Monoclonal Antibodies
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs)
Antibodies that are clones from one parent cell, specific to one type of antigen.
ability to bind to only one protein antigen → target chemicals and cells in the body
Production of monoclonal antibodies
Specific antigen injected into an animal (e.g. mouse)
Mice lymphocytes producing complementary antibodies extracted
Lymphocytes fused with myeloma cells (tumour cells → divide rapidly) to form hybridoma cells
Hybridoma cells divide to produce clones of itself → produce same antibody
Monoclonal antibodies collected and purified.
Uses of monoclonal antibodies
Detection of pathogens
Location of cancer cells and blood clots
Used in pregnancy test kits
Myeloma cells
Type of tumour cell.
Uses of monoclonal antibodies - Pregnancy kit tests
Used to detect a hormone, hCG, in the urine of pregnant women
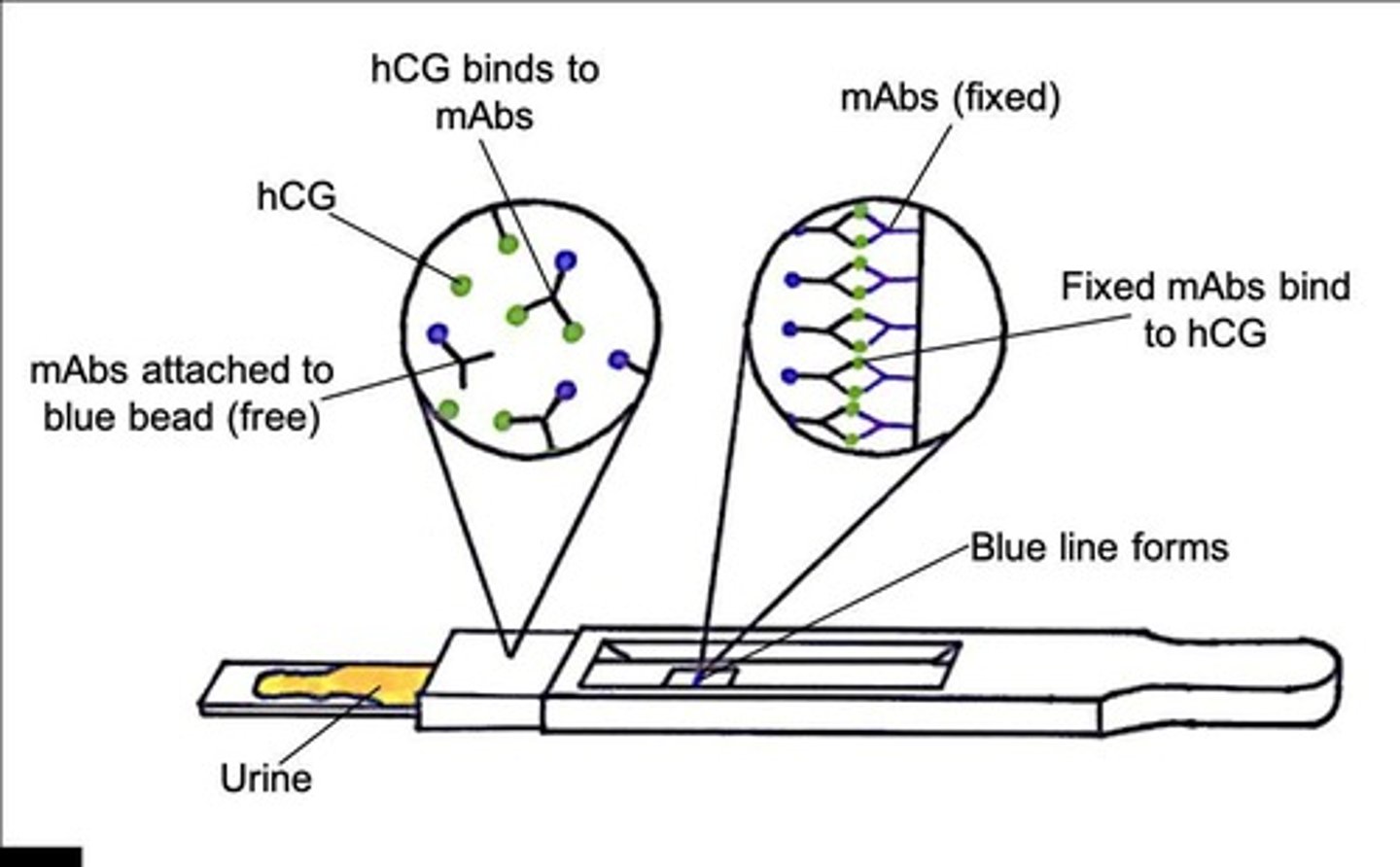
How pregnancy test works
There are two sections of the stick:
→ first section: mobile mAbs complemetary to hCG hormone - attached to blue beads
→ second section: stationary mAbs which are stuck to the stick
Individual urinates on first section: If hCG present, it binds to mobile mAbs attached to blue beads to form hCG / antibody complexes
Carried in the flow of liquid to second section
Stationary mAbs bind to hCG / antibody complexes
As each are bound to a blue bead, results shown as blue line → indicating pregnancy
Pregnancy test results if pregnant - simple
hCG in urine binds to mAbs attached to a blue bead
mAbs with hCG diffuse up the stick
mAbs fixed to the stick bind to hCG
Blue line forms
Pregnancy test results if not pregnant
No hCG in urine so a blue line is not formed.
Uses of monoclonal antibodies - Measure and monitor
Used to measure and monitor levels of hormones or chemicals in the blood.
mAbs modified to bind to molecule wanted
mAbs bound to fluorescent dye
if molecules present, the mAbs bind to it, and dye can be observed
E.g. Blood screening for HIV infections
Uses of monoclonal antibodies - Cancer treament
Producing mAbs that bind to tumour markers to stimulate immune system to attack that cell.
Using mAbs to bind to receptor sites on cell membrane of cancer cells → growth-stimulating molecules cannot bind → stops cell divison
Using mAbs to transport toxic drugs, chemicals or radioactive substances → only damage cancer cells
Advantages of monoclonal antibodies
Specific to one particular antigen - healthy cells not affected
Can treat many different conditions
Disadvantages of mAbs
Difficult too attach mAbs to drugs
expensive to develop
produced from mice lymphocytes - trigger immune response in humans