Multiple Regression
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Homoscedasticity
ANOVA - equal variances within each group
regression - constant across all x values
Dependent Variable
goal of the study; outcomes in a study
Regressors
variables that are being used to predict some outcome measure; can be independent or control
Independent Variable
variables that are of interest to our research question; focus of our study
Control Variable
variables that help explain the dependent variable but aren’t of interest to the research question; a variable expected to influence the outcome measures but is not related to the primary research question
How are control and independent variables treated differently?
mathematical processes of calculating regression eqn (no difference) but interpreting the results of the study is since independents are given the most weight in the presentation of results and discussion while including control variables is not considered as contributing to Type 1 error
Why do we include control variables in the model?
may explain some of the variance making the overall prediction better; control variable may be somewhat correlated w/ both the independent and dependent variable
Goal of Multiple Regression Model
use least squares method to calcuulate bo, b1, and b2
Assumptions
same as simple regression; regressors are not strongly correlated w/ each other (can have some correlation but don’t have strong correlation)
Process
perform single regression between regressors (calc least squares eqn. of regressor A as a fcn of regressor B)
calculate regressor controlled for other regressor (calc deviation of each datum from least squares line) (repeat this and above for regressor B as a fcn of A)
perform simple correlation between controlled regressor and dependent variable
perform simple regression between regressors
calculate regressor controlled for each regressor
perform simple correlation between controlled regressor and dependent variable
solve for bo using the mean value for all 3 variables (finds intercept value)
Problems with Multiple Regression when 2 Regressors are well Correlated
r² ~ 1; when trying to control either way, the values would be basically 0 if not 0
Problems with Highly Correlated Values
controlled for variables will be small (need enough spread to see a line → need more variance); difficult to know which variable is affecting your outcome
How to Treat Multiple Regressors that are well Correlated
only include 1 regressor in model at a time; may choose to select regressor that is expected to be stronger based on theory or has a better case for causality; may try regression w/ each variable separtely and pick regressor w/ better fit
R
R² represents the amount of experimental variance predicted by the model
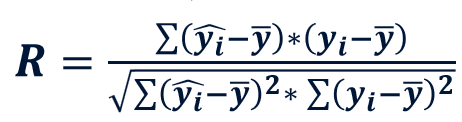
Advantages of Including Control Variables
more certainity in correlation and control more of the variance
Risk of Including Control Variables
low variance because small control values