Portage Exam 2 (2.3, 2.4, and 2.5)
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
What is a carbohydrate? how much kcal/gram do they provide?
CHO is comprised of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen molecules.
They provide 4 kcal/gram
When glucose is stored, what is it called? And where is it stored?
Glycogen, which is stored in the muscle or liver
Glycogen converts to glucose when… (?)
Blood sugar levels decline!
Name the 3 Monosaccharides
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
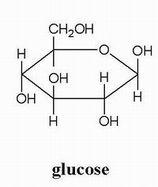
What is glucose often referred to as?
Blood sugar
True or false: By the end of the digestive process, almost all CHO are converted to glucose.
TRUE
True or False: The glucose in our diet is only a SMALL result of the breakdown of starches and other sugars.
FALSE: MUCH of the glucose in our diet is a result of the breakdown of starches and other sugars.
What is Fructose referred to as?
Fruit sugar
True or false: Fructose is typically bound to glucose
FALSE: GALACTOSE is usually bound to glucose
What is galactose?
Primary sugar in milk
(usually bound to glucose)
Name the 3 dissacharides
Sucrose
Lactose
Maltose
Glucose + Fructose = ???
Sucrose
Glucose + Galactose = ???
Lactose
Glucose + glucose = ???
Maltose
What is Sucrose? Where is it found?
Glucose + Fructose
Found in table sugar, honey, and maple syrup
What is lactose?
Glucose + Galactose
Milk Sugar
What is maltose? Where is it found?
Glucose x2!
Found in food, used to convert sugar to alcohol
What is a polysaccharide? Give a few examples.
complex CHO are made up of many glucose units joined together.
Examples include starch, glycogen, and fiber.
Plants store CHO as starch; sources include vegetables, beans, breads, pasta, and rice.
What are 3 types of fiber?
Insoluble (non-fermentable)
Does not dissolve in water
Not broken down by intestinal bacteria
increases stool mass
speeds passage through the large intestine
Soluble (viscous)
Dissolves in water
Broken down by intestinal bacteria
Slows glucose absorption and can lower cholesterol
Provides satiety to a meal
Functional
Fiber that is added to a product
Promotes intestinal health
What are good sources of starch?
Dried beans, peas, and whole grains (often used to make cereal and bread)
What is the CHO rule of thumb in picking food?
Foods that are often high in starch are also good sources of fiber.
Choosing foods that are (1) high in fiber, (2) whole grains, (3) fruits, and (4) vegetables can lead to a healthier life.
Which enzyme breaks down polysaccharides into mono & disaccharides? Which organ releases this?
Pancreatic amylase from the pancreas
Maltase digests…
maltose and the results are two glucose units.
Sucrase digests…
sucrose and yields glucose and fructose.
Lactase digests…
lactose to produce glucose and galactose.
Lactose intolerance — what is it, what are symptoms, and what food can they tolerate?
Either lack the ability to produce lactase or make limited amounts either of which results in an inability to effectively break down lactose.
Symptoms include bloating and abdominal gas formation after ingestion of dairy products.
Most individuals with this condition can tolerate cheese and yogurt and a small amount of milk.
True or false: most monosaccharides are actively absorbed, and fructose uses facilitated absorption
TRUE
Where do monosaccharides get transported to after absorption?
to the liver and either released as glucose into the blood stream, stored as glycogen for later use, or used for fat production.
Which two hormones regulate blood glucose levels? When blood sugar levels rise, which is released? When blood sugar levels decline, which is released?
Insulin released when blood sugars rise
Glucagon when blood sugars decline
Which two main actions occur when insulin is released?
(1) the liver takes up glucose from the blood and stores it as glycogen
(2) muscles, adipose tissue, and various cells absorb the glucose into their cells.
What are some similarities between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes? Patho & Symptoms?
Blood sugar levels are high
Lack of insulin
Symptoms: polydipsia, polyuria, increased hunger, fatigue, weight loss, and ketosis
Why does ketosis occur?
Because fat is being used for energy due to the lack of insulin production
What is the difference between insulin production in T2DM and T1DM?
In T1DM, the pancreas does NOT make insulin
In T2DM, the pancreas makes SOME insulin, but your body either becomes resistant to it or does not produce enough
True or False: T2DM is genetic and is diagnosed early in life
FALSE: T1DM has a genetic link and is diagnosed early in life
How would you treat someone with T1DM?
Insulin therapy, diet changes, and exercise
When is T2DM typically diagnosed? Can a child be diagnosed with it?
Typically in adulthood, but children are starting to be diagnosed due to the obesity epidemic
How would you treat someone with T2DM?
Diet changes, exercise, and oral medications
Why should someone with T2DM add soluble fiber to their diet?
In order to help with blood sugar control, weight control, lower cholesterol, and improve bowel health
Why can carbohydrates have a negative effect on your health?
Because sugar has no calories but no nutritive value
What 5 associations (risks) are linked with Syndrome X (AKA, metabolic syndrome)?
(1) obesity,
(2) poor glucose control
(3) hypertension
(4) increased blood triglycerides
(5) low HDL cholesterol levels.
What dietary changes would you recommend to someone who has Syndrome X, or metabolic syndrome?
Choose fiber rich fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Limit foods and beverages that are high in sugar
How much kcal/gram do proteins provide?
4 kcal/gram
What is the building block of a protein? Which atoms are included in the atomic structure?
Amino Acids
C, H, O, N
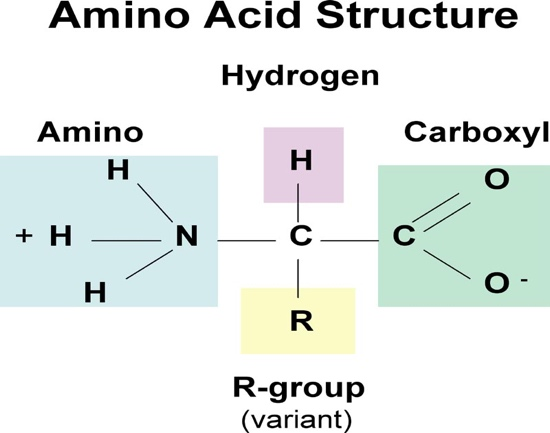
What are the two types of amino acids and why?
Nonessential amino acids: our body can manufacture, derive, or convert them from existing matter
Essential amino acids: we must consume them in our diets as our bodies cannot naturally synthesize them
What kinds of chemical bonds hold chains of amino acids together?
Peptide bonds
Please explain the relationship between structure and function of an amino acid chain
The order and combination (also known as the sequence) of the amino acid chain determines the shape of each protein, and, in turn, the shape determines the function.
What is denaturation and which factors makes this occur to a protein shape?
Denaturation is the process of disrupting and destroying a protein's structure.
Heat, enzymes, acid, or agitation can disrupt the normal protein structure (shape) and its function.
What is the purpose of Pepsin in the digestive system?
Pepsin is an enzyme produced in the stomach that continues denaturing proteins
When is gastrin released in the digestive process? What does it do?
When we think about or actually eat food, the hormone gastrin is released
Once released into the stomach, gastrin activates pepsin and digestion continues further.
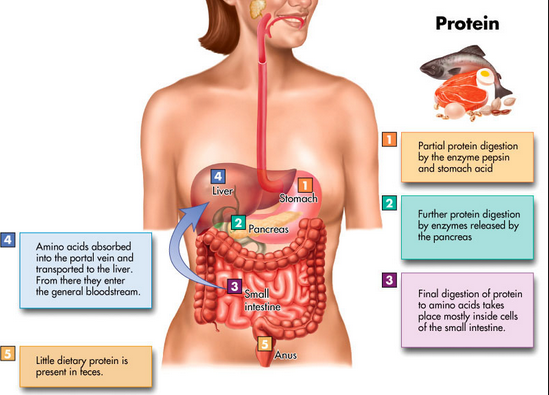
Where is CCK released and what is its function in regards to the partially digested proteins?
Cholecystokinin (CCK) is released in the small intestine, travels to the pancreas, and causes the release of trypsin
(Remember, this inhibits hunger!)
What is trypsin and what is its role?
Trypsin is an enzyme that breaks the chains of amino acids into smaller units in the small intestines.
Because of this, Trypsin is vital to absorption in the small intestines because the proteins would have been too large to be directly absorbed.
Once the amino acid chains are broken down by Trypsin in the small intestines, where do they go?
Absorbed into the PORTAL VEIN, transported to teh LIVER, and then enter the BLOODSTREAM
What does the body do with excess protein?
Convert it into fat for long-term storage
Break down protein absorption into 5 steps from figure 2.9!
Name 6 crucial functions of proteins
1. Body structure: Muscles, connective tissue, mucus, hair, skin and nails are all comprised of protein.
2. Maintaining fluid balance: Blood proteins attract fluid, thus preventing tissue edema (swelling).
3. Contribute to acid base balance: Proteins act as buffers to maintain proper pH.
4. Hormones and enzymes: Needed to regulate body processes and catalyze reactions.
5. Contribute to immune function: Proteins form antibodies that attack bacteria and viruses.
6. Provide energy and satiety: Used for energy during exercise and calorie restriction.
Define protein turnover
Proteins are constantly being broken down and repaired
What is protein equilibrium?
Protein equilibrium describes a state when protein intake is equivalent to the amount of protein lost.
What is the difference between positive protein balance and negative protein balance? When is the anabolic state and when is the catabolic state?
Positive protein balance occurs when we take in more protein than we lose.
Anabolic state is used to indicate that growth is occurring and muscle is being built.
Negative protein balance occurs when protein loss is greater than intake.
Catabolic state is used to indicate that a loss or breakdown of muscle is occurring.
Example of positive protein balance
Examples of someone in this state would be a pregnant mom, a growing child or teenager, or someone recovering from an illness.
Example of a negative protein balance
This may occur during an illness or fasting, due to a trauma such as an accident or burn, or inadequate calorie intake. Muscle wasting and loss of body mass is usually the result.
What are the current recommendations for protein intake?
10-35% of our calorie intake
What are the two categories of protein? Where do each come from?
High-quality (complete) proteins — Animals
Low-quality (incomplete) proteins — Plants (exceptions)
What is a high-quality (complete) protein and where does it come from?
All essential amino acids are provided and can be used efficiently by the body
Comes from animals
What are low-quality (incomplete) proteins and what do they come from?
They lack one or more of the essential amino acids
Comes from plants
Which plant foods are considered complete protein?
Soy, buckwheat, and quinoa
Define complementary protein
The process of consuming two incomplete proteins to make a complete protein
What are some good sources of protein?
Dairy, meat, and bean groups
What are the nutritional values of nuts, seeds, and legumes?
Good source of protein
Low in fat
High in fiber, vitamins, and minerals
Define protein-calorie malnutrition
Occurs when an inadequate intake of protein and calories over a period of time leads to muscle wasting and an increased risk of infection due to a compromised immune system
2 types of protein-calorie malnutrition in children are…
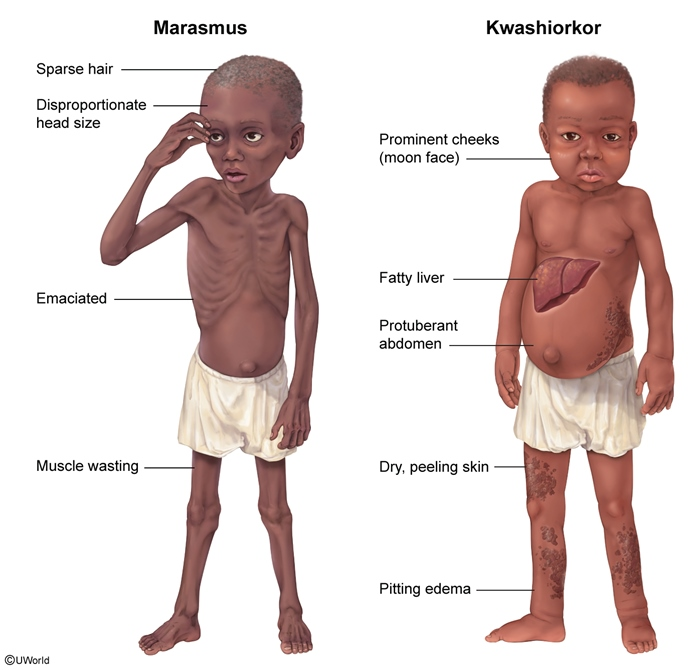
Kwashiorkor is defined as a severe protein deficiency as well as moderate energy or calorie deficiencies.
Marasmus is defined by severe deficiencies in both calories and protein.
True or false: Marasmus develops gradually and means to waste away (Greek)
True
True or false: Kwashiorkor is rapid onset with mild to moderate weight loss
TRUE
True or false: Marasmus involves edema-retaining fluids in the legs and abdomen, whiles Kwashiorkor involves skin and bones appearance
FALSE: Kwashiorkor involves edema-retaining fluids in the legs and abdomen, whiles Marasmus involves skin and bones appearance
Complete the table:
Kwashiorkor | Marasmus |
(1)____-retaining fluids in the legs and abdomen | Means (2)_____ in Greek. The child slowly starves to death |
(3)_____ weight loss | Develops (4)____ |
Growth impairment | (5)___ weight loss |
(6)____ onset that occurs when a child is weaned from breast milk | Wasting of (7)____ and ____, a result of famine or another illness in addition to lack of food |
(8) ____ liver | (9)___ and ____ appearance |
(10) _____, tired, change in ___ and ____ | Severe growth impairment |
(1) Edema
(2) to waste away
(3) Mild to moderate
(4) gradually
(5) Severe
(6) Rapid
(7) muscle; body fat
(8) Fatty liver
(9) Skin; bones
(10) Listlessness; hair; skin
Name the 6 types of vegetarian eating, as well as what they mean.
Semi-vegetarian: Consumption usually includes fish and poultry in their diet, but no red meat.
Lacto-ovo vegetarian: Consumption includes milk and eggs, but no animal flesh.
Lacto vegetarian: Consumption includes dairy products but no eggs or animal flesh.
Pesco vegetarian: Consumption includes fish but no other animal flesh.
Vegan: Consumption of plant foods only.
Fruitarian: Consumption of only fruits, nuts, honey, and vegetable oil.
Note: This plan is not recommended as it leads to nutrient deficiencies.
Your patient is inquiring in general about a vegetarian diet. What would you tell them the benefits are?
A vegetarian diet usually consists of a lowered fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol intake, while the intake of fiber is increased.
Notably, reduced risk for heart disease, obesity, hypertension, and cancer are often associated with this type of diet.
What would you recommend for a vegetarian in order to receive all vital nutrients?
1. Choose whole grains and unrefined foods.
2. Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables. As a rule of thumb, the more colors on your plate, the more nutrients you are likely to receive.
3. Choose low fat dairy products.
4. Eggs are an excellent protein source.
5. As B12 only occurs naturally in animal foods, choose a regular source of vitamin B12 and D either through fortified foods or supplements.
6. Eat a variety of foods.
How many kcal/gram do lipids provide?
9 kcal/gram
What is one characteristic all lipids share?
They do not dissolve easily in water
Name the 3 types of lipids
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Sterols
What are Triglycerides?
Fats and oils composed of fatty acids
Describe the structure of fatty acids
fatty acids are a chain of carbons linked together and surrounded by hydrogen molecules. At one end of the chain is an acid group, and at the other a methyl group. At the most basic level fats can be divided into being either saturated or unsaturated.
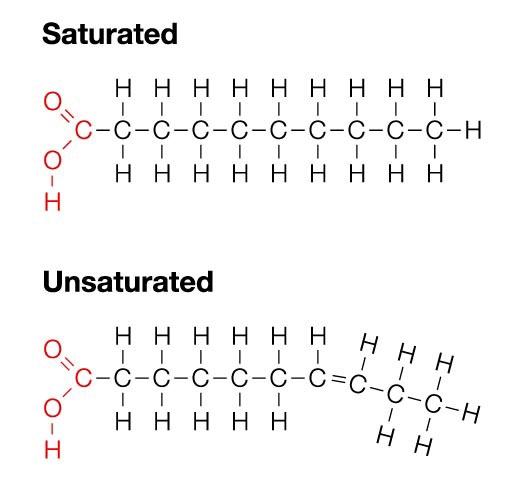
What is the difference between saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acids": all single carbon-carbon bonds, and the carbons are surrounded by the maximum number of hydrogen molecules.
(saturated with hydrogens)
Monounsaturated fatty acids: contain a single (mono) double bond between carbon atoms (C=C).
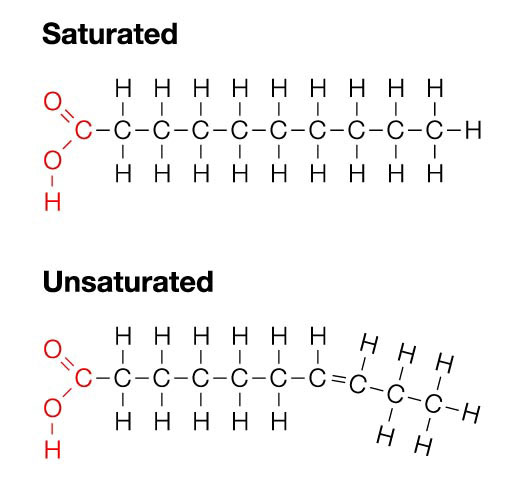
What kind of fatty acid has two or more carbon-carbon double bonds?
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
On polyunsaturated fatty acids, when the number double bonds increase, the number of hydrogen bonds must proportionally _____.
decrease
Define Omega 3
The placement of the first carbon-carbon double bond in the fatty acid.
This double bond is located on the third carbon from the left side, commonly referred to as the methyl (-CH3) end.
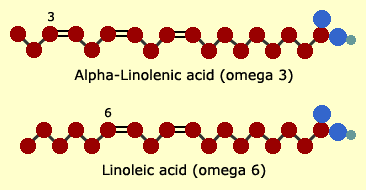
Define Omega 6
When the first double bond is located on the sixth carbon from the methyl end
Define Trans unsaturated fatty acids. What is the other name/abbreviation for this? What foods is this found in?
(trans fat) are found in food products such as stick margarine, shortening, and deep-fried foods.
Trans fats are a type of partially hydrogenated unsaturated fat that is largely a byproduct of the food industry.
What is hydrogenation?
Hydrogen atoms are added to an unsaturated fatty acid, which breaks the existing carbon-carbon double bonds, producing a chain of singly bonded carbons surrounded by hydrogens.
Basically, makes an unsaturated fat into a solid fat
A complete hydrogenation reaction effectively makes a liquid (___) fat into a solid (_____) fat.
unsaturated; saturated
What does an incomplete hydrogenation reaction produce?
partially hydrogenated fats —> trans unsaturated fatty acids
What is a negative health risks of saturated fats?
A significantly higher impact on raising cholesterol levels than saturated fats
Describe the structure of a triglyceride
three fatty acids bond together with a glycerol molecule
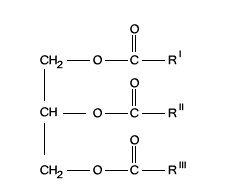
What is the function of a triglyceride?
potential source of energy (including a stored form of energy in adipose tissue), can provide insulation and protection, serve as a carrier of fat soluble vitamins, and they can improve the taste of food.
What are the two major components of a phospholipid?
(1) a phosphate group, also known as the head group
(2) two fatty acid chains, also known as the tail group
Phospholipids function
Phospholipids play an important role in the formation of cell membranes, are used to transport lipoproteins, and also act as emulsifiers
Name some phospholipid foods
Egg yolks, peanuts, liver, soybeans
What makes up the class called sterols?
Hormones (steroids) and cholesterol
How is the structure of sterols different than triglycerides or phospholipids?
There are NO glycerol backbones
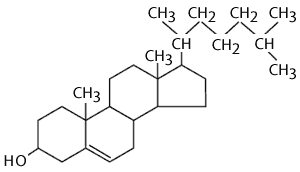
Is cholesterol essential to our diet? Why?
NO
The liver makes all the cholesterol that our body requires