bio honors ch. 6+7 (cellular respiration and photosynthesis)
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
photosynthesis equation
6CO(2) + 6H2O = C(6)H(12)O(6) + 6O(2)
cellular respiration equation
C(6)H(12)O(6) + 6O(2) = 6CO(2) + 6H2O
reactants of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide and water
products of photosynthesis
glucose and oxygen
reactants of cellular respiration
glucose and oxygen
products of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide and water
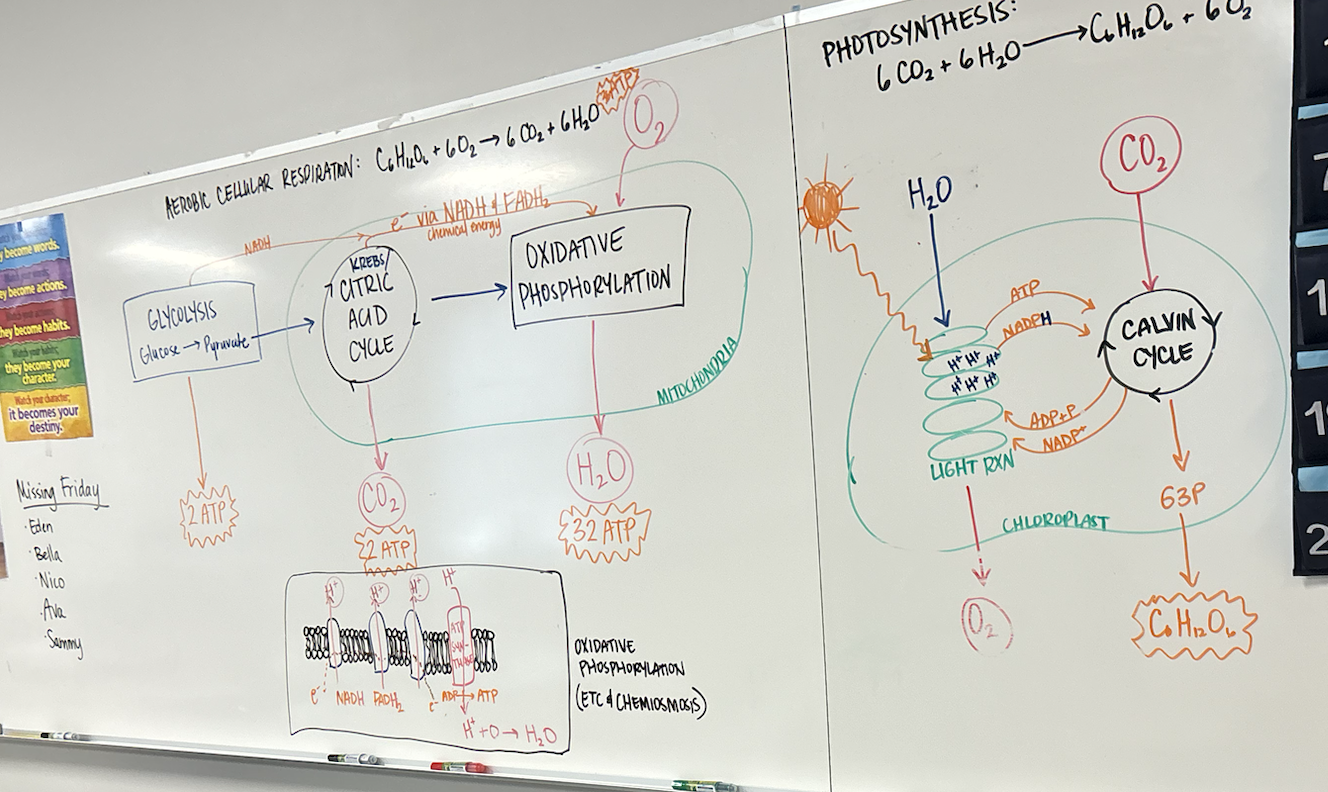
two main events of photosynthesis
light reactions and calvin cycle
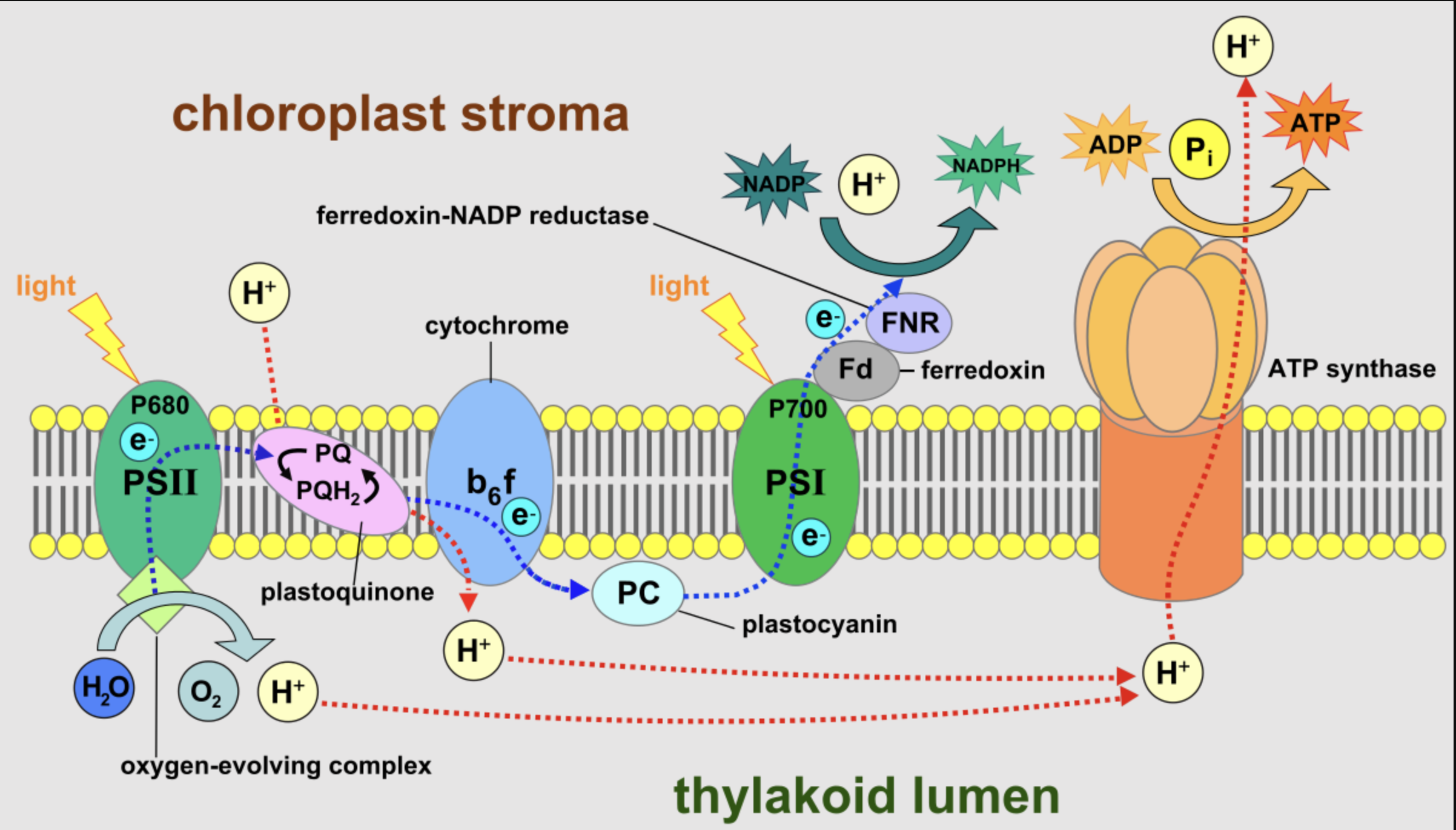
reactants of light dependent reactions
water, ADP, NADP+
products of light dependent reactions
oxygen, ATP, NADPH
byproduct of light dependent reactions
oxygen (released by water splitting)
molecule reduced during light dependent reactions
NADP+ (becomes NADPH)
three stages of the calvin cycle (in order)
carbon fixation, reduction, regeneration
reactants of the calvin cycle
CO2, ATP, NADPH
products of the calvin cycle
G3P, ADP, NADP+
molecule oxidized during the calvin cycle
NADPH (becomes NADP+)
why does the calvin cycle normally slow down during dark
it is dependent on the light reactions
sugar made from carbon dioxide in the calvin cycle
G3P
pigment in plants that processes light energy
chlorophyll
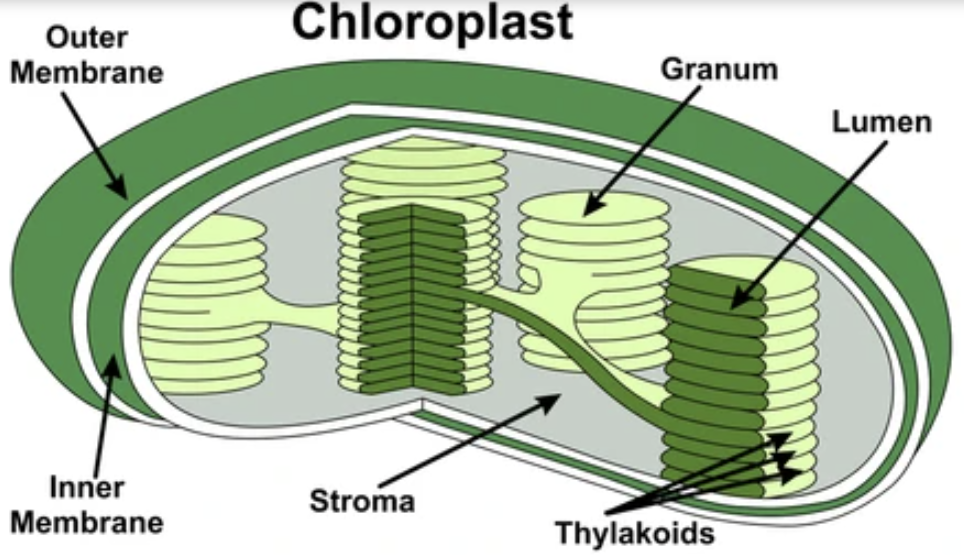
where light dependent reactions take place
the thylakoid membrane (or grana) of chloroplasts
where the calvin cycle takes place
the stroma (thick fluid inside the chloroplasts)
the role of RuBP/rubisco
helps to form 3-PGA in carbon fixation
carbon fixation
when carbon from CO2 is fixed to inorganic compounds
reduction
where 3-PGA molecules are converted into G3P by gaining electrons from NADPH
regeneration
the final stage where molecules of G3P are rearranged and recycled to reform RuBP allowing the cycle to continue
redox reactions
where electrons are transferred between reactants, with one substance losing electrons (oxidizing) while another gains electrons (reducing) simultaneously
three main events in cellular respiration
glycolysis, krebs/citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation
glycolysis
first step of cellular respiration where glucose molecules (6-carbons each) are split to form two molecules of pyruvate (3-carbons each) in the cytoplasm of cells; anaerobic process
krebs cycle
second step of cellular respiration where acetyl-CoA combines with oxaloacetate to generate citric acid, which then undergoes further oxidation in the mitochondrial matrix of cells; aerobic process
molecules produced during krebs cycle
CO2 (waste product), ATP, NADH, FADH2
gross and net ATPS produced in glycolysis
gross- 4, net- 2
amount of molecules produced in the krebs cycle
one turn: 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP
full cycle: 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP
oxidative phosphorylation
the last step of cellular respiration where electrons are passed along the electron transport chain, causing H+ to be pumped across the mitochondrial membrane, creating a gradient, driving the synthesis of ATP through the ATP synthase
chemiosmosis
the process where hydrogen ions (protons) move across the mitochondrial membrane down their concentration gradient
alcholic fermentation
a type of anaerobic respiration where (usually) yeast converts sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide, producing a small amount of ATP
lactic acid fermentation
a type of anaerobic respiration where glucose is converted into lactic acid to produce a small amount of ATP in the absence of oxygen, primarily occurring in muscle cells during intense exercise and certain bacteria
reactants/products for each step of cellular respiration
Glycolysis (cytoplasm):
Reactants: Glucose, ATP, NAD+
Products: 2 Pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
Krebs Cycle (mitochondrial matrix):
Reactants: Acetyl CoA, NAD+, FAD, ADP
Products: Carbon dioxide, ATP, NADH, FADH2
Electron Transport Chain (inner mitochondrial membrane):
Reactants: NADH, FADH2, Oxygen
Products: Water, ATP
energy carrier molecules in cellular respiration
NADH and FADH2
the final electron acceptor and why it is important
oxygen, which allows for the continuous flow of electrons through the chain, enabling the generation of a proton gradient (without oxygen the chain would become clogged and ATP production would cease, making aerobic respiration impossible)
why the H+ gradient is important
it stores potential energy that is used by ATP synthase to generate ATP
phosphorylation
the process of adding a phosphate group to a molecule, in the context of cellular energy, it refers to the creation of ATP by adding a phosphate group to ADP
remember this
also this one
and this too
energy is released from ATP when
the bond is broken between two phosphate groups
how is oxygen released
as a byproduct of splitting water molecules
which stage produces the most ATP
chemiosmosis/etc