2.2F: Benzene and Resonance
1/10
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are Orbitals?
regions where there is a high probability that electrons can be found
Tell me about benzene
C6H6
One of these structures is benzene, which contains a six-sided carbon ring with 120° bond angles
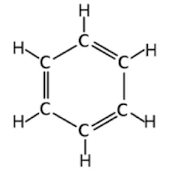
Tell me about the structure of benzene
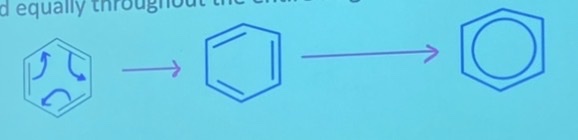
explanation for true structure of benzene is resonance
Electrons in the double bonds of benzene are delocalized and can spread equally throughout the entire ring
This results in carbon-carbon bonds that are equal in length and strength
What are the properties of Benzene?
resonance makes benzene very stable
Usually, substances with such a high carbon to hydrogen ratio are more reactive.
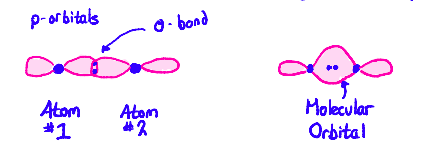
Tell me about Molecular Orbitals in regards to sigma bonds.
when two orbitals overlap head-on, a (sigma) σ-bond is formed. Each orbital donates one electron to the sigma bond. The two orbitals forming the σ-bond fuse into a molecular orbital. Both electrons would go into the molecular orbital
What bonds do σ-bonds form from? (# bond)
single
σ-bonds can form between which shapes?
between any shape of orbital
Tell me about (pi) π-bonds
formed when two p-orbitals overlap side-to-side
Each orbital donates an electron to the bond
form double and triple bonds
There are many π-bonds in benzene
The six electrons in those π-bonds are distributed into 3 molecular orbitals with two electrons in each orbital
What is the definition of Resonance?
when more than one Lewis structure can be drawn for a molecule
Tell me about Resonance Hybrids
best descriptions of actual compound
show delocalized electrons