Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) is a congenital heart condition involving abnormalities in the structure of the heart's chambers and valves. Here's an expanded explanation of the condition and its classifications: ### Definition - **Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD):** This condition involves a defect in the septal structures that separate the heart's chambers and an anomaly in the valve that regulates blood flow between these chambers. Typically, a heart has separate left and right atrioventricular (AV) valves, but in AVSD, there is a single common AV valve that opens into both the left and right ventricles. ### Types of AVSD 1. **Complete AVSD:** - **Defects:** There are holes in both the atrial and the ventricular septa, directly above and below the common AV valve. - **Valve involvement:** The common AV valve often bridges the gap between the left and right sides of the heart, regulating blood flow to both ventricles simultaneously. 2. **Partial AVSD:** - **Defect:** This type typically involves a defect in the atrial septum (often the primum atrial septum) and may include a cleft in the mitral valve, affecting its function but not typically involving the ventricular septum. - **Valve involvement:** The mitral valve (left AV valve) is often affected with a cleft or division, impairing its ability to close properly and possibly leading to mitral regurgitation. ### Balance Classification 1. **Balanced AVSD:** - In this form, the blood flow is relatively equally divided between the left and right ventricles during the heart’s filling phase (diastole). This balance means that despite the structural defects, the heart functions in a more compensated manner. 2. **Unbalanced AVSD:** - This form is characterized by a significant disproportion in the blood flow to the ventricles, usually due to additional complications like obstruction in one of the ventricular outflow tracts. This disproportion can lead to more severe heart dysfunction, often requiring different surgical approaches or earlier intervention. ### Clinical Implications and Management - **Symptoms** can include difficulty breathing, frequent respiratory infections, and failure to thrive in infants. Older children might experience shortness of breath during exertion, fatigue, and irregular heart rhythms. - **Diagnosis** is typically achieved through imaging techniques such as echocardiography, which provides a detailed view of the structural anomalies. - **Treatment** often involves surgery to repair the septal defects and the malfunctioning valve(s). The timing and approach of surgery depend on the severity of the defect and the balance of blood flow. - **Prognosis** varies depending on the type and severity of the defect, as well as the timing and success of surgical intervention. Close monitoring by a cardiologist specializing in congenital heart disease is crucial. Understanding the specifics of AVSD, including its classification into complete or partial and balanced or unbalanced types, helps in tailoring the management approach to optimize outcomes for affected individuals. # Ultrasound Features of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD) ## Overview Ultrasound imaging is pivotal in diagnosing Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD), allowing visualization of structural abnormalities in the heart chambers and valves. It assists in differentiating between complete and partial forms of the condition, as well as assessing the balance between the ventricles. ## Key Ultrasound Views and Findings ### Four-Chamber View - **Valve Insertion**: The AV valves typically show a linear insertion with no offset, indicating a common valve scenario. - **Diastolic Phase Observations**: In a complete AVSD, this view reveals defects centrally located at the septum, showing absence of the crux. ### Apical Four-Chamber View in Systole - **Valve Assessment**: Best view to assess the AV valve offset, crucial for identifying common AV valve formations. ## Specific Features by AVSD Type ### Complete AVSD - **Central Defects**: Visible defects in both the atrial and ventricular septum during diastole. - **Color Doppler Findings**: Shows a unified blood flow channel across the remnants of the ventricular septum and potential regurgitation jets from the common AV valve. ### Partial AVSD - **Atrial Septum Defect**: A defect is typically noted in the septum primum without accompanying ventricular septal defect. - **Intact Ventricular Septum**: The integrity of the ventricular septum remains, distinguishing this from the complete AVSD. ## Balanced vs. Unbalanced AVSD ### Balanced AVSD - **Ventricular Equality**: Both ventricles appear equal in size, indicating balanced blood flow and pressure. ### Unbalanced AVSD - **Ventricular Disproportion**: Marked by significant size differences between the ventricles, typically due to outflow tract obstruction or stenosis. - **Outflow Tract Observation**: Usually shows one of the tracts being of smaller caliber, supporting findings of potential obstructions. ## Conclusion Ultrasound imaging, especially through detailed views like the four-chamber and apical views, plays a critical role in diagnosing and assessing the severity of AVSD. The distinct features observed help in planning appropriate clinical management and surgical interventions.
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the full form of AVSD?
Atrioventricular septal defect
What are other common names for AVSD?
Av canal defect
How is AVSD classified based on structural defects?
Complete or partial
What defines a complete AVSD?
Answer: Defects in both atrial and ventricular septa
What is characteristic of a partial AVSD?
Answer: Atrial defect and mitral cleft
What does balanced AVSD mean?
Answer: Equal ventricular blood drainage
What does unbalanced AVSD indicate?
Answer: Unequal ventricular drainage
What common complication is associated with partial AVSD?
Answer: Mitral regurgitation
What ultrasound view is optimal for examining AV valve arrangement in AVSD?
The four-chamber view is optimal for examining AV valve arrangement in AVSD.
What indicates a common AV valve on an ultrasound in AVSD?
A linear insertion of AV valves with no offset indicates a common AV valve.
The loss of AV valve offset is best observed in systole.
3.
2. What AVL ratio is considered normal, and what AVL ratio suggests AVSD?
-
Normal: 0.5; AVSD: > 0.6.
1. What is the purpose of the atrioventricular length ratio (AVL ratio) in detecting atrioventricular septal defects (AVSD)?
-
To determine if the atria are larger in fetal hearts with AVSD.
Why is situs evaluation important in cases of AVSD?
-
Because many cases are associated with heterotaxy.
5. What chromosomal abnormality is AVSD often associated with?
-
Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), in 58% of cases.
4. What are some associated cardiac defects with AVSD?
-
Tetralogy of Fallot, double outlet ventricle, right aortic arch, and other conotruncal anomalies.
DD
Isolated inlet ventricular septal defect (VSD)
● Dilated coronary sinus, in cases of persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC)
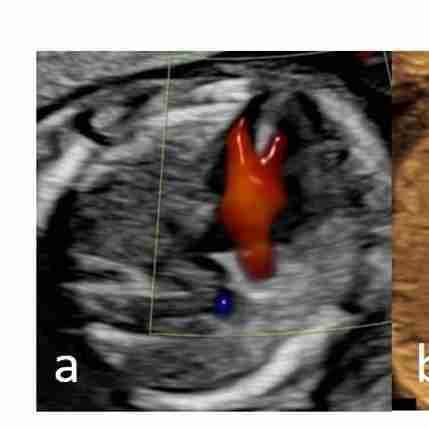
Color Doppler showing a single channel of blood during diastole that divides over the remnant of the ventricular septum in a case of AVSD
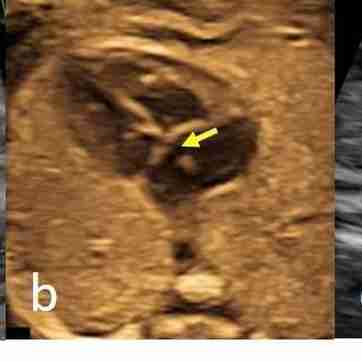
Partial AVSD; linear insertion of AV valves; a small defect in the septum primum of the atrium (arrow
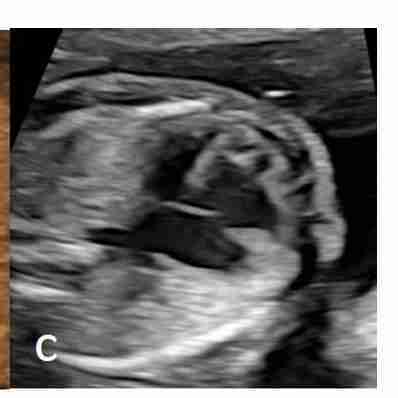
Unbalanced AVSD; linear insertion of the AV valves; and ventricular asymmetry
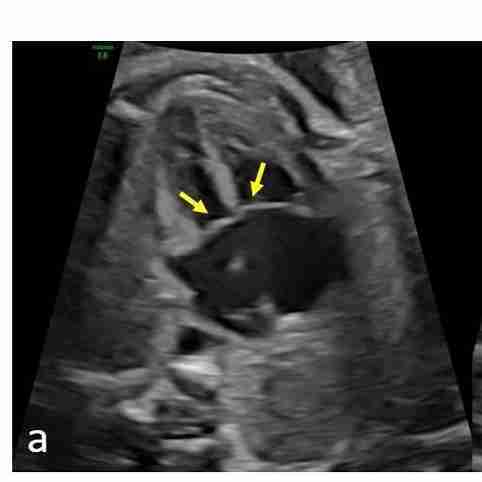
Complete balanced AVSD (a) Equal sized ventricles. Linear insertion of AV valves (arrows)
In diastole, a hole in the center of the heart is seen (arrow) due to absent crux