior is often criminal.”
Person with this order:
Breaks the law repeatedly
Lies, steals, and fight often
Disregard the safety of self and others
Demonstrates a leak of guilt
Had a childhood diagnosis (or symptoms of disorder) in misconduct
Aaron Beck’s Cognitions
Force or cunning is the best way to get things done
People will get me if I don’t get them first
It is not important to keep promises or honor debt
Lying and cheating are ok as long as you don’t get caught
I have been unfairly treated and am entitled to get my fair share by whatever means I can
Other people are weak and deserve to be taken
I should do whatever I can get away with
Amygdala
Approximately 18% smaller in psychopaths
Borderline personality Disorder
Emotions
Shifts in mood lasting only a few hours
Anger that is inappropriate, intense or uncontrollable
Borderline personality Disorder
Behavior
Self-destructive acts, such as self-mutilation or suicidal threats
Two potentially self-damaging impulsive behaviors
Borderline personality Disorder
Identity
Marked
Chronic feelings of emptiness or boredom
Borderline personality Disorder
Relationships
Unstable, chaotic intense relationships
Transient
BPD Linehan’s Diathesis-Stress Model

BPD Linehan’s Diathesis-Stress Model
Explained more
They have a significantly smaller hippocampus and somewhat smaller amygdala
