6th grade Grammar
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Noun
Name people, places,things, or ideas, such as grandfather, peacock, kitchen, etc.

Proper nouns
Name particular people, places, things, or ideas. They are always capitalized.
For example, William Loman, Islam, Zaire, Machu Picchu and Barack Obama.

Collective nouns
Name groups. The singular form is sometimes considered singular and sometimes plural.
For example, committee or choir.

Abstract noun
Ideas, qualities, or characteristic.
For example, fear, spirit, love, and kindness.
Verb
Express action, state, or a relation between two things, and that may be inflected for tense, aspect, voice, mood, and to show agreement with their subject or object.
For example, the woman holds the balloons in her hands on the beach.
Linking Verbs
Connect the subject of a sentence with words or groups of words that identify or describe it. For example, tomorrow will be bright and sunny.
Helping Verbs
Always comes before an action or linking verb. Examples include: is, be, am, are, was, were, been, being, etc
Adjectives
Modify nouns and pronouns. For example, the man has a blue jacket on.

Comparative adjectives
Are used when comparing two nouns. For example, The brown cat is older, than the black cat. My house is bigger than my sister's house. The man is bigger than the woman.
Superlative adjectives
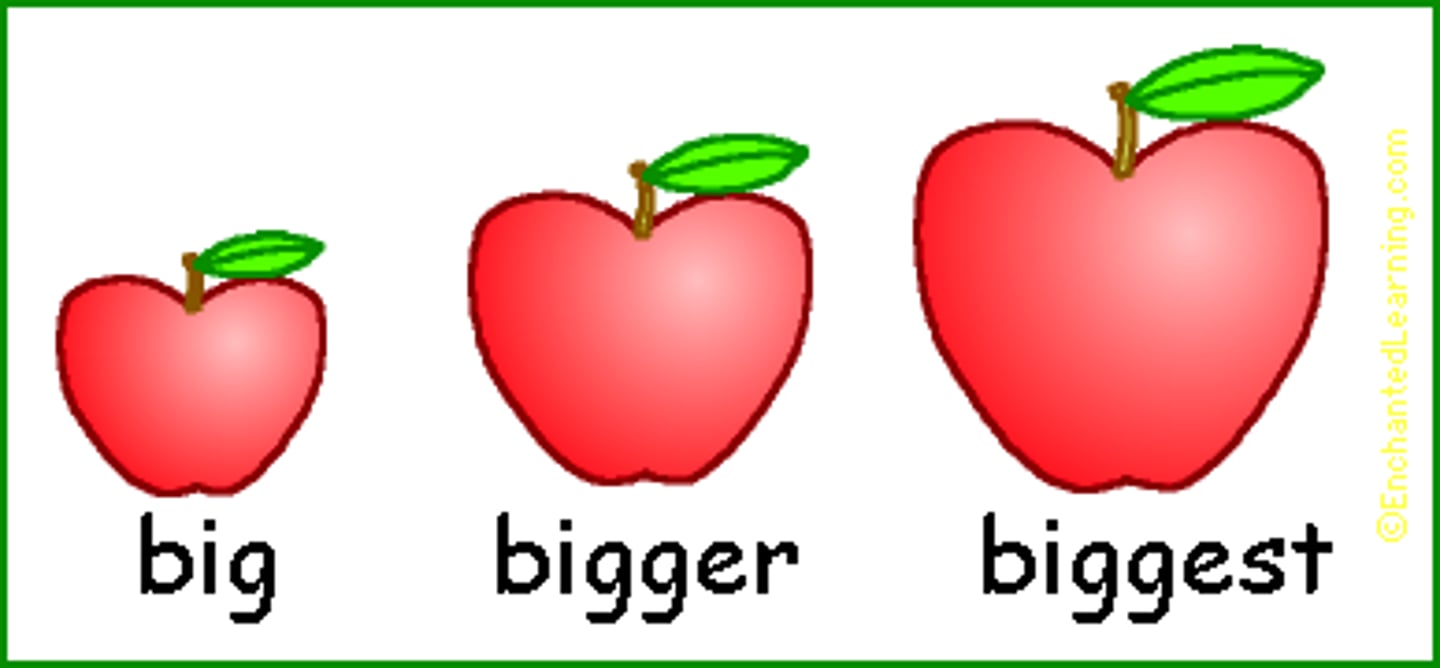
Are used to compare at least 3 things or 3 groups of things. For example, I am in the smallest class in the school. The car at the end of the street is the nicest.
Adverbs
Modify verbs and adjectives.
Examples: run quickly, deeply embarrassed, Quite nicely, rather handsome., and just barely.

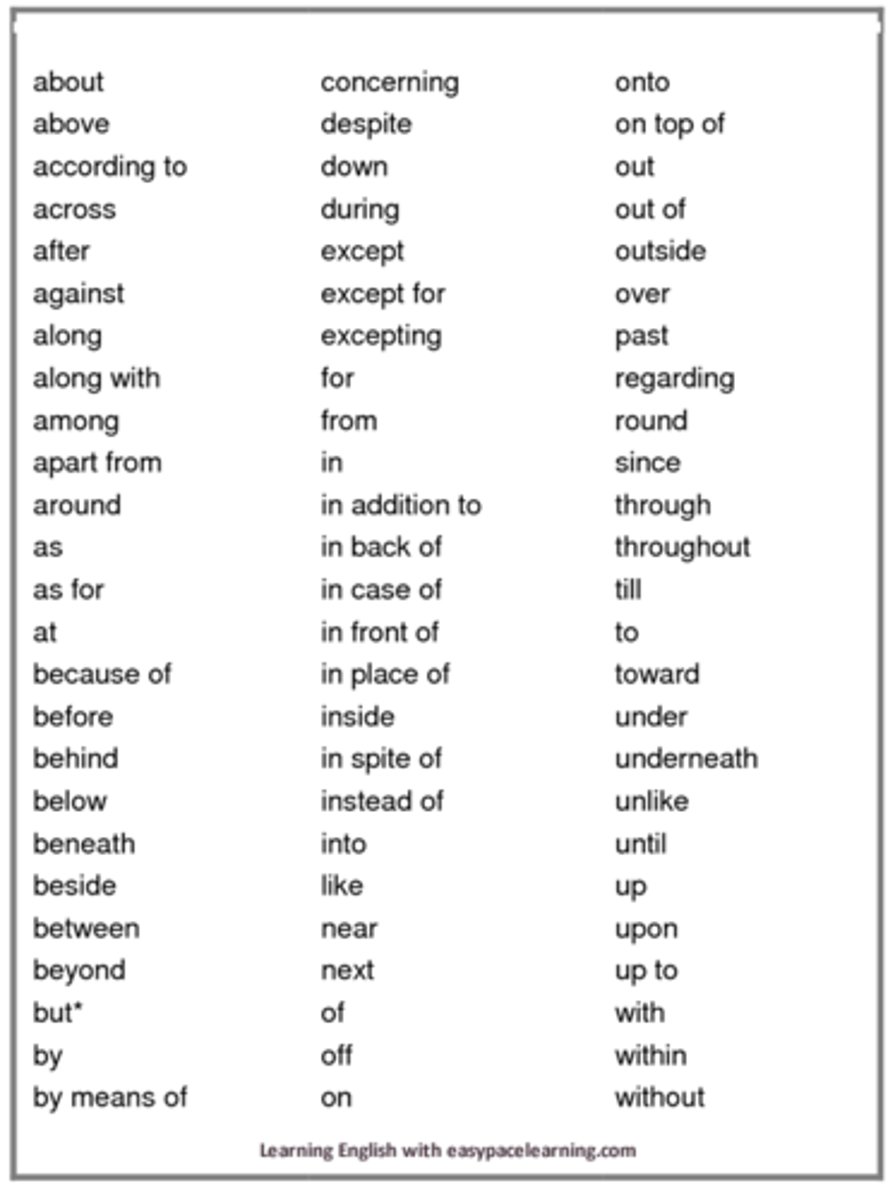
Prepositions
Shows relationship of nouns and pronoun to other words in the sentence. These relationship often indicate space or time.
In the closet, after lunch, outside the perimeter.
Action Verb
Describe physical or mental action, such as jog, smile, think, and worry.
For example, Wolverine fights the bad guys.
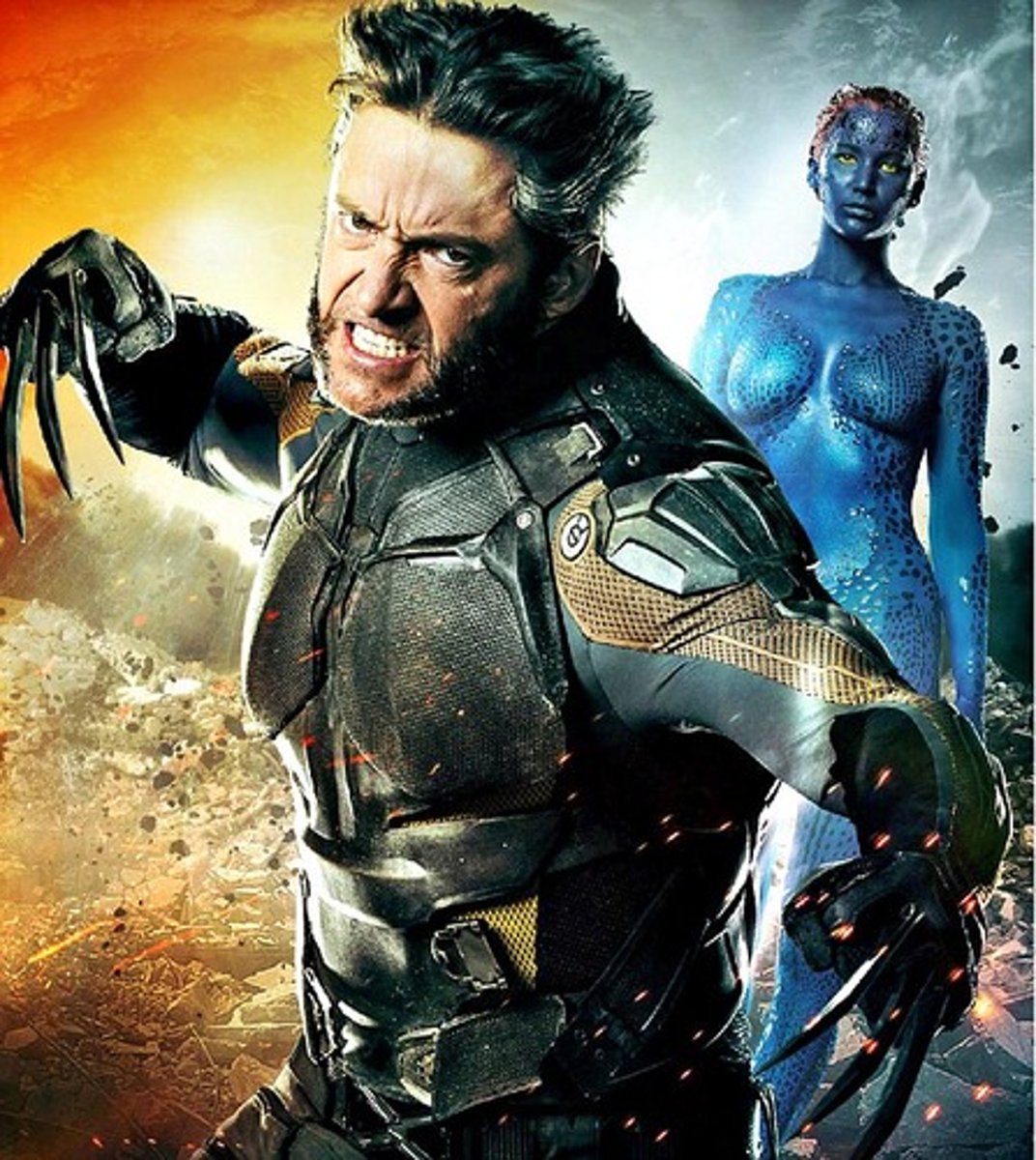

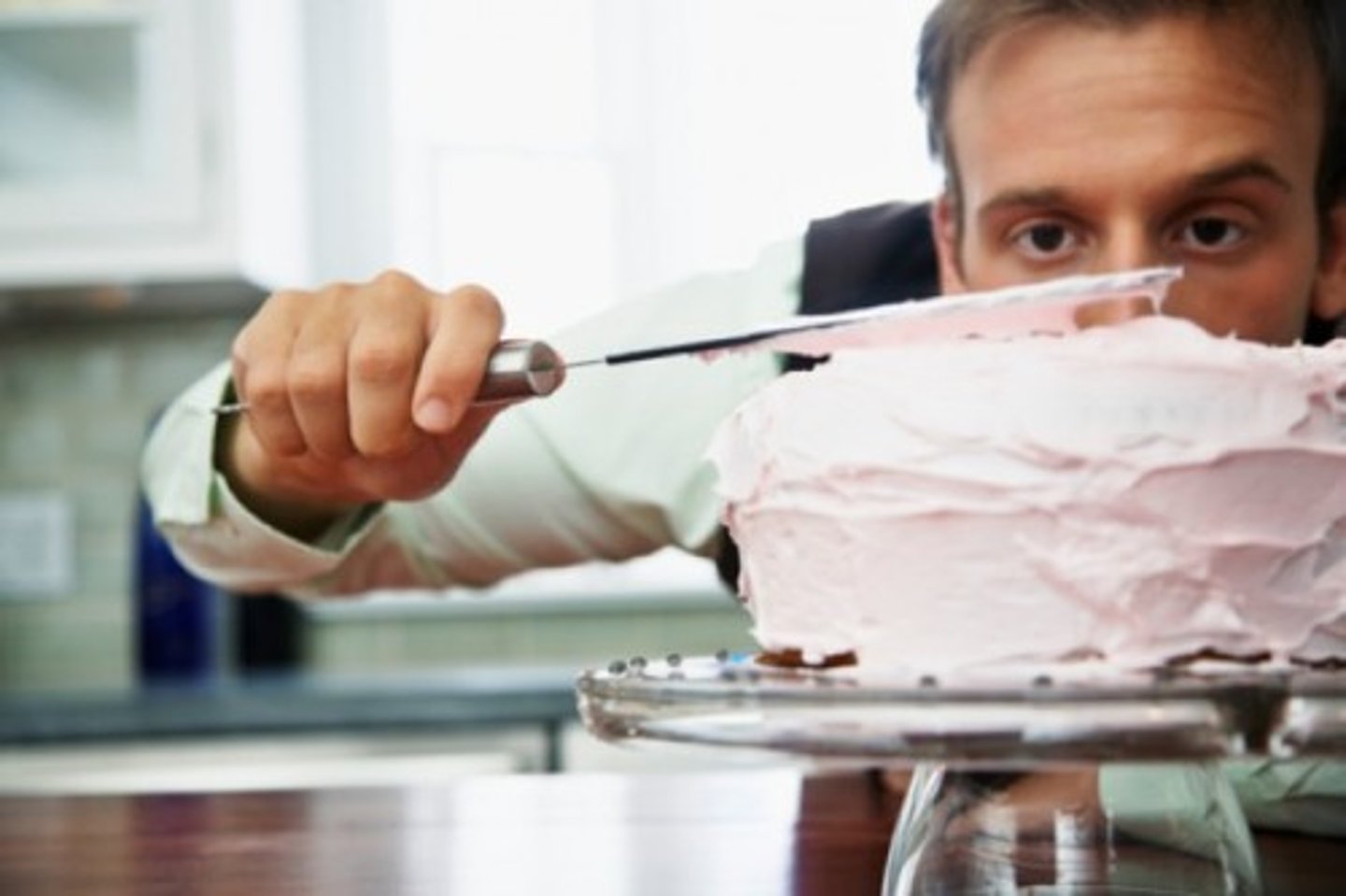
Transitive Verb
Are action verbs followed by words that answer what? or whom?
Jack made his own cake.

Compound prepositions
Consist of more than one word in showing relationships of noun, and pronouns to other words in a sentence. According to the law, on top of the old Smokey, and out of the ordinary are all compound prepositions.
Subordinating Conjuctions
Join two clauses so that one clause depends grammatically upon the other.
Common nouns
Are general names of people,places, things, etc. For example, fire fighter, coffee shop, waiter, boy, and area. They do not start with a capital letter unless they are at the beginning of the sentence.
Colons
this is primarily used to introduce information. It can start lists also
Example:
"There were several things that Susan had to get at the store: bread, cereal, lettuce, and tomatoes."
semicolons
these are used like "super commas". They show a stronger stop than a comma doe, but are not the same as a period. Semicolons are primarily used to separate independent clauses. They can also be used in a lists if one or more element in the list is itself made up of a smaller list.
Example:
"Chris went to the shore; he bought chips and salsa."
Commas
the most commonly used punctuation mark in English. Commas can break the flow of writing to give it a more natural sounding style, and they are the main punctuation mark used to separate ideas. Commas also separate lists, introductory adverbs, introductory prepositional phrases, dates, and addresses.
Pronouns
takes the place of a noun
Nominative pronoun
I, you, he, she, it, they, and we. These are the pronouns that are usually the subject of a sentence - and they do the action in that sentence
Objective Pronoun
is a type of personal pronoun that is normally used as a grammatical object, either as the direct or indirect object of a verb, or as the object of a preposition. These pronouns always take the objective case, whether they are indirect object pronouns or direct object pronouns.
Possessive pronoun
pronoun indicating ownership, for example mine, yours, hers, theirs.
Articles
a, an, the
Conjunctions
joins words, phrases, or clauses
Coordinating Conjunction
FANBOYS, For, and, nor, but, or, yet, so
subordinating conjunction
starts and adverb dependent clause, will be followed by a subject and a verb
Correlating conjunction
either member of a matched pair of words, of which the second is a coordinating conjunction, as either ... or, neither ... nor, both ... and, or not only ... but.
helping verb
always comes before the action verb. is, am, be, being, been, etc. Assists the action verb
linking verb
connects two words together. Connects the subject to a discriptor/modifier
Simple subject
the who or what completing the verb
complete subject
the who or what completing the verb plus all of its modifiers
simple predicate/verb
the verb in the sentence
complete predicate/verb
the verb in the sentence plus all of its modifiers such as adverbs, adverb prepositional phrases, the direct object...
Direct object
comes after a transitive verb, answers the who or what of the verb
transitive verb
to find, say subject + verb who or what?
intransitive verb
will not answer who or what of the verb, answers everything else such as where, when, how, or there is nothing after the verb at all
object of the preposition
answers the who or what of the preposition. To find, say preposition who or what. Ex: To who or what? To the store.
Propositional phrase
the preposition plus its object and any modifiers.
Independent clause
has a subject and a verb and can stand alone
dependent clause
has a subject and a verb, but relies on the rest of the sentence to make sense. Cannot stand alone.
simple sentence
one independent clause
compound sentence
two or more independent clauses joined by a conjunction
complex sentence
one independent clause plus one or more dependent clauses
declarative sentence
makes a statement, ends in a period
interrogative sentence
asks a questions
imperative sentence
gives a command
exclamatory sentence
espresses strong feelings and ends with an exclamation point.