Chapter 18: Active Galaxies, Quasars, and Black Holes
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Active galaxies
Bright and unusual objects in the universe.
Quasars
Distant, luminous objects that are a type of active galaxy.
BL Lac objects
Extremely powerful active galaxies.
Supermassive black holes
Central engines for radio galaxies, quasars, Seyfert galaxies, and BL Lac objects.
Fast radio bursts
Brief, intense bursts of radio emissions from distant galaxies.
Cygnus A (3C 405)
One of the brightest radio sources in the sky, located 750 million light-years from Earth.
Hubble law
A law that relates the redshift of an object to its distance from Earth.
Redshift
The phenomenon where light from an object is shifted to longer wavelengths, indicating its distance.
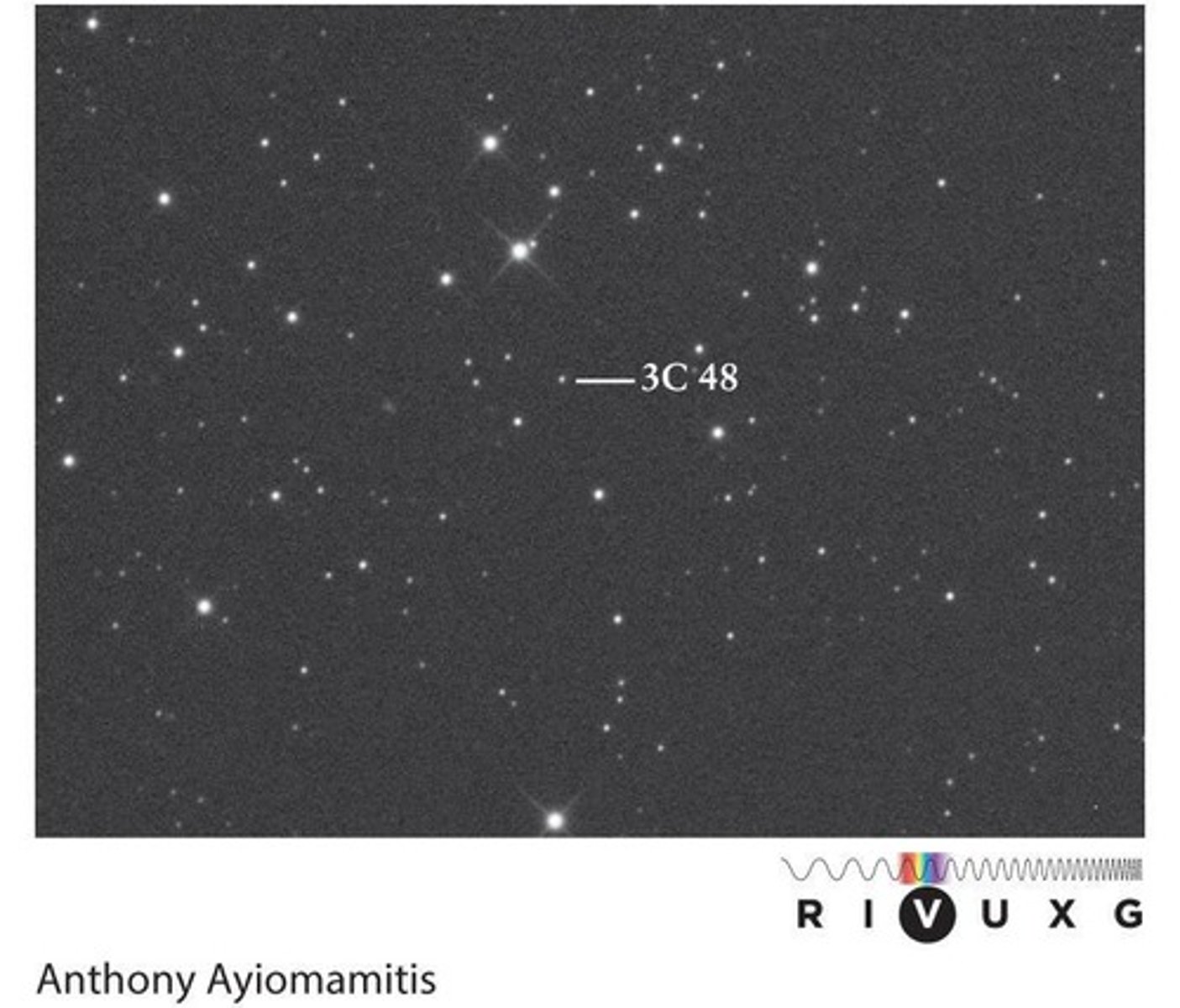
Quasar 3C 48
A quasar that was initially mistaken for a nearby star; it is roughly 4 billion light-years away.
Quasar 3C 273
A quasar with a redshift indicating it is nearly 2 billion light-years from Earth.

Emission lines
Bright lines in a spectrum that indicate the presence of specific elements, such as hydrogen.
Lyman-alpha forest
A series of absorption lines in the spectrum of a quasar caused by intergalactic gas clouds.
Brightness of 3C 279
Variations in brightness of the quasar 3C 279, with notable outbursts in 1937 and 1943.
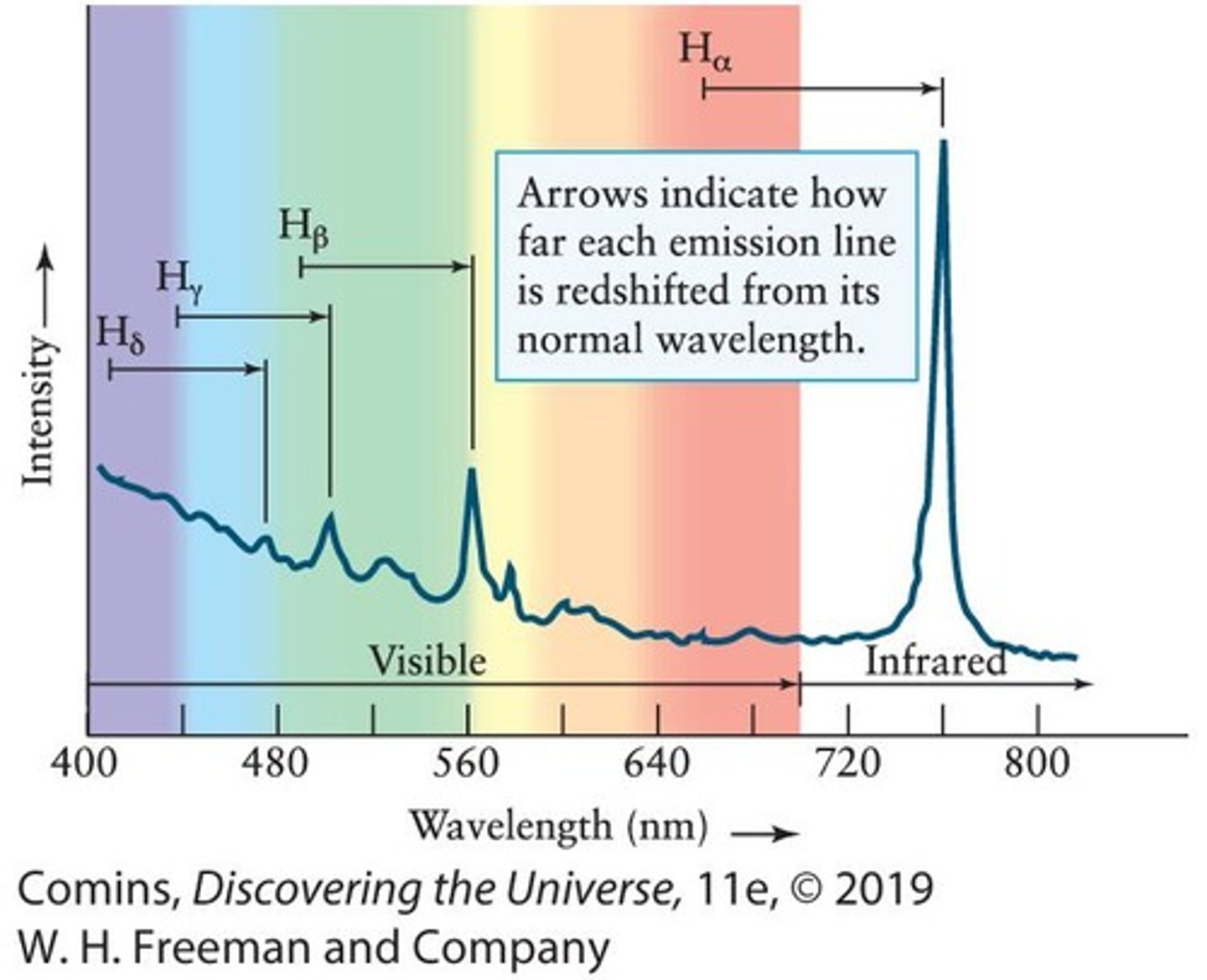
Spectra of 3C 273
Dominated by four bright emission lines generated by hydrogen, redshifted nearly 16%.
PKS 2000-330
A quasar with highly redshifted light, showing spectral emission lines at visible wavelengths.
Absorption lines
Dark lines in a spectrum indicating the absorption of specific wavelengths by elements.
Hydrogen absorption
Occurs when hydrogen in intergalactic clouds absorbs photons from a quasar.
Quasar formation
The process by which quasars are formed, with greater redshift indicating greater distance and age.
Variations in brightness
Changes in the luminosity of a quasar over time.
Chandra X-ray Observatory
An observatory that captures X-ray images of astronomical objects.
Radio lobes
Regions of radio emission extending from the central galaxy, as seen in Cygnus A.
Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs)
Powerhouses located at the centers of active galaxies.
Seyfert Galaxy NGC 1566
An Sc galaxy located some 60 Mly (18.4 Mpc) from Earth in the southern constellation Dorado.
Peculiar Galaxy NGC 5128 (Centaurus A)
An extraordinary radio galaxy located in the constellation Centaurus, 11 million light-years from Earth.
X-ray Jet
A jet protruding from the nucleus of NGC 5128 along a direction perpendicular to the galaxy's dust lane.
Head-Tail Source NGC 1265
An active elliptical galaxy moving at a high speed through the intergalactic medium.
Binary Head-Tail Source
A combined radio and X-ray image of 3C 75 showing head-tail sources from supermassive black holes in merging galaxies.
Luminosity of the Sun
4×10^26 watts.
Luminosity of the Milky Way Galaxy
10^37 watts.
Luminosity of Seyfert galaxies
10^36−10^38 watts.
Luminosity of Radio galaxies
10^36−10^38 watts.
Luminosity of Quasars
10^38−10^42 watts.
BL Lacertae
An object with a redshift indicating it is about 900 Mly (280 Mpc) from Earth.
Elliptical Galaxy M32
A small galaxy that is a satellite of M31.
Giant Elliptical Galaxy M87
Located near the center of the Virgo cluster, about 50 million light-years from Earth, M87 has a bright nucleus and gas jets resulting from a 3-billion-solar-mass black hole.
Sombrero Galaxy (M104)
A spiral galaxy in Virgo that is nearly edge-on to Earth, containing a billion-solar-mass black hole at its center.
Supermassive Black Holes as Engines for Galactic Activity
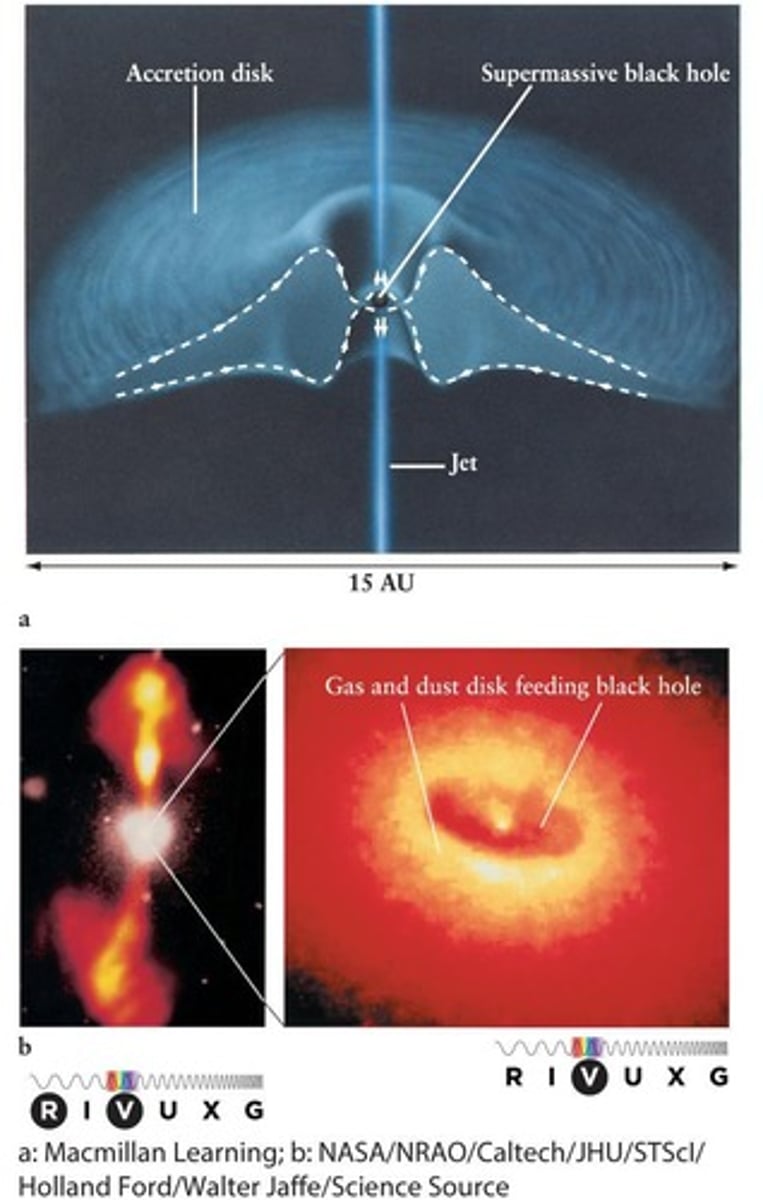
In the accretion disk around a supermassive black hole, gas heats and expands, some of it is expelled in two jets.
NGC 4261
A giant elliptical galaxy located in the Virgo cluster, about 100 million light-years from Earth, with a disk of gas and dust about 800 light-years in diameter orbiting a supermassive black hole.
Focusing Jets by Pressure
If a high-speed jet of gas or liquid encounters little pressure, it will spread out; if it encounters high pressure, it will maintain its shape as a column.
Focusing Jets by Magnetic Fields
The hot, ionized accretion disk around a central black hole creates a twisted magnetic field that directs gas into two jets.
Orientation of the Central Engine and Its Jets
BL Lacertae objects, quasars, and double-radio sources are the same type of object viewed from different directions, with jets aimed at Earth producing different observations.
active galaxy
An extremely luminous galaxy that has one or more unusual features such as a bright nucleus, strong emission lines, rapid variations in luminosity, and jets of radiation.
blazar
A type of active galaxy that is characterized by rapid variability in brightness and strong emissions across the electromagnetic spectrum.
BL Lacertae (BL Lac) object
An active galaxy with a bright nucleus that shows rapid variations in luminosity.
double-radio source
Active galactic nuclei located between two characteristic radio lobes.
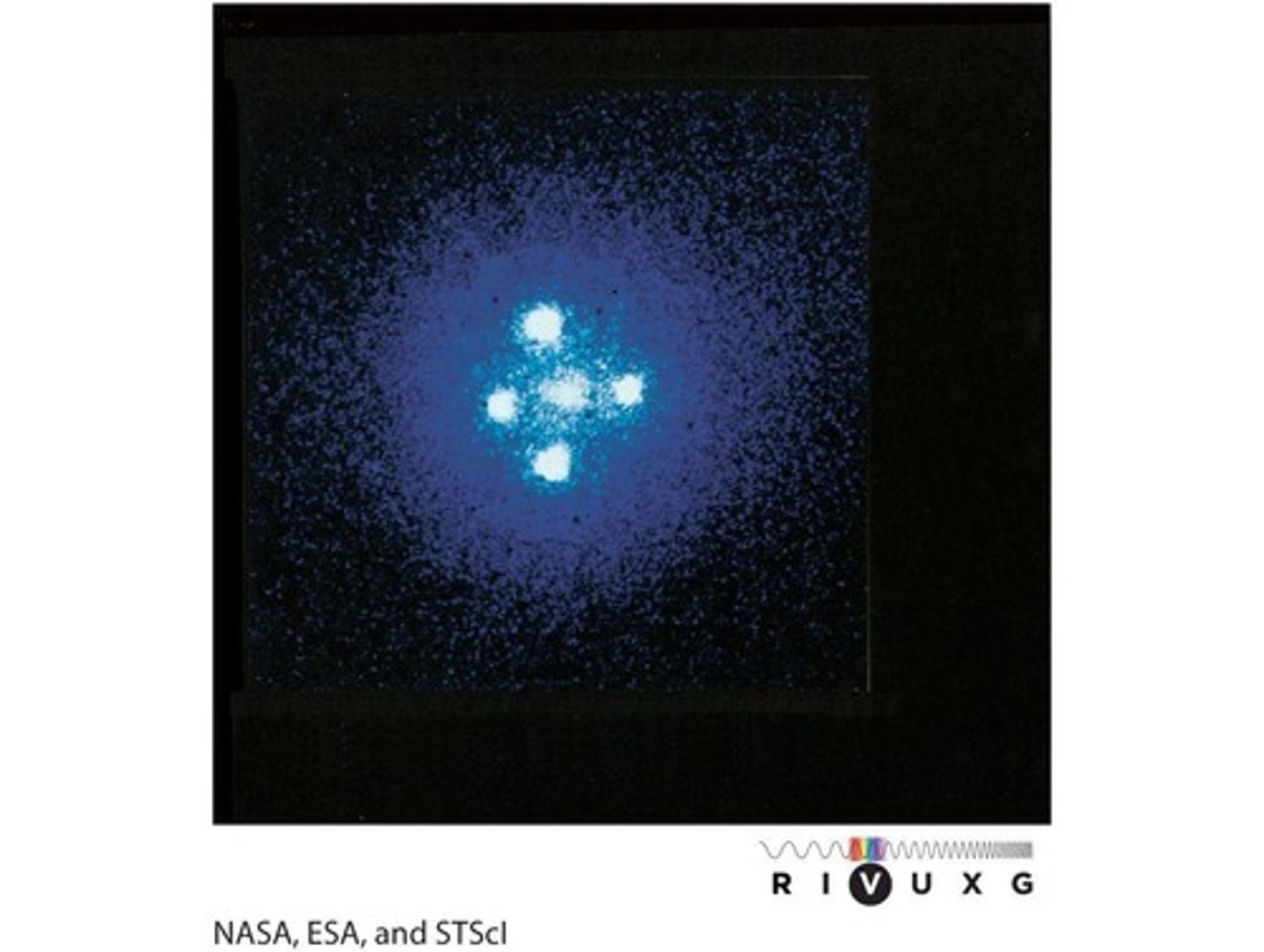
Einstein cross
A pattern formed when a quasar is seen as four separate images surrounding a galaxy due to gravitational lensing.
Einstein ring
A ring-like structure formed by the gravitational lensing of light from a distant object.
fast radio burst
A transient radio pulse that lasts for only milliseconds and is believed to originate from outside the Milky Way Galaxy.
head-tail source
A type of radio source that shows evidence of jets of high-speed particles emerging from an active galaxy.
peculiar galaxy (pec)
A galaxy that exhibits unusual characteristics or morphology.
quasar (quasi-stellar radio source)
An object that resembles a star but has a significant redshift, indicating it is billions of light-years away.
quasi-stellar object (QSO)
Another term for a quasar, emphasizing its star-like appearance.
radio galaxies
Active galaxies that emit strong radio waves and have a bright nucleus with jets.
radio lobe
The extended regions of radio emission associated with some active galaxies.
Seyfert galaxy
An active spiral galaxy characterized by a bright, starlike nucleus and strong emission lines in its spectrum.
supermassive black hole
A massive black hole located at the center of many galaxies, believed to be the source of energy for quasars and other active galaxies.
gravitational lensing
The bending of light from a distant object due to the gravitational field of an intervening mass, resulting in multiple images.
luminosity
The intrinsic brightness of an astronomical object, often measured in terms of how it compares to the Sun.